文章目录
1. memcpy使用和模拟实现2. memmove使用和模拟实现3. memset函数的使用4. memcmp函数的使用
1. memcpy使用和模拟实现
void * memcpy ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );memcpy从source的位置开始向后复制num个字节的数据到destination指向的内存位置。这个函数在遇到 \0 的时候并不会停下来。如果source和destination有任何的重叠,复制的结果都是未定义的。 示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main(){int arr1[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };int arr2[10] = { 0 };memcpy(arr2, arr1, 20);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", arr2[i]);}return 0;}对于重叠的内存,交给memmove来处理。
memcpy函数的模拟实现:
void* my_memcpy(void* dst, const void* src, size_t count){void* ret = dst;assert(dst);assert(src);/** copy from lower addresses to higher addresses*/while (count--) {*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;dst = (char*)dst + 1;src = (char*)src + 1;}return(ret);}2. memmove使用和模拟实现
void * memmove ( void * destination, const void * source, size_t num );memcpy的差别就是memmove函数处理的源内存块和目标内存块是可以重叠的。如果源空间和目标空间出现重叠,就得使用memmove函数处理。 示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main(){int arr1[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };memmove(arr1 + 2, arr1, 20);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("%d ", arr1[i]);}return 0;}输出结果如下:
1 2 1 2 3 4 5 8 9 10memmove的模拟实现:
void* my_memmove(void* dst, const void* src, size_t count){void* ret = dst;if (dst <= src || (char*)dst >= ((char*)src + count)) {/** Non-Overlapping Buffers* copy from lower addresses to higher addresses*/while (count--) {*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;dst = (char*)dst + 1;src = (char*)src + 1;}}else {/** Overlapping Buffers* copy from higher addresses to lower addresses*/dst = (char*)dst + count - 1;src = (char*)src + count - 1;while (count--) {*(char*)dst = *(char*)src;dst = (char*)dst - 1;src = (char*)src - 1;}}return(ret);}3. memset函数的使用
void * memset ( void * ptr, int value, size_t num );memset是用来设置内存的,将内存中的值以字节为单位设置成想要的内容。
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main(){char str[] = "hello world";memset(str, 'x', 6);printf(str);return 0;}输出结果:
xxxxxxworld4. memcmp函数的使用
int memcmp ( const void * ptr1, const void * ptr2, size_t num );ptr1和ptr2指针指向的位置开始,向后的num个字节返回值如下: 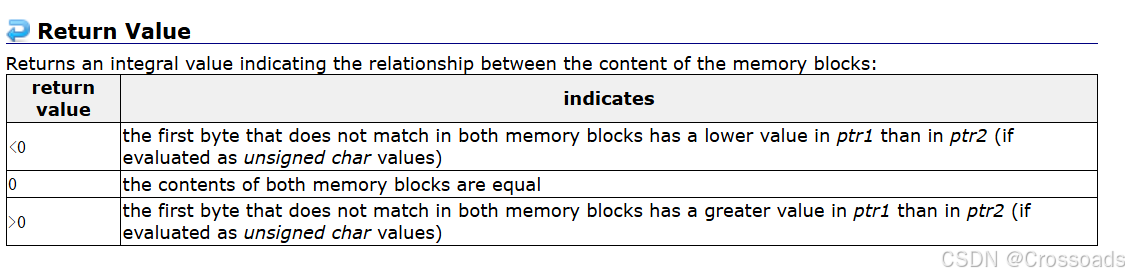
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main(){char buffer1[] = "DWgaOtP12df0";char buffer2[] = "DWGAOTP12DF0";int n;n = memcmp(buffer1, buffer2, sizeof(buffer1));if (n > 0)printf("'%s' is greater than '%s'.\n", buffer1, buffer2);else if (n < 0)printf("'%s' is less than '%s'.\n", buffer1, buffer2);elseprintf("'%s' is the same as '%s'.\n", buffer1, buffer2);return 0;}输出结果:
'DWgaOtP12df0' is greater than 'DWGAOTP12DF0'.