
送给大家一句话:
不管前方的路有多苦,只要走的方向正确,不管多么崎岖不平,都比站在原地更接近幸福。 —— 宫崎骏《千与千寻》
自主shell命令编写
1 前言2 项目实现2.1 创建命令行2.2 获取命令2.3 分割命令2.4 运行命令 3 源代码Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ谢谢阅读!!!下一篇文章见!!!
1 前言
前几篇文章,我们学习进程的相关知识:进程概念,进程替换,进程控制。熟悉了进程到底是个什么事情,接下来我们来做一个实践,来运用我们所学的相关知识。这个项目就是手搓一个shell模块,模拟实现Xshell中的命令行输入。
用下图的时间轴来表示事件的发生次序。其中时间从左向右。shell由标识为sh的方块代表,它随着时间的流逝从左向右移动。shell从用户读入字符串"ls"。shell建立一个新的进程,然后在那个进程中运行ls程序并等待那个进程结束: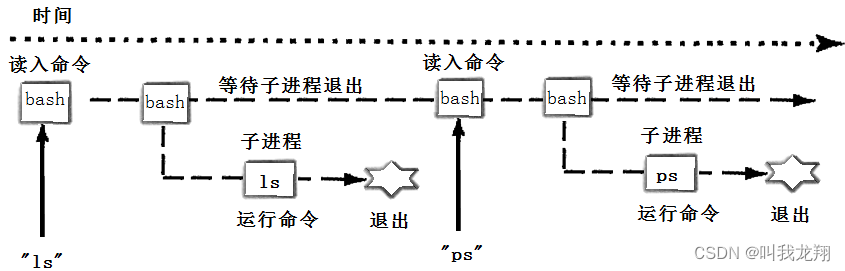
然后shell读取新的一行输入,建立一个新的进程,在这个进程中运行程序 并等待这个进程结束。
所以要写一个shell,需要循环以下过程:
根据这些思路,和我们前面的学的技术,就可以自己来实现一个shell了
2 项目实现
为了保证项目文件的优雅美观,我们按照功能来书写不同函数:
创建自己的命令行获取命令分割命令创建进程执行命令2.1 创建命令行
该模块我们需要实现类似:
获取这些信息大家应该都知道吧!通过对环境变量我们就可以获取到这些信息。使用getenv()函数就可以完成操作。
#include<stdio.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/wait.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 #include<unistd.h> 6 #include<string.h> 7 //大小宏 8 #define SIZE 256 9 //获取用户名 10 const char* GetUsername() 11 { 12 const char* name = getenv("USER"); 13 if(name == NULL) return "NONE"; 14 return name; 15 } 16 //获取机器信息 17 const char* GetHostName() 18 { 19 const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); 20 return hostname; 21 } 22 //获取当前目录 23 const char* GetCwd() 24 { 25 const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); 26 if(cwd == NULL) return "NONE"; 27 return cwd; 28 } 29 30 void MakeCommandLineAndPrint() 31 { //设置命令行字符串 32 char line[SIZE]; 33 const char* username = GetUsername(); 34 const char* hostname = GetHostName(); 35 const char* cwd = GetCwd(); //将获取的三个数据写入命令行中 36 sprintf(line,"[%s@%s %s]> ",username,hostname,cwd); 37 printf("%s",line); 38 fflush(stdout);//为了将命令行刷新出来 39 } 40 41 int main() 42 { 43 //创建我们自己的命令行 44 MakeCommandLineAndPrint(); 45 int a = 0; scanf("%d",&a); //阻断一下方便查看 46 return 0; 47 }这里使用的sprintf()函数是向流中写入格式化信息的好工具。这一段函数大家都可以看明白,就是获取三个变量,然后通过Line数组进行中转,然后打印出来。来看效果: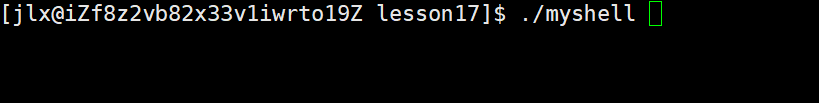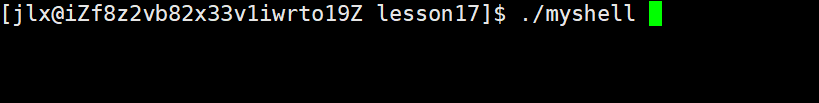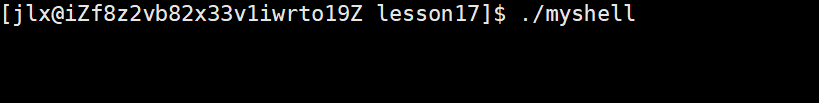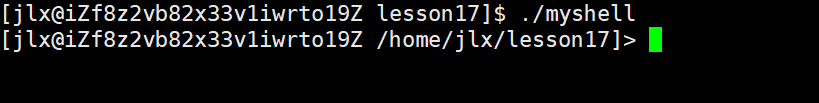
这时候发现,我们的所在目录全部都别打印出来了,我们可以进行一下优化:
#define SkipPath(p) do{ p += strlen(p)-1 ;while(*p != '/') p--; p++; }while(0); 通过这个宏定义就可以只保留最后的目录。这里之所以不使用函数,是因为使用函数会涉及二级指针,会比较复杂!!!
来看效果: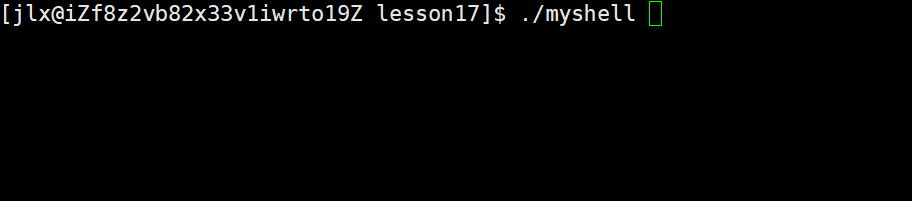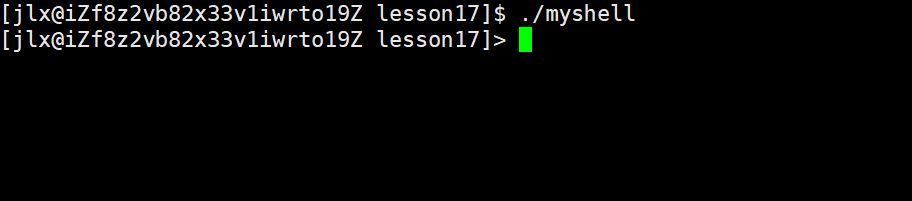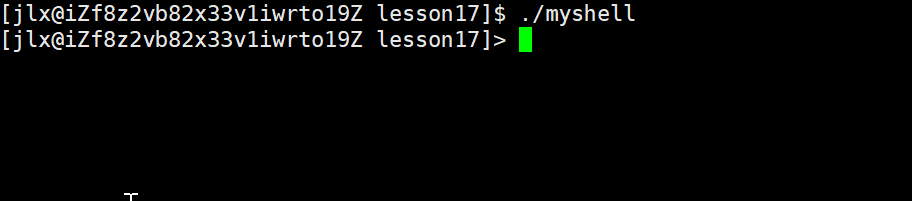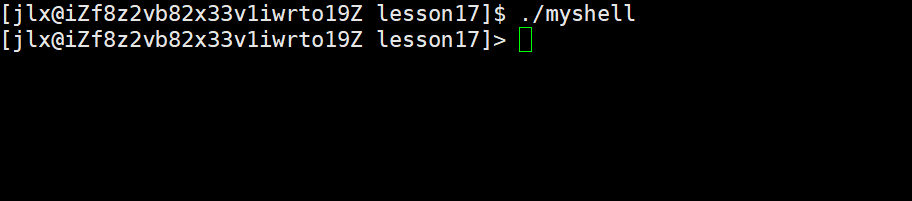
这样就非常完美了!!!
2.2 获取命令
这个模块可以说是非常关键的一步了,只有正确获取了对应命令,我们才好打开新进程来执行命令。
#define ZERO '\0' 45 int GetUserCommand(char* command,int n) 46 { 47 if(command == NULL) return -1; 48 fgets(command,n,stdin); 49 command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; 50 return strlen(command); 51 }这样我们就可以获取命令行输入的字符串了。
2.3 分割命令
获取命令之后,我们还需要对输入的一串命令来进行分割,来保证我们可以正常执行命令
12 #define SEP " " ... 14 //全局命令 方便操作 15 char* gArgv[NUM]; ... 58 void SplitCommand(char command[] , size_t n) 59 { 60 (void)n; 61 gArgv[0] = strtok(command,SEP); 62 int index = 1; 63 // done, 故意写成=,表示先赋值,在判断. 分割之后,strtok会返回NULL,刚好让gArgv最后一个元素是NULL, 并且while判断结束 64 while((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL,SEP))); 65 } 我们使用来strtok()函数:
char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim)第一次调用strtok(),传入的参数str是要被分割的字符串{aaa - bbb -ccc},而成功后返回的是第一个子字符串{aaa};
第二次调用strtok的时候,传入的参数应该为NULL,这样使该函数默认使用上一次未分割完的字符串继续分割 ,就从上一次分割的位置作为本次分割的起始位置,直到分割结束。(strtok内部会记录相应信息)
这样就成功分割命令,来看效果: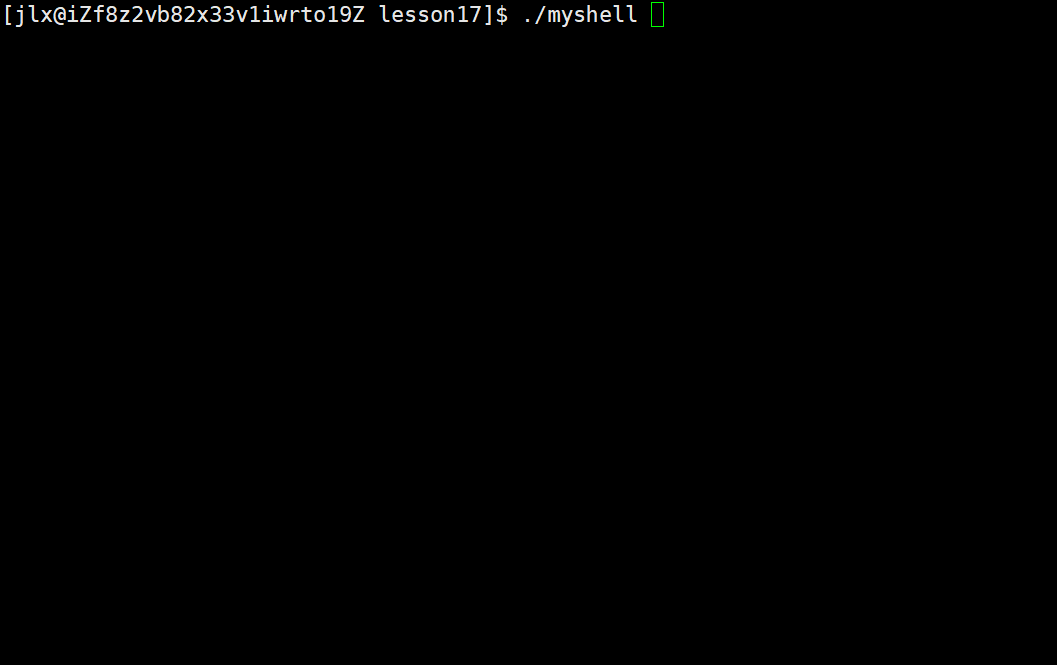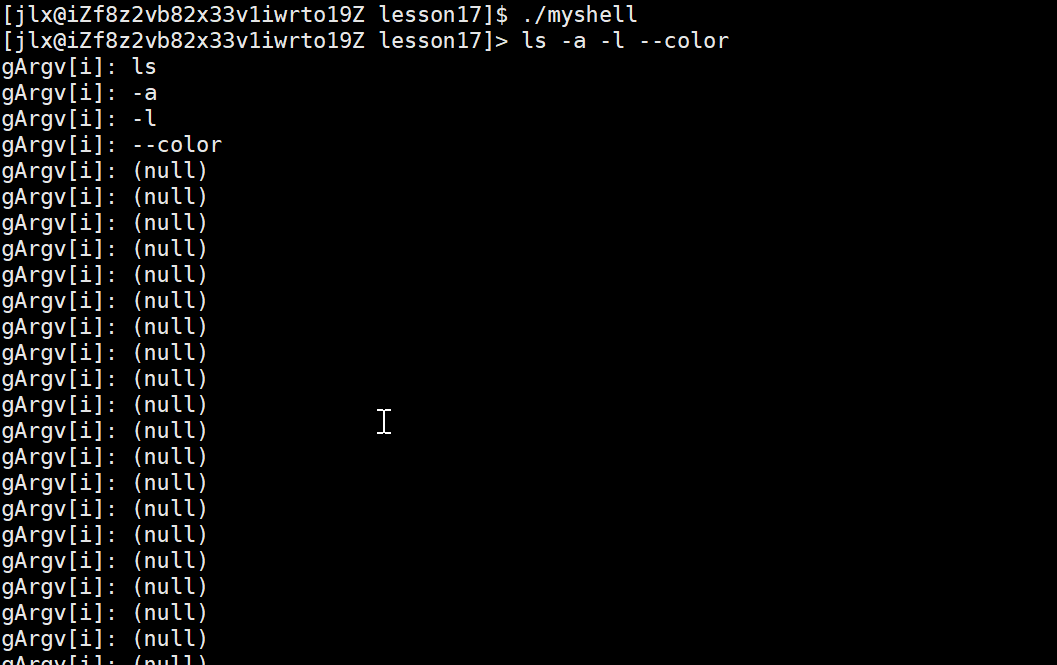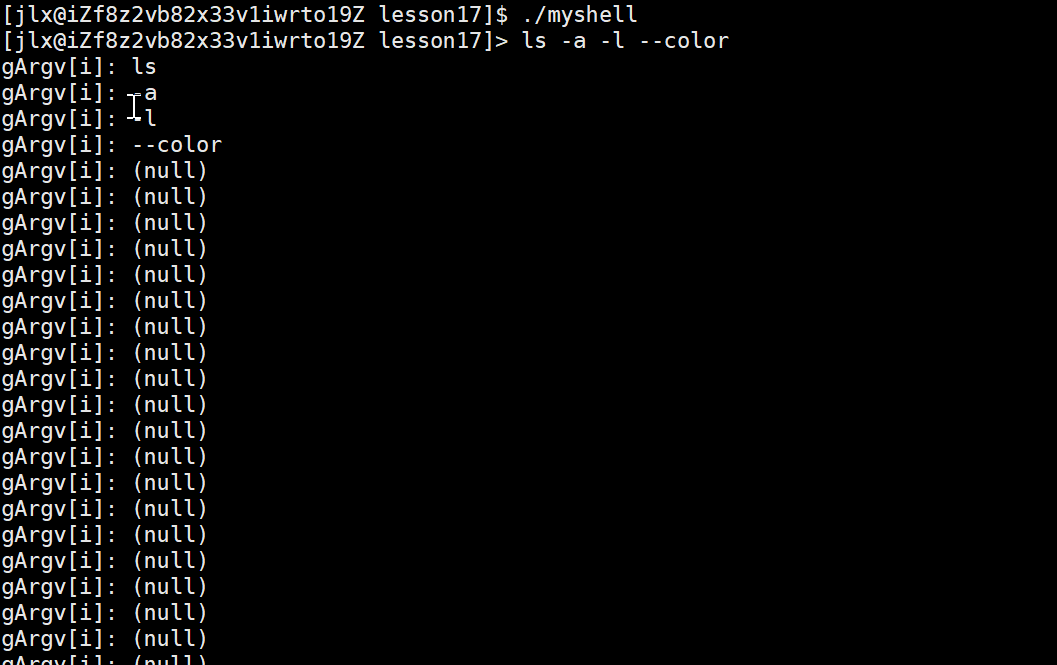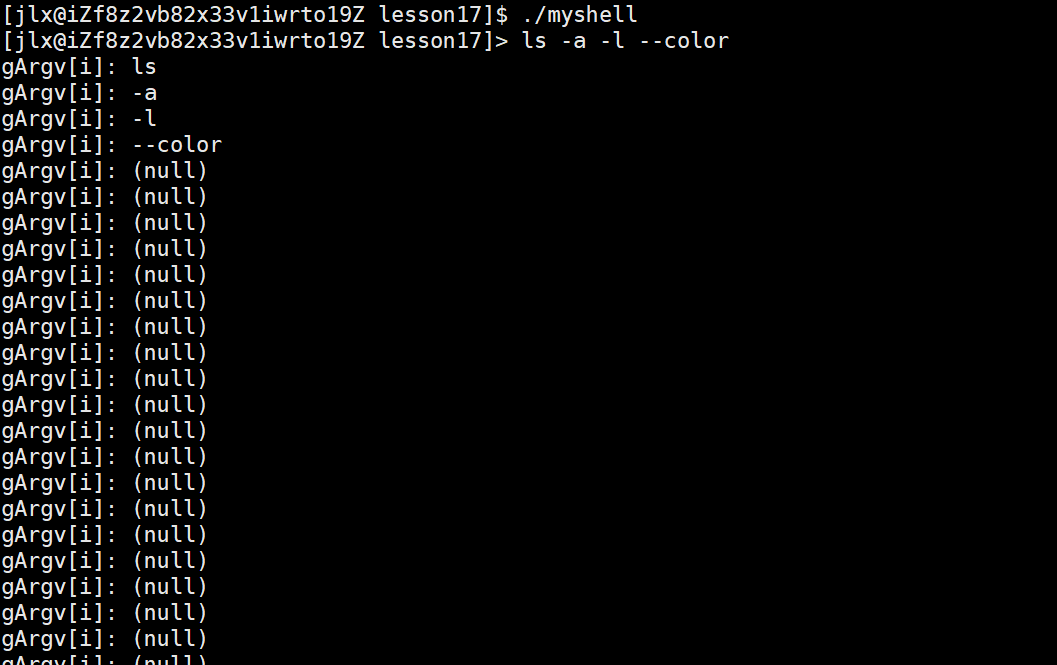
我们的准备工作做完了,接下来就可以进行最终的操作:创建新进程来执行命令!
2.4 运行命令
运行命令就要使用:
创建子进程进程替换这两个加在一起就有了非常牛批的力量,究极POWER!。
68 //执行命令 69 void ExecuteCommand() 70 {//创建子进程 71 pid_t id = fork(); 72 if(id == 0) 73 { //进程替换 74 execvp(gArgv[0],gArgv); 75 exit(errno); 76 } 77 else 78 { 79 int status = 0; 80 pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);//进程等待 81 if(rid > 0) 82 { //如果错误打印错误信息 83 int lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status); 84 if(lastcode != 0) printf("%s:%s:%d\n",gArgv[0],strerror(lastcode),lastcode); 85 } 86 } 87 } 前面已经做好大部分工作了,执行命令这一步就很简单了。来看效果:
这样就完成了绝大部分的代码编写。我们在加上一个while循环,让命令行一直运行试试: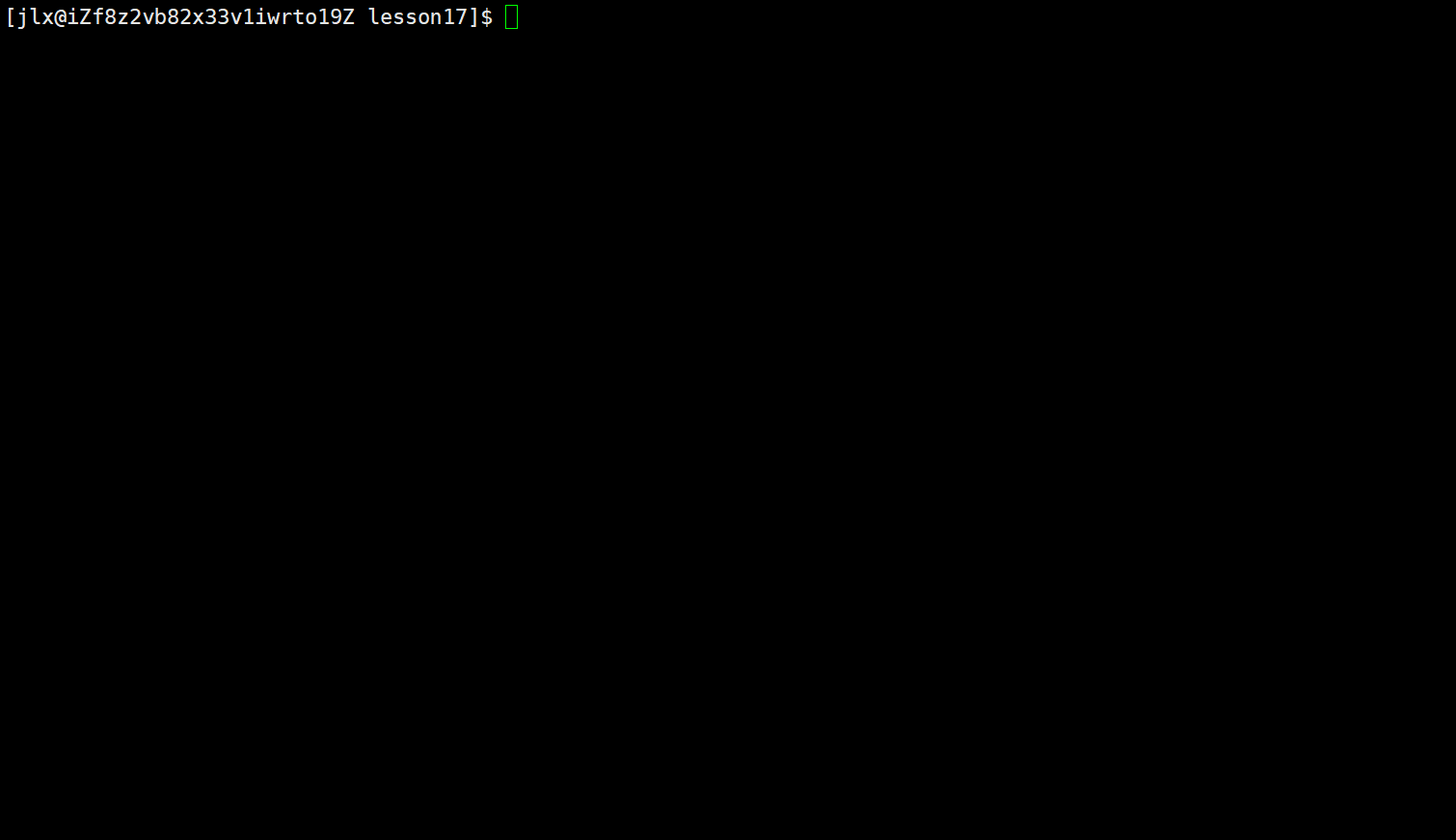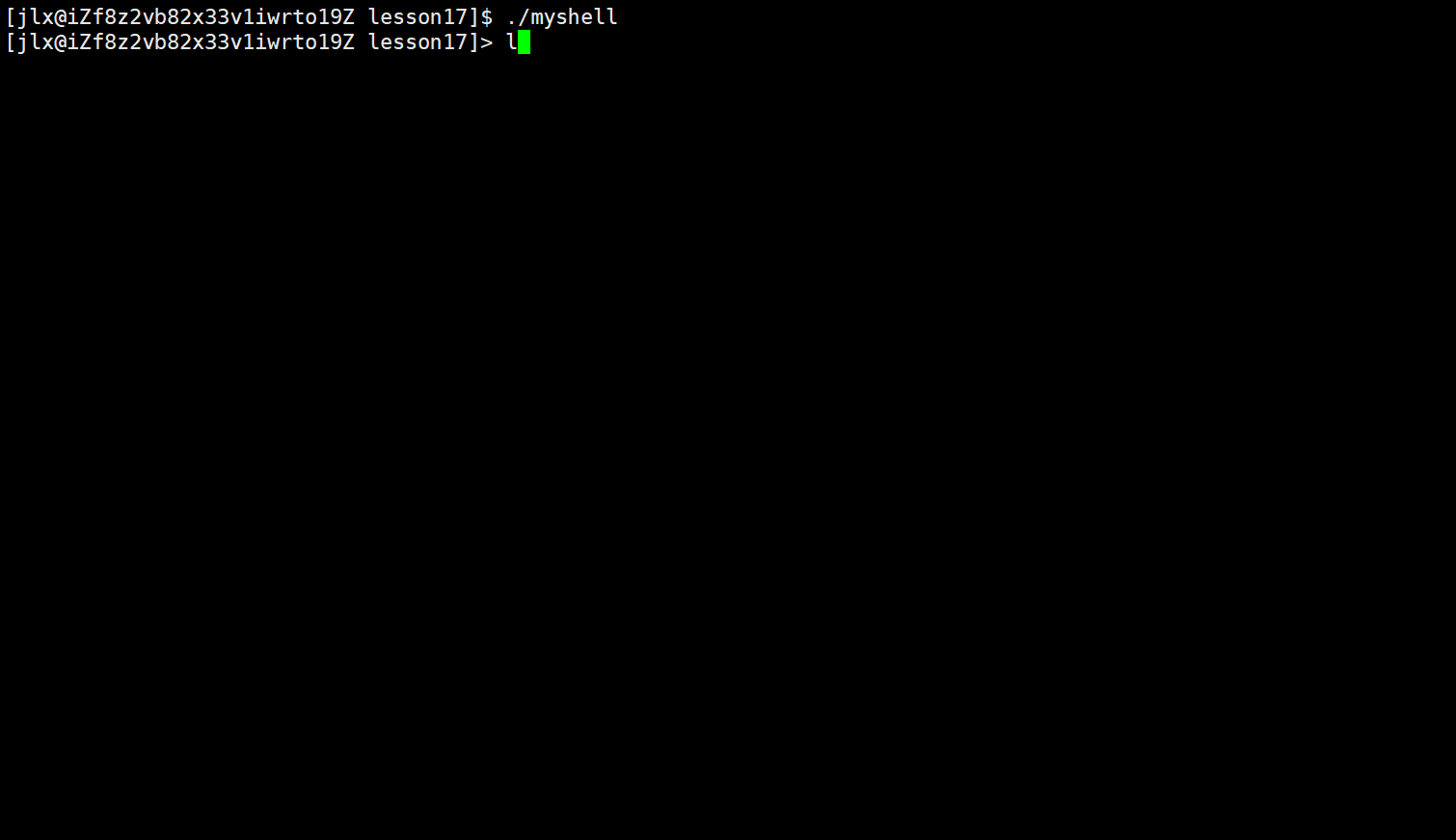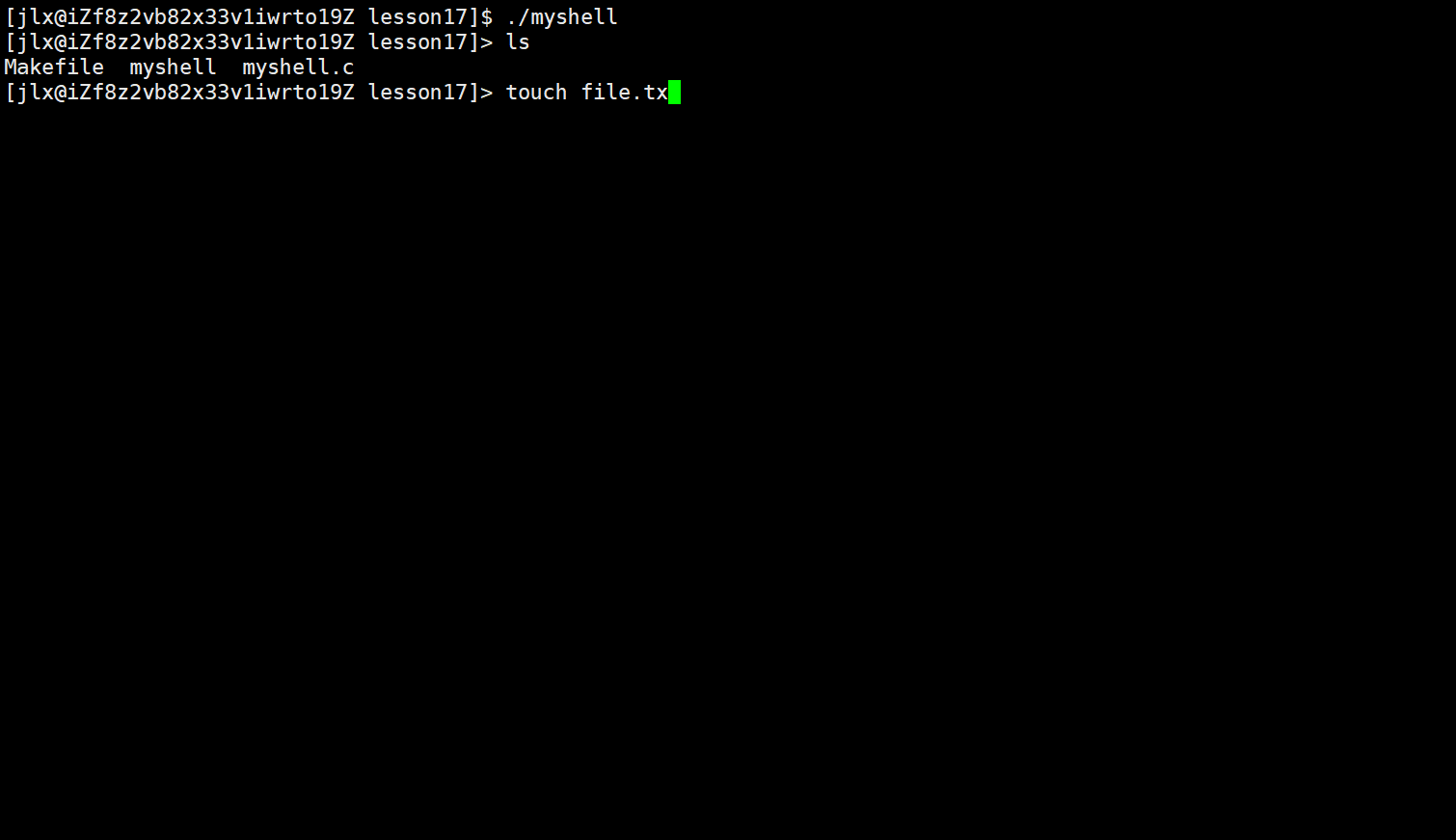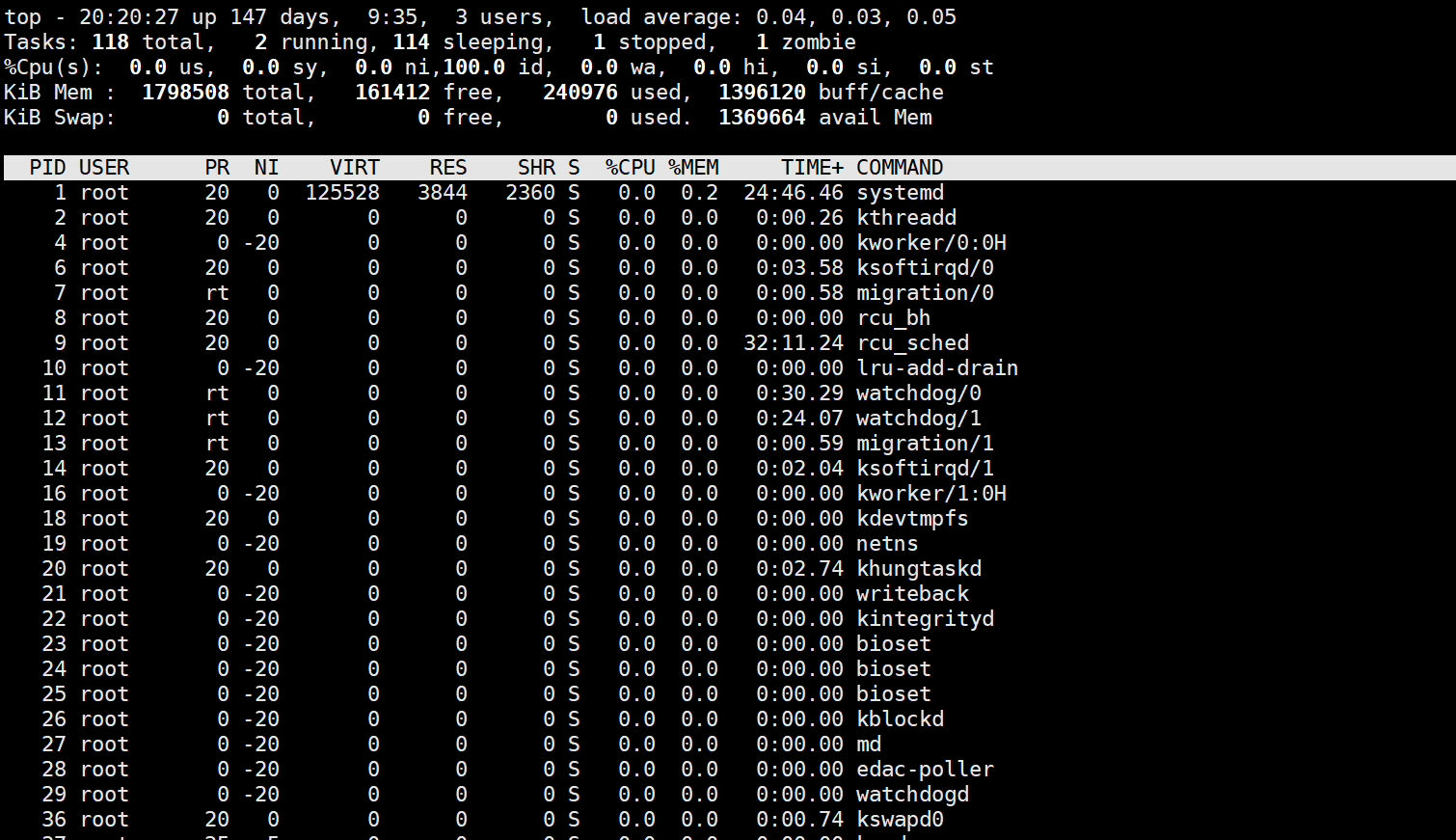
这样就实现了shell的大部分功能,但是还是有一些功能没有做到:比如我们运行cd等内建命令时,会无法运行,所以我要加上特殊情况来保证内建命令可以执行!!!
90 char* GetHome() 91 { 92 char* home = getenv("HOME"); 93 return home; 94 } 95 96 char cwd[SIZE]; 97 98 void cd() 99 {100 const char* path = gArgv[1];101 if(path == NULL) path = GetHome();102 chdir(path);103 104 char temp[SIZE];105 getcwd(temp,sizeof(temp)); 106 snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp);107 putenv(cwd);108 }109 110 //检查是否为内建命令 并单独执行111 bool CheckBuildin()112 {113 bool yes = false;114 //if语句判断即可,内建命令是有限的115 if(strcmp(gArgv[0],"cd") == 0)116 {117 cd();118 yes = true;119 }120 return yes;121 }123 int main()124 {125 int quit = 0; 126 127 while(!quit)128 {129 130 //创建我们自己的命令行131 MakeCommandLineAndPrint();132 133 //获取命令行信息134 char usercommand[SIZE];135 int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));136 if(n <= 0) return 1;137 138 //分割命令行信息139 SplitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));140 141 bool judge = CheckBuildin();142 if(judge) continue;143 144 //执行命令145 ExecuteCommand();146 }147 148 149 return 0;150 } 这样把内建命令单独进行运行就可以了,我这里只写了一个cd命令。来看效果: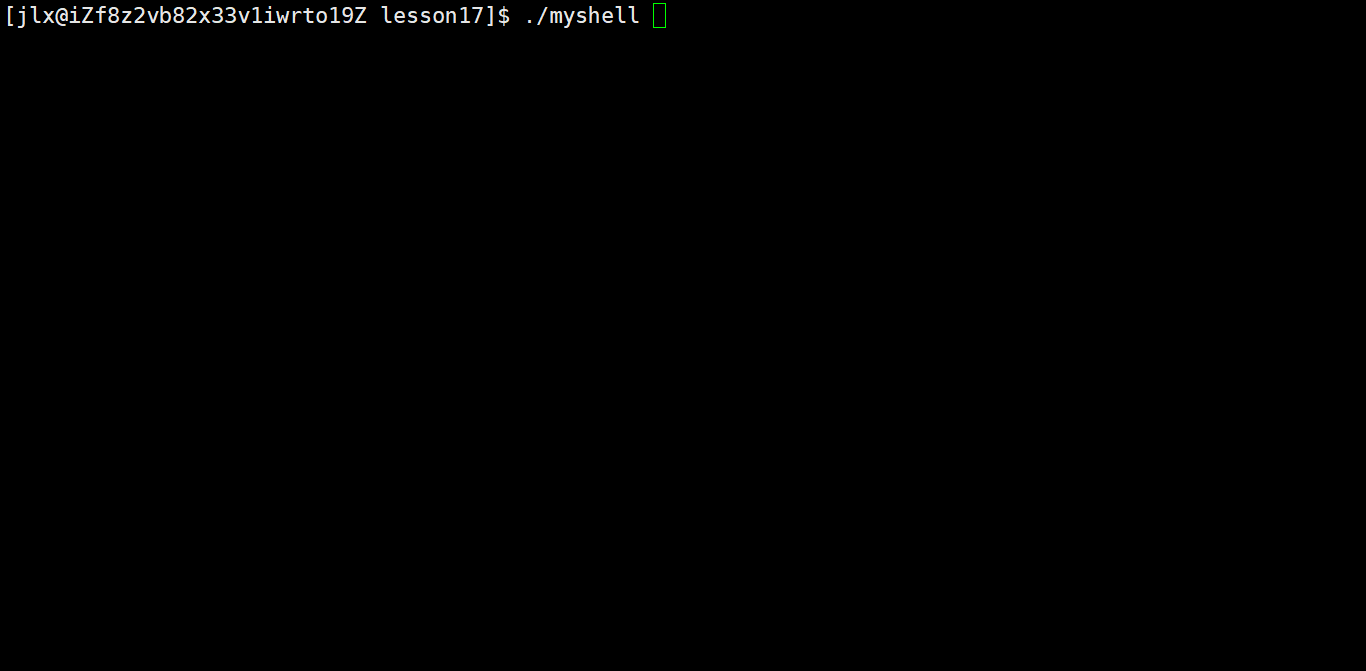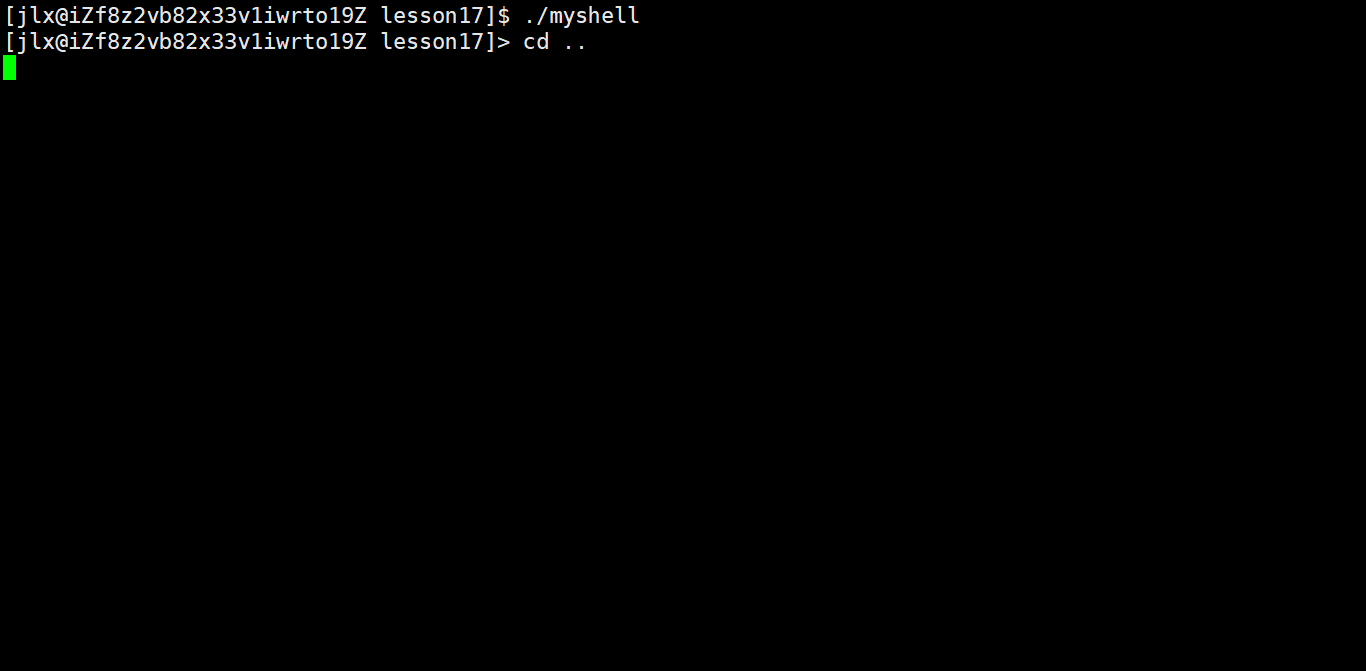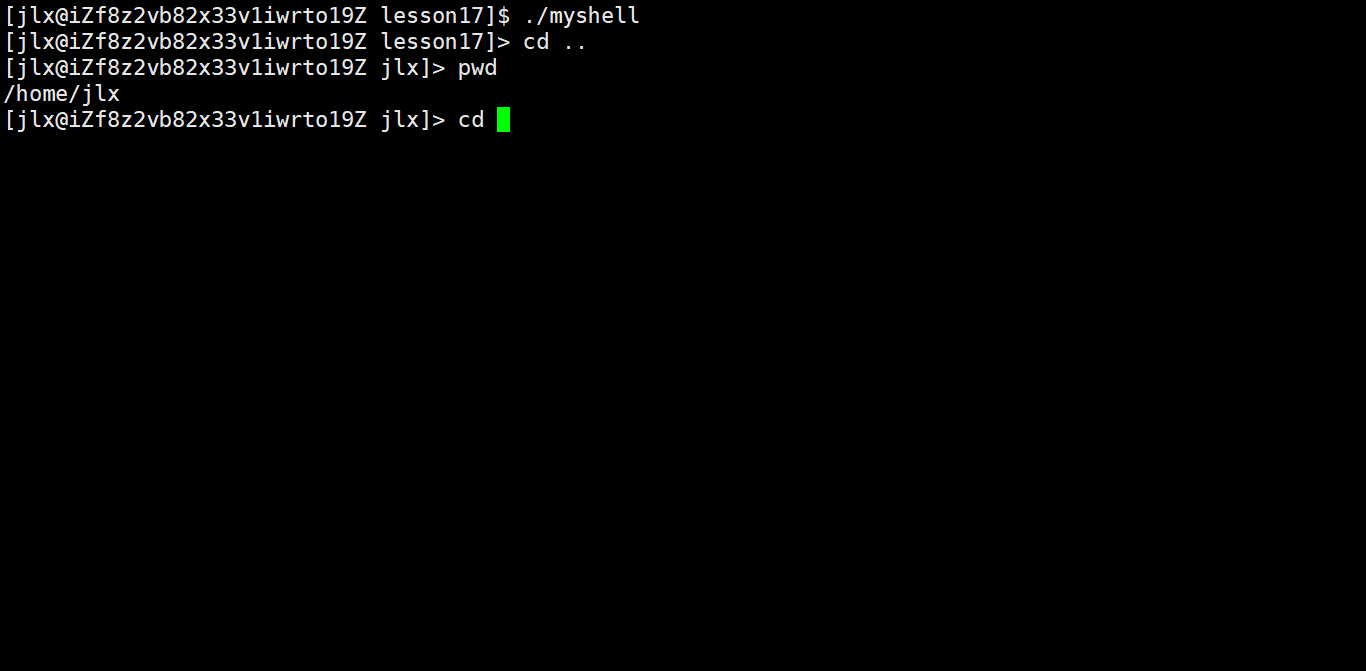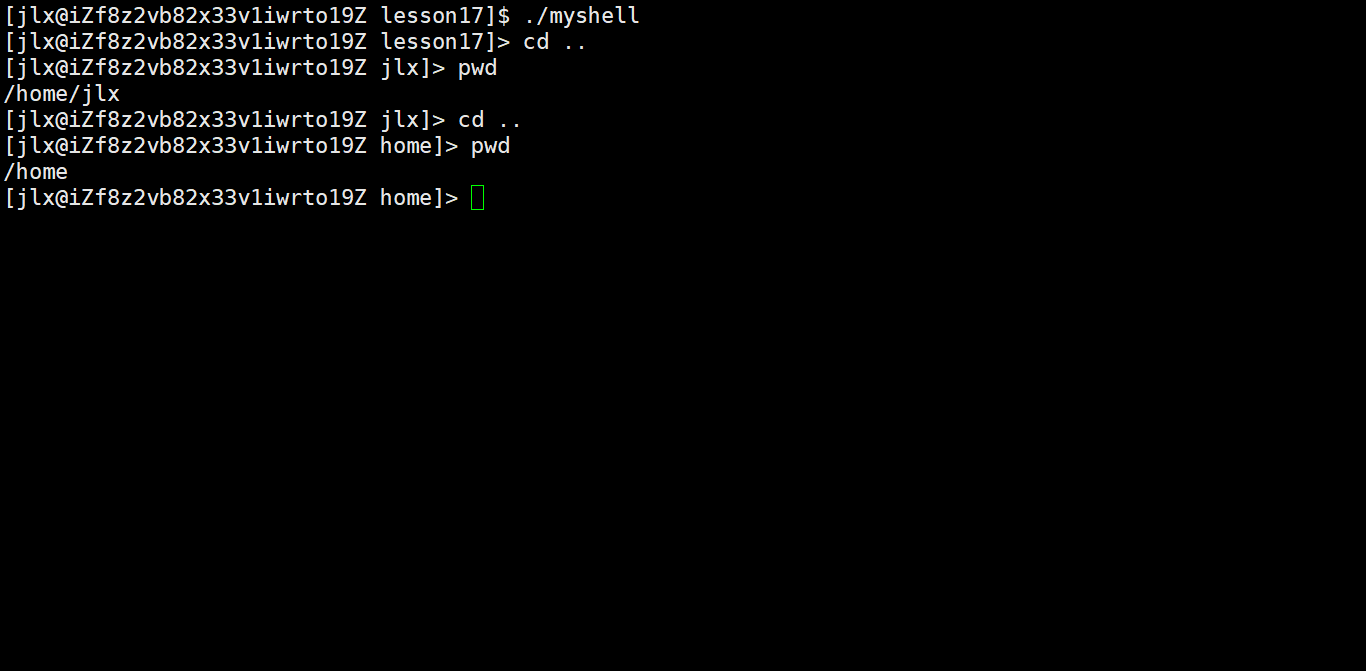
这样就完成了我们的自主shell编写!!!
3 源代码
#include<stdio.h> 2 #include<sys/types.h> 3 #include<sys/wait.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 #include<unistd.h> 6 #include<string.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 #include<stdbool.h> 9 10 #define SIZE 256 11 #define SkipPath(p) do{ p += strlen(p)-1 ;while(*p != '/') p--; }while(0); 12 #define ZERO '\0' 13 #define NUM 32 14 #define SEP " " 15 16 //命令 17 char* gArgv[NUM]; 18 int lastcode = 0; 19 char cwd[SIZE]; 20 21 const char* GetUsername() 22 { 23 const char* name = getenv("USER"); 24 if(name == NULL) return "NONE"; 25 return name; 26 } 27 28 const char* GetHostName() 29 { 30 const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); 31 return hostname; 32 } 33 34 const char* GetCwd() 35 { 36 const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); 37 if(cwd == NULL) return "NONE"; 38 return cwd; 39 } 40 41 void MakeCommandLineAndPrint() 42 { 43 char line[SIZE]; 44 const char* username = GetUsername(); 45 const char* hostname = GetHostName(); 46 const char* cwd = GetCwd(); 47 SkipPath(cwd); 48 sprintf(line,"[%s@%s %s]> ",username,hostname,strlen(cwd) == 1?"/":cwd + 1); 49 printf("%s",line); 50 fflush(stdout); 51 } 52 53 int GetUserCommand(char command[] ,size_t n) 54 { 55 char* s = fgets(command,n,stdin); 56 if(s == NULL) return -1; 57 command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; 58 return strlen(command); 59 } 60 61 void SplitCommand(char command[] , size_t n) 62 { 63 (void)n; 64 gArgv[0] = strtok(command,SEP); 65 int index = 1; 66 // done, 故意写成=,表示先赋值,在判断. 分割之后,strtok会返回NULL,刚好让gArgv最后一个元素是NULL, 并且while判断结束 67 while((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL,SEP))); 68 } 69 70 //执行命令 71 void ExecuteCommand() 72 { 73 pid_t id = fork(); 74 if(id == 0) 75 { 76 execvp(gArgv[0],gArgv); 77 exit(errno); 78 } 79 else 80 { 81 int status = 0; 82 pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0); 83 if(rid > 0) 84 { 85 lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status); 86 if(lastcode != 0) printf("%s:%s:%d\n",gArgv[0],strerror(lastcode),lastcode); 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 91 char* GetHome() 92 { 93 char* home = getenv("HOME"); 94 return home; 95 } 96 97 98 void cd() 99 {100 const char* path = gArgv[1];101 if(path == NULL) path = GetHome();102 chdir(path);103 104 char temp[SIZE];105 getcwd(temp,sizeof(temp));106 snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp);107 putenv(cwd);108 }109 110 //检查是否为内建命令 并单独执行111 bool CheckBuildin()112 {113 bool yes = false;114 //if语句判断即可,内建命令是有限的115 if(strcmp(gArgv[0],"cd") == 0)116 {117 cd();118 yes = true;119 }120 return yes;121 }122 123 int main()124 {125 int quit = 0;126 127 while(!quit)128 {129 130 //创建我们自己的命令行131 MakeCommandLineAndPrint();132 133 //获取命令行信息134 char usercommand[SIZE];135 int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand,sizeof(usercommand));136 if(n <= 0) return 1;137 138 //分割命令行信息139 SplitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));140 141 bool judge = CheckBuildin();142 if(judge) continue;143 144 //执行命令145 ExecuteCommand();146 }147 148 149 return 0;150 }