目录
商品对象信息获取
商品对象信息输入
商品对象信息计算
商品对象信息统计
学生数据管理实现
商品对象信息获取
题目要求是这样的:
定义数组存储3个商品对象。
商品的属性:商品的id,名字,价格,库存。
创建三个商品对象,并把商品对象存入到数组当中。
创建Goods类封装商品信息类管理商品数据,里面有商品的私有信息,以及获取和设置成员变量的值的方法,通过调用Goods对象中的方法来对数据进行增删改查操作:
public class Goods { private String id; private String name; private double price; private int count; // 创建构造函数 public Goods(String id, String name, double price, int count) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.price = price; this.count = count; } // 创建getter和setter public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; }}新创建一个Java类,这个类包含了一个main()方法,该方法用于测试Goods类的功能。在 main()方法中,首先创建了一个 Goods 类型的数组 arr,并且创建了三个 Goods 对象 g1、g2 和 g3,分别表示三种手机商品。然后,将这三个商品对象添加到数组中。最后,通过循环遍历数组,输出每个商品对象的信息(id、name、price、count):
public class GoodsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个数组 Goods[] arr = new Goods[3]; // 创建三个商品对象 Goods g1 = new Goods("001", "华为手机", 8000, 5); Goods g2 = new Goods("002", "苹果手机", 11000.0, 7); Goods g3 = new Goods("003", "安卓手机", 6000.9, 1); // 将商品添加到数组当中 arr[0] = g1; arr[1] = g2; arr[2] = g3; // 遍历数组 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { Goods goods = arr[i]; System.out.println(goods.getId()+", "+goods.getName()+", "+goods.getPrice()+", "+goods.getCount()); } }}最终呈现的效果如下:

商品对象信息输入
题目要求是这样的:
定义数组存储3部汽车对象。
汽车的属性:品牌,价格,颜色。
创建三个汽车对象,数据通过键盘录入而来,并把数据存入到数组当中。
创建Car类封装汽车信息类管理汽车数据,里面有汽车的私有信息,以及获取和设置成员变量的值的方法,通过调用Car对象中的方法来对数据进行增删改查操作:
public class Car { private String brand; private int price; private String color; // 创建构造函数 public Car() {} public Car(String brand, int price, String color) { this.brand = brand; this.price = price; this.color = color; } // 创建getter和setter方法 public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; }}创建了一个名为CarTest的Java类。这个类用于测试Car类的功能。首先创建了一个 Car 类型的数组 arr,用来存储三个汽车对象。然后使用 Scanner 类从键盘输入汽车的品牌、价格和颜色,并将这些信息设置到每个汽车对象中。接着,将每个汽车对象添加到数组中。最后,通过循环遍历数组,输出每个汽车对象的品牌、价格和颜色。
import java.util.Scanner;public class CarTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个数组用来存储3个汽车对象 Car[] arr = new Car[3]; // 创建汽车对象,数据键盘录入 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // 创建空的汽车对象 Car c = new Car(); // 录入品牌 System.out.println("请输入汽车的品牌"); String brand = sc.next(); c.setBrand(brand); // 间键盘录入的数据写入 // 录入价格 System.out.println("请输入汽车的价格"); int price = sc.nextInt(); c.setPrice(price); // 录入颜色 System.out.println("请输入汽车的颜色"); String color = sc.next(); c.setColor(color); // 把汽车对象添加到数组中 arr[i] = c; } // 遍历数组 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { Car car = arr[i]; System.out.println(car.getBrand()+", "+car.getPrice()+", "+car.getColor()); } }}最终呈现的效果如下:

商品对象信息计算
题目要求是这样的:
定义数组存储3部手机对象。
手机的属性:品牌,价格,颜色。
要求计算出三部手机的平均价格。
创建Phone类封装手机信息类管理手机数据,里面有手机的私有信息,以及获取和设置成员变量的值的方法,通过调用Phone对象中的方法来对数据进行增删改查操作:
public class Phone { private String brand; private int price; private String color; // 创建构造函数 public Phone() {} public Phone(String brand, int price, String color) { this.brand = brand; this.price = price; this.color = color; } // 创建getter和setter方法 public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; }}创建了一个名为 PhoneTest 的 Java 类。这个类用于测试 Phone 类的功能。在 main() 方法中,首先创建了一个 Phone 类型的数组 arr,用来存储三个手机对象。然后,通过使用 Phone 类的构造函数,创建了三个手机对象,并分别设置了品牌、价格和颜色。
接下来,将每个手机对象添加到数组中的对应位置。然后,通过循环遍历数组,计算所有手机的总价格,并将结果保存在变量 sum 中。最后,计算手机价格的平均值,并输出结果。
public class PhoneTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个数组 Phone[] arr = new Phone[3]; // 创建手机对象 Phone p1 = new Phone("小米", 4900, "黑色"); Phone p2 = new Phone("苹果", 7900, "白色"); Phone p3 = new Phone("华为", 4200, "蓝色"); // 将手机对象添加到数组当中 arr[0] = p1; arr[1] = p2; arr[2] = p3; // 获取三部手机的总价格 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { Phone phone = arr[i]; sum+= phone.getPrice(); } // 获取平均值 int avg = sum / arr.length; System.out.println(avg); }}最终呈现的效果如下:
商品对象信息统计
定义数组存储4个电脑的对象
电脑的属性:品牌、价格、颜色、种类
要求1:计算出4个电脑的平均价格
要求2:统计价格比平均值低的电脑有几个?并把它们的所有信息打印出来。
创建Computer类封装电脑信息类管理电脑数据,里面有电脑的私有信息,以及获取和设置成员变量的值的方法,通过调用Computer对象中的方法来对数据进行增删改查操作:
public class Computer { private String brand; // 品牌 private double price; // 价格 private String color; // 颜色 private String type; // 种类 public Computer() { } public Computer(String brand, double price, String color, String type) { this.brand = brand; this.price = price; this.color = color; this.type = type; } public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; }}下面这段代码主要展示了面向对象编程中类和对象的使用,以及数组的操作和循环遍历的应用。通过这个例子可以更好地理解 Java 中的类和对象的概念,以及如何进行简单的数据处理和统计分析:
public class ComputerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义数组存入电脑对象 Computer[] arr = new Computer[4]; // 创建电脑对象 Computer cp1 = new Computer("戴尔", 4900.0, "白色", "笔记本"); Computer cp2 = new Computer("神舟", 8200.0, "蓝色色", "台式"); Computer cp3 = new Computer("联想", 6900.0, "黑色", "笔记本"); Computer cp4 = new Computer("机器人", 3900.0, "红色", "台式"); // 把对象添加到数组中 arr[0] = cp1; arr[1] = cp2; arr[2] = cp3; arr[3] = cp4; // 求和 double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { Computer cp = arr[i]; sum += cp.getPrice(); } System.out.println("求和值为:"+ sum); // 平均值 double avg = sum / arr.length; System.out.println("平均值为:"+ avg); // 统计价格比平均值低的有几个,并打印其信息 int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { Computer cp = arr[i]; if(cp.getPrice()<avg){ System.out.println(cp.getBrand()+", "+cp.getPrice()+", "+cp.getColor()+", "+cp.getType()); count++; } } System.out.println("低于平均价格的数量为:"+ count); }}最终呈现的效果如下:

学生数据管理实现
定义数组存储4个电脑的对象
定义一个长度为3的数组,数组存储1~3名学生对象作为初始数据,学生对象的学号,姓名各不相同,学生的属性:学号,姓名,年龄。
要求1:再次添加一个学生对象,并在添加的时候进行学号的唯一性判断。
要求2:添加完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
要求3:通过id删除学生信息,如果存在,则删除,如果不存在,则提示删除失败。
要求4:删除完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
要求5:查询数组id为“heima002”的学生,如果存在,则将他的年龄+1岁
创建Students类封装学生信息类管理学生数据,里面有学生的私有信息,以及获取和设置成员变量的值的方法,通过调用Students对象中的方法来对数据进行增删改查操作:
public class Students { private int id; private String name; private int age; public Students() { } public Students(int id, String name, int age) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }}下面这段代码实现了对一个学生对象数组的增、删、改、查操作,具体实现思路如下:
1)创建一个存储学生对象的数组,长度为3:
Students[] arr = new Students[3];2)创建三个学生对象,将它们添加到数组中:
Students stu1 = new Students(1,"zhangsan",20);Students stu2 = new Students(2,"lisi",35);Students stu3 = new Students(3,"wangwu",10);arr[0] = stu1;arr[1] = stu2;arr[2] = stu3;3)添加一个新学生对象,并进行学号的唯一性判断:
Students stu4 = new Students(4,"xiaoming",15);boolean flag = contains(arr, stu4.getId());if (flag) { System.out.println("当前id值重复,请修改id后再进行添加");} else { // 执行添加操作}4)如果数组已满,则创建一个新数组,否则直接在原数组上添加:
if(count == arr.length){ Students[] newArr = createNewArr(arr); newArr[count] = stu4; printArr(newArr);} else { arr[count] = stu4; printArr(arr);}5)通过学号删除一个学生对象,先找到该学生在数组中的位置,然后将其删除:
int index = getIdIndex(newArr, 4);if (index >= 0) { if (arr.length < index){ arr[index] = null; printArr(arr); }else { newArr[index] = null; printArr(newArr); }} else { System.out.println("当前的id不存在,删除失败");}6)修改一个学生对象的年龄,先找到该学生在数组中的位置,然后将其年龄加1:
int index1 = getIdIndex(newArr, 2);if (index1>0){ Students stu = arr[index1]; int newAge = stu.getAge() + 1; stu.setAge(newAge); printArr(newArr);}else { System.out.println("当前的id不存在,修改失败");}还有其他辅助方法包括:打印数组元素、创建新数组、获取数组元素个数、判断学号是否重复等。总体思路是基于一个学生数组对象进行操作,对其增删改查等多个操作都需要先找到该学生在数组中的索引位置,然后再进行相关操作。同时还需要注意学号唯一性等问题,具体代码如下:
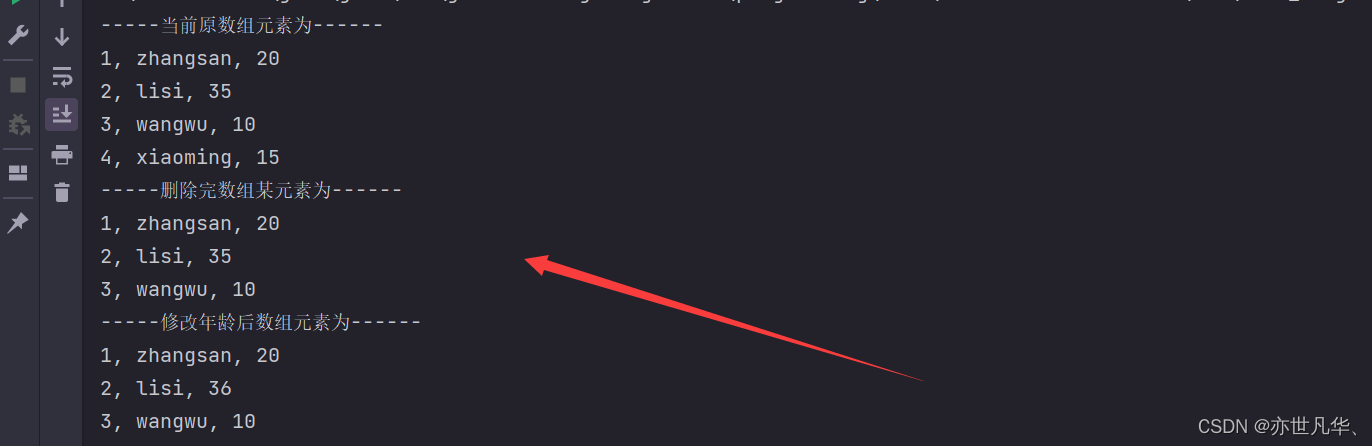
public class StudentsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个数组用来存储学生对象 Students[] arr = new Students[3]; // 创建学生对象并添加到数组当中 Students stu1 = new Students(1,"zhangsan",20); Students stu2 = new Students(2,"lisi",35); Students stu3 = new Students(3,"wangwu",10); // 把学生对象添加到数组当中 arr[0] = stu1; arr[1] = stu2; arr[2] = stu3; // 再次添加一个学生对象,并在添加的时候进行学号的唯一性判断 Students stu4 = new Students(4,"xiaoming",15); // 唯一性判断 boolean flag = contains(arr, stu4.getId()); Students[] newArr = createNewArr(arr); if (flag) { // 数组元素已存在,不用添加 System.out.println("当前id值重复,请修改id后再进行添加"); }else { // 数组元素不存在,可以把学生对象添加进数组中 int count = getCount(arr); if(count == arr.length){ // 数组长度已经存满,创建一个新数组,长度=老数组的长度+1,然后把老数组的元素拷贝到新数组当中 newArr[count] = stu4; // 添加完毕之后,遍历所有的学生信息 System.out.println("-----当前原数组元素为------"); printArr(newArr); } else { // 数组长度没有存满,假设数组已经存了两个 [stu1, stu2, null] // getCount获取到的是2,表示数组当中已经有了2个元素,如果下一次要添加数据,就是添加到数组长度的位置,即2索引,值就是count arr[count] = stu4; // 添加完毕之后,遍历所有的学生信息 printArr(arr); System.out.println("-----当前原数组元素为------"); } } // 通过id删除学生信息 int index = getIdIndex(newArr, 4); if (index >= 0) { System.out.println("-----删除完数组某元素为------"); if (arr.length < index){ arr[index] = null; printArr(arr); }else { newArr[index] = null; printArr(newArr); } }else { // 如果不存在,则表示删除失败 System.out.println("当前的id不存在,删除失败"); } // 查询数组id为2的学生,如果存在则将他的年龄+1 int index1 = getIdIndex(newArr, 2); if (index1>0){ // 存在 System.out.println("-----修改年龄后数组元素为------"); Students stu = arr[index1]; int newAge = stu.getAge() + 1; stu.setAge(newAge); printArr(newArr); } else { // 不存在直接显示 System.out.println("当前的id不存在,修改失败"); } } // 找到id在数组当中的索引 public static int getIdIndex(Students[] arr, int id) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // 依次得到每一个学生对象 Students stu = arr[i]; // 对stu进行一个非空判断 if (stu != null) { int sid = stu.getId(); if(sid == id){ return i; } } } return -1; } // 打印数组元素 public static void printArr(Students[] arr) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { Students stu = arr[i]; if (stu != null) { System.out.println(stu.getId()+", "+stu.getName()+", "+stu.getAge()); } } } // 创建新数组用于添加新元素 public static Students[] createNewArr(Students[] arr) { Students[] newArr = new Students[arr.length + 1]; // 循环遍历老数组中的元素 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { newArr[i] = arr[i]; } // 把新数组返回 return newArr; } // 定义一个方法判断数组中已经存在了几个元素 public static int getCount(Students[] arr) { // 统计变量 int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { if (arr[i] != null){ count++; } } // 返回数组元素个数 return count; } // 添加新数据到数组中进行学号的唯一性判断 public static boolean contains(Students[] arr, int id) { // 依次获取到数组里面的每一个学生对象 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // 依次获取到数组里面的每一个学生对象 Students stu = arr[i]; if (stu != null){ // 获取数组中学生对象的id int sid = stu.getId(); // 比较 if (sid == id) { return true; } } } // 当循环结束之后,没有找到id那么就表示数组中要查找的id是不存在的 return false; }}得到的结果如下: