MHT代码阅读(3)
3. updateClusters
3.1 论文内容
聚类的过程是将通过共同观察链接起来的所有轨迹的集合。共享观测的轨迹被定义为不兼容的,并且每次扫描都保留不兼容轨迹的记录。当轨迹被删除以及根据当前扫描的观察结果形成新轨迹时,该记录会更新。
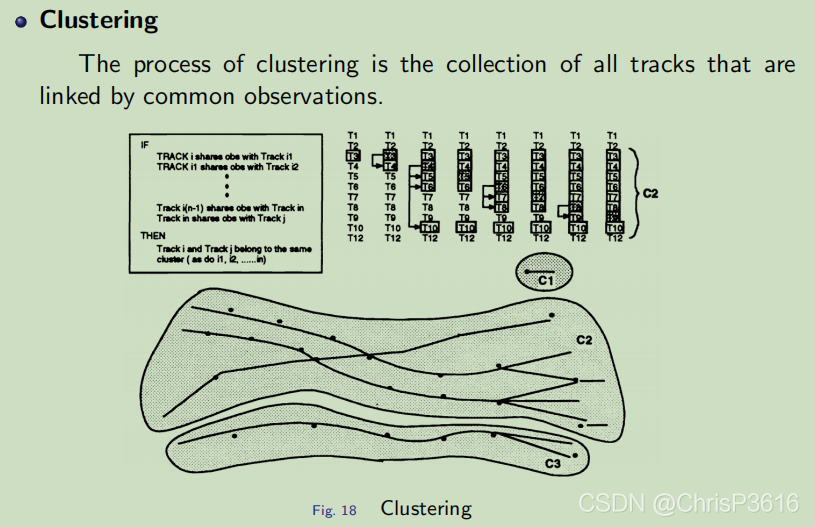
一个集群可以包括不直接共享观测但都与第三个跟踪共享观测的轨迹。因此,如果轨道 1 与轨道 2 共享一个观测值,而轨道 2 与轨道 3 共享另一个观测值,则所有三个轨道都在同一个集群中。标准算法可用于聚类。
具有大量轨道的集群的形成可能导致假设形成所需的时间量无法接受。因此,为了维护包含不超过数百个轨道的集群,采用了稍后讨论的几种技术。
聚类的结果是相互作用的轨迹列表(通过共同观察链接)。这些轨迹按 LLR(前面讨论的评分函数)的顺序排列。下一步是形成兼容轨道的假设。
3.2 代码阅读
-
每个树节点都可以通过它的 familyID 和 trackID 访问
- 初始化 familyNo 和 other_param.currentTrackNo
- 利用cell函数初始化 clusterFamilyList 和 clusterFamilyIndex
- %cell数组一般被叫做元胞数组,它的每个单元可以储存不同的数据类型,可以是数值,字符或矩阵或元胞数组等,类似于学过的c语言里的结构体
- %利用函数cell() 可以创建一个元胞数组,还可以规定其大小。cell(familyNo,1)表示 行数=familyNo,列数=1
- 利用zeros函数初始化familyClusters
-
进入循环,得到 ICL_sel 和 clusterFamilyList{i}
- %sel为select的简写?
- %unique筛除向量中的重复值,产生的结果按升序排列
-
进入循环得到 clusterFamilyIndex{i}
-
进入while循环,得到 familyClusters(clusterFamilyIndex{i})=w
-
ICL_clusters=cell(w,1); clusters=cell(w,1);
-
-
进入循环,更新 ICL_sel 、ICL_clusters{k} 、clusters{k}
- %cellfun将函数用于元胞数组中的每个cell。isempty(A) ;判断A是否为空,如果为空,结果为1,否则为0.
-
计算每个簇中的轨道数
3.3 代码附录
function [clusters,ICL_clusters,other_param]=updateClusters...
(incompabilityListTreeSet, incompabilityListTreeNodeIDSet, ...
activeTreeSet, other_param)
%%
% Each tree node can be accessed by its familyID and trackID
familyNo=length(incompabilityListTreeSet);
other_param.currentTrackNo=0;
if familyNo == 0
clusters=[];
ICL_clusters=[];
return
end
%cell数组一般被叫做元胞数组,它的每个单元可以储存不同的数据类型,可以是数值,字符或矩阵或元胞数组等,类似于学过的c语言里的结构体
clusterFamilyList=cell(familyNo,1);%利用函数cell() 可以创建一个元胞数组,还可以规定其大小。行数=familyNo,列数=1
clusterFamilyIndex=cell(familyNo,1);
%返回一个familyNo*1的0矩阵
familyClusters=zeros(familyNo,1);
for i=1:familyNo
treeInd=findleaves(incompabilityListTreeSet(i));
%sel为select的简写?
ICL_sel=[];
for j=treeInd
if activeTreeSet(i).get(j) ~= 1
continue;
end
ICL_sel_tmp=incompabilityListTreeNodeIDSet(i).get(j);
ICL_sel=[ICL_sel; ICL_sel_tmp(:,1)];
end
%unique筛除向量中的重复值,产生的结果按升序排列
ICL_sel=unique(ICL_sel);
clusterFamilyList{i}=ICL_sel;
end
for i=1:length(clusterFamilyList)
ICL_sel=clusterFamilyList{i};
clusterFamilyIndex{i}=i;
if i ~= length(clusterFamilyList)
for j=i+1:length(clusterFamilyList)
ICL_sel2=clusterFamilyList{j};
for k=1:length(ICL_sel2)
if sum(ICL_sel == ICL_sel2(k)) ~= 0
clusterFamilyIndex{i}=[clusterFamilyIndex{i}; j];
break;
end
end
end
end
end
w=0;
todolist=1:familyNo;
%~isempty(A) ;表示将 isempty(A) 的结果取反,也就是说如果A为空,结果为0,否则为1。
while ~isempty(todolist)
w=w+1;
i=todolist(1);
cl_index=clusterFamilyIndex{i};
cl_index=cl_index';
for j=cl_index
if i == j
continue;
end
clusterFamilyIndex{i}=[clusterFamilyIndex{i}; clusterFamilyIndex{j}];
clusterFamilyIndex{j}=[];
end
clusterFamilyIndex{i}=unique(clusterFamilyIndex{i});
todolist=setdiff(todolist,cl_index');
if sum(familyClusters(clusterFamilyIndex{i})) == 0
familyClusters(clusterFamilyIndex{i})=w;
else
cl_parent=find(familyClusters(clusterFamilyIndex{i})~=0);
clusterNums=unique(familyClusters(clusterFamilyIndex{i}(cl_parent)));
for k=1:length(clusterNums)
indSel=find(familyClusters==clusterNums(k));
familyClusters(indSel)=w;
end
familyClusters(clusterFamilyIndex{i})=w;
end
end
ICL_clusters=cell(w,1);
clusters=cell(w,1);
for k=1:max(familyClusters)
ICL_sel=[];
ICL_Ind_sel=[];
indSel=find(familyClusters == k);
indSel=indSel';
for i=indSel
treeInd=findleaves(incompabilityListTreeSet(i));
for j=treeInd
if activeTreeSet(i).get(j) ~= 1
continue;
end
ICL_sel_tmp=incompabilityListTreeSet(i).get(j);
ICL_sel=[ICL_sel; ICL_sel_tmp(:,2)];
ICL_Ind_sel=[ICL_Ind_sel; [i j]];
end
end
ICL_sel=unique(ICL_sel);
ICL_clusters{k}=ICL_sel;
clusters{k}=ICL_Ind_sel;
end
%cellfun将函数用于元胞数组中的每个cell。isempty(A) ;判断A是否为空,如果为空,结果为1,否则为0.
ICL_clusters(cellfun('isempty',ICL_clusters))=[];
clusters(cellfun('isempty',clusters))=[];
% count the number of tracks in each cluster
other_param.currentTrackNo=zeros(length(clusters),1);
for i=1:length(clusters)
%其中r=size(A,1)该语句返回的是矩阵A的行数, c=size(A,2) 该语句返回的是矩阵A的列数
other_param.currentTrackNo(i)=size(clusters{i},1);
if size(clusters{i},1) ~= size(ICL_clusters{i},1)
error('error');
end
end
end