
?个人专栏:《Linux操作系统》《经典算法试题 》《C++》 《数据结构与算法》
☀️走在路上,不忘来时的初心
文章目录
一、Shell程序思路二、Shell代码展示
一、Shell程序思路
用下图的时间轴来表示事件的发生次序。其中时间从左向右。shell由标识为sh的方块代表,它随着时间的流逝从左向右移动。shell从用户读入字符串"ls"。shell建立一个新的进程,然后在那个进程中运行ls程序并等待那个进程结束。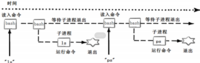
然后shell读取新的一行输入,建立一个新的进程,在这个进程中运行程序 并等待这个进程结束。
根据这些思路,和我们前面的学的技术,就可以自己来实现一个shell了。
二、Shell代码展示
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#define NUM 1024#define SIZE 64#define SEP " "//#define Debug 1char cwd[1024];char enval[1024]; // for testint lastcode = 0;char *homepath(){ char *home = getenv("HOME"); if(home) return home; else return (char*)".";}const char *getUsername(){ const char *name = getenv("USER"); if(name) return name; else return "none";}const char *getHostname(){ const char *hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if(hostname) return hostname; else return "none";}const char *getCwd(){ const char *cwd = getenv("PWD"); if(cwd) return cwd; else return "none";}int getUserCommand(char *command, int num){ printf("[%s@%s %s]# ", getUsername(), getHostname(), getCwd()); char *r = fgets(command, num, stdin); // 最终你还是会输入\n if(r == NULL) return -1; // "abcd\n" "\n" command[strlen(command) - 1] = '\0'; // 有没有可能越界?不会 return strlen(command);}void commandSplit(char *in, char *out[]){ int argc = 0; out[argc++] = strtok(in, SEP); while( out[argc++] = strtok(NULL, SEP));#ifdef Debug for(int i = 0; out[i]; i++) { printf("%d:%s\n", i, out[i]); }#endif}int execute(char *argv[]){ pid_t id = fork(); if(id < 0) return -1; else if(id == 0) //child { // exec command execvp(argv[0], argv); // cd .. exit(1); } else // father { int status = 0; pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0); if(rid > 0){ lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status); } } return 0;}void cd(const char *path){ chdir(path); char tmp[1024]; getcwd(tmp, sizeof(tmp)); sprintf(cwd, "PWD=%s", tmp); // bug putenv(cwd);}// 什么叫做内键命令: 内建命令就是bash自己执行的,类似于自己内部的一个函数!// 1->yes, 0->no, -1->errint doBuildin(char *argv[]){ if(strcmp(argv[0], "cd") == 0) { char *path = NULL; if(argv[1] == NULL) path=homepath(); else path = argv[1]; cd(path); return 1; } else if(strcmp(argv[0], "export") == 0) { if(argv[1] == NULL) return 1; strcpy(enval, argv[1]); putenv(enval); // ??? return 1; } else if(strcmp(argv[0], "echo") == 0) { if(argv[1] == NULL){ printf("\n"); return 1; } if(*(argv[1]) == '$' && strlen(argv[1]) > 1){ char *val = argv[1]+1; // $PATH $? if(strcmp(val, "?") == 0) { printf("%d\n", lastcode); lastcode = 0; } else{ const char *enval = getenv(val); if(enval) printf("%s\n", enval); else printf("\n"); } return 1; } else { printf("%s\n", argv[1]); return 1; } } else if(0){} return 0;}int main(){ while(1){ char usercommand[NUM]; char *argv[SIZE]; // 1. 打印提示符&&获取用户命令字符串获取成功 int n = getUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); if(n <= 0) continue; // 2. 分割字符串 // "ls -a -l" -> "ls" "-a" "-l" commandSplit(usercommand, argv); // 3. check build-in command n = doBuildin(argv); if(n) continue; // 4. 执行对应的命令 execute(argv); }}