leetcode每日一题-423:从英文中重建数字
链接
从英文中重建数字
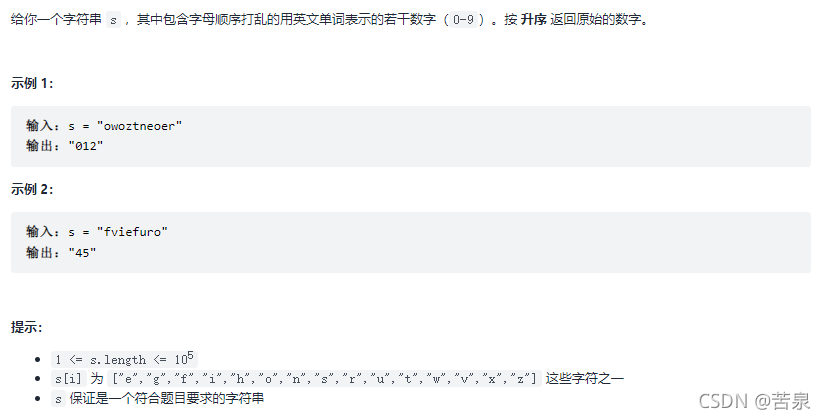
题目
分析
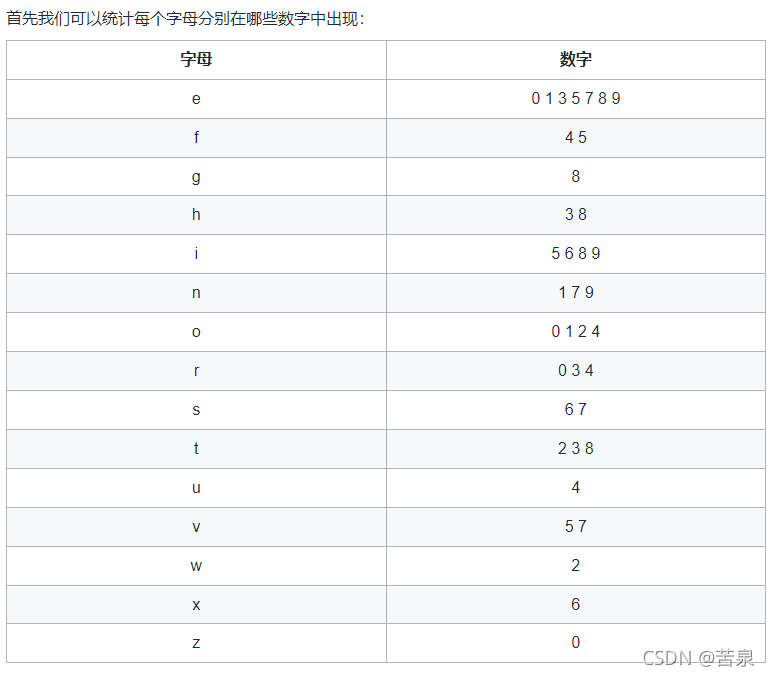
首先我们先分析每个字母的组成,然后发现一些字符只在一个单词中出现,我们先去统计一下这些单词个数。
z,w,u,x,g都只出现在一个数字中,也就是0,2,4,6,8,我们用哈希表统计一下s字符串中各个字符的数量,就可以知道0,2,4,6,8的数量,然后我们注意一下只在两个数字中出现的字符。
- h 只在 3,8 中出现。由于我们已经知道了 8 出现的次数,因此可以计算出 3 出现的次数。
- f 只在 4,5 中出现。由于我们已经知道了 4 出现的次数,因此可以计算出 5 出现的次数。
- s 只在 6,7 中出现。由于我们已经知道了 6 出现的次数,因此可以计算出 7 出现的次数。
此时,只剩下1和9还不知道,但是字符含有o的其他数字我们都已经知道了,那么剩下的数量就是1的数量。
然后此时含有i的就只有9了,统计一下9的数量即可。
统计完次数,按升序排列即可。
代码
C++
我的代码
class Solution {
public:
string originalDigits(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> m;
string nums[10] = {"zero", "one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight", "nine"};
string res;
for(char ch : s) m[ch]++;
// 0
if(m['z'] > 0)
{
for(int i=0 ; i<m['z'] ; i++) res += '0';
int x = m['z'];
m['z'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
m['r'] -= x;
m['o'] -= x;
}
// 2
if(m['w'] > 0)
{
int x = m['w'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '2';
m['t'] -= x;
m['w'] -= x;
m['o'] -= x;
}
// 4
if(m['u'] > 0)
{
int x = m['u'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '4';
m['f'] -= x;
m['o'] -= x;
m['u'] -= x;
m['r'] -= x;
}
// 5
if(m['f'] > 0)
{
int x = m['f'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '5';
m['f'] -= x;
m['i'] -= x;
m['v'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
}
// 6
if(m['x'] > 0)
{
int x = m['x'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '6';
m['s'] -= x;
m['i'] -= x;
m['x'] -= x;
}
// 7
if(m['s'] > 0)
{
int x = m['s'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '7';
m['s'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
m['v'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
m['n'] -= x;
}
// 8
if(m['g'] > 0)
{
int x = m['g'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '8';
m['e'] -= x;
m['i'] -= x;
m['g'] -= x;
m['h'] -= x;
m['t'] -= x;
}
// 1
if(m['o'] > 0)
{
int x = m['o'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '1';
m['o'] -= x;
m['n'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
}
// 3
if(m['t'] > 0)
{
int x = m['t'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '3';
m['t'] -= x;
m['h'] -= x;
m['r'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
}
// 9
if(m['i'] > 0)
{
int x = m['i'];
for(int i=0 ; i<x ; i++) res += '9';
m['n'] -= x;
m['i'] -= x;
m['n'] -= x;
m['e'] -= x;
}
sort(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};
C++
官方题解
class Solution {
public:
string originalDigits(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> c;
for (char ch: s) {
++c[ch];
}
vector<int> cnt(10);
cnt[0] = c['z'];
cnt[2] = c['w'];
cnt[4] = c['u'];
cnt[6] = c['x'];
cnt[8] = c['g'];
cnt[3] = c['h'] - cnt[8];
cnt[5] = c['f'] - cnt[4];
cnt[7] = c['s'] - cnt[6];
cnt[1] = c['o'] - cnt[0] - cnt[2] - cnt[4];
cnt[9] = c['i'] - cnt[5] - cnt[6] - cnt[8];
string ans;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt[i]; ++j) {
ans += char(i + '0');
}
}
return ans;
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
Java
class Solution {
public String originalDigits(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> c = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
c.put(ch, c.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
}
int[] cnt = new int[10];
cnt[0] = c.getOrDefault('z', 0);
cnt[2] = c.getOrDefault('w', 0);
cnt[4] = c.getOrDefault('u', 0);
cnt[6] = c.getOrDefault('x', 0);
cnt[8] = c.getOrDefault('g', 0);
cnt[3] = c.getOrDefault('h', 0) - cnt[8];
cnt[5] = c.getOrDefault('f', 0) - cnt[4];
cnt[7] = c.getOrDefault('s', 0) - cnt[6];
cnt[1] = c.getOrDefault('o', 0) - cnt[0] - cnt[2] - cnt[4];
cnt[9] = c.getOrDefault('i', 0) - cnt[5] - cnt[6] - cnt[8];
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt[i]; ++j) {
ans.append((char) (i + '0'));
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution