?个人主页: 鑫宝Code
?热门专栏: 闲话杂谈| 炫酷HTML | JavaScript基础
?个人格言: "如无必要,勿增实体"

文章目录
React 生命周期完全指南一、生命周期概述二、生命周期的三个阶段2.1 挂载阶段(Mounting)2.2 更新阶段(Updating)2.3 卸载阶段(Unmounting) 三、常用生命周期方法详解3.1 constructor(构造函数)3.2 componentDidMount3.3 componentDidUpdate3.4 componentWillUnmount 四、生命周期的最佳实践4.1 性能优化4.2 错误处理 五、新旧生命周期的变化5.1 已废弃的生命周期方法5.2 新增的生命周期方法 六、Hooks 时代的生命周期七、总结
React 生命周期完全指南
一、生命周期概述
React 组件的生命周期是指组件从创建、更新到销毁的整个过程。合理地使用生命周期方法可以让我们更好地控制组件的行为,优化性能,并处理副作用。
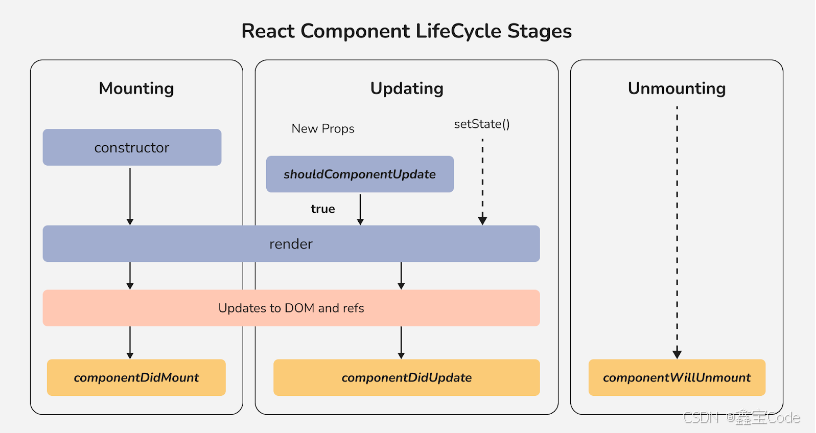
二、生命周期的三个阶段
2.1 挂载阶段(Mounting)
组件实例被创建并插入 DOM 的过程
class MyComponent extends React.Component { // 1. 构造函数 constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { count: 0 }; console.log('1. constructor'); } // 2. 静态方法,很少使用 static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) { console.log('2. getDerivedStateFromProps'); return null; } // 3. 渲染方法 render() { console.log('3. render'); return <div>{this.state.count}</div>; } // 4. 挂载完成 componentDidMount() { console.log('4. componentDidMount'); }}2.2 更新阶段(Updating)
当组件的 props 或 state 发生变化时触发更新
class MyComponent extends React.Component { // 1. 静态方法 static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) { return null; } // 2. 是否应该更新 shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) { return true; } // 3. 渲染 render() { return <div>{this.state.count}</div>; } // 4. 获取更新前的快照 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) { return null; } // 5. 更新完成 componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) { // 处理更新后的操作 }}2.3 卸载阶段(Unmounting)
组件从 DOM 中移除的过程
class MyComponent extends React.Component { componentWillUnmount() { // 清理工作,比如清除定时器、取消订阅等 console.log('组件即将卸载'); }}三、常用生命周期方法详解
3.1 constructor(构造函数)
constructor(props) { super(props); // 初始化状态 this.state = { count: 0, data: [] }; // 绑定方法 this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);}使用场景:
初始化组件的 state绑定事件处理方法不要在这里调用 setState避免在这里执行副作用操作3.2 componentDidMount
componentDidMount() { // 发起网络请求 fetch('api/data') .then(res => res.json()) .then(data => { this.setState({ data }); }); // 添加事件监听 window.addEventListener('resize', this.handleResize); // 设置定时器 this.timer = setInterval(() => { this.setState(state => ({ count: state.count + 1 })); }, 1000);}使用场景:
发起网络请求DOM 操作添加订阅设置定时器3.3 componentDidUpdate
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) { // 比较 props 变化 if (this.props.userID !== prevProps.userID) { this.fetchData(this.props.userID); } // 比较 state 变化 if (this.state.count !== prevState.count) { document.title = `点击次数:${this.state.count}`; }}使用场景:
对比更新前后的数据根据条件执行副作用注意避免无限循环3.4 componentWillUnmount
componentWillUnmount() { // 清除定时器 clearInterval(this.timer); // 移除事件监听 window.removeEventListener('resize', this.handleResize); // 取消订阅 this.subscription.unsubscribe();}使用场景:
清理定时器取消网络请求清除事件监听取消订阅四、生命周期的最佳实践
4.1 性能优化
class OptimizedComponent extends React.Component { shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) { // 只在必要时更新 return ( this.props.value !== nextProps.value || this.state.count !== nextState.count ); } render() { return ( <div> <h1>{this.props.value}</h1> <p>{this.state.count}</p> </div> ); }}4.2 错误处理
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component { state = { hasError: false }; static getDerivedStateFromError(error) { return { hasError: true }; } componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) { // 记录错误日志 console.error('错误信息:', error); console.error('错误详情:', errorInfo); } render() { if (this.state.hasError) { return <h1>出错了!</h1>; } return this.props.children; }}五、新旧生命周期的变化
5.1 已废弃的生命周期方法
componentWillMountcomponentWillReceivePropscomponentWillUpdate5.2 新增的生命周期方法
getDerivedStateFromPropsgetSnapshotBeforeUpdate六、Hooks 时代的生命周期

function HooksComponent() { // 相当于 constructor 和 componentDidMount const [count, setCount] = useState(0); // 相当于 componentDidMount 和 componentDidUpdate useEffect(() => { document.title = `点击次数:${count}`; }, [count]); // 相当于 componentDidMount 和 componentWillUnmount useEffect(() => { const handler = () => console.log('窗口大小改变'); window.addEventListener('resize', handler); // 清理函数 return () => { window.removeEventListener('resize', handler); }; }, []); return <div>计数:{count}</div>;}七、总结
React 生命周期方法为我们提供了在组件不同阶段执行代码的机会。合理使用这些方法可以:
优化组件性能正确处理副作用管理组件状态避免内存泄漏在实际开发中,最常用的生命周期方法是:
constructor:初始化componentDidMount:副作用处理componentDidUpdate:更新后的操作componentWillUnmount:清理工作随着 React Hooks 的普及,函数组件正在逐渐取代类组件。但理解生命周期概念对于深入理解 React 的工作原理仍然至关重要。