讲解基于springboot + vue + axios项目。
Content-Type位于请求头和响应头,在请求中指示请求体的数据类型;在响应中指示响应体的数据类型。在HTTP请求中,默认的Content-Type类是"application/x-www-form-urlencoded",而在HTTP响应中,默认的Content-Type类型取决于所返回的内容类型,如HTML、纯文本或JSON等,springboot通常返回JSON数据,则Content-Type为application/jsonget请求可以用于提交表单,但是表单数据会以查询参数的形式拼接到url中,这样有两个弊端,url长度是受限的和数据明文暴露不安全。提交表单一般使用post请求,这种请求方式先设置Content-Type为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,表单数据会跟据Content-Type类型进行url编码,使得表单数据在传输过程中相对安全,表单数据会放到请求体中。将表单数据封装到请求体中是由浏览器或HTTP请求库(比如axios)来完成的:通过前端页面点击按钮提交表单是浏览器将表单数据封装到请求体的,通过axios代码提交表单是由HTTP请求库(即axios)将表单数据封装到请求体的请求发送过程:(1)axios设置请求体中数据的类型,即设置Content-Type的类型。(2)前端工程师组织请求参数。(3)axios自动将请求参数转化为Content-Type规定的类型并将其封装到请求体中。(4)springboot接收到请求,查看请求头中的Content-Type并跟据其指定的类型解析请求体,先解析出JSON类型的请求参数来。(5)springboot的类型转换器开始工作,将JSON类型的请求参数转换为处理方法的参数类型,这是自动的过程,表现出的效果就是后端得到了处理方法所需要的参数类型的请求参数springboot中的请求传参方式:(1)路径参数,相关注解为@PathVariable。@PathVariable用于将路径参数绑定到方法参数上。使用方法:
@GetMapping(“/{id}”)
public User queryById(@PathVariable(“id”) String userId){
return userService.getById(userId);
}或
@GetMapping(“/{id}”)
public User queryById(@PathVariable String id){
return userService.getById(id);
}
(2)查询参数即在url中通过?拼接参数,相关注解为@RequestParam,注意@RequestParam可以处理查询参数,但查询参数的处理并不一定需要@RequestParam,也可以不用任何注解
(3)请求体参数,相关注解为@RequestBody,@RequestBody用来接收请求体中的数据,@RequestBody 注解将请求体自动转换为 Java 对象。@RequestBody标注一个对象,请求中的JSON数据的字段,能与它标注的对象的属性对应的,就给属性赋值。springboot中的请求风格及相关注解:(1)普通请求 (2)restful请求
(1)普通请求
//增 @PostMapping public boolean add(@RequestBody User user){ return userService.save(user); } //删 @DeleteMapping public boolean delete(@RequestParam String id){ return userService.removeById(id); } //改 @PutMapping public boolean update(@RequestParam String id, @RequestBody User user){ user.setId(Integer.valueOf(id)); return userService.updateById(user); } //查 @GetMapping public User select(@RequestParam String id){ return userService.getById(id); }增加:post请求,body中选JSON,添加json格式的数据,此时Headers中会自动加上Content-Type=application/json,因为传递JSON数据时,Content-Type=application/json是必须的,Content-Type用来指定请求体的数据格式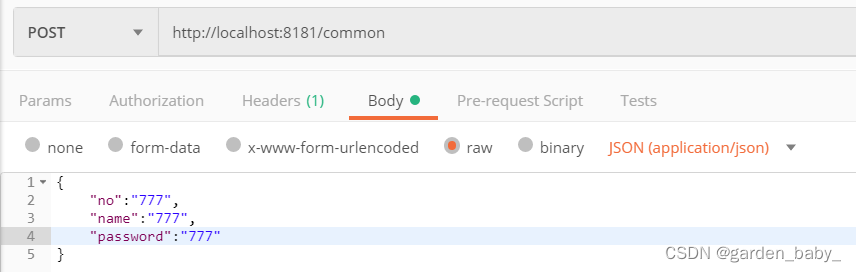
删除:delete请求,在Params中填id=7,不需要在Headers中填Content-Type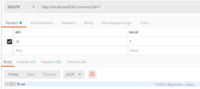
修改:put请求,Params中填查询参数id=7,body中选择JSON,填写要提交的数据,此时Headers中会自动加上Content-Type=application/json,因为传递JSON数据时,Content-Type=application/json是必须的,Content-Type用来指定请求体的数据格式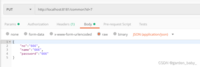
查询:Params中填写id=7,不需要在Headers中填Content-Type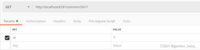
(2)restful请求
//增 @PostMapping public boolean save(@RequestBody User user){ return userService.save(user); } //删 @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public boolean remove(@PathVariable String id){ return userService.removeById(id); } //改 @PutMapping("/{id}") public boolean updateById(@PathVariable String id,@RequestBody User user){ user.setId(Integer.parseInt(id)); return userService.updateById(user); } //跟据id查询 @GetMapping("/{id}") public User queryById(@PathVariable String id){ return userService.getById(id); }postman设置:
增加,Headers中填Content-Type=application/json,Body中选raw,再选JSON(application/json),post请求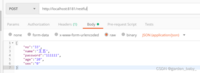
删除,Headers中不填Content-Type,body中选none,注意路径上填写目标记录的id,delete请求
修改,Headers中填Content-Type=application/json,Body中选raw,再选JSON(application/json),注意路径上填写目标记录的id,put请求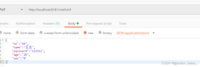
查询,Headers中不填Content-Type,body中选none,注意路径上填写目标记录的id,get请求
@GetMapping
public User select(@RequestParam String id){
return userService.getById(id);
}
和
@GetMapping
public User select(String id){
return userService.getById(id);
}`
都能正确处理请求,不同之处是,被@RequestParam标注的方法所处理的请求中必须包含名为 “id” 的参数,如果没有该参数,将会抛出异常;情况二没有使用 @RequestParam ,直接定义了方法参数:String id。这种情况下,Spring 会根据后端方法参数名 “id” 尝试在请求中查找同名的参数,并将其绑定到后端方法参数"id"上。如果请求中没有传递名为 “id” 的参数,后端方法参数"id"将被设置为 null。
Map 类型也可以接收前端的请求参数。可接收的参数包括URL中通过 ? 拼接的查询参数和请求体中的表单参数。
前者使用方法:后端直接map.get(“前端请求参数名”)即可得到前端请求参数值
示例:
前端请求:http://localhost:8181/common/conditional?no=666&name=666&age=18
后端代码:
@GetMapping(“/conditional”)
public User conditionalQuery(@RequestParam Map map){
//不指定Map的泛型时,键和值的类型都默认为Object。因为前端通过地址栏传参(前端使用查询参数),所以请求参数的键和值到后端时都为String类型
String no = (String) map.get(“no”);
String name = (String) map.get(“name”);
String age = (String) map.get(“age”);
int intAge = Integer.parseInt(age);
System.out.println(no);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(intAge);
return userService.conditionalQuery(no,name,intAge);
}
后者代码如下:
@PostMapping(“/conditional/reqbody”)
public User conditionalQueryReqBody(@RequestBody Map map){
//没有指定Map泛型的话,前端参数如果以JSON格式传来,那么map中的键和值都为String类型;如果指定泛型的话,@RequestBody会将查询参数值的类型转换为泛型类型,举例:
//@RequestBody Map<String,Integer> map中,@RequestBody会将JSON格式的查询参数值转换为Integer
//http://localhost:8181/common/conditional/reqbody?no=666&name=666&age=18中,no=666、name=666和age=18称为查询参数,no为查询参数的键,666为查询参数的值
System.err.println(map.get(“age”) instanceof String);//true
String no = (String) map.get(“no”);
String name = (String) map.get(“name”);
String age = (String) map.get(“age”);
int intAge = Integer.parseInt(age);
System.out.println(no);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(intAge);
return userService.conditionalQuery(no,name,intAge);
}
表单:可以在前端使用 HTML 表单构建页面,用户填写表单后,可以通过 POST 请求将表单数据发送到后端的指定路由,并在后端进行处理。
JSON:可以通过 JavaScript 将表单数据转换为 JSON 对象,然后使用 Ajax 或其他方式将 JSON 数据以 POST 或其他 HTTP 请求方式发送给后端的 API 接口。
表单适用于页面的数据提交和表单校验,而 JSON 则适用于 API 的数据交换和传输。
@RequestBody 注解常用于接收表单数据或者 JSON/XML 数据,@RequestParam 注解用于接收普通的键值对数据
@RequestParam(“userId”) String id对应的请求参数为userId;@RequestParam String id对应的请求参数为id。
可以通过将 URL 中的参数名与后端方法的参数名一致来获取请求参数。举例:假设 URL 为 /example?name=John&age=25,后端方法的定义如下:
@GetMapping(“/example”)
public void handleRequest(String name, int age) {
// 直接通过参数名获取请求参数值
}
前端通过请求体传参,用@RequestBody;通过路径参数传参,用@PathVariable;通过查询参数传参,用@RequestParam或不用任何注解利用请求参数名=后端方法名的方式接收请求参数
POST、PUT、PATCH 这类需要传输请求参数的请求,通常需要设置 Content-Type 来指定请求体的数据格式。这样可以告诉服务器如何解析请求体并正确处理其中的数据。如果不设置 Content-Type,服务器可能无法正确处理请求体,或者默认使用某种配置,这可能导致数据解析错误。
GET 、DELETE请求通常不需要设置 Content-Type,因为 GET和DELETE 请求很少包含请求体。HTTP协议允许GET和DELETE包含请求体,但有的服务器可能会忽略这两种请求的请求体
JSON、XML、HTML、FormData 等是数据格式