目录
一、deployment.yaml文件
二、Pod yaml文件
三、Service yaml文件
四、yaml文件
1.YAML 语法格式
2.查看 api 资源版本标签
3.写一个yaml文件demo
(1)创建资源对象
(2)查看创建的pod资源
(3)创建service服务对外提供访问并测试
(4)创建资源对象
(5)查看创建的service
五、port
1.port
2.nodePort
3.targetPort
4.containerPort
一、deployment.yaml文件
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 接口版本kind: Deployment 接口类型metadata: name: cango-demo Deployment名称 namespace: cango-prd 命名空间 labels: app: cango-demo 标签spec: replicas: 3 strategy: rollingUpdate: 由于replicas为3,则整个升级,pod个数在2-4个之间 maxSurge: 1 滚动升级时会先启动1个pod maxUnavailable: 1 滚动升级时允许的最大Unavailable的pod个数 template: metadata: labels: app: cango-demo 模板名称必填 sepc: 定义容器模板,该模板可以包含多个容器 containers: - name: cango-demo 镜像名称 image: swr.cn-east-2.myhuaweicloud.com/cango-prd/cango-demo:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT 镜像地址 command: [ "/bin/sh","-c","cat /etc/config/path/to/special-key" ] 启动命令 args: 启动参数 - '-storage.local.retention=$(STORAGE_RETENTION)' - '-storage.local.memory-chunks=$(STORAGE_MEMORY_CHUNKS)' - '-config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml' - '-alertmanager.url=http://alertmanager:9093/alertmanager' - '-web.external-url=$(EXTERNAL_URL)' 如果command和args均没有写,那么用Docker默认的配置。 如果command写了,但args没有写,那么Docker默认的配置会被忽略而且仅仅执行.yaml文件的command(不带任何参数的)。 如果command没写,但args写了,那么Docker默认配置的ENTRYPOINT的命令行会被执行,但是调用的参数是.yaml中的args。 如果command和args都写了,那么Docker默认的配置被忽略,使用.yaml的配置。 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent #如果不存在则拉取 livenessProbe: #表示container是否处于live状态。如果LivenessProbe失败,LivenessProbe将会通知kubelet对应的container不健康了。随后kubelet将kill掉container,并根据RestarPolicy进行进一步的操作。默认情况下LivenessProbe在第一次检测之前初始化值为Success,如果container没有提供LivenessProbe,则也认为是Success; httpGet: path: /health 如果没有心跳检测接口就为/ port: 8080 scheme: HTTP initialDelaySeconds: 60 启动后延时多久开始运行检测 timeoutSeconds: 5 successThreshold: 1 failureThreshold: 5 readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /health 如果没有心跳检测接口就为/ port: 8080 scheme: HTTP initialDelaySeconds: 30 启动后延时多久开始运行检测 timeoutSeconds: 5 successThreshold: 1 failureThreshold: 5 resources: CPU内存限制 requests: cpu: 2 memory: 2048Mi limits: cpu: 2 memory: 2048Mi env: 通过环境变量的方式,直接传递pod=自定义Linux OS环境变量 - name: LOCAL_KEY 本地Key value: value - name: CONFIG_MAP_KEY 局策略可使用configMap的配置Key, valueFrom: configMapKeyRef: name: special-config configmap中找到name为special-config key: special.type 找到name为special-config里data下的key ports: - name: http containerPort: 8080 对service暴露端口 volumeMounts: 挂载volumes中定义的磁盘 - name: log-cache mount: /tmp/log - name: sdb 普通用法,该卷跟随容器销毁,挂载一个目录 mountPath: /data/media - name: nfs-client-root 直接挂载硬盘方法,如挂载下面的nfs目录到/mnt/nfs mountPath: /mnt/nfs - name: example-volume-config 高级用法第1种,将ConfigMap的log-script,backup-script分别挂载到/etc/config目录下的一个相对路径path/to/...下,如果存在同名文件,直接覆盖。 mountPath: /etc/config - name: rbd-pvc 高级用法第2中,挂载PVC(PresistentVolumeClaim) 使用volume将ConfigMap作为文件或目录直接挂载,其中每一个key-value键值对都会生成一个文件,key为文件名,value为内容, volumes: 定义磁盘给上面volumeMounts挂载 - name: log-cache emptyDir: {} - name: sdb 挂载宿主机上面的目录 hostPath: path: /any/path/it/will/be/replaced - name: example-volume-config 供ConfigMap文件内容到指定路径使用 configMap: name: example-volume-config ConfigMap中名称 items: - key: log-script ConfigMap中的Key path: path/to/log-script 指定目录下的一个相对路径path/to/log-script - key: backup-script ConfigMap中的Key path: path/to/backup-script 指定目录下的一个相对路径path/to/backup-script - name: nfs-client-root 供挂载NFS存储类型 nfs: server: NFS服务器地址 path: /opt/public showmount -e 看一下路径 - name: rbd-pvc 挂载PVC磁盘 persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: rbd-pvc1 挂载已经申请的pvc磁盘二、Pod yaml文件
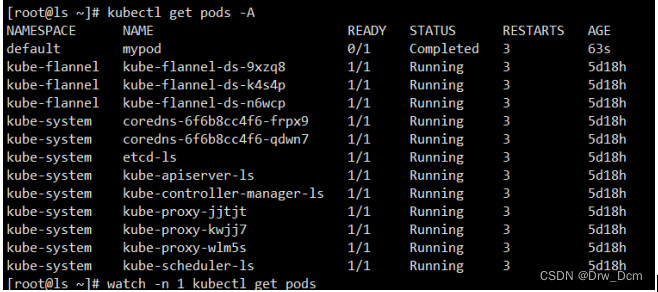
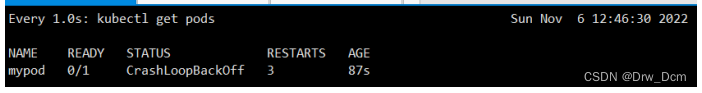
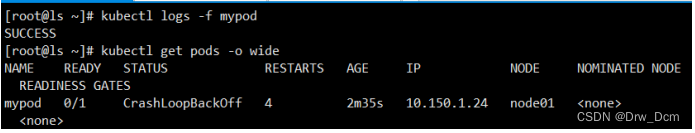
apiVersion: v1 必选,版本号,例如v1kind: Pod 必选,Podmetadata: 必选,元数据 name: string 必选,Pod名称 namespace: string 必选,Pod所属的命名空间 labels: 自定义标签 - name: string 自定义标签名字 annotations: 自定义注释列表 - name: stringspec: 必选,Pod中容器的详细定义 containers: 必选,Pod中容器列表 - name: string 必选,容器名称 image: string 必选,容器的镜像名称 imagePullPolicy: [Always | Never | IfNotPresent]获取镜像的策略:Alawys表示总是下载镜像,IfnotPresent表示优先使用本地镜像,否则下载镜像,Nerver表示仅使用本地镜像 command: [string] 容器的启动命令列表,如不指定,使用打包时使用的启动命令 args: [string] 容器的启动命令参数列表 workingDir: string 容器的工作目录 volumeMounts: 挂载到容器内部的存储卷配置 - name: string 引用pod定义的共享存储卷的名称,需用volumes[]部分定义的的卷名 mountPath: string 存储卷在容器内mount的绝对路径,应少于512字符 readOnly: boolean 是否为只读模式 ports: 需要暴露的端口库号列表 - name: string 端口号名称 containerPort: int 容器需要监听的端口号 hostPort: int 容器所在主机需要监听的端口号,默认与Container相同 protocol: string 端口协议,支持TCP和UDP,默认TCP env: 容器运行前需设置的环境变量列表 - name: string 环境变量名称 value: string 环境变量的值 resources: 资源限制和请求的设置 limits: 资源限制的设置 cpu: string Cpu的限制,单位为core数,将用于docker run --cpu-shares参数 memory: string 内存限制,单位可以为Mib/Gib,将用于docker run --memory参数 requests: 资源请求的设置 cpu: string Cpu请求,容器启动的初始可用数量 memory: string 内存清楚,容器启动的初始可用数量 livenessProbe: 对Pod内个容器健康检查的设置,当探测无响应几次后将自动重启该容 器,检查方法有exec、httpGet和tcpSocket,对一个容器只需设置其中一种方法即可 exec: 对Pod容器内检查方式设置为exec方式 command: [string] exec方式需要制定的命令或脚本 httpGet: 对Pod内个容器健康检查方法设置为HttpGet,需要制定Path、port path: string port: number host: string scheme: string HttpHeaders: - name: string value: string tcpSocket: 对Pod内个容器健康检查方式设置为tcpSocket方式 port: number initialDelaySeconds: 0 容器启动完成后首次探测的时间,单位为秒 timeoutSeconds: 0 对容器健康检查探测等待响应的超时时间,单位秒,默认1秒 periodSeconds: 0 对容器监控检查的定期探测时间设置,单位秒,默认10秒一次 successThreshold: 0 failureThreshold: 0 securityContext: privileged:false restartPolicy: [Always | Never | OnFailure]Pod的重启策略,Always表示一旦不管以何种方式终止运行,kubelet都将重启,OnFailure表示只有Pod以非0退出码退出才重启,Nerver表示不再重启该Pod nodeSelector: obeject设置NodeSelector表示将该Pod调度到包含这个label的node上,以key:value的格式指定 imagePullSecrets:Pull镜像时使用的secret名称,以key:secretkey格式指定 - name: string hostNetwork:false是否使用主机网络模式,默认为false,如果设置为true,表示使用宿主机网络 volumes:在该pod上定义共享存储卷列表 - name: string共享存储卷名称 (volumes类型有很多种) emptyDir: {}类型为emtyDir的存储卷,与Pod同生命周期的一个临时目录。为空值 hostPath: string类型为hostPath的存储卷,表示挂载Pod所在宿主机的目录 path: stringPod所在宿主机的目录,将被用于同期中mount的目录 secret:类型为secret的存储卷,挂载集群与定义的secre对象到容器内部 scretname: string items: - key: string path: string configMap:类型为configMap的存储卷,挂载预定义的configMap对象到容器内部 name: string items: - key: string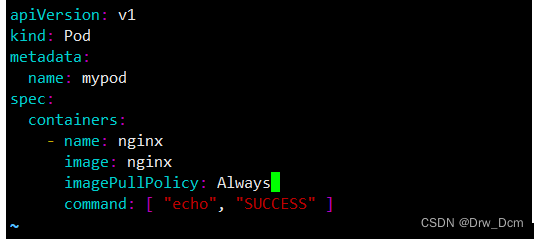

![]()

![]()
三、Service yaml文件
apiVersion: v1kind: Servicematadata: 元数据 name: string service的名称 namespace: string 命名空间 labels: 自定义标签属性列表 - name: string annotations: 自定义注解属性列表 - name: stringspec: 详细描述 selector: [] label selector配置,将选择具有label标签的Pod作为管理 范围 type: string service的类型,指定service的访问方式,默认为 clusterIp clusterIP: string 虚拟服务地址 sessionAffinity: string 是否支持session ports: service需要暴露的端口列表 - name: string 端口名称 protocol: string 端口协议,支持TCP和UDP,默认TCP port: int 服务监听的端口号 targetPort: int 需要转发到后端Pod的端口号 nodePort: int 当type = NodePort时,指定映射到物理机的端口号 status: 当spce.type=LoadBalancer时,设置外部负载均衡器的地址 loadBalancer: 外部负载均衡器 ingress: 外部负载均衡器 ip: string 外部负载均衡器的Ip地址值 hostname: string 外部负载均衡器的主机名四、yaml文件
Kubernetes 支持 YAML 和 JSON 格式管理资源对象
JSON 格式:主要用于 api 接口之间消息的传递
YAML 格式:用于配置和管理,YAML 是一种简洁的非标记性语言,内容格式人性化,较易读
1.YAML 语法格式
1)大小写敏感
2)使用缩进表示层级关系
3)不支持Tab键制表符缩进,只使用空格缩进
4)缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可,通常开头缩进两个空格
5)符号字符后缩进一个空格,如冒号,逗号,短横杆(-)等
6)“---”表示YAML格式,一个文件的开始,用于分隔文件间
7)“#”表示注释
2.查看 api 资源版本标签
kubectl api-versionsadmissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1apiregistration.k8s.io/v1apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1apps/v1 如果是业务场景一般首选使用 apps/v1apps/v1beta1 带有beta字样的代表的是测试版本,不用在生产环境中apps/v1beta2authentication.k8s.io/v1authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1authorization.k8s.io/v1authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1autoscaling/v1autoscaling/v2beta1autoscaling/v2beta2batch/v1batch/v1beta1certificates.k8s.io/v1beta1coordination.k8s.io/v1beta1events.k8s.io/v1beta1extensions/v1beta1networking.k8s.io/v1policy/v1beta1rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1scheduling.k8s.io/v1beta1storage.k8s.io/v1storage.k8s.io/v1beta1v13.写一个yaml文件demo
mkdir /opt/democd demo/vim nginx-deployment.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1 指定api版本标签kind: Deployment 定义资源的类型/角色,deployment为副本控制器,此处资源类型可以是 Deployment、Job、Ingress、Service等metadata: 定义资源的元数据信息,比如资源的名称、namespace、标签等信息 name: nginx-deployment 定义资源的名称,在同一个namespace空间中必须是唯一的 labels: 定义Deployment资源标签 app: nginxspec: 定义deployment资源需要的参数属性,诸如是否在容器失败时重新启动 容器的属性 replicas: 3 定义副本数量 selector: 定义标签选择器 matchLabels: 定义匹配标签 app: nginx 需与.spec.template.metadata.labels 定义的标签保持一致 template: 定义业务模板,如果有多个副本,所有副本的属性会按照模板的相关配置 进行匹配 metadata: labels: 定义Pod副本将使用的标签,需与 .spec.selector.matchLabels 定义 的标签保持一致 app: nginx spec: containers: 定义容器属性 - name: nginx 定义一个容器名,一个 - name: 定义一个容器 image: nginx:1.15.4 定义容器使用的镜像以及版本 ports: - containerPort: 80 定义容器的对外的端口(1)创建资源对象
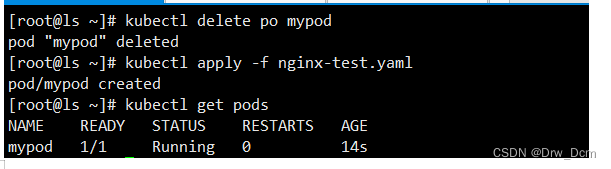
kubectl create -f nginx-deployment.yaml(2)查看创建的pod资源
kubectl get pods -o wide(3)创建service服务对外提供访问并测试
vim nginx-service.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx-service labels: app: nginx spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 80 selector: app: nginx(4)创建资源对象
kubectl create -f nginx-service.yaml(5)查看创建的service
kubectl get svc在浏览器输入 nodeIP:nodePort 即可访问
五、port
1.port
port 是 k8s 集群内部访问service的端口,即通过 clusterIP: port 可以从 Pod 所在的 Node 上访问到 service。
2.nodePort
nodePort 是外部访问 k8s 集群中 service 的端口,通过 nodeIP: nodePort 可以从外部访问到某个 service。
3.targetPort
targetPort 是 Pod 的端口,从 port 或 nodePort 来的流量经过 kube-proxy 反向代理负载均衡转发到后端 Pod 的 targetPort 上,最后进入容器。
4.containerPort
containerPort 是 Pod 内部容器的端口,targetPort 映射到 containerPort。
kubectl run --dry-run=client 打印相应的 API 对象而不执行创建
kubectl run nginx-test --image=nginx --port=80 --dry-run=clientkubectl create deployment nginx-deploy --image=nginx --port=80 --replicas=3 --dry-run=client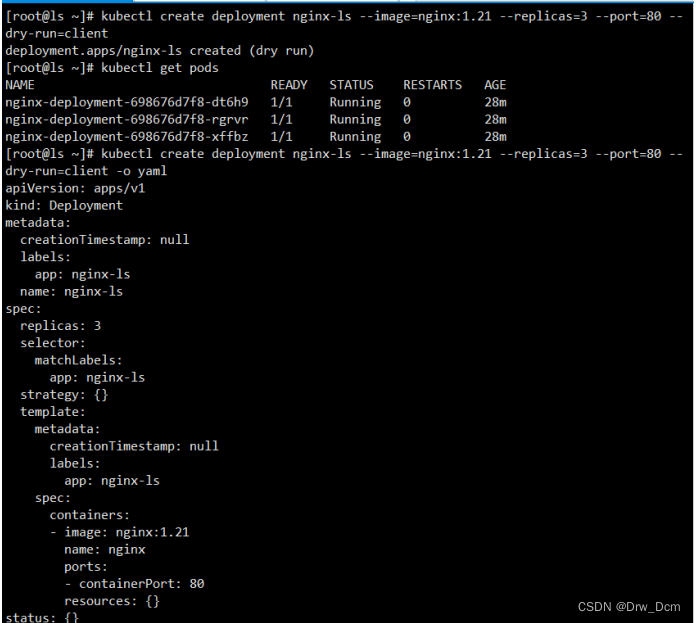
![]()
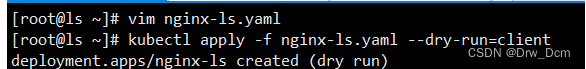
查看生成yaml格式
kubectl run nginx-test --image=nginx --port=80 --dry-run=client -o yamlkubectl create deployment nginx-deploy --image=nginx --port=80 --replicas=3 --dry-run=client -o yaml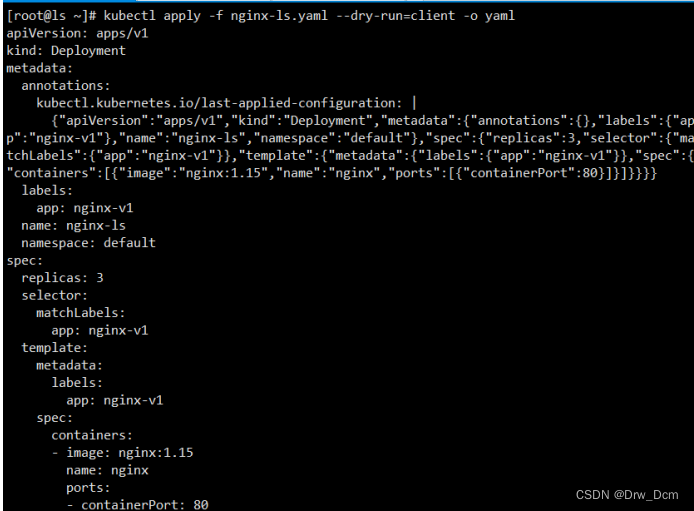
查看生成json格式
kubectl run nginx-test --image=nginx --port=80 --dry-run=client -o jsonkubectl create deployment nginx-deploy --image=nginx --port=80 --replicas=3 --dry-run=client -o json使用yaml格式导出生成模板,并进行修改以及删除一些不必要的参数
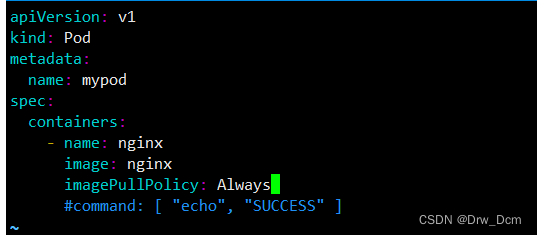
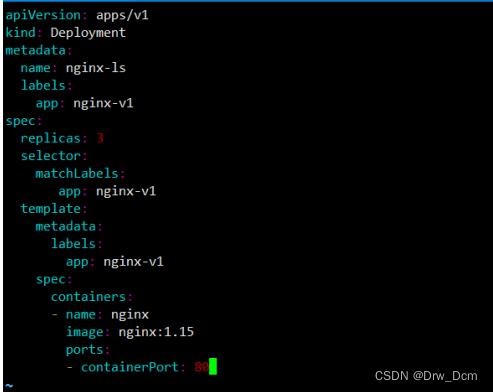
kubectl run nginx-test --image=nginx --port=80 --dry-run=client -o yaml > nginx-test.yamlkubectl create deployment nginx-deploy --image=nginx --port=80 --replicas=3 --dry-run=client -o yaml > nginx-deploy.yamlvim nginx-test.yamlapiVersion: v1kind: Podmetadata: creationTimestamp: null 删除 labels: run: nginx-test name: nginx-testspec: containers: - image: nginx name: nginx-test ports: - containerPort: 80 resources: {} 删除 dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Alwaysstatus: {} 删除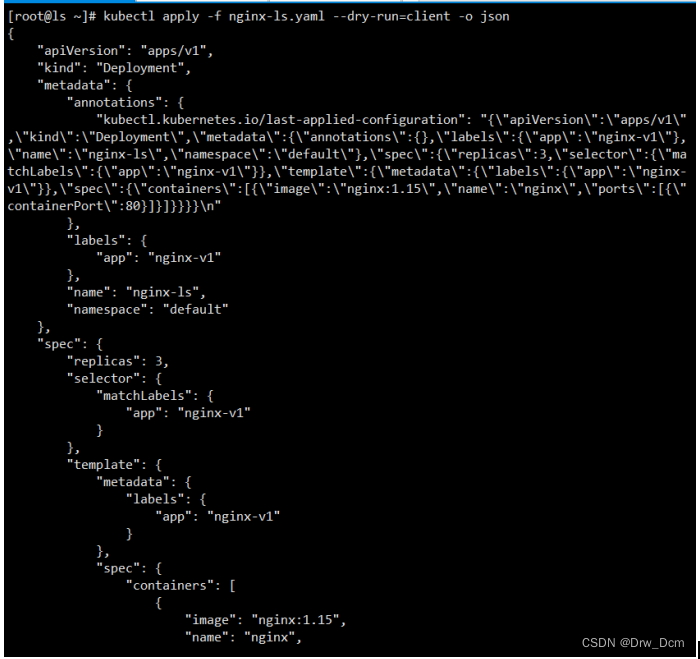
将现有的资源生成模板导出
kubectl get svc nginx-service -o yaml保存到文件中
kubectl get svc nginx-service -o yaml > my-svc.yaml查看字段帮助信息,可一层层的查看相关资源对象的帮助信息
kubectl explain deployments.spec.template.spec.containers或kubectl explain pods.spec.containers