一、Compose 介绍
google 在 07月28日 发布了compose 1.0正式版,代表着其api结构已经趋于稳定,作为一个合格(天天划水)的android developer,也是时候开始了解它了。
以下内容引用自官网内容
Jetpack Compose 是一个适用于 Android 的新式声明性界面工具包。Compose 提供声明性 API,让您可在不以命令方式改变前端视图的情况下呈现应用界面,从而使编写和维护应用界面变得更加容易。
二、Compose 创建
1.新建应用
- 下载安装 Android Studio Arctic Fox,以便于在
Jetpack Compose进行开发时获得最佳体验 - 创建应用
New Project选择Empty Compose Activity,然后Next,在填写好相关信息后Finish进入应用主界面,等待构建完成。 - 在手机/模拟器上运行你的第一个
Compose
至此,compose 创建完成,工具下载及应用构建建议科学上网。
三、查看初始 Compose 应用结构
一个新建的Compose应用内包含了一个MainActivity.kt,以及ui.theme包内颜色、主题等配置文件
1. MainActivity
1.1. 父类
MainActivity继承自 ComponentActivity,ComponentActivity 又继承自 Activity,说明View还是通过setContentView()加载。
1.2. onCreate() 方法
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
Compose_oneTheme {
// A surface container using the 'background' color from the theme
Surface(color = MaterialTheme.colors.background) {
Greeting()
}
}
}
}方法内 setContent{}就比较陌生了,通过源码可以看到setContent()是ComponentActivity的一个拓展方法,其中的content参数需要传入一个由@Composable注解的函数,值得注意的是@Composable并非传统意义上的注解处理器,Compose 在 Kotlin 编译器的类型检测与代码生成阶段依赖 Kotlin 编译器插件工作,所以无需注解处理器即可使用 Compose。@Composable的作用更像一个关键字,比如 suspend,@Composable 与其工作方式相同:它可以改变函数类型。重点是,当使用 @Composable 注解一个函数类型时,会导致它类型的改变:未被注解的相同函数类型与注解后的类型互不兼容。源码如下
public fun ComponentActivity.setContent(
parent: CompositionContext? = null,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
val existingComposeView = window.decorView
.findViewById<ViewGroup>(android.R.id.content)
.getChildAt(0) as? ComposeView
if (existingComposeView != null) with(existingComposeView) {
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
setContent(content)
} else ComposeView(this).apply {
// Set content and parent **before** setContentView
// to have ComposeView create the composition on attach
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
setContent(content)
// Set the view tree owners before setting the content view so that the inflation process
// and attach listeners will see them already present
setOwners()
setContentView(this, DefaultActivityContentLayoutParams)
}
}可以发现,在setContent内部,程序会去寻找Activity的根布局,若未找到则创建一个,然后将由@Conposable注解函数内的声明式布局创建。
1.3. Greeting() 方法
@Composable
fun Greeting() {
Text(text = "Hello,Jetpack Compose!")
}该方法由@Composable注解(最终需要传入到setContent方法中的都需要注解,不论多少层),其内容则是要创建的视图内容的具体声明描述了。
1.4. DefaultPreview() 方法
@Preview(showBackground = true )
@Composable
fun DefaultPreview() {
Compose_oneTheme {
Greeting()
}
}值得注意的是 DefaultPreview()除了添加了@Composable注解外,还添加了@Preview, @Preview注解的方法可以在不运行App的情况下就可以确认布局的情况。
如下图所示
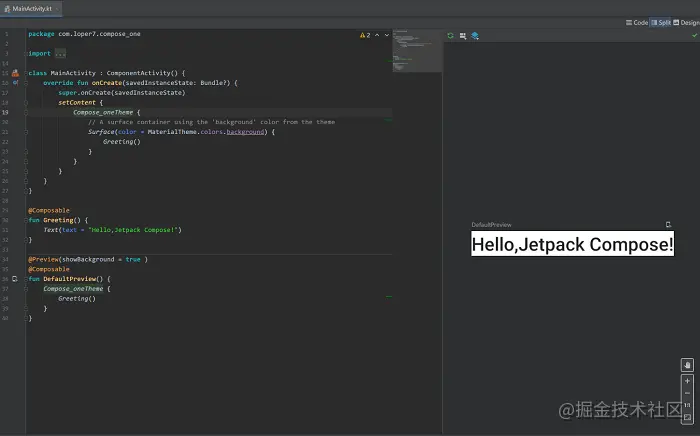
@Preview的注解中比较常用的参数如下:
name: String: 为该Preview命名,该名字会在布局预览中显示。showBackground: Boolean: 是否显示背景,true为显示。backgroundColor: Long: 设置背景的颜色。showDecoration: Boolean: 是否显示Statusbar和Toolbar,true为显示。group: String: 为该Preview设置group名字,可以在UI中以group为单位显示。fontScale: Float: 可以在预览中对字体放大,范围是从0.01。- widthDp: Int: 在Compose中渲染的最大宽度,单位为dp。heightDp: Int: 在Compose中渲染的最大高度,单位为dp。
注意:强烈建议您不要向生产函数(即使其不带参数)添加 @Preview 注释,而是编写一个封装函数并在其中添加 @Preview 注释。 这便是 DefaultPreview存在的意义,详见 developer.android.google.cn/jetpack/com…
2. ui.theme 包
包内包含了Color.kt、Shape.kt、Type.kt、Theme.kt,分别是颜色、形状、类型、主题的描述文件,可以理解为代替了传统android项目内res内的xml配置文件;在后面的文章中会专门讲到。
四、在现有应用中使用 Compose
1. 添加依赖
- 将
Gradle升级至7.0
buildscript {
...
dependencies {
classpath "com.android.tools.build:gradle:7.0.0"
...
}
}- 将
Kotlin升级至1.5.21 - 配置
Gradle
需要将应用的最低 API 级别设置为 21 或更高级别,并在应用的 build.gradle 文件中启用 Jetpack Compose,如下所示。另外还要设置 Kotlin 编译器插件的版本。
android {
defaultConfig {
...
minSdkVersion 21
}
buildFeatures {
// Enables Jetpack Compose for this module
compose true
}
...
// Set both the Java and Kotlin compilers to target Java 8.
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = "1.8"
}
composeOptions {
kotlinCompilerExtensionVersion '1.0.1'
kotlinCompilerVersion '1.5.21'
}
}- 添加
Jetpack Compose工具包依赖项
dependencies {
// Integration with activities
implementation 'androidx.activity:activity-compose:1.3.1'
// Compose Material Design
implementation 'androidx.compose.material:material:1.0.1'
// Animations
implementation 'androidx.compose.animation:animation:1.0.1'
// Tooling support (Previews, etc.)
implementation 'androidx.compose.ui:ui-tooling:1.0.1'
// Integration with ViewModels
implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-compose:1.0.0-alpha07'
// UI Tests
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.compose.ui:ui-test-junit4:1.0.1'
}2. 在XML中使用Compopse
在xml中可以将 ComposeView 作为一个普通的view来使用,然后在代码内通过setContent方法注入compose
<...>
<!-- Other content -->
<androidx.compose.ui.platform.ComposeView
android:id="@+id/greeting"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</...>class MyActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// ...
val greeting = findViewById<ComposeView>(R.id.greeting)
greeting.setContent {
MdcTheme { // or AppCompatTheme
Greeting()
}
}
}
}
@Composable
private fun Greeting() {
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.greeting),
style = MaterialTheme.typography.h5,
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(horizontal = dimensionResource(R.dimen.margin_small))
.wrapContentWidth(Alignment.CenterHorizontally)
)
}3. 在Activity/Fragment...中使用Compopse
可参考新建compose应用内的实现方式,直接使用setContent方法。
五、最后
好记性不如烂笔头,初识 Jetpack Compose 系列是我自己的学习笔记,在加深知识巩固的同时,也可以锻炼一下写作技能。文章中的内容仅作参考,如有问题请留言指正。
为了方便大家更好的学习Kotlin,我特地将下面的文档整合到Github中,希望能帮助到感兴趣的读者。
项目地址:Github