注:机翻,未校。
How to Determine the Current User Account in Linux
Key Takeaways
Linux distributions normally display the username of the current user in the Terminal as (Username)@ComputerName. If your Linux distribution doesn’t, run “who” or “whoami” in the Terminal to get the username instead. You can use the “w” command to get even more detailed information.
Linux 发行版通常在终端中将当前用户的用户名显示为 (Username)@ComputerName。如果您的 Linux 发行版没有,请在终端中运行“who”或“whoami”以获取用户名。您可以使用“w”命令来获取更详细的信息。
If Linux means anything, it means choice. You can achieve even a simple task like identifying the current user in many ways. This tutorial will show you how to use some of the quickest and easiest methods.
如果说Linux有什么意义,那它就意味着选择。您甚至可以完成一项简单的任务,例如以多种方式识别当前用户。本教程将向您展示如何使用一些最快和最简单的方法。
Why would you need to find the identity of the current user? In many cases the owner of the computer is the only user and, without getting too existential, they probably know themselves. Perhaps, but it is also common for people to create additional user accounts to allow family members to have access to the computer. And, if you’re connected to a remote shell on a server somewhere, you may need a quick reminder of the username you’re logged in with. If you see a logged in session with no one in attendance, how do you identify the current user from the command line?
你为什么需要找出当前用户的身份呢?虽然在许多情况下,计算机的所有者可能是唯一的用户,且他们可能对自己有很清楚的认识,但实际上,人们经常会创建额外的用户账户,以便家庭成员可以访问计算机。此外,如果你通过远程终端连接到某个服务器,你可能需要快速查看你当前登录的用户名。如果你看到一个登录会话却没有人在使用,你怎么通过命令行来识别当前的用户呢?
Find Your Current User by Looking at the Terminal
Let’s try the easiest option first. All we need to do is look at the command prompt. By default, Linux distributions have the username in the prompt. Simple. We didn’t even have to type a thing. You can see the username — Dave, in this case — next to “@howtogeek”. Generally this will be displayed YourName@YourPCName,
让我们先尝试最简单的选项。我们需要做的就是查看命令提示符。默认情况下,Linux 发行版的提示符中包含用户名。简单。我们甚至不需要输入任何东西。您可以在“@howtogeek”旁边看到用户名 - 在本例中为 Dave。通常,这将显示在YourName@YourPCName,

If the user has changed their prompt to some other format we need to try something else.
如果用户已将他们的提示更改为其他格式,我们需要尝试其他方法。
1、Use who to Get the Current User
who
The who command will give us the information we are looking for on any Linux distro.
who 命令将为我们提供在任何 Linux 发行版上寻找的信息。
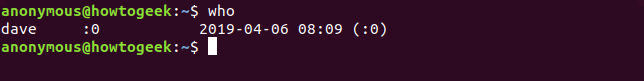
The output from who gives you the name of the current user, the terminal they are logged in at, the date and time when they logged in. If it is a remote session, it also tell us where they are logged in from.
who 的输出为您提供当前用户的名称、他们登录的终端、他们登录的日期和时间。如果是远程会话,它还会告诉我们他们从哪里登录。
2、Use whoami to Find the Current User
The whoami command will also display the current user.
whoami 命令还将显示当前用户。
By comparison to the who, the whoami command provides a very pithy answer. It only displays the username and nothing else.
与 who 相比,whoami 命令提供了一个非常简洁的答案。它只显示用户名,不显示其他任何内容。
whoami
~

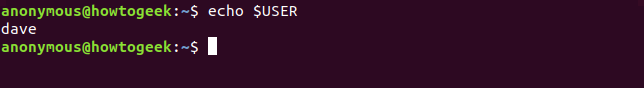
echo $USER
You can get the same one-word answer by echoing the $USER environment variable to the screen.
您可以通过将 $USER 环境变量回显到屏幕上来获得相同的字符信息。
3、Use w to Find the Current User and Extra Information
w
The one-letter command w requires less typing and provides more information.
单字母命令 w 需要较少的键入并提供更多信息。
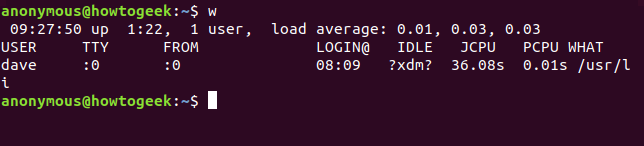
The w command provides us with the user name which is what we wanted, and a bonus set of data for that user. Note that if there are multiple users logged into the Linux system, the w command will list them all. You’d need to know which terminal the user you were interested in had logged in on. If they’ve logged directly onto the Linux computer itself, that’ll be pts/o, so look for :0 in the output from w .
w 命令为我们提供了我们想要的用户名,以及该用户的一组额外数据。请注意,如果有多个用户登录到 Linux 系统,则 w 命令将列出所有用户。您需要知道您感兴趣的用户登录了哪个终端。如果他们直接登录到 Linux 计算机本身,那将是 pts/o,因此可以看到 :0 在 w 的输出中。
The w command provides the boot time, uptime and average load for the previous five, ten and fifteen minutes, and the following information regarding the current user.
w 命令提供前 5 分钟、10 分钟和 15 分钟的启动时间、运行时间和平均负载,以及有关当前用户的以下信息。
USER:用户名。TTY: The type of terminal they are logged in at. This will usually be a pts (a pseudo-teletype). :0 means the physical keyboard and screen connected to this computer.
TTY:他们登录的终端类型。这通常是 pts(伪电传打字机)。:0表示连接到此计算机的物理键盘和屏幕。FROM: The name of the remote host if this is a remote connection.
FROM:如果这是远程连接,则为远程主机的名称。LOGIN@: The time at which the user logged in.
LOGIN@:用户登录的时间。IDLE: Idle time. This shows ?xdm? in the screenshot because we’re running under an X-windows Display Manager, which does not provide that information.
IDLE:空闲时间。这显示了?xdm?因为我们在 X-windows 显示管理器下运行,它不提供该信息。JCPU: Joint CPU time, this is the CPU time used by all processes that have been attached to this tty. In other words, the total CPU time of this user in this logged in session.
JCPU:联合 CPU 时间,这是已附加到此 tty 的所有进程使用的 CPU 时间。换言之,此用户在此登录会话中的总 CPU 时间。PCPU: Process CPU time, this is the CPU time used by the current process. The current process is named in the WHAT column.
PCPU:进程 CPU 时间,这是当前进程使用的 CPU 时间。当前进程在 WHAT 列中命名。WHAT: The command line of this user’s current process.
WHAT:此用户当前进程的命令行。
What Can You Do With a Username?
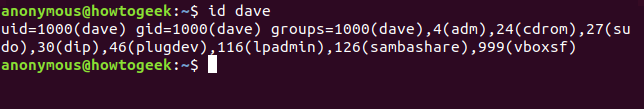
id
Now that we know who this user is, we can obtain more information about them. The id command is a good place to start. Type id, a space, the name of the user and press enter.
现在我们知道了这个用户是谁,我们可以获取有关他们的更多信息。id 命令是一个很好的起点。键入 id、空格、用户名称,然后按 Enter 键。
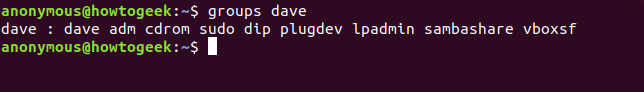
groups
This gives us their user ID (uid), group ID (gid) and the groups they’re a member of. A less cluttered display of the groups can be obtained by using the groups command.
这为我们提供了他们的用户 ID (uid)、组 ID (gid) 以及他们所属的组。可以使用 groups 命令获得较少杂乱的组显示。
finger
A nice summary is provided by the finger command. Use apt-get to install this package onto your system if you’re using Ubuntu or another Debian-based distribution. On other Linux distributions, use your Linux distribution’s package management tool instead.
finger 命令提供了一个很好的摘要。如果您使用的是 Ubuntu 或其他基于 Debian 的发行版,请使用 apt-get 将此软件包安装到您的系统上。在其他 Linux 发行版上,请改用 Linux 发行版的包管理工具。
sudo apt-get install fingerOnce you have finger installed, you can use it to display some information about the user in question.
安装 finger 后,您可以使用它来显示有关相关用户的一些信息。
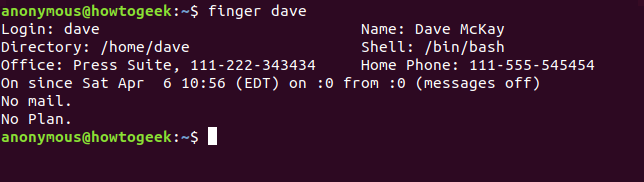
On most Linux systems, some of these fields will be blank. The office, full name, and phone numbers are not populated by default. The “No Plan” field refers to an old scheme where you could provide a few notes for whoever was interested, about what you were working on, or planning to do. If you edit the .plan file in your home folder, the contents of that file are appended to the output from finger .
在大多数 Linux 系统上,其中一些字段将为空。默认情况下,不会填充办公室、全名和电话号码。“无计划”字段是指一个旧计划,您可以在其中为任何感兴趣的人提供一些关于您正在做什么或计划做什么的注释。如果编辑主文件夹中的 .plan 文件,则该文件的内容将追加到 finger 的输出中。
In some distros you may find the name of the current user displayed in the System Menu in the upper right corner of your screen, but that varies depending on your desktop environment.
在某些发行版中,您可能会在屏幕右上角的系统菜单中找到当前用户的名称,但这会根据您的桌面环境而有所不同。
via:
How to Determine the Current User Account in Linux By Dave McKay Updated Sep 10, 2023
https://www.howtogeek.com/410423/how-to-determine-the-current-user-account-in-linux/