文章目录
1. IOC/DI注解开发1.1 Component注解@Component@Controller @Service @Repository 1.2 纯注解开发模式1.3 注解开发bean管理@Scope@PostConstruct @PreDestroy 1.4 注解开发依赖注入@Autowired @Qualifier@Value@PropertySource 1.5 第三方bean管理@Bean@import(多个Config类)引用类型的注入总结 1.6 XML配置和注解配置对比 2. Spring整合MyBatis2.1 mybatis写法回顾2.2 整合:导入依赖:pom.xml2.3 整合:环境准备2.4 整合:Spring核心配置文件SpringConfig.javaJdbcConfig.javaMybatisConfig.java 2.5 运行和说明 3. Spring整合JUnit4. AOP4.1 AOP核心概念4.2 AOP入门案例@EnableAspectJAutoProxy @Aspect @Pointcut @Before 4.3 AOP原理AOP工作流程AOP核心概念 - 代理 4.4 AOP切入点表达式4.5 AOP通知类型4.6 案例:业务层接口执行效率4.7 AOP通知获取数据 5. AOP事务管理5.1 Spring事务简介5.2 Spring事务案例无事务管理情况开启事务处理 5.3 Spring事务角色5.4 Spring事务属性事务配置案例:转账业务追加案例事务传播行为从Spring2开始引入注解,Spring3已经可以纯注解开发,以避免使用复杂的配置文件
1. IOC/DI注解开发
1.1 Component注解
@Component
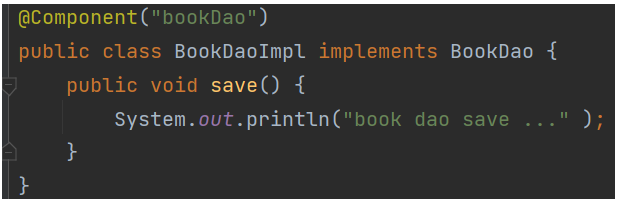
在对应类上添加Component注解
在applicationContext.xml指定要扫描的路径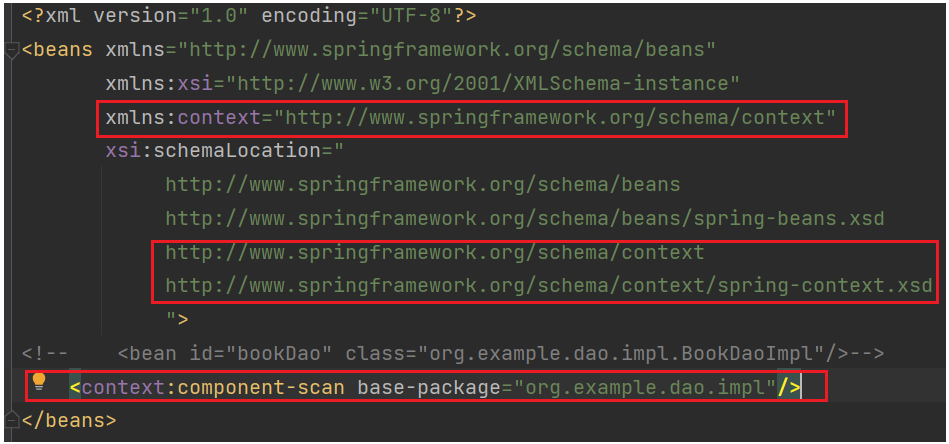
注意:这里首先创建了context命名空间,然后使用了component-scan 和 base-package,之后就可以正常获取bean了
测试BookService
//BookServiceImpl.java@Component//可以不添加名称,之后按类型获取//applicationContext.xml<context:component-scan base-package="org.example"/>//App.javaBookService bookService = ctx.getBean(BookService.class);bookService.save();@Controller @Service @Repository
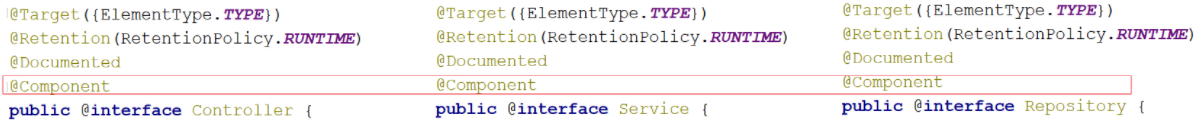
这三个注解是Component的衍生注解,作用和Component相同,只是为了区分某个类是属于表现层、业务层还是数据层的类
1.2 纯注解开发模式
不再写applicationContext.xml配置文件,而是用Config类替代
创建Config类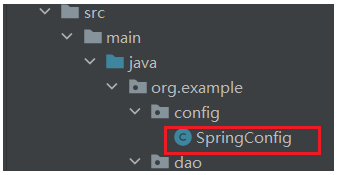
@Configuration//表示这是个配置类,相当于applicationContext.xml默认部分,如命令空间xmlns那一块内容@ComponentScan("org.example.dao")//相当于设置了<bean>标签public class SpringConfig {}之前的applicationContext.xml已经可以删除了
@Configuration:设置该类为spring配置类
@ComponentScan:设置spring配置类扫描路径,此注解只能添加一次,多个数据用{}格式,如
@ComponentScan({"org.example.dao", "org.example.service"})BookDaoImpl.java
package org.example.dao.impl;@Repository("bookDao")public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { public void save() { System.out.println("book dao save ..."); }}使用SpringConfig:AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
public class APP { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); BookDao bookDao = (BookDao) ctx.getBean("bookDao"); System.out.println(bookDao); BookService bookService = ctx.getBean(BookService.class); System.out.println(bookService); }}1.3 注解开发bean管理
@Scope
设置是否为单例模式
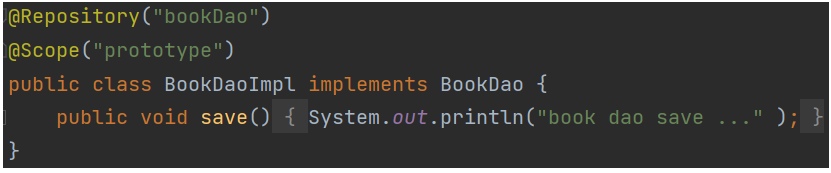
@PostConstruct @PreDestroy
管理生命周期 init() 和 destroy()
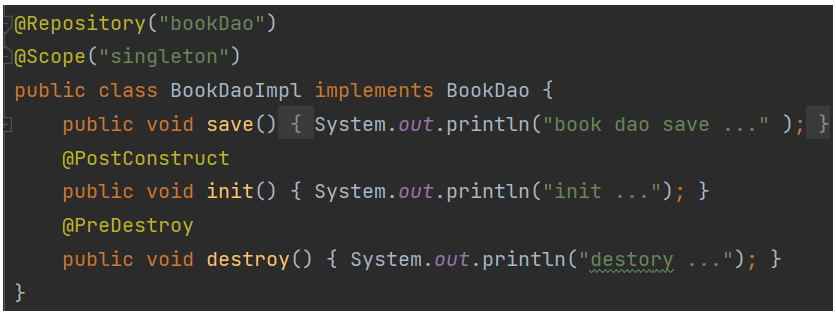
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);BookDao bookDao = (BookDao) ctx.getBean("bookDao");System.out.println(bookDao);ctx.close();//关闭容器,从而可以看到destroy()的信息1.4 注解开发依赖注入
@Autowired @Qualifier
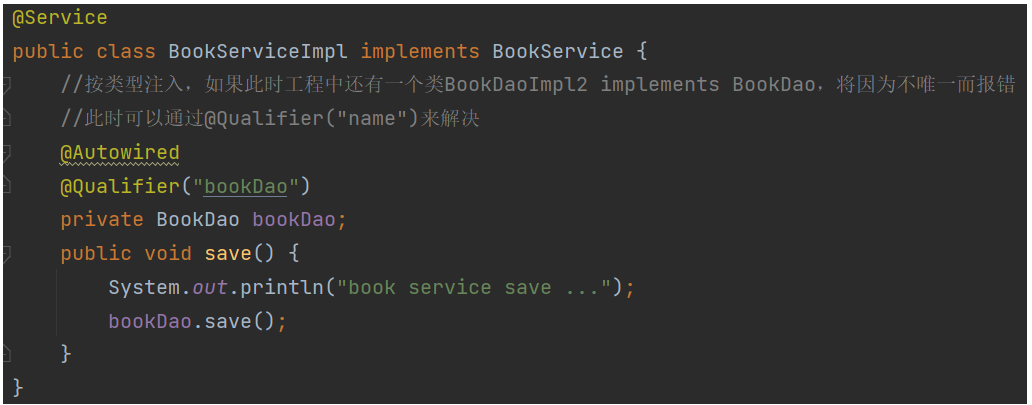
如果只有一个实现类implements BookDao时,仅需@Autowired即可自动注入
如果只有多个实现类implements BookDao时,还需@Qualifier(“name”)指定哪一个实现类
使用@Autowired可以省略setter方法
@Value
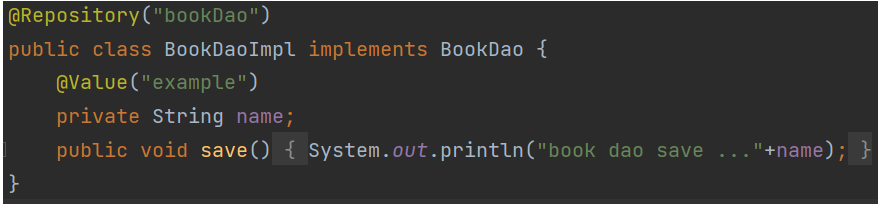
name变量被注入了值 “example”
这样单纯使用@Value是没有意义的,注解主要是为了加载properties文件,使得变量值可更改
@PropertySource
读取Properties配置文件
新建jdbc.properties
name=example配置Config类
package org.example.config;@Configuration@ComponentScan({"org.example.dao", "org.example.service"})@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")public class SpringConfig {}注入
package org.example.dao.impl;@Repository("bookDao")public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { @Value("${name}") private String name; public void save() { System.out.println("book dao save ..."+name); }}注意事项:(1)多个properties配置文件同样使用{}格式;(2)不支持通配符
1.5 第三方bean管理
@Bean
导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.16</version></dependency>配置Config文件
@Configurationpublic class SpringConfig { //1. 定义一个方法获得要管理的对象 //2. 添加@Bean,表示当前方法的返回值是一个bean @Bean public DataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"); ds.setUsername("root"); ds.setPassword("root"); return ds; }}获取Bean并运行
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);DataSource dataSource = ctx.getBean(DataSource.class);System.out.println(dataSource);@import(多个Config类)
像是上面的dataSource()这类的通常会专门创建一个Config类,如JdbcConfig,现在需要使其生效
方法一(不推荐)
JdbcConfig.java
@Configurationpublic class JdbcConfig { @Bean public DataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"); ds.setUsername("root"); ds.setPassword("root"); return ds; }}还需要配置SpringConfig.java
@Configuration@ComponentScan("org.example.config")public class SpringConfig {}方法二(推荐)
JdbcConfig.java
public class JdbcConfig {//注意,没再使用@Configuration @Bean public DataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"); ds.setUsername("root"); ds.setPassword("root"); return ds; }}配置SpringConfig.java
@Configuration@Import(JdbcConfig.class)public class SpringConfig {}练习:使用@Value和properties文件修改上述代码
引用类型的注入
BookDaoImpl.java
@Repositorypublic class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { public void save() { System.out.println("book dao save ..."); }}SpringConfig.java
@Configuration@ComponentScan("org.example.dao")//关联到BookDaoImpl@Import(JdbcConfig.class)public class SpringConfig {}JdbcConfig.java
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")public class JdbcConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource dataSource(BookDao bookDao){ System.out.println(bookDao); DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(driver); ds.setUrl(url); ds.setUsername(username); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; }}自动装配
上面仅提供了一个形参bookDao,即可自动注入
这是因为@Bean使其认为形参应当被自动提供,于是将自动寻找相应的类,并注入到形参中
总结
1.第三方Bean管理 @Bean 2.第三方依赖注入 引用类型:方法形参简单类型:成员变量1.6 XML配置和注解配置对比
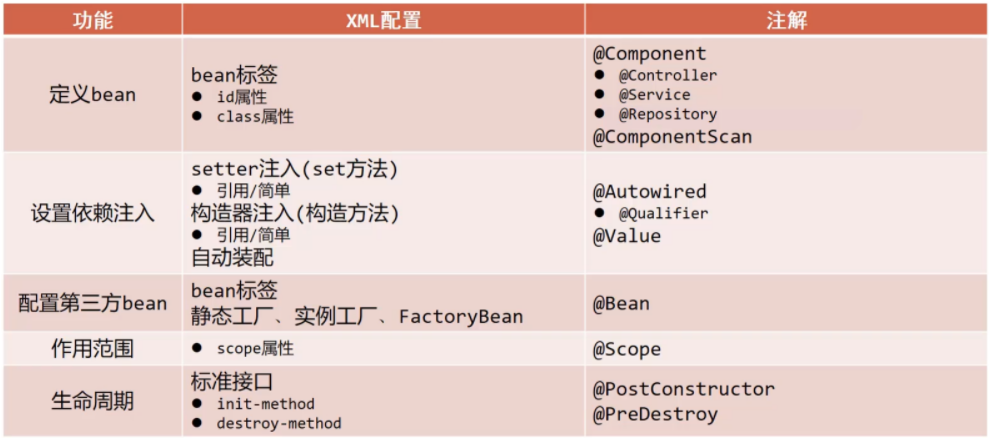
2. Spring整合MyBatis
2.1 mybatis写法回顾
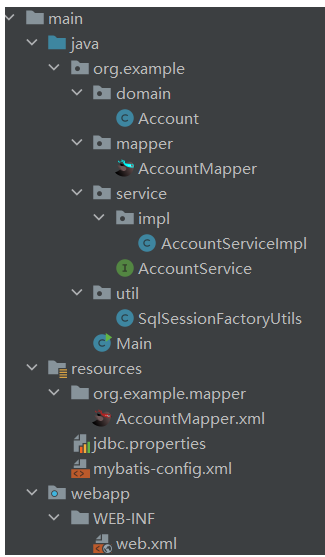
创建javaweb项目,在pom.xml添加<packaging>war</packaging>
配置pom.xml依赖和插件
<dependencies> <!-- mysql --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.46</version> </dependency> <!-- mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.5</version> </dependency></dependencies><build> <plugins> <!--Tomcat插件,非必要 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> </plugin> </plugins></build>编写mybatis-config.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration> <properties resource="jdbc.properties"/> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <!--数据库连接信息--> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <package name="org.example.mapper"/></mappers></configuration>jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverjdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///spring_db?useSSL=false&useServerPrepStmts=truejdbc.username=rootjdbc.password=123456创建AcccountMapper.xml和AccontMapper接口
AccountMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="org.example.mapper.AccountMapper"></mapper>AccontMapper接口
package org.example.mapper;public interface AccountMapper { @Insert("insert into tbl_account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money})") void save(Account account); @Delete("delete from tbl_account where id = #{id} ") void delete(Integer id); @Update("update tbl_account set name = #{name} , money = #{money} where id = #{id} ") void update(Account account); @Select("select * from tbl_account") List<Account> findAll(); @Select("select * from tbl_account where id = #{id} ") Account findById(Integer id);}在这一部分定义sql语句
编写service方法负责业务逻辑层,主要是调用数据库
准备工具类:SqlSessionFactoryUtils
package org.example.util;public class SqlSessionFactoryUtils { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; static{ try { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory(){ return sqlSessionFactory; }}编写AccountService接口
public interface AccountService { List<Account> findAll();}AccountService.java
package org.example.service.impl;public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { private SqlSessionFactory factory = SqlSessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSessionFactory(); @Override public List<Account> findAll() { SqlSession session = factory.openSession(); AccountMapper mapper = session.getMapper(AccountMapper.class); List<Account> accounts = mapper.findAll(); session.close(); return accounts; }}接下来应该是在servlet类里面调用service方法,这里写在main函数里面
package org.example;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { AccountService service = new AccountServiceImpl(); List<Account> accounts = service.findAll(); System.out.println(accounts); }}即可成功获取到数据库数据
当Spring需要整合mybatis时,真正需要交给Spring管理的是SqlSessionFactory
2.2 整合:导入依赖:pom.xml
<dependencies> <!-- spring-context --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- druid --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.16</version> </dependency> <!-- mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.5</version> </dependency> <!-- mysql --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.46</version> </dependency> <!-- spring-jdbc --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- mybatis-spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>1.3.0</version> </dependency></dependencies>2.3 整合:环境准备
步骤1:准备数据库表
create database spring_db character set utf8;use spring_db;create table tbl_account( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(35), money double);insert into tbl_account values (null, 'zhangsan', 1999.10);insert into tbl_account values (null, '张三', 32.43);步骤2:创建基础文件
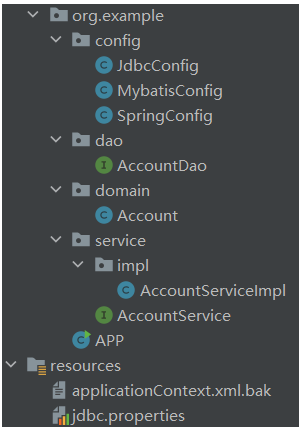
Account.java
package org.example.domain;public class Account{ private Integer id; private String name; private Double money;}//省略getter, setter, toStringAccountDao接口
这里的AccountDao就是AccountMapper的作用,需要加上注解
package org.example.dao;@Repository("accountDao")public interface AccountDao { @Insert("insert into tbl_account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money})") void save(Account account); @Delete("delete from tbl_account where id = #{id} ") void delete(Integer id); @Update("update tbl_account set name = #{name} , money = #{money} where id = #{id} ") void update(Account account); @Select("select * from tbl_account") List<Account> findAll(); @Select("select * from tbl_account where id = #{id} ") Account findById(Integer id);}Service接口和实现类
接口是没有变化的
package org.example.service;public interface AccountService { void save(Account account); void delete(Integer id); void update(Account account); List<Account> findAll(); Account findById(Integer id);}实现类变化很大,和之前相比,spring会接管SqlSessionFactory对象的创建,因此这次不需要创建了
重点:@Service和自动注入
package org.example.service.impl;@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired//自动注入 @Qualifier("accountDao") private AccountDao accountDao; public void save(Account account) { accountDao.save(account); } public void update(Account account){ accountDao.update(account); } public void delete(Integer id) { accountDao.delete(id); } public Account findById(Integer id) { return accountDao.findById(id); } public List<Account> findAll() { return accountDao.findAll(); }}jdbc.properties
resources目录下添加,用于配置数据库连接四要素
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverjdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db?useSSL=falsejdbc.username=rootjdbc.password=123456useSSL:关闭MySQL的SSL连接
2.4 整合:Spring核心配置文件
在没有整合之前,mybatis的service类里面会创建SqlSessionFactory对象,来与数据库互通
在整合后,可以看到新的service类里面不再具备这样的功能
spring核心配置文件就是用来设置配置信息的,用以替代mybatis-config.xml等配置文件 ,并管理bean之间的依赖关系
SpringConfig.java
主配置类,推荐在这个配置类里面import其他配置类
package org.example.config;@Configuration//说明这是一个配置类@ComponentScan("org.example")//定义扫描路径@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")//引入连接信息资源文件@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MybatisConfig.class})//要么这里导入,要么在 JdbcConfig 前面加 @Configurationpublic class SpringConfig {}JdbcConfig.java
package org.example.config;//定义数据源//本来是需要引入jdbc.properties的,但这里选择将所有文件都放在SpringConfig里面引入public class JdbcConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}")//自动注入 private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource dataSource(BookDao bookDao){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(driver); ds.setUrl(url); ds.setUsername(username); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; }}MybatisConfig.java
SqlSessionFactoryBean来源于org.mybatis.spring,可以直接获取SqlSessionFactory
package org.example.config;import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import javax.sql.DataSource;public class MybatisConfig { //sqlSessionFactoryBean完成了mybatis-config里面的<environment>部分 @Bean public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource){ //dataSource也是一个Bean,所以这里能够自动注入 SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("org.example.domain");//取别名,domain是实体类包,相当于之前的pojo包 ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);//设置数据源,即连接相关信息 return ssfb; } //mapperScannerConfigurer完成了mybatis-config里面的<mappers>部分 @Bean public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer(){ MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer(); msc.setBasePackage("org.example.dao");//这里的dao包实际上就是之前学mybatis里面的mapper包 return msc; }}2.5 运行和说明
App.java
package org.example;public class App { public static void main(String[] args){ ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); AccountService accountService = ctx.getBean(AccountService.class);//@Service标注会自动生成bean Account account = accountService.findById(1);//即使后面AccountServiceImpl修改,也不影响这里的代码 System.out.println(account); }}说明
运行流程
- 程序启动时候检测使用了@Configuration注解的配置类SpringConfig- SpringConfig中引入了MybatisConfig和JdbcConfig,相当于这三个文件都成为一个配置文件- MybatisConfig通过JdbcConfig获取到了dataSource,里面带有配置数据库连接的信息,从而成功创建 SqlSessionFactory- 由于AccountServiceImpl.java上使用了注解@Service,且配置类SpringConfig定义了扫描路径"org.example",于是它将被纳入bean管理- 执行ctx.getBean(AccountService.class),这里实际上是以接口类去接实现类,类似于Father father = new Son();- 调用实现类的findById方法关于Spring注入的是接口还是实现类?
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51697147/article/details/126802648
在配置文件模式中,配置bean
<bean id="bookService" class="org.example.service.BookServiceImpl"> <property name="bookDao" ref="bookDao"/></bean>获取bean
BookService bookService = ctx.getBean(BookService.class);在注解开发模式中,配置bean
@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired @Qualifier("accountDao") private AccountDao accountDao; ...}获取bean
AccountService accountService = ctx.getBean(AccountService.class);从spring容器中获取一个类,如果这个类实现了一个接口并且该类存在一个AOP的切入点方法,那么通过getBean()获取到的bean类型只能是这个类的接口类型,不能是具体实现
getBean()必须面向接口,这是因为底层实现用了代理,并由Proxy的内部实现决定
优点:如果之后实现类发生改变,例如修改为AccountServiceImpl2.java,那么App.java里面的内容不必修改
思考:如果有多个实现类继承了AccountService,这也写将会报错,那么如何处理?
3. Spring整合JUnit
1.导入依赖
<!-- junit --><dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope></dependency><!-- spring test --><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version></dependency>2.编写测试类
package org.example.service;@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//设定类运行器@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)//加载配置类//@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})//加载配置文件public class AccountServiceTest { //支持自动装配注入bean @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Test public void testFindById(){ System.out.println(accountService.findById(2)); } @Test public void testFindAll(){ System.out.println(accountService.findAll()); }}要测试哪个方法,就在哪个方法那里点击执行
单元测试,如果测试的是注解配置类,则使用@ContextConfiguration(classes = 配置类.class)单元测试,如果测试的是配置文件,则使用@ContextConfiguration(locations={配置文件名,...})Junit运行后是基于Spring环境运行的,所以Spring提供了一个专用的类运行器,这个务必要设置,这个类运行器就在Spring的测试专用包中提供的,导入的坐标就是这个东西SpringJUnit4ClassRunner上面两个配置都是固定格式,当需要测试哪个bean时,使用自动装配加载对应的对象 知识点1:@RunWith
| 名称 | @RunWith |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 测试类注解 |
| 位置 | 测试类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置JUnit运行器 |
| 属性 | value(默认):运行所使用的运行期 |
知识点2:@ContextConfiguration
| 名称 | @ContextConfiguration |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 测试类注解 |
| 位置 | 测试类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置JUnit加载的Spring核心配置 |
| 属性 | classes:核心配置类,可以使用数组的格式设定加载多个配置类 locations:配置文件,可以使用数组的格式设定加载多个配置文件名称 |
4. AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,一种编程范式,指导开发者如何组织程序结构OOP(Object Oriented Programming)面向对象编程
Spring有两个核心的概念,一个是IOC/DI,一个是AOP
作用:AOP是在不改原有代码的前提下对其进行增强
Spring理念:无入侵时/无侵入式
4.1 AOP核心概念
package org.example.dao.impl;import org.example.dao.BookDao;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repositorypublic class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { public void save() { //记录程序当前执行执行(开始时间) Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //业务执行万次 for (int i = 0;i<10000;i++) { System.out.println("book Dao"); } //记录程序当前执行时间(结束时间) Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //计算时间差 Long totalTime = endTime-startTime; //输出信息 System.out.println("执行万次消耗时间:" + totalTime + "ms"); } public void update(){ System.out.println("book dao update ..."); } public void delete(){ System.out.println("book dao delete ..."); } public void select(){ System.out.println("book dao select ..."); }}需求:希望对update、delete函数执行和save一样的流程,即执行10000次,然后打印时间差
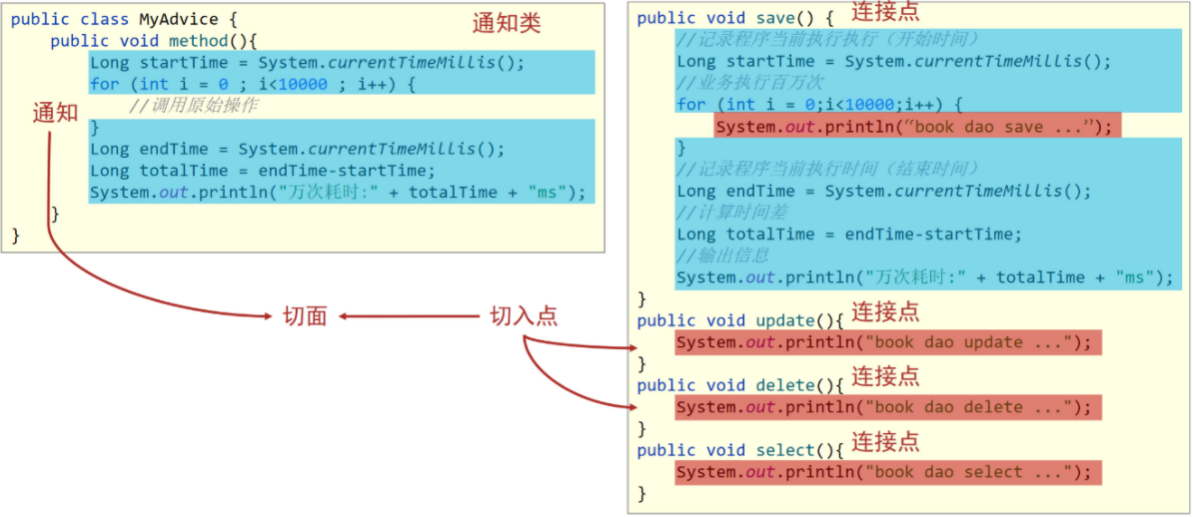
AOP中的核心概念
连接点(JoinPoint):程序执行过程中的任意位置,粒度为执行方法、抛出异常、设置变量等
在SpringAOP中,理解为方法的执行AOP将每一个方法调用,即连接点作为编程的入口,针对方法调用进行编程切入点(Pointcut):匹配连接点的式子
指需要被增强的方法切入点是连接点,但连接点不一定是切入点通知(Advice):在切入点处执行的操作,也就是共性功能
如上面的计算万次执行消耗时间作为共性功能,被抽取到一个方法中,这个方法就是通知 在SpringAOP中,功能最终以方法的形式呈现通知类:定义通知的类
切面(Aspect):描述通知与切入点的对应关系。
通知是要增强的内容,会有多个,切入点是需要被增强的方法,也会有多个,通知与切入点的对应关系叫切面4.2 AOP入门案例
需求:在方法执行前输出当前系统时间。
开发模式:XML 和 注解
步骤:
导入坐标(pom.xml)
<!-- spring-context里面包含了aop --><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version></dependency><!-- aspectjweaver --><dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.4</version></dependency>制作连接点(原始操作,Dao接口与实现类)
package org.example.dao;public interface BookDao { public void save(); public void update();}package org.example.dao.impl;@Repositorypublic class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { public void save(){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("book dao save ..."); } public void update(){ System.out.println("book dao update ..."); }}制作共性功能(通知类与通知)
新建包aop,新建MyAdvice通知类,printTime即为通知方法
定义切入点
切入点即 pt() ,需要注解@Pointcut注明哪些方法需要被增强
绑定切入点与通知关系(切面)
@Before说明切入点与通知的关系
配置Spring环境
package org.example.aop;//6. 配置Spring环境@Component//需要将其交给Spring管理@Aspect//告诉Spring当作AOP处理,而非Beanpublic class MyAdvice { //4. 定义切入点 @Pointcut("execution(void org.example.dao.BookDao.update())") private void pt(){} //5. 绑定切入点与通知关系(切面) @Before("pt()")//在pt()方法前执行 //3. 制作共性功能(通知类与通知) public void printTime(){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); }}package org.example.config;@Configuration@ComponentScan("org.example")@EnableAspectJAutoProxy//开启Spring对AOP注解驱动支持public class SpringConfig {}运行
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);bookDao.update();@EnableAspectJAutoProxy @Aspect @Pointcut @Before
| 名称 | @EnableAspectJAutoProxy |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 配置类注解 |
| 位置 | 配置类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 开启注解格式AOP功能 |
| 名称 | @Aspect |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 切面类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前类为AOP切面类 |
| 名称 | @Pointcut |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 切入点方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置切入点方法 |
| 属性 | value(默认):切入点表达式 |
| 名称 | @Before |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 方法注解 |
| 位置 | 通知方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前通知方法与切入点之间的绑定关系,当前通知方法在原始切入点方法前运行 |
4.3 AOP原理
AOP工作流程
由于AOP是基于Spring容器管理的bean做的增强,所以整个工作过程需要从Spring加载bean说起
工作流程
流程1:Spring容器启动
容器启动就需要去加载bean,带有@Component,@Service ,@Controller 的类都是spring 要创建的bean对象
需要被增强的类BookDaoImpl,通知类MyAdvice注意此时bean对象还没有创建成功流程2:读取所有切面配置中的切入点
@Component@Aspectpublic class MyAdvice { @Pointcut("execution(void org.example.dao.BookDao.save())") private void ptx(){} @Pointcut("execution(void org.example.dao.BookDao.update())") private void pt(){} @Before("pt()") public void printTime(){ System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); }}有两个切入点,其中切入点ptx()并没有被使用,所以不会被读取
流程3:初始化bean
在容器启动的时候,bean对象还没有被创建成功
在创建bean对象时,需要判定bean对应的类中的方法是否匹配到任意切入点,以BookDao为例
目标对象)的代理对象 匹配成功说明需要对其进行增强对哪个类做增强,这个类对应的对象就叫做目标对象因为要对目标对象进行功能增强,而采用的技术是动态代理,所以会为其创建一个代理对象最终运行的是代理对象的方法,在该方法中会对原始方法进行功能增强 流程4:获取bean并执行方法
获取的bean是原始对象时,调用方法并执行,完成操作获取的bean是代理对象时,根据代理对象的运行模式运行原始方法与增强的内容,完成操作验证代理
System.out.println(bookDao);System.out.println(bookDao.getClass());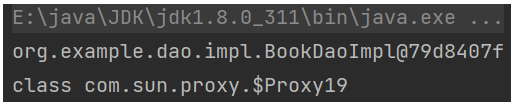
打印bookDao时,由于代理里面重写了toString,所以看到的是BookDaoImpl
打印Class就可以看到,最终生成的是目标对象的代理对象
AOP核心概念 - 代理
目标对象(Target):原始功能去掉共性功能对应的类产生的对象,这种对象是无法直接完成最终工作的代理(Proxy):目标对象无法直接完成工作,需要对其进行功能回填,通过原始对象的代理对象实现SpringAOP是在不改变原有设计(代码)的前提下对其进行增强的,它的底层采用的是代理模式实现的,所以要对原始对象进行增强,就需要对原始对象创建代理对象,在代理对象中的方法把通知[如:MyAdvice中的method方法]内容加进去,就实现了增强,这就是我们所说的代理(Proxy)。
SpringAOP的本质或者可以说底层实现是通过代理模式
4.4 AOP切入点表达式
切入点:要进行增强的方法
切入点表达式:要进行增强的方法的描述方式
接口描述
execution(void org.example.dao.BookDao.update())实现类描述
execution(void org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl.update())因为调用接口方法的时候最终运行的还是其实现类的方法,所以上面两种描述方式都是可以的
切入点表达式标准格式
动作关键字(访问修饰符 返回值 包名.类/接口名.方法名(参数) 异常名)execution(public User org.example.service.UserService.findById(int))切入点通配符
*:单个独立的任意符号,可以独立出现,也可以作为前缀或者后缀的匹配符出现
execution(public * org.example.*.UserService.find*(*))匹配org.example包下的任意包中的UserService类或接口中所有find开头的带有一个参数的方法
..:多个连续的任意符号,可以独立出现,常用于简化包名与参数的书写
execution(public User org..UserService.findById(..))匹配org包下的任意包中的UserService类或接口中所有名称为findById的方法
+:专用于匹配子类类型
execution(* *..*Service+.*(..))很少使用。*Service+,表示所有以Service结尾的接口的子类。
切入点表达式练习
//匹配接口,能匹配到execution(void org.example.dao.BookDao.update())//匹配实现类,能匹配到execution(void org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl.update())//返回值任意,能匹配到execution(* org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl.update())//返回值任意,但是update方法必须要有一个参数,无法匹配,要想匹配需要在update接口和实现类添加参数execution(* org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl.update(*))//返回值为void,org包下的任意包三层包下的任意类的update方法,匹配到的是实现类,能匹配execution(void org.*.*.*.*.update())//返回值为void,org包下的任意两层包下的任意类的update方法,匹配到的是接口,能匹配execution(void org.*.*.*.update())//返回值为void,方法名是update的任意包下的任意类,能匹配execution(void *..update())//匹配项目中任意类的任意方法,能匹配,但是不建议使用这种方式,影响范围广execution(* *..*(..))//匹配项目中任意包任意类下只要以u开头的方法,update方法能满足,能匹配execution(* *..u*(..))//匹配项目中任意包任意类下只要以e结尾的方法,update和save方法能满足,能匹配execution(* *..*e(..))//返回值为void,org包下的任意包任意类任意方法,能匹配,*代表的是方法(这个代表方法的*不能省略)execution(void org..*())//将项目中所有业务层方法的以find开头的方法匹配execution(* org.example.*.*Service.find*(..))//将项目中所有业务层方法的以save开头的方法匹配execution(* org.example.*.*Service.save*(..))书写技巧
所有代码按照标准规范开发描述切入点通常描述接口,而不描述实现类,如果描述到实现类,就出现紧耦合了访问控制修饰符针对接口开发均采用public描述(可省略访问控制修饰符描述)返回值类型对于增删改类使用精准类型加速匹配,对于查询类使用*通配快速描述包名书写尽量不使用..匹配,效率过低,常用*做单个包描述匹配,或精准匹配接口名/类名书写名称与模块相关的采用*匹配,例如UserService书写成*Service,绑定业务层接口名方法名书写以动词进行精准匹配,名词采用*匹配,例如getById书写成getBy*,selectAll书写成selectAll参数规则较为复杂,根据业务方法灵活调整通常不使用异常作为匹配规则 4.5 AOP通知类型
5种通知类型
前置通知
@Before("pt()")后置通知
@After("pt()")环绕通知(重点)
package org.example.aop;@Component@Aspectpublic class MyAdvice { @Pointcut("execution(void org.example.dao.BookDao.update())") private void pt(){} @Around("pt()") public void aroundSelect(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { //前置 System.out.println("before advice"); //原始操作 pjp.proceed(); //后置 System.out.println("after advice"); }}有返回值的情况
package org.example.aop;@Component@Aspectpublic class MyAdvice { @Pointcut("execution(int org.example.dao.BookDao.select())") private void pt(){} @Around("pt()") public Object aroundUpdate(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { //前置 System.out.println("before advice"); //原始操作 Object ret = pjp.proceed(); //后置 System.out.println("after advice"); return ret; }}返回后通知(了解)
@AfterReturning("pt()")返回后通知是需要在原始方法select正常执行后才会被执行,如果过程中出现了异常,那么返回后通知是不会被执行
后置通知是不管原始方法有没有抛出异常都会被执行
抛出异常后通知(了解)
@AfterThrowing("pt()")如果有异常才会执行
注意事项
环绕通知必须依赖形参ProceedingJoinPoint才能实现对原始方法的调用对原始方法的调用可以不接收返回值,通知方法设置成void即可,如果接收返回值,最好设定为Object类型由于无法预知原始方法运行后是否会抛出异常,因此环绕通知方法必须要处理Throwable异常 4.6 案例:业务层接口执行效率
需求:任意业务层接口执行均可显示其执行效率(执行时长)
环境准备:使用前面整合MyBatis和Junit之后的项目
添加pom.xml依赖
<!-- spring-context --><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version></dependency><!-- aspectjweaver --><dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.4</version></dependency>配置SpringConfig环境
package org.example.config;@Configuration@ComponentScan("org.example")@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MybatisConfig.class})@EnableAspectJAutoProxypublic class SpringConfig {}创建通知类 org.example.aop.ProjectAdvice
编写通知方法
package org.example.aop;@Component@Aspectpublic class ProjectAdvice { //1. 切入点:匹配业务层的所有方法 @Pointcut("execution(* org.example.service.*Service.*(..))") private void servicePt(){} //2. 环绕方法 @Around("ProjectAdvice.servicePt()") public void runSpeed(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{ //ProceedingJoinPoint:连接点,携带原始方法信息 Signature signature = pjp.getSignature(); String className = signature.getDeclaringTypeName(); String methodName = signature.getName(); //前置:获取开始时间 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0; i<10000; ++i){ //调用原始方法 Object ret = pjp.proceed(); } //后置:获取结束时间 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("万次执行:"+className+"."+methodName+" 时间为:"+(end-start)+"ms"); }}测试类
package org.example.service;@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//设定类运行器@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)public class AccountServiceTest { @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Test public void testFindById(){ accountService.findById(2); } @Test public void testFindAll(){ accountService.findAll(); }}4.7 AOP通知获取数据
获取切入点方法的参数,所有的通知类型都可以获取参数 JoinPoint:适用于前置、后置、返回后、抛出异常后通知ProceedingJoinPoint:适用于环绕通知 获取切入点方法返回值,前置和抛出异常后通知是没有返回值,后置通知可有可无,所以不做研究 返回后通知环绕通知 获取切入点方法运行异常信息,前置和返回后通知是不会有,后置通知可有可无,所以不做研究 抛出异常后通知环绕通知 获取参数
package org.example.aop;@Component@Aspectpublic class MyAdvice { @Pointcut("execution(* org.example.dao.BookDao.findName(..))") private void pt(){} @Before("pt()") public void before(JoinPoint jp){ Object[] args = jp.getArgs(); } @After("pt()") public void after(JoinPoint jp){ Object[] args = jp.getArgs(); } @Around("pt()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{ Object[] args = pjp.getArgs(); args[0] = 666;//可以中途修改参数 Object ret = pjp.proceed(args); return ret; }}环绕方法可以修改传递过来的参数,有时可以用作对参数清洗
返回值
@AfterReturning(value = "pt()", returning = "ret")public void afterReturning(JoinPoint jp, Object ret){//注意如果有JoinPoint参数,它必须得在第一位 System.out.println("afterReturning advice ..."+ret);//ret即为返回值}获取异常
@AfterThrowing(value = "pt()", throwing = "t")public void afterThrowing(Throwable t){ System.out.println("afterThrowing advice .."+t);}5. AOP事务管理
5.1 Spring事务简介
事务作用:在数据层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功同失败Spring事务作用:在数据层或业务层保障一系列的数据库操作同成功同失败Spring为了管理事务,提供了一个平台事务管理器PlatformTransactionManager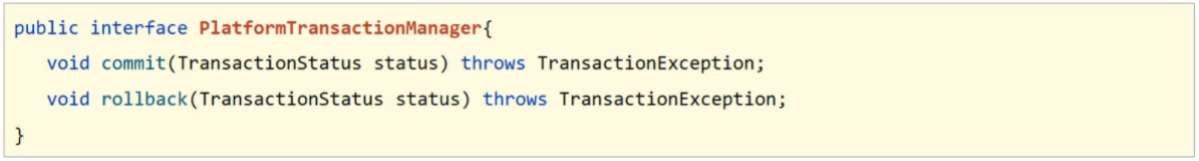
commit是用来提交事务,rollback是用来回滚事务
PlatformTransactionManager只是一个接口,Spring还为其提供了一个具体的实现
只需要给它一个DataSource对象,它就可以帮你去在业务层管理事务。其内部采用的是JDBC的事务
所以如果你持久层采用的是JDBC相关的技术,就可以采用这个事务管理器来管理事务。而Mybatis内部采用的就是JDBC的事务,所以后期Spring整合Mybatis就采用的这个DataSourceTransactionManager事务管理器。
5.2 Spring事务案例
无事务管理情况
需求: 实现任意两个账户间转账操作,A账户减钱和B账户加钱必须是同成功或同失败
准备工作:第2节中整合MyBatis中的spring-mybatis项目
步骤1:准备数据库表
含有 id name money 三个属性的数据库表
步骤2:创建项目导入jar包
步骤3:根据表创建模型类
即Account类
步骤4:创建Dao接口
在AccountDao.java中加入
@Update("update tbl_account set money = money + #{money} where name = #{name}")void inMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);@Update("update tbl_account set money = money - #{money} where name = #{name}")void outMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);步骤5:编写Service接口和实现类
package org.example.service;public interface AccountService { /** * 转账 * @param out:转出账户 * @param in:转入账户 * @param money:转账金额 */ public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money);}package org.example.service.impl;@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { //自动注入accountDao @Autowired @Qualifier("accountDao") private AccountDao accountDao; @Override public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) { accountDao.outMoney(out, money); accountDao.inMoney(in, money); }}步骤6:编写配置类
SpringConfig,JdbcConfig,MybatisConfig,jdbc.properties
步骤7:编写测试类
package org.example.service;@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)public class AccountServiceTest { @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @Test public void testTransfer() throws IOException{ accountService.transfer("zhangsan", "lisi", 100D); }}问题
当增加和修改两个操作中间出现异常时,会出现一个账户减少了,而另一个账户却没增加的错误!,如:
public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) { accountDao.outMoney(out, money); int i = 1/0; accountDao.inMoney(in, money);}开启事务处理
步骤1:添加@Transactional注解
可以写在接口类上、接口方法上、实现类上和实现类方法上
写在接口类上,该接口的所有实现类的所有方法都会有事务写在接口方法上,该接口的所有实现类的该方法都会有事务写在实现类上,该类中的所有方法都会有事务写在实现类方法上,该方法上有事务常写在方法前package org.example.service;public interface AccountService { @Transactional public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money);}步骤2:在JdbcConfig类中配置事务管理器
package org.example.config;public class JdbcConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}")//自动注入 private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(driver); ds.setUrl(url); ds.setUsername(username); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; } @Bean public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){//自动注入dataSource DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(); transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource); return transactionManager; }}事务管理器要根据使用技术进行选择,Mybatis框架使用的是JDBC事务,可以直接使用DataSourceTransactionManager
步骤3:在SpringConfig中开启事务注解
package org.example.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;@Configuration@ComponentScan("org.example")@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MybatisConfig.class})//开启注解式事务驱动@EnableTransactionManagementpublic class SpringConfig {}至此即可实现transfer函数的同成功或同失败
5.3 Spring事务角色
事务管理员:发起事务方,在Spring中通常指代业务层开启事务的方法,如transfer()
事务协调员:加入事务方,在Spring中通常指代数据层方法,也可以是业务层方法,如outMoney()和inMoney
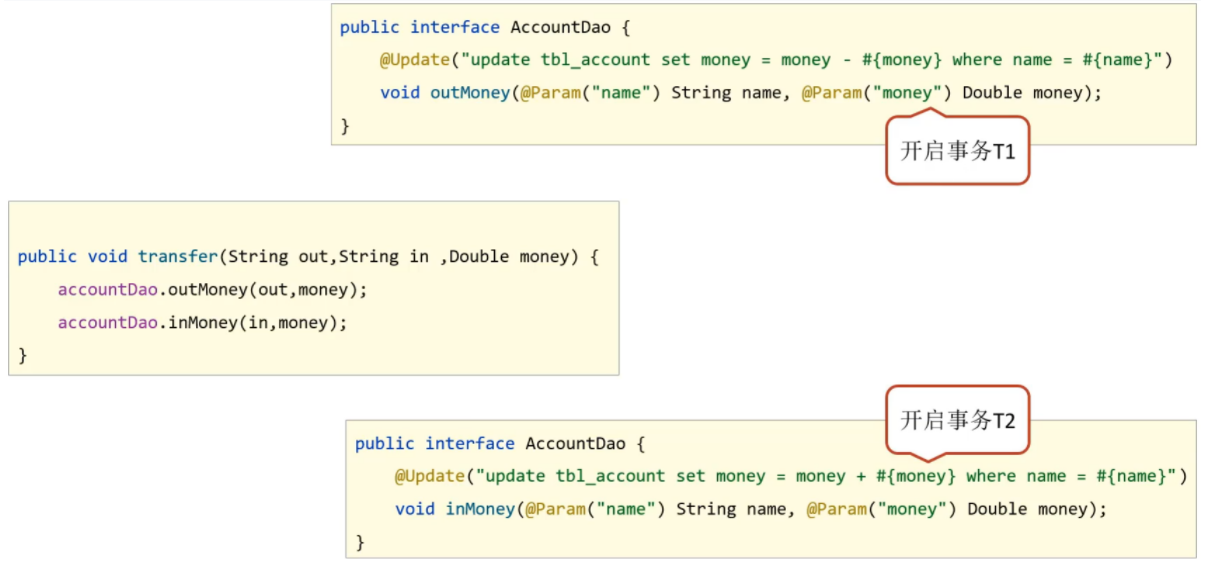
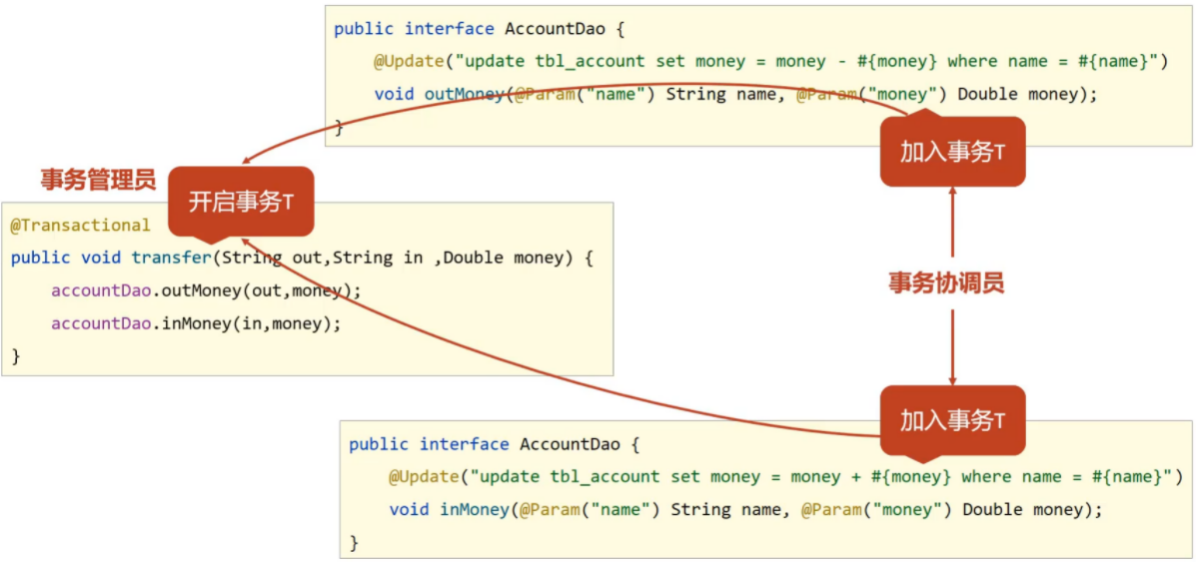
目前的事务管理是基于DataSourceTransactionManager和SqlSessionFactoryBean使用的是同一个数据源
5.4 Spring事务属性
事务配置
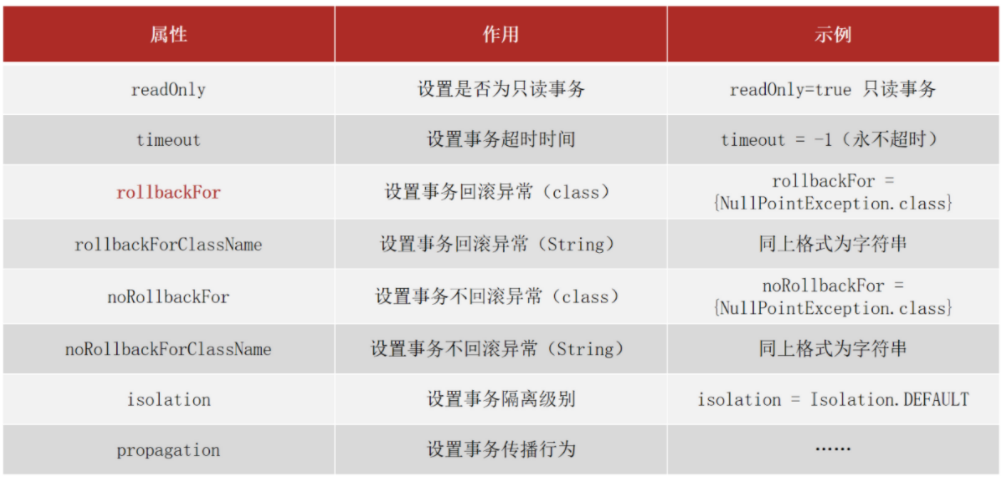
@Transactional(readOnly = true, timeout = -1)rollbackFor(重点)
当transfer()的代码如下时,先前的事务管理失效,仍然导致一方改变了,而另一方未改变
@Overridepublic void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) throws IOException { accountDao.outMoney(out, money); if(true) throw new IOException(); accountDao.inMoney(in, money);}原因:Spring的事务只会对Error异常和RuntimeException异常及其子类进行事务回滚,其他的异常类型是不会回滚的,对应IOException不符合上述条件所以不回滚
修改:设置rollbackFor
@Transactional(rollbackFor = {IOException.class})public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) throws IOException;readOnly:true只读事务,false读写事务,增删改要设为false,查询设为true。
timeout:设置超时时间单位秒,在多长时间之内事务没有提交成功就自动回滚,-1表示不设置超时时间。
noRollbackFor:当出现指定异常不进行事务回滚
rollbackForClassName:等同于rollbackFor,只不过属性为异常的类全名字符串
noRollbackForClassName:等同于noRollbackFor,只不过属性为异常的类全名字符串
isolation设置事务的隔离级别(见MySQL数据库相关知识)
DEFAULT:默认隔离级别, 会采用数据库的隔离级别READ_UNCOMMITTED : 读未提交READ_COMMITTED : 读已提交REPEATABLE_READ : 重复读取SERIALIZABLE: 串行化案例:转账业务追加案例
需求:无论转账操作是否成功,均进行转账操作的日志留痕
准备工作:基于前面5.2节的案例
步骤1:添加数据库表
create table tbl_log( id int primary key auto_increment, info varchar(255), createDate datetime)步骤2:添加LogDao接口
package org.example.dao;@Repositorypublic interface LogDao { @Insert("insert into tbl_log (info, createDate) values (#{info}, now())") void log(String info);}步骤3:添加LogService接口与实现类
package org.example.service;public interface LogService { @Transactional public void log(String out, String in, Double money);}package org.example.service.impl;@Servicepublic class LogServiceImpl implements LogService { @Autowired private LogDao logDao; @Override public void log(String out, String in, Double money) { logDao.log("转账操作由"+out+"到"+in+",金额:"+money); }}步骤4:在转账的业务中添加记录日志
package org.example.service;public interface AccountService { @Transactional public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money);}package org.example.service.impl;@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired @Qualifier("accountDao") private AccountDao accountDao; @Autowired private LogService logService; @Override public void transfer(String out, String in, Double money) { try { accountDao.outMoney(out, money); int i = 1/0; accountDao.inMoney(in, money); } finally { logService.log(out, in, money); } }}注意:结果如果报异常,记录不会被写入tbl_log表中去,
因为此时日志记录和转账操作隶属于一个事务,同成功同失败,那么转账被回滚了失败了,日志记录自然也失败了
但是需求是:无论转账是否成功,都记录日志
此时需要:转账的两个操作inMoney和outMoney加入到transfer事务中,但记录日志的log操作单独启动一个事务
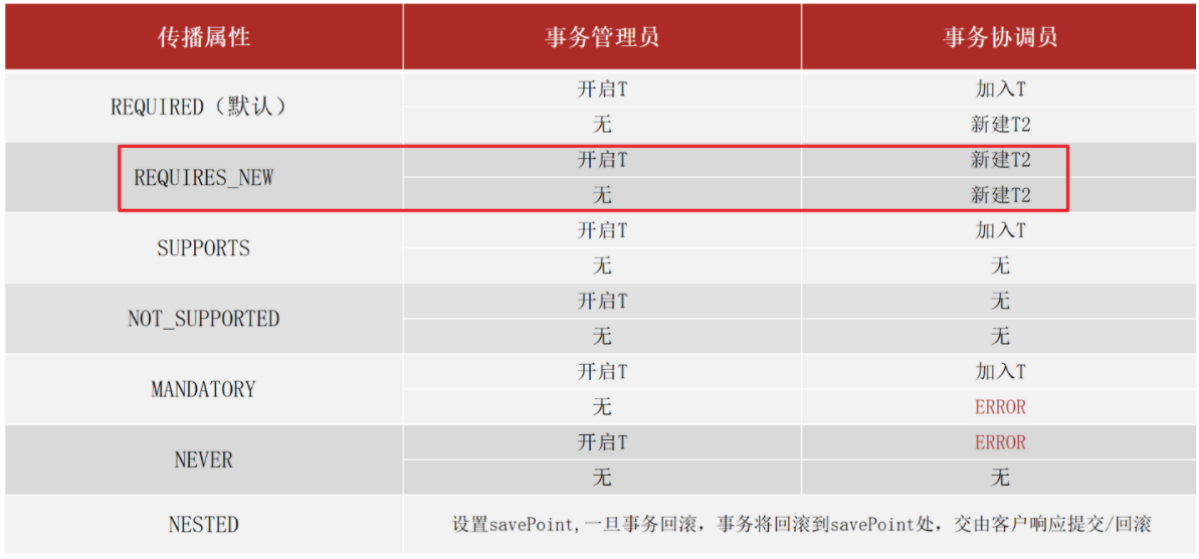
事务传播行为
修改日志的事务属性:propagation
package org.example.service;public interface LogService { @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)//开启新事物 public void log(String out, String in, Double money);}package org.example.service.impl;@Servicepublic class LogServiceImpl implements LogService { @Autowired private LogDao logDao; @Override public void log(String out, String in, Double money) { logDao.log("转账操作由"+out+"到"+in+",金额:"+money); }}此时即可实现失败转账操作回滚,但日志仍被记录