当我们学过了进程替换之后,本篇文章可以根据进程替换的知识带你自主实现一个shell命令行
实现步骤
1.显示命令行提示
2.读取输入指令以及对应选项
3.分割第二步的指令以及选项到命令行参数表中
4.处理内建命令
5.进程替换
1.显示命令行提示

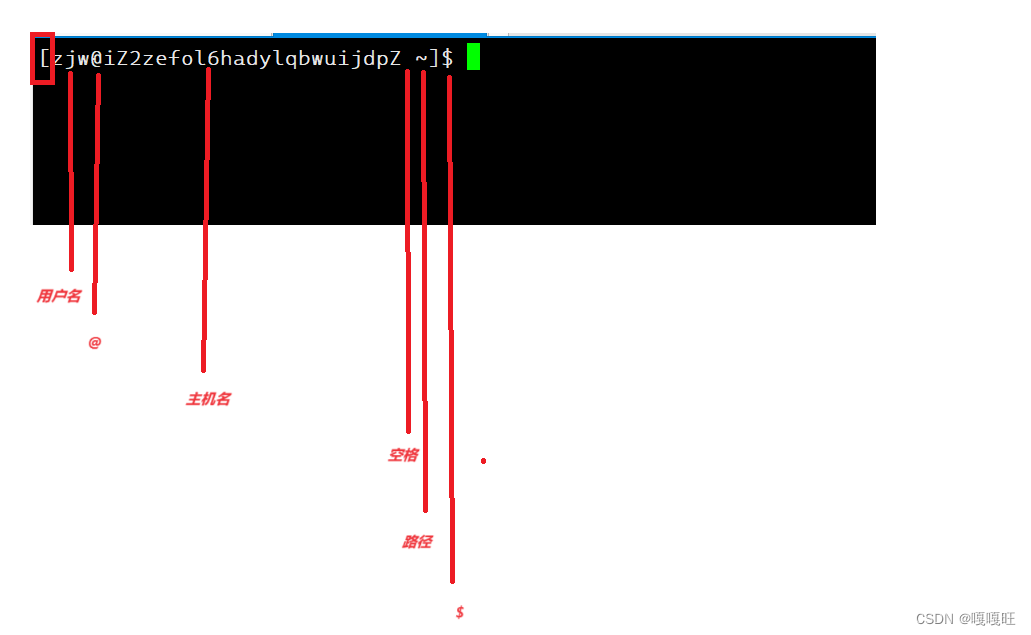
我们通过观察bash的命令行提示发现他是由三部分组成的
1.用户名
2.主机名
3.当前路径
而这三部分的信息都对应保存在我们的环境变量中
我们可以通过env指令查到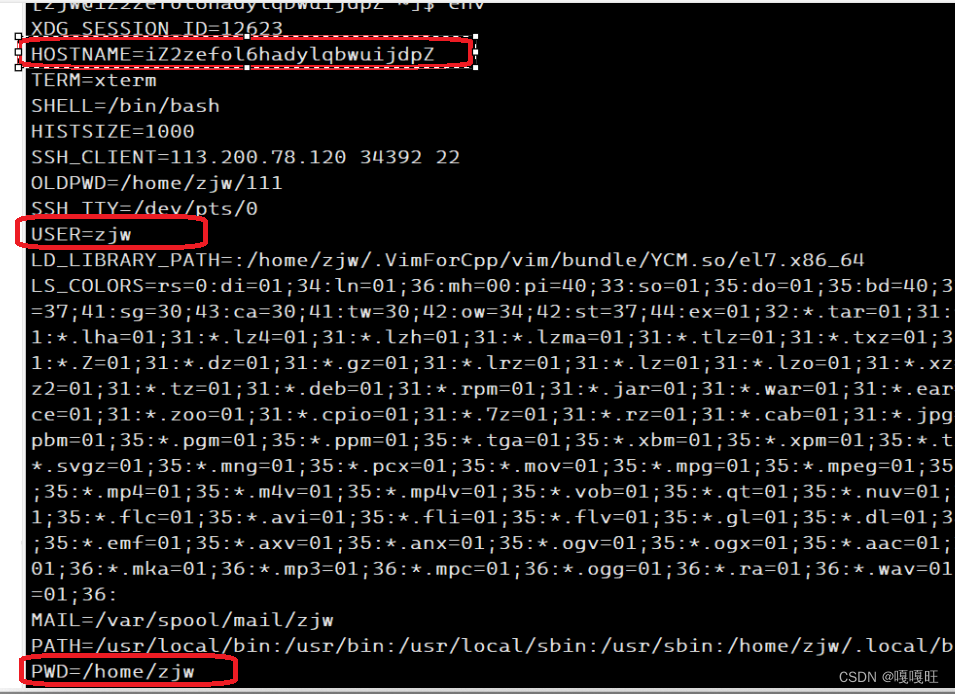
这里要介绍一个getenv函数,他可以将对应的环境变量对应的字符串打印出来,返回对应字符串的起始地址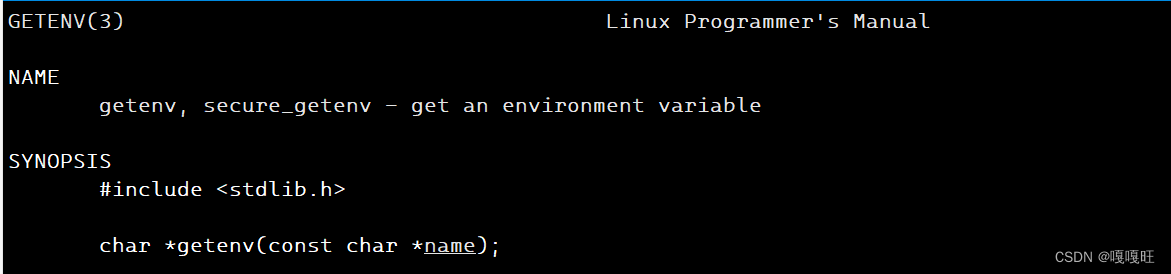
我们可以封装3个函数分别来获取对应用户名,主机名,路径,这三个环境变量的字符串
//获取用户名的函数
char*getname() { char *name=getenv("USER"); if(name==NULL)return NULL; return name; }name指针保存USER环境变量值对应字符串的首地址,如果为NULL ,就返回空(说明不存在这个环境变量)
//获取主机名的函数
char*gethostname() { char*hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); if(hostname==NULL)return NULL; return hostname; }hostname指针保存HOSTNAME环境变量值对应字符串的首地址,如果为NULL ,就返回空(说明不存在这个环境变量)
//获取路径的函数
char*getpwd() { char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; return pwd; }pwd指针保存PWD环境变量值对应字符串的首地址,如果为NULL,就返回空(说明不存在这个环境变量)
我们根据bash命令行的提示用getcommandline()函数来进行打印我们自己的命令行提示
void getcommandline() { printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethostname(),getpwd()); }当前步骤代码展示
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 char*getname() 4 { 5 char *name=getenv("USER"); 6 if(name==NULL)return NULL; 7 return name; 8 } 9 char*gethostname() 10 { 11 char*hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); 12 if(hostname==NULL)return NULL; 13 return hostname; 14 } 15 char*getpwd() 16 { 17 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 18 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 19 return pwd; 20 } 21 void getcommandline() 22 { 23 printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethostname(),getpwd()); 24 } 25 int main() 26 { 27 getcommandline(); 28 29 } 效果展示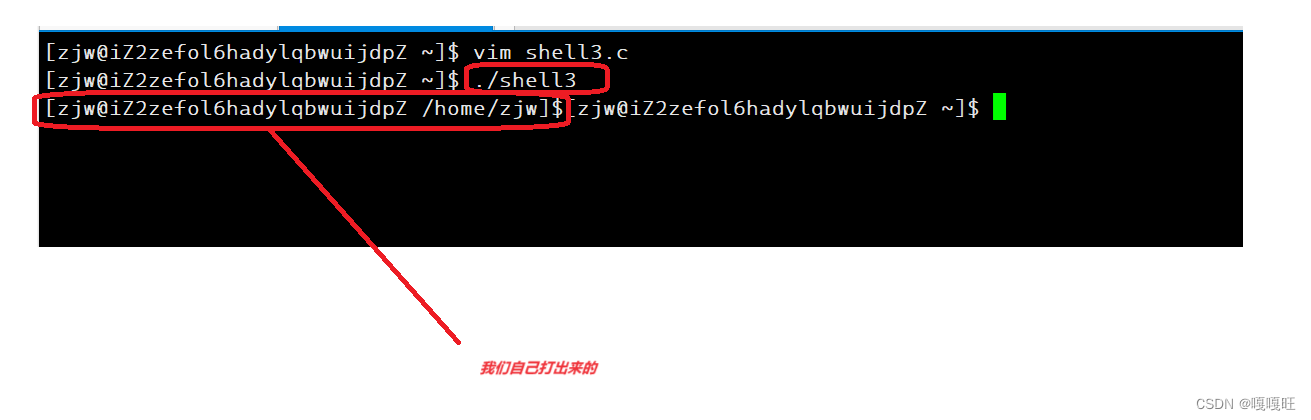
2.读取输入指令以及对应选项
为了处理我们输入的指令,我们需要将输入的指令以及选项保存在一个字符串中,就类比为命令行参数表.
我们应该如何读取字符串呢??
试想一下我们可以用scanf读字符串吗?
答案是不能的,因为我们在输入指令以及选项时,会带空格分割开来,而scanf会将空格作为分隔符,不会读取进来。
所以我们要使用的是fgets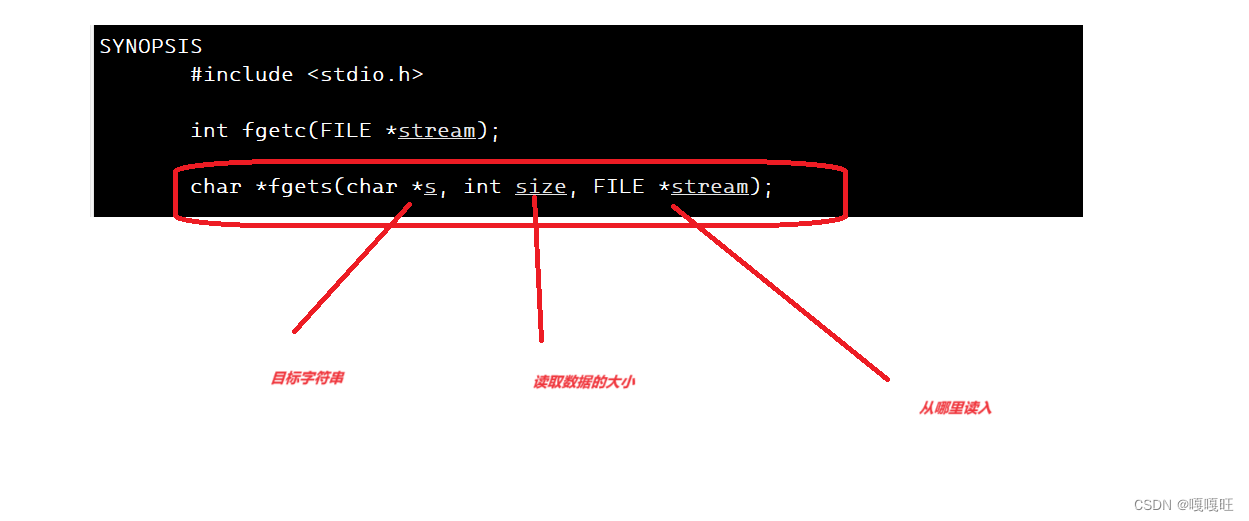
#include <stdio.h> char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream);我们定义一个全局的字符串数组来保存输入的指令以及选项的字符串
char arr[512];因为我们要从屏幕上读指令以及选项,所以fgets第三个参数为stdin(标准输入流).
我们先将其读到arr中,读取512个字节,然后使用strlen找到结尾添加‘\0’;比方说一个字符串为char arr[]=“abcdefg”;strlen(arr)=8; 我们需要在下标为strlen(arr)-1的位置添加一个‘\0’;
我们将获取指令,选项字符串封装在函数里面getcommandstr()
27 void getcommandstr() 28 { 29 fgets(arr,sizeof(arr),stdin); 30 arr[strlen(arr)-1]='\0'; 31 32 } 为了测试arr是否读到,我们遍历打印一下arr数组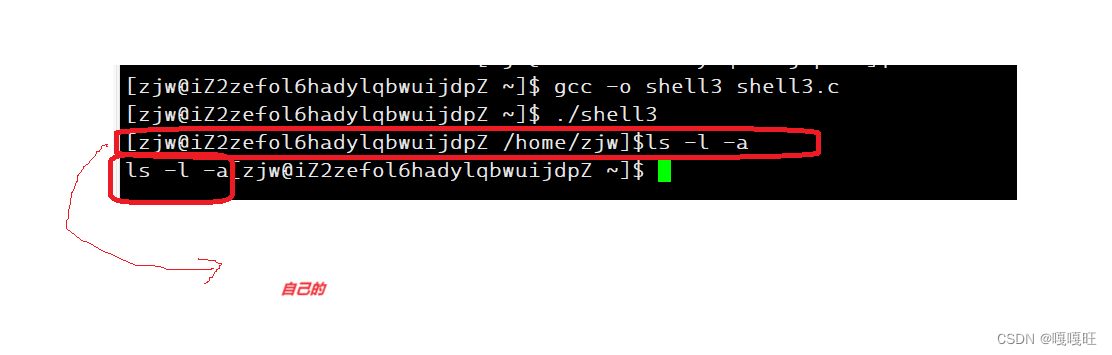
为了区别系统的和我们自己实现的,我们将]后面的$换成¥
效果展示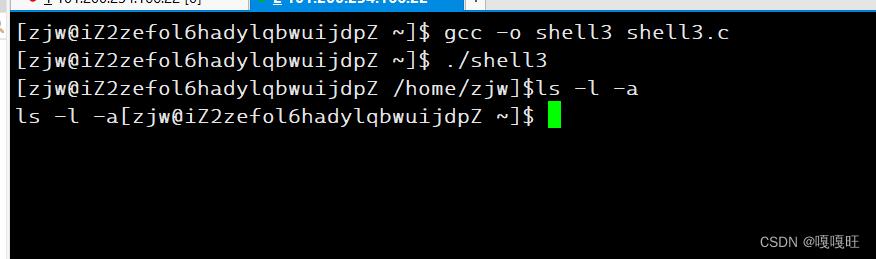
当前步骤代码展示
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 char arr[512]; 5 6 char*getname() 7 { 8 char *name=getenv("USER"); 9 if(name==NULL)return NULL; 10 return name; 11 } 12 char*gethostname() 13 { 14 char*hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); 15 if(hostname==NULL)return NULL; 16 return hostname; 17 } 18 char*getpwd() 19 { 20 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 21 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 22 return pwd; 23 } 24 void getcommandline() 25 { 26 printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethostname(),getpwd()); 27 } 28 void getcommandstr() 29 { 30 fgets(arr,sizeof(arr),stdin); 31 arr[strlen(arr)-1]='\0'; 32 33 } 34 int main() 35 { 36 getcommandline(); 37 getcommandstr(); 38 printf("%s",arr); 39 40 }3.分割第二步的指令以及选项到命令行参数表中
我们定义一个指针数组存放对应指令或者选项字符串的首地址,使用全局变量
默认可以存放32个字符串(指令或选项)的地址
#define NUM 32char* str[NUM];我们分隔字符串用strtok函数,可以去看看我的这边文章
strtok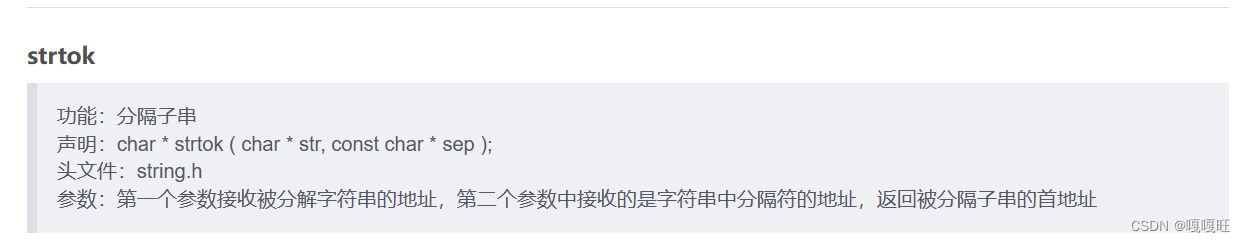
我们要分隔开arr数组,所以arr数组是第一个参数,而要用空格分开
#define SEP ' ' 而第二个参数我们传SEP就好了
而返回的地址则是第一个空格之前的字符串指令
接着我们给第一个参数传NULL,至于为什么,也在那个文章中讲到了
37 void splidcomandstr()38 {39 40 str[0]=strtok(arr,SEP);41 int index=1;42 while(str[index++]=strtok(NULL,SEP));43 }将分开的第一个指令字符串的起始地址放在arr[0]中,然后循环将每个分隔开的字符串指令放在str[index]中,然后让index++,当arr字符串分割完之后,strtok返回NULL,给str[index],然后返回NULL,循环结束
效果展示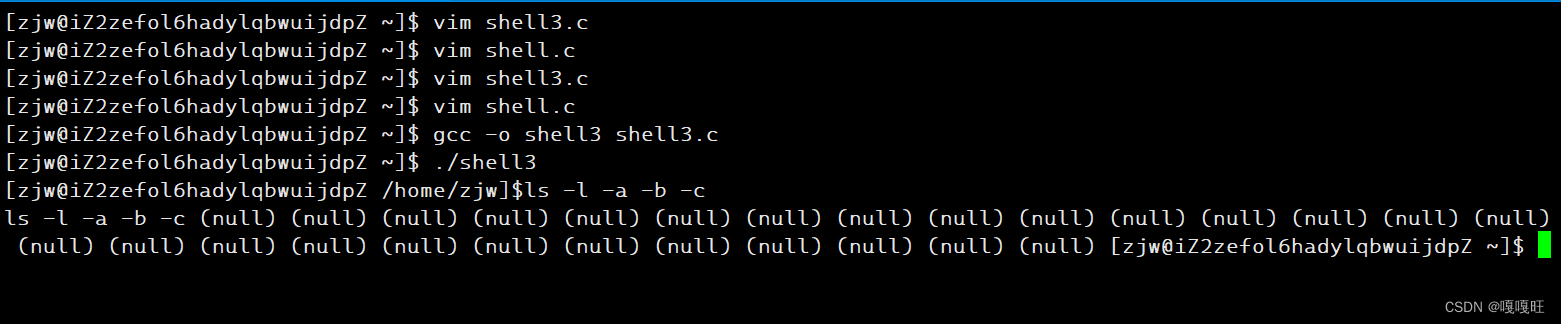
当前步骤代码展示
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 char arr[512]; 5 #define NUM 32 6 char* str[NUM]; 7 #define SEP " " 8 9 char*getname() 10 { 11 char *name=getenv("USER"); 12 if(name==NULL)return NULL; 13 return name; 14 } 15 char*gethostname() 16 { 17 char*hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); 18 if(hostname==NULL)return NULL; 19 return hostname; 20 } 21 char*getpwd() 22 { 23 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 24 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 25 return pwd; 26 } 27 void getcommandline() 28 { 29 printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethostname(),getpwd()); 30 } 31 void getcommandstr() 32 { 33 fgets(arr,sizeof(arr),stdin); 34 arr[strlen(arr)-1]='\0'; 35 36 } 37 void splidcomandstr() 38 { 39 40 str[0]=strtok(arr,SEP); 41 int index=1; 42 while(str[index++]=strtok(NULL,SEP)); 43 } 44 int main() 45 { 46 getcommandline(); 47 getcommandstr(); 48 splidcomandstr(); 49 int i; 50 for( i=0;i<32;i++) 51 {printf("%s ",str[i]);} 52 53 54 }5.进程替换
本来要先处理是否是内建命令的,但是我们先可以看这步,我们在第3步中,将分割开的指令字符串地址放在了str指针数组中,相当于命令行参数表,这一步我们要将对应的命令让子进程替换成对应命令的实现,大家可以去看一下之前的文章
进程的替换
针对我们已经有的命令行参数表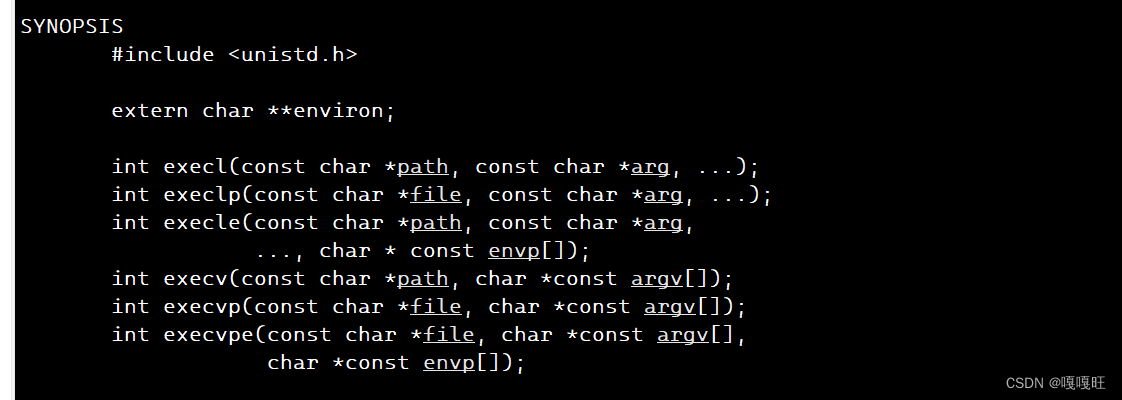
我们要使用的函数为
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[])
而str[0]是指令的地址,所以他是第一个参数,第二个参数为命令行参数表,所以是str
头文件
#include <unistd.h>由于我们要用子进程替换,所以我们会使用到fork函数来创建子进程,在子进程中调用 execvp函数,父进程需要等待回收子进程的pcb的结构内的退出码,以及退出状态,将子进程的内存释放,所以需要使用waitpid函数,这一模块的代码也在进程替换那篇文章讲过
48 void finishcommand() 49 { 50 int id=fork(); 51 if(id>0) 52 { 53 execvp(str[0],str); 54 exit(exitcode); 55 } 56 int status=0; 57 int ref=waitpid(id,&status,0); 58 if(ref>0) 59 { 60 61 exitcode=WEXITSTATUS(status); 62 if(exitcode!=0)printf("%s:%s:%d\n",str[0],strerror(exitcode),exitcode); 63 } 64 65 }此时我们已经可以用非内建命令了,为了让我们一直可以在我们自己写的命令行里跑指令,我们就加一个while循环
效果展示
top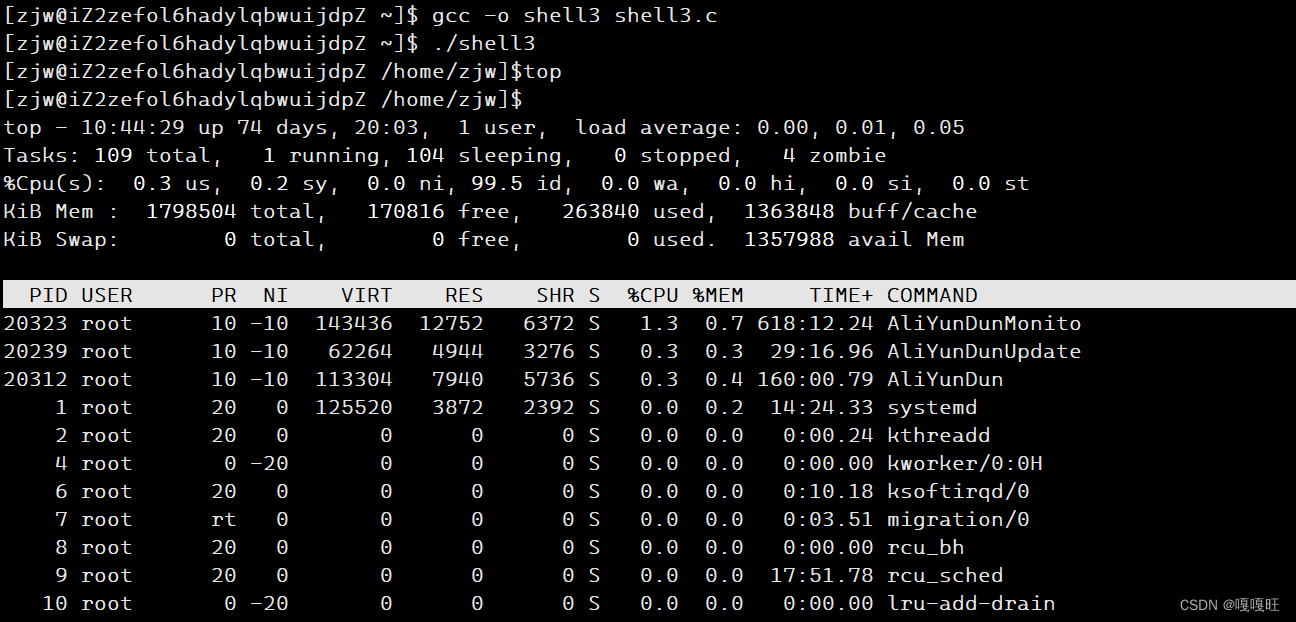
ls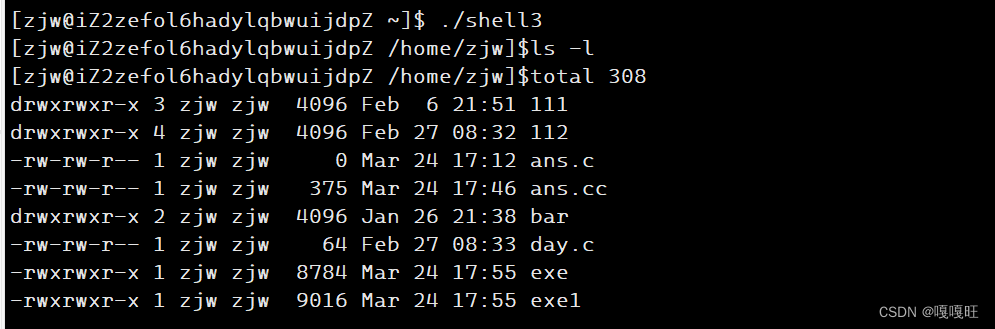
修改bug:
bug1:如果这里gethostname()报错的话,可能和库里面的名字冲突了,修改gethostname为gethost()
bug 2:如果这里陷入死循环,是因为fork给子进程返回的是0,这里写错了
48 void finishcommand() 49 { 50 int id=fork(); 51 if(id==0) 52 { 53 execvp(str[0],str); 54 exit(exitcode); 55 } 56 int status=0; 57 int ref=waitpid(id,&status,0); 58 if(ref>0) 59 { 60 61 exitcode=WEXITSTATUS(status); 62 if(exitcode!=0)printf("%s:%s:%d\n",str[0],strerror(exitcode),exitcode); 63 } 64 65 }当前步骤代码展示
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <sys/wait.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 char arr[512]; 9 #define NUM 32 10 char* str[NUM]; 11 #define SEP " " 12 int exitcode=0; 13 char*getname() 14 { 15 char *name=getenv("USER"); 16 if(name==NULL)return NULL; 17 return name; 18 } 19 char*gethost() 20 { 21 char*hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); 22 if(hostname==NULL)return NULL; 23 return hostname; 24 } 25 char*getpwd() 26 { 27 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 28 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 29 return pwd; 30 } 31 void getcommandline() 32 { 33 printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethost(),getpwd()); 34 } 35 void getcommandstr() 36 { 37 fgets(arr,sizeof(arr),stdin); 38 arr[strlen(arr)-1]='\0'; 39 40 } 41 void splidcomandstr() 42 { 43 44 str[0]=strtok(arr,SEP); 45 int index=1; 46 while((str[index++]=strtok(NULL,SEP))); 47 } 48 void finishcommand() 49 { 50 int id=fork(); 51 if(id==0) 52 { 53 execvp(str[0],str); 54 exit(exitcode); 55 } 56 int status=0; 57 int ref=waitpid(id,&status,0); 58 if(ref>0) 59 { 60 61 exitcode=WEXITSTATUS(status); 62 if(exitcode!=0)printf("%s:%s:%d\n",str[0],strerror(exitcode),exitcode); 63 } 64 65 } 66 int main() 67 { 68 int quit=0; 69 while(!quit) 70 { getcommandline(); 71 getcommandstr(); 72 splidcomandstr(); 73 finishcommand(); 74 75 }}4.处理内建命令
在处理内建命令前,需要处理一下命令行提示的路径,我们需要修改为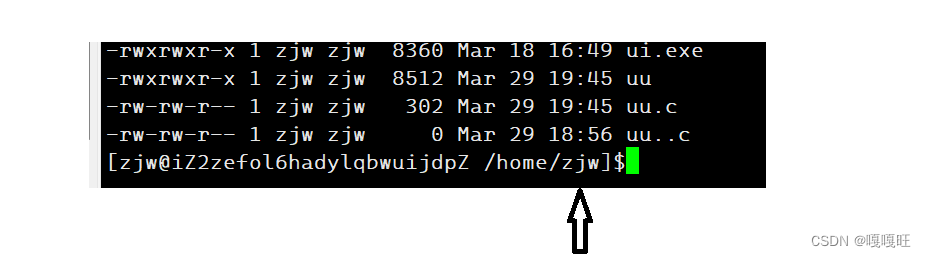
只保留最后一个/后面的路径,所以我们要修改一下getpwd函数
25 char*getpwd() 26 { 27 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 28 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 29 char*p=pwd+strlen(pwd)-1; 30 while((*p)!='/') 31 { 32 33 p--; 34 35 } 36 return p+1; 37 } 让p指针指向最后一个字母,然后遍历找最后一个‘/’,找到返回下一个位置的地址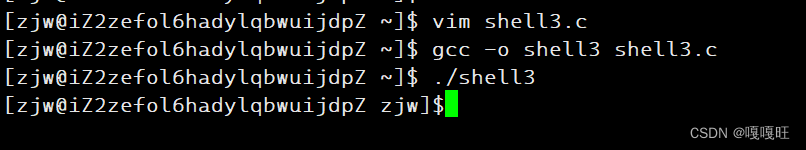
这里的~就是家目录zjw
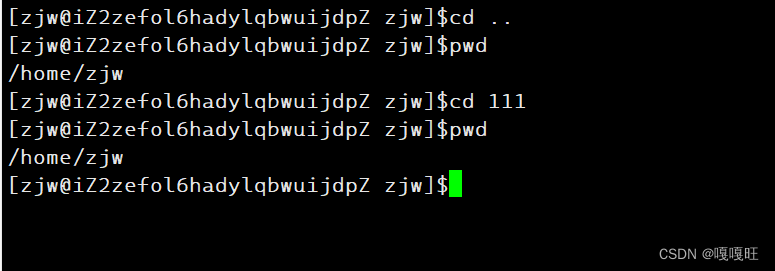
我们发现在命令行输入cd命令,怎么路径不变呢??
是因为执行命令的是子进程,改变路径的也是子进程,而我们打印的命令行是父进程在环境变量中拿到的值,子进程改变的环境变量不会写入环境变量表中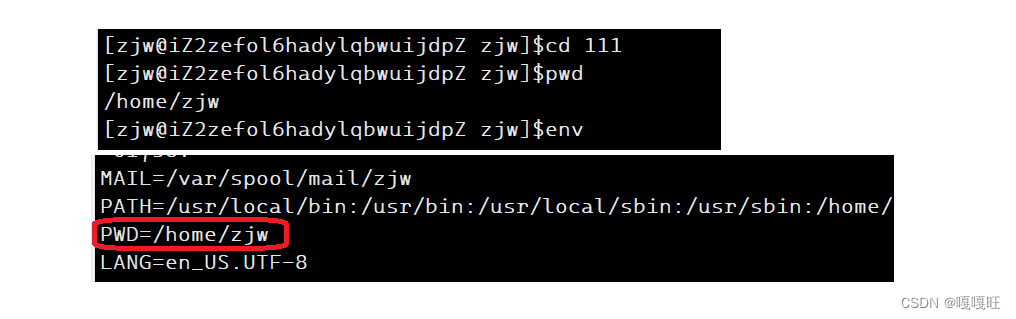
因为进程具有独立性
90 int Built_incommands() 91 { int yes=0; 92 char* built=str[0]; 93 if(strcmp(built,"cd")==0) 94 { 95 yes=1; 96 cd(); 97 } 98 else if(strcmp(built,"echo")==0&&strcmp(str[1],"$?")==0) 99 {100 yes=1;101 printf("%d\n",exitcode);102 exitcode=0;103 }104 105 return yes;106 107 }处理内建命令,如果第一个字符串为cd的话,yes置1,说明是内建命令,就不执行子进程的命令了,直接continue;
78 void cd() 79 { 80 char* path=str[1]; 81 if(path==NULL)path=gethome(); 82 chdir(path); 83 84 char cwd[1024]; 85 char temp[1024]; 86 getcwd(temp,sizeof(temp)); 87 snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp); 88 putenv(cwd); 89 }在cd函数内 如果输入的指令cd 没有加指令,所以str[1]就为NULL,path保存家目录地址,chdir函数为修改当前进程的路径,但是没有导入到环境变量中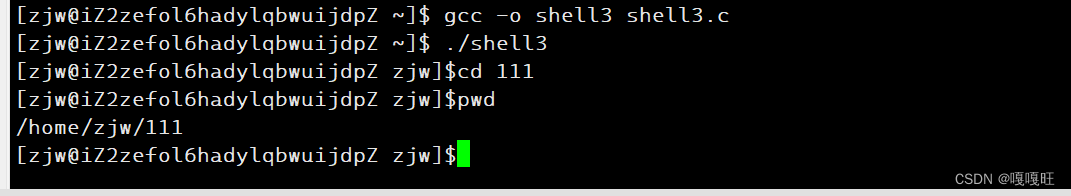
pwd为查看当前路径.而命令行提示中的路径为环境变量中的路径,getcwd会将当前进程的绝对路径保存在temp字符串中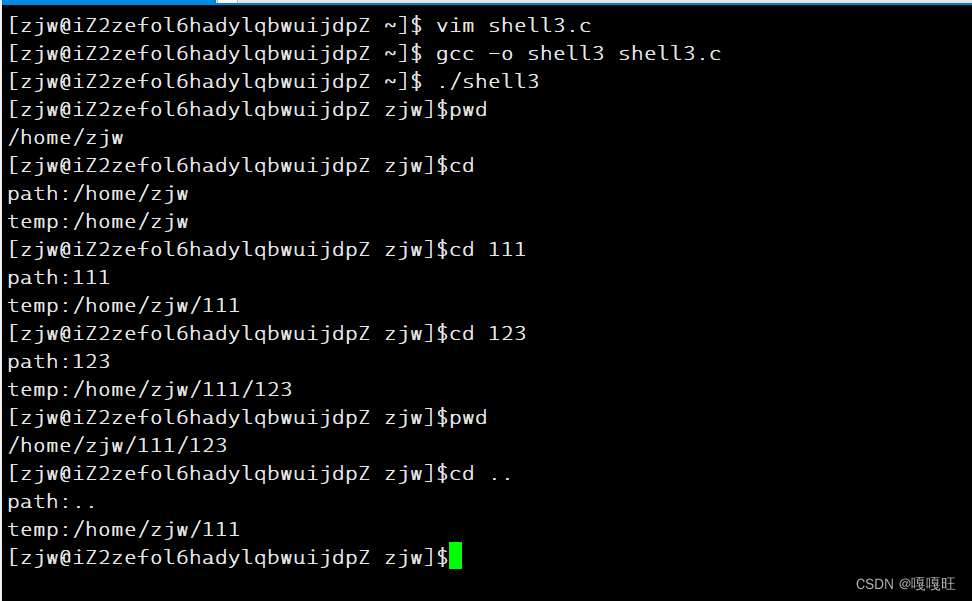
现在要做的是将temp字符串按照环境变量格式导入到环境变量表去.
使用 snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),“PWD=%s”,temp);
将temp的内容按PWD=temp的格式放到cwd字符串中去。
然后使用putenv导入环境变量。
这里为什么不直接将path按照环境变量格式导入到环境变量表去.因为cd …的话,path就是…了,如果导进去的话,命令行参数的路径就成为…了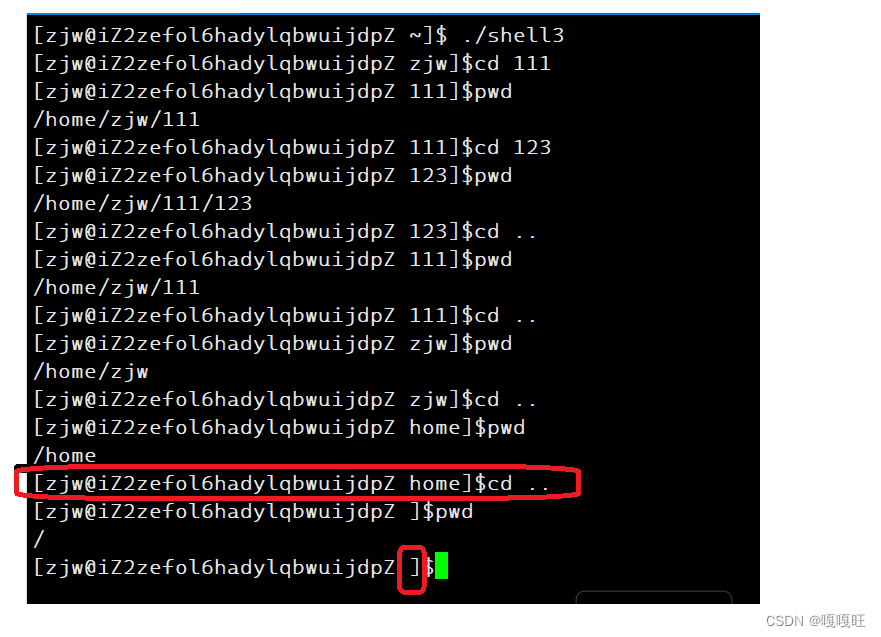
这里为了防止命令行参数中到家目录后在cd…到根目录,路径消失,如果getpwd()获取的字符串长度为1的话,就说明到根目录了,就不会消失了
void getcommandline() { printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethost(),strlen(getpwd())==1? "/" : getpwd()); }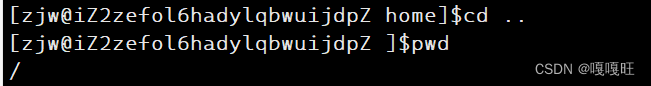
这里发现怎么还是不在呢??
因为getpwd是从最后一个/的下一个位置返回的,所以没有/了,所以我们直接在getpwd中返回/位置就行了,不要+1了,这时候strlen(getpwd())在家目录下就是1了,然后不在家目录下,就让返回的地址+1即可
30 char*getpwd() 31 { 32 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 33 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 34 char*p=pwd+strlen(pwd)-1; 35 while((*p)!='/') 36 { 37 38 p--; 39 40 } 41 return p; 42 }43 void getcommandline() 44 { 45 printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethost(),strlen(getpwd())==1? "/" : getpwd()+1); 46 }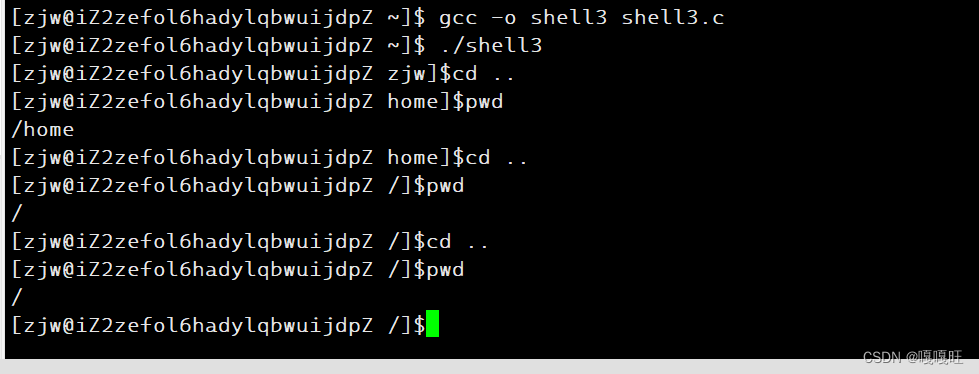
这样子就好了
在处理内建命令时,我们会使用 echo $?来查看子进程给父进程的退出码,我们在 Built_incommands() 函数中也需要处理,如果命令行参数第一个字符串为echo,并且第二个字符串为 $ ?,我们直接打印退出码即可,为了确保下次退出时,退出码重置为0.
在 finishcommand()中父进程得到子进程的退出码后,如果退出码不为0的话,我们使用strerror将对应的错误码对应的原因打印出啦
头文件为
#include<errno.h>6 源码分享
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <sys/wait.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 char arr[512]; 9 #define NUM 32 10 char* str[NUM]; 11 #define SEP " " 12 int exitcode=0; 13 char*getname() 14 { 15 char *name=getenv("USER"); 16 if(name==NULL)return NULL; 17 return name; 18 } 19 char*gethost() 20 { 21 char*hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); 22 if(hostname==NULL)return NULL; 23 return hostname; 24 } 25 char*gethome() { 26 char*home=getenv("HOME"); 27 if(home==NULL)return NULL; 28 return home; 29 } 30 char*getpwd() 31 { 32 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 33 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 34 char*p=pwd+strlen(pwd)-1; 35 while((*p)!='/') 36 { 37 38 p--; 39 40 } 41 return p; 42 } 43 void getcommandline() 44 { 45 printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethost(),strlen(getpwd())==1? "/" : getpwd()+1); 46 } 47 void getcommandstr() 48 { 49 fgets(arr,sizeof(arr),stdin); 50 arr[strlen(arr)-1]='\0'; 51 52 } 53 void splidcomandstr() 54 { 55 56 str[0]=strtok(arr,SEP); 57 int index=1; 58 while((str[index++]=strtok(NULL,SEP))); 59 } 60 void finishcommand() 61 { 62 int id=fork(); 63 if(id==0) 64 { 65 execvp(str[0],str); 66 exit(exitcode); 67 } 68 int status=0; 69 int ref=waitpid(id,&status,0); 70 if(ref>0) 71 { 72 73 exitcode=WEXITSTATUS(status); 74 if(exitcode!=0)printf("%s:%s:%d\n",str[0],strerror(exitcode),exitcode); 75 } 76 77 } 78 void cd() 79 { 80 char* path=str[1]; 81 if(path==NULL)path=gethome(); 82 chdir(path); 83 84 85 char cwd[1024]; 86 char temp[1024]; 87 getcwd(temp,sizeof(temp)); 88 89 snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp); 90 putenv(cwd); 91 } 92 int Built_incommands() 93 { int yes=0; 94 char* built=str[0]; 95 if(strcmp(built,"cd")==0) 96 { 97 yes=1; 97 yes=1; 98 cd(); 99 }100 else if(strcmp(built,"echo")==0&&strcmp(str[1],"$?")==0)101 {102 yes=1; 103 printf("%d\n",exitcode);104 exitcode=0;105 }106 107 return yes;108 109 }110 int main()111 {112 int quit=0;113 while(!quit)114 { getcommandline();115 getcommandstr();116 splidcomandstr();117 if(Built_incommands())118 continue;119 finishcommand();120 }121 }7.增加重定向功能
思路:我们将第二步处理过的指令以及选项的字符串拷贝到另一个字符串数组(copyarr)中,我们要遍历这个数组,找>(输出重定向),找>>(追加输出重定向),找<(输入重定向),定义全局变量表示当前指令以及选项中到底是哪种重定向方式
char copyarr[512]; #define None_Redir 0 #define In_Redir 1 #define Out_Redir 2 #define App_Redir 3 int redir_type=None_Redir;//首先还没有遍历无重定向 char *filename=NULL; //存放字符串中重定向后面的文件名的起始地址void redirection()142 {143 int begin=0;144 int end=strlen(copyarr);145 while(begin<end)146 {147 if(copyarr[begin]=='>')148 {149 if(copyarr[begin+1]=='>')150 {151 copyarr[begin++]=0;152 begin++;153 redir_type=App_Redir; 154 while(copyarr[begin]==' ')155 {begin++;}156 filename=copyarr+begin;157 }158 else159 { copyarr[begin++]=0;160 redir_type=Out_Redir;161 while(copyarr[begin]==' ') 162 {begin++;}163 filename=copyarr+begin;164 }165 166 }167 else if(copyarr[begin]=='<')168 {169 copyarr[begin++]=0; 170 redir_type=In_Redir;171 while(copyarr[begin]==' ') 172 {begin++;}173 filename=copyarr+begin;174 175 176 177 }178 else 179 {180 begin++;181 182 183 184 185 }186 187 }188 memset(arr,'\0',512);189 memcpy(arr,copyarr,strlen(copyarr));190 }上面这个函数就是读取指令字符串,将指令以及选项和后面的文件名分隔开,由于已经在第一个>或<或>>的第一个位置放0,所以处理后的copyarr是前面的指令带选项,而filename保存的是后面文件的起始地址,因为我们在第三步要分隔第二步处理好的字符串,所以我们再没有重定向标识,已经文件名的字符串又拷贝回arr中等待第三步分割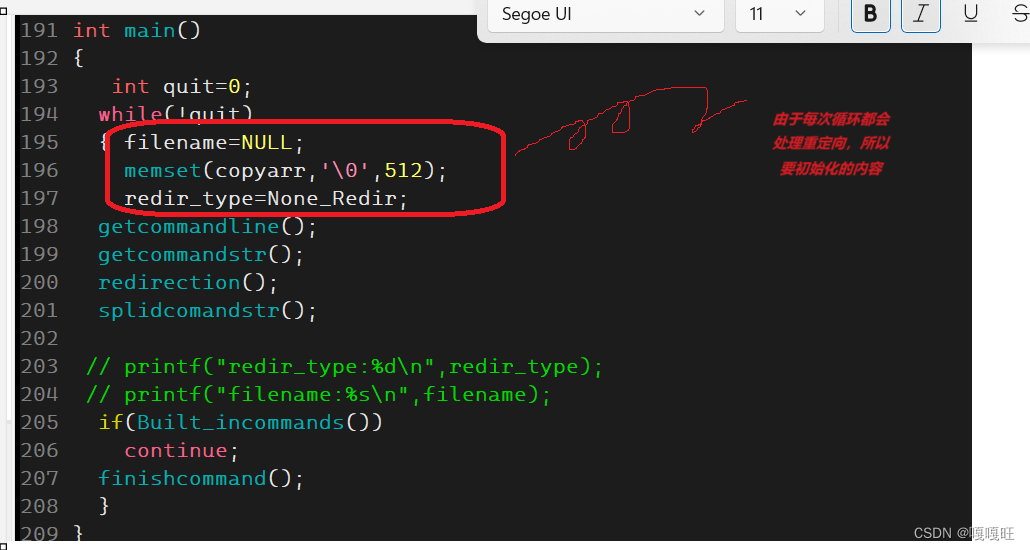
由于让子进程做进程替换不会影响父进程打开的文件,所以我们需要在子进程替换前进行处理重定向部分内容.
69 void finishcommand() 70 { 71 int id=fork(); 72 if(id==0) 73 { 74 if(filename!=NULL) 75 { 76 if(redir_type==App_Redir) 77 { 78 int fd=open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666); 79 dup2(fd,1); 80 } 81 else if(redir_type==Out_Redir) 82 { 83 int fd=open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666); 84 dup2(fd,1); 85 } 86 else if(redir_type==In_Redir) 87 { 88 89 int fd=open(filename,O_RDONLY); 90 dup2(fd,0); 91 } 92 else 93 {} 94 } 95 execvp(str[0],str); 96 exit(exitcode); 97 } 98 int status=0; 99 int ref=waitpid(id,&status,0);100 if(ref>0)101 {102 103 exitcode=WEXITSTATUS(status);104 if(exitcode!=0)printf("%s:%s:%d\n",str[0],strerror(exitcode),exitcode);105 }106 107 }这里说一下dup2这个函数,具体放在下一篇博客里面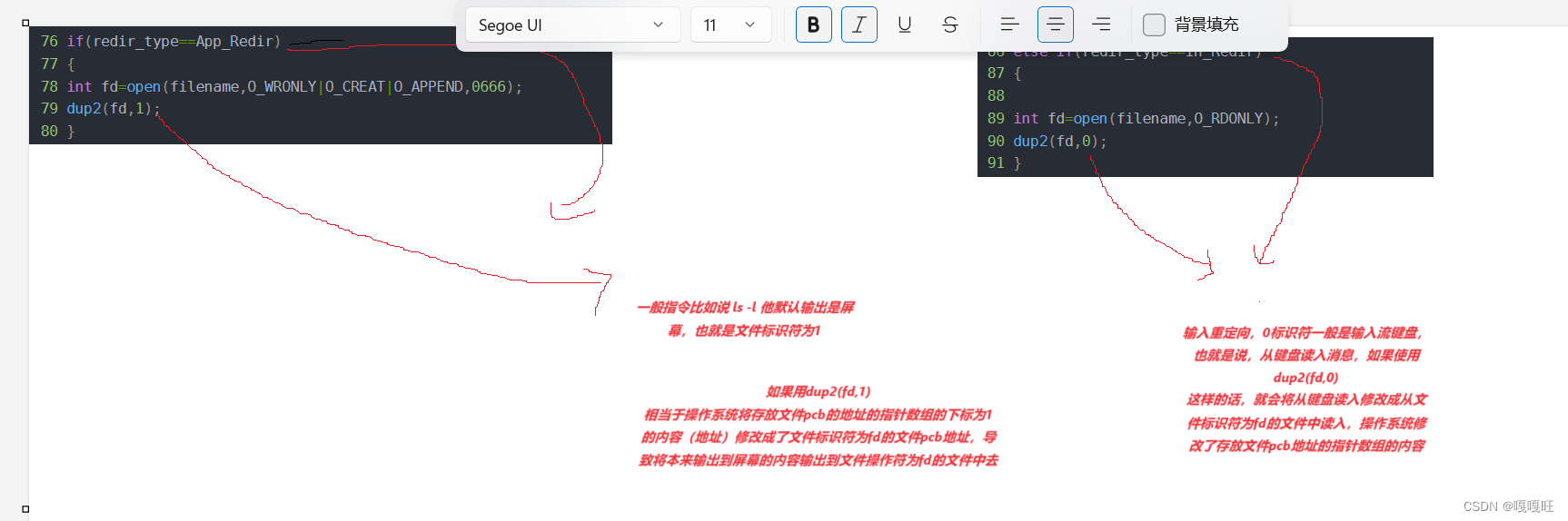
8.源码分享终
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <sys/wait.h> 7 #include<errno.h> 8 #include <sys/stat.h> 9 #include <fcntl.h> 10 char arr[512]; 11 char copyarr[512]; 12 #define NUM 32 13 char* str[NUM]; 14 #define SEP " " 15 #define None_Redir 0 16 #define In_Redir 1 17 #define Out_Redir 2 18 #define App_Redir 3 19 int redir_type=None_Redir; 20 int exitcode=0; 21 char *filename=NULL; 22 char*getname() 23 { 24 char *name=getenv("USER"); 25 if(name==NULL)return NULL; 26 return name; 27 } 28 char*gethost() 29 { 30 char*hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); 31 if(hostname==NULL)return NULL; 32 return hostname; 33 } 34 char*gethome() { 35 char*home=getenv("HOME"); 36 if(home==NULL)return NULL; 37 return home; 38 } 39 char*getpwd() 40 { 41 char*pwd=getenv("PWD"); 42 if(pwd==NULL)return NULL; 43 char*p=pwd+strlen(pwd)-1; 44 while((*p)!='/') 45 { 46 47 p--; 48 49 } 50 return p; 51 } 52 void getcommandline() 53 { 54 printf("[%s@%s %s]$",getname(),gethost(),strlen(getpwd())==1? "/" : getpwd()+1); 55 } 56 void getcommandstr() 57 { 58 fgets(arr,sizeof(arr),stdin); 59 arr[strlen(arr)-1]='\0'; 60 memcpy(copyarr,arr,strlen(arr)); 61 } 62 void splidcomandstr() 63 { 64 65 str[0]=strtok(arr,SEP); 66 int index=1; 67 while((str[index++]=strtok(NULL,SEP))); 68 } 69 void finishcommand() 70 { 71 int id=fork(); 72 if(id==0) 73 { 74 if(filename!=NULL) 75 { 76 if(redir_type==App_Redir) 77 { 78 int fd=open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666); 79 dup2(fd,1); 80 } 81 else if(redir_type==Out_Redir) 82 { 83 int fd=open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666); 84 dup2(fd,1); 85 } 86 else if(redir_type==In_Redir) 87 { 88 89 int fd=open(filename,O_RDONLY); 90 dup2(fd,0); 91 } 92 else 93 {} 94 } 95 execvp(str[0],str); 96 exit(exitcode); 97 } 98 int status=0; 99 int ref=waitpid(id,&status,0);100 if(ref>0)101 {102 103 exitcode=WEXITSTATUS(status);104 if(exitcode!=0)printf("%s:%s:%d\n",str[0],strerror(exitcode),exitcode);105 }106 107 }108 void cd()109 {110 char* path=str[1];111 if(path==NULL)path=gethome();112 chdir(path);113 114 115 char cwd[1024];116 117 char temp[1024];118 getcwd(temp,sizeof(temp));119 120 snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp); 121 putenv(cwd); 122 }123 int Built_incommands() 124 { int yes=0;125 char* built=str[0];126 if(strcmp(built,"cd")==0)127 {128 yes=1;129 cd();130 }131 else if(strcmp(built,"echo")==0&&strcmp(str[1],"$?")==0)132 {133 yes=1;134 printf("%d\n",exitcode);135 exitcode=0;136 }137 138 return yes;139 140 }141 void redirection()142 {143 int begin=0;144 int end=strlen(copyarr); 145 while(begin<end)146 {147 if(copyarr[begin]=='>')148 {149 if(copyarr[begin+1]=='>')150 {151 copyarr[begin++]=0;152 begin++;153 redir_type=App_Redir;154 while(copyarr[begin]==' ')155 {begin++;}156 filename=copyarr+begin;157 }158 else159 { copyarr[begin++]=0;160 redir_type=Out_Redir;161 while(copyarr[begin]==' ') 162 {begin++;}163 filename=copyarr+begin;164 }165 166 }167 else if(copyarr[begin]=='<')168 { 169 copyarr[begin++]=0; 170 redir_type=In_Redir;171 while(copyarr[begin]==' ') 172 {begin++;}173 filename=copyarr+begin;174 175 176 177 }178 else 179 {180 begin++;181 182 183 184 185 }186 187 }188 memset(arr,'\0',512);189 memcpy(arr,copyarr,strlen(copyarr));190 }191 int main()192 {193 int quit=0;194 while(!quit)195 { filename=NULL; 196 memset(copyarr,'\0',512);197 redir_type=None_Redir;198 getcommandline();199 getcommandstr();200 redirection(); 201 splidcomandstr();202 203 // printf("redir_type:%d\n",redir_type);204 // printf("filename:%s\n",filename);205 if(Built_incommands())206 continue;207 finishcommand();208 }209 } 输出重定向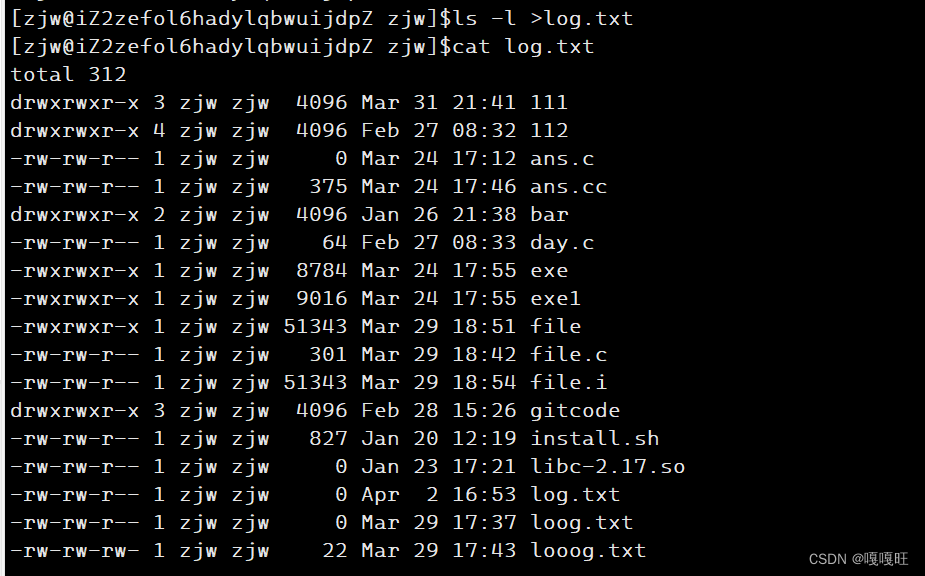
追加重定向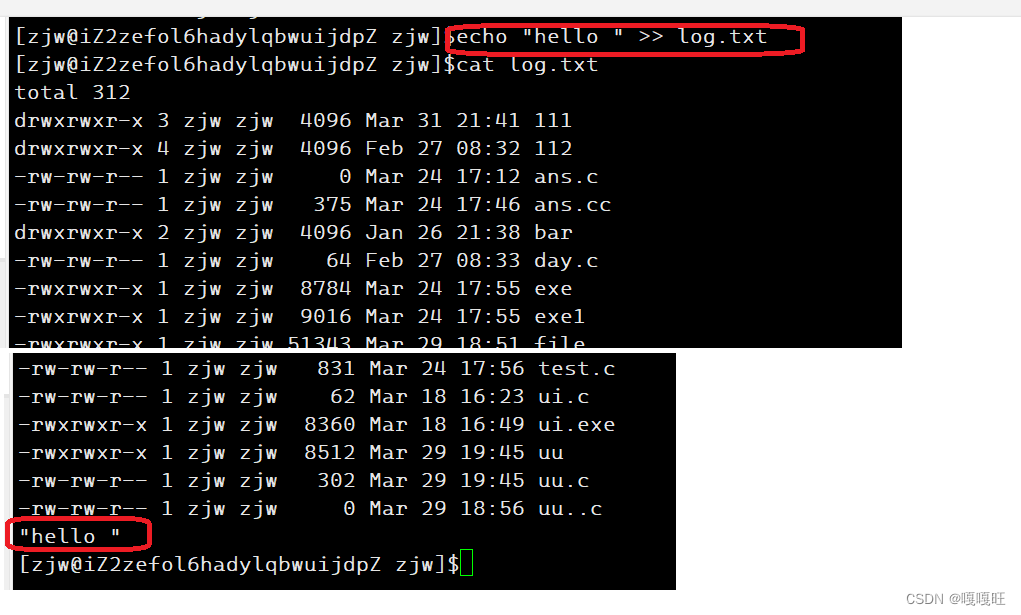
输入重定向