编写一个的Java计算器可以帮助我们学习java组件、监视器、表达式算法等等,本篇用于讲解如何用Java编写一个简单的计算器。
在正式讲解之前,我们先看一下本项目实现的效果,如下所示:
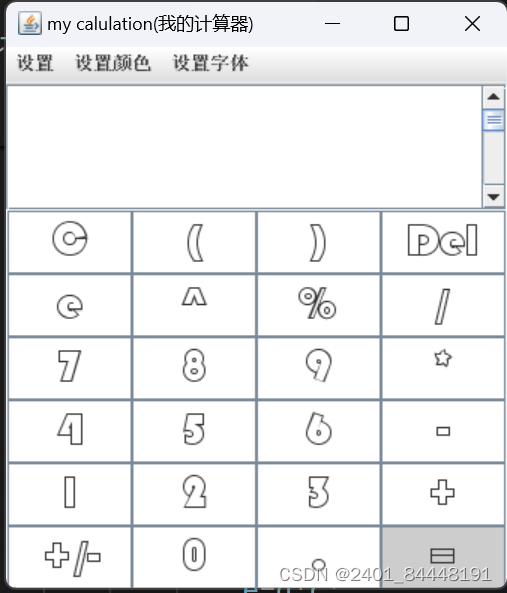 java计算器界面
java计算器界面 1.需求分析
1.1功能声明
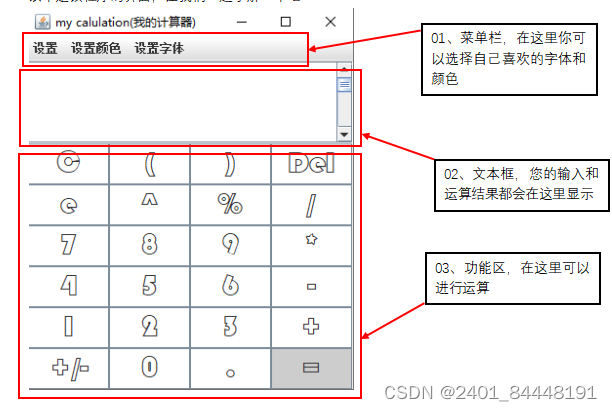 功能区介绍
功能区介绍 (1)设置窗体颜色、字体。
(2)支持“(”和“)”的操作。
(3)支持求相反数的功能。
(4)支持删除、清除操作。
(5)支持小数运算。
(6)实现算术加法、减法、乘法、除法的基本功能。
(7)实现幂、科学计数、求余的功能。
(8)支持错误检测。
1.2概念模型
计算器的设计分为菜单条设计、按钮设计、窗体设计、功能设计四个部分进行。
1.菜单条设计
菜单条的设计分为设置、设置颜色、设置字体三个部分
(1).设置:

退出:关闭该计算器
恢复默认设置:返回初始设置的背景色和字体样式
(2).设置颜色
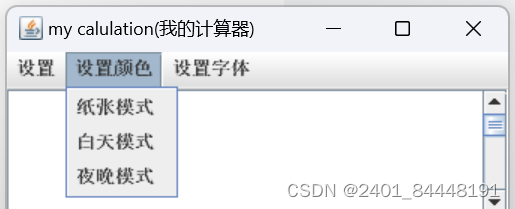
纸张模式:设置主题背景颜色为黄色
白天模式:设置主题背景颜色为白色
夜晚模式:设置主题背景颜色为黑色
(3).设置字体
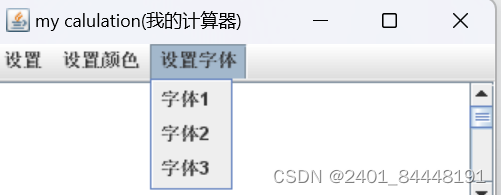
 字体1:(STHUPO)
字体1:(STHUPO)  字体2:(STXINWE)
字体2:(STXINWE)  字体3:(STCAIYUN)
字体3:(STCAIYUN) 字体说明
2.按钮设计
 按钮功能示意图
按钮功能示意图 特殊的功能说明:(公式中的a、b表示操作数)
(1)幂次 ^:a^b=pow(a,b)
(2)科学计数法 e: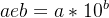
(3)求余 %:a对b取余(这时a和b只能是整数,且b不能是0)
(4)清除 C:清空文本框信息
(5)取相反数 +/-:对操作数1取相反数,在文本框开头加一个负号
3.窗体设计(UI设计)
设计方法:创建一个calulation_make的类继承自JFrame类,将计算器所需部件和属性都放入calulation_make中,主函数中只用创建一个calulation_make类,即可完成计算器的实现。
将计算机窗口分成3个模块进行设计【菜单条、文本区、功能按钮区】:
1.菜单条(JMenuBar menu)
说明:f为窗口变量名
//设置菜单条menu基本属性 JMenuBar menu=new JMenuBar(); //菜单条 JMenu jMenu0=new JMenu("设置"); JMenuItem tc=new JMenuItem("退出"); tc.addActionListener(e->{System.exit(0);}); //设置退出 jMenu0.add(tc); JMenuItem hf=new JMenuItem("恢复默认设置"); jMenu0.add(hf); menu.add(jMenu0); JMenu jMenu1=new JMenu("设置颜色"); JMenuItem item1=new JMenuItem("纸张模式"); JMenuItem item2=new JMenuItem("白天模式"); JMenuItem item3=new JMenuItem("夜晚模式"); jMenu1.add(item1); jMenu1.add(item2); jMenu1.add(item3); menu.add(jMenu1); JMenu jMenu2=new JMenu("设置字体"); JMenuItem Font1=new JMenuItem("字体1"); JMenuItem Font2=new JMenuItem("字体2"); JMenuItem Font3=new JMenuItem("字体3"); jMenu2.add(Font1); jMenu2.add(Font2); jMenu2.add(Font3); menu.add(jMenu2); f.setJMenuBar(menu);2.文本区设计
将文本区(JTextArea text)放在一个带滚条的面板(JScrollPane m0)里
//文本区设计 JTextArea text=new JTextArea(100,10); text.setLineWrap(true); //相当于自动换行(取消横向方向的滚动条) text.setFont(font); text.setCaretPosition(text.getDocument().getLength()); JScrollPane m0 = new JScrollPane(text); //带滚动条的面板(JPanel) m0.setBounds(0,0,f.getWidth()-12, 100);//绝对地址+尺寸 (但好像xy的值不会影响成果) f.add(m0);3. 功能按钮区设计
以按钮所示字符串,创建字符串组(s),再根据字符串组生成按钮,按钮的布局为一行四个按钮
m1.setLayout(new GridLayout(0, 4)); //设置面板每列的按钮个数 (实现分层)JPanel m1=new JPanel(); m1.setLayout(new GridLayout(0, 4)); //设置面板每列的按钮个数 (实现分层) String[] s={ "C","(",")","Del", "e","^","%","/", "7","8","9","*", "4","5","6","-", "1","2","3","+", "+/-","0",".","=" }; JButton[] an=new JButton[s.length]; for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++) { an[i]= new JButton(s[i]);// 宽度100像素, 高度50像素 an[i].setFont(font); m1.add(an[i]); } an[s.length-1].setBackground(Color.lightGray); f.getContentPane().add(m1,BorderLayout.SOUTH); //表方位,一定要加,否则会覆盖2.功能设计
2.1菜单功能设计
通过对菜单项增加监视器,并设置方法完成菜单项对应功能。
(1)退出功能设置
JMenu jMenu0=new JMenu("设置");JMenuItem tc=new JMenuItem("退出");tc.addActionListener(e->{System.exit(0);}); //设置退出jMenu0.add(tc);(2)设置主题颜色
把R,G,B作为参数,传入方法SetColor中,分别修改滚动面板(JScrollPane m0)、文本区(JTextArea text)、按钮(JButton an[])的背景颜色,从而实现主题色的改变。
//子函数设计static public void SetColor(JScrollPane m,JTextArea a,JButton an[],int n){//颜色设置子函数 m.setBackground(new Color(R,G,B)); a.setBackground(new Color(R,G,B)); for (int i =0;i<an.length;i++){ if("="==an[i].getText()) an[i].setBackground(new Color(R-n,G-n,B-n)); else an[i].setBackground(new Color(R,G,B)); } }//添加功能 item1.addActionListener(e->{ R=240;G=230;B=140;//设置黄色 SetColor(m0,text,an,20); }); item2.addActionListener(e->{ R=G=B=255;//设置白色 SetColor(m0,text,an,50); }); item3.addActionListener(e->{ R=G=B=70;//夜间模式-->黑色 SetColor(m0,text,an,10); });(3)设置字体功能
把i作为参数,表示要使用第i个字体,传入方法SetFont中,分别修改文本区(JTextArea text)、按钮(JButton an[])的字体,从而实现主题字体的改变。
//字体设置函数 static public void SetFont(JTextArea a,JButton an[],int n){//字体设置子函数 String[] s={"STHUPO","STXINWEI","STCAIYUN"}; Font font = new Font(s[n], Font.PLAIN, 12); font = font.deriveFont(font.getSize() * (float) 2.5);// 设置行高为2.5倍字体大小 (设置文字的一种格式) a.setFont(font); for (int i =0;i<an.length;i++) { an[i].setFont(font); an[i].setSize(50,50); } } //添加功能 Font1.addActionListener(e->{ SetFont(text,an,0); }); Font2.addActionListener(e->{ SetFont(text,an,1); }); Font3.addActionListener(e->{ SetFont(text,an,2); });(4)设置恢复初始设置
为‘恢复初始设置’的菜单项增加监视器,当被点击时调用自定义的SetFont和SetColor方法完成最初样式的设计。
hf.addActionListener(e->{ R=G=B=255; SetColor(m0,text,an,50);//恢复颜色 SetFont(text, an,2);//恢复字体 }); 2.2键盘功能设计
(1)通过按钮输入
因为按钮是根据字符串组s生成的,可以利用s与按钮an的角标对应关系,完成通过按钮输入的功能。有四个按钮点击时不用输入(‘+/-’、‘C’、‘Del’、‘=’)需要特别添加监视器。
for(int i=1;i<s.length-1;i++) //取消C和=的输入 {//用鼠标把数据放到text中 if(i==20 || i==3)//取消‘Del’和‘+/-’的输入 continue; int j=i; an[i].addActionListener(e->text.append(s[j])); //必须用j=i来给text末尾加上数字 直接用i行不通 }(2)设置特殊按钮的功能
因为按钮面板变化不定,为增强代码的可变性,自定义了look_s方法,获得对应功能在按钮组中的位置
//获取角标的方法static public int look_s(String[] s,String s1){ int i=0; for(i=0;i<s.length;i++) { if(s[i].equals(s1)) return i; } return -1; }//特殊功能按钮设置 an[look_s(s,"C")].addActionListener(e->{ text.setText("");//把文本框清空 osChar.clear(); osValue.clear();//把所有的东西都清空 }); //取相反数 an[look_s(s,"+/-")].addActionListener(e->{ String t1=text.getText(); if(t1.startsWith("-"))//表判断是不是以"-"开头 要和运算中的减号区分开 不然总是说运算出差 text.setText(text.getText().substring(1,text.getText().length()));//截取1到最后(去掉-号) else text.setText("-"+text.getText()); }); //删除功能 an[look_s(s, "Del")].addActionListener(e->{ try { text.setText(text.getText().substring(0,text.getText().length()-1)); } catch (Exception cw) { } }); //等号功能 an[look_s(s, "=")].addActionListener(e->{ try{ System.out.println(text.getText());//输出text中的数 double x = calculate(text.getText()+"#"); //加“#”使无运算符时 可以正常输出当前结果 text.setText("");//清空文本 text.append(String.valueOf(x)); //输入结果 }catch(Exception cw){ //运算过程可能会出错(需要捕捉错误) if(cw.getMessage()==null) { text.setText("计算错误!"); } else text.setText(cw.getMessage()); } }); 2.3运算功能设计
计算功能设置,通过获取文本区的字符串作为运算符,当按下等号后进行运算。主要分为提取数据、运算、输入输出三个部分,通过栈(osValue)存储操作数和栈(oschar)存储操作符,通过哈希表(HashMap<String, Integer> operator)存储运算符的优先级,进行运算。
实现原理(利用栈的先入后出实现运算的优先级设置):
每当遇到非数字字符时入栈,若为括号或者#则只有操作符入栈,否则操作数和操作符都入栈,当当前插入操作符优先级小于等于栈顶
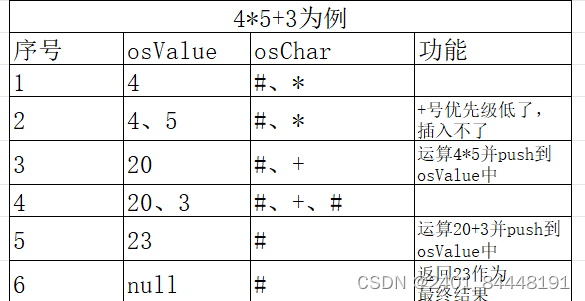 4*5+3的运算原理(一般的运算)
4*5+3的运算原理(一般的运算) 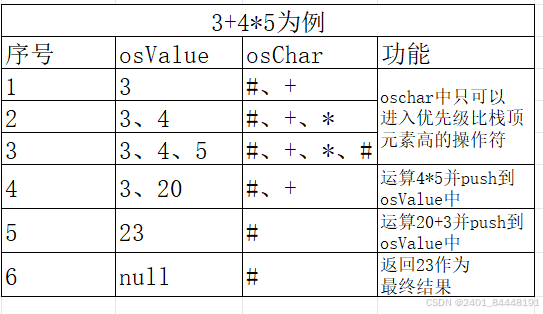 3+4*5的运算原理(带优先级的运算)
3+4*5的运算原理(带优先级的运算) 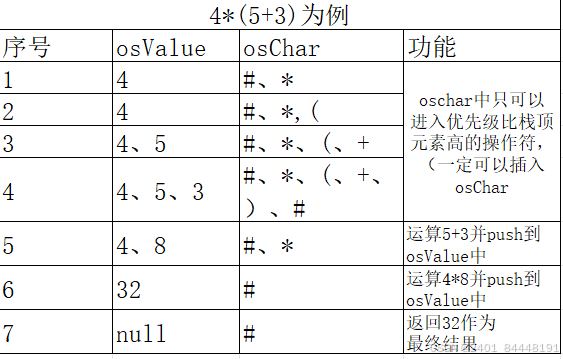 4*(5+3)的运算原理(带括号的运算)
4*(5+3)的运算原理(带括号的运算) (1)进行一般运算
将一次简单的运算和push功能封装在方法calculate()中。假定数据以正常放入栈中(以完成数据处理),直接获取osValue栈顶两个元素作为操作数,和osChar栈顶一个元素作为操作符,实现运算,并将计算结果push到osValue作为最终结果或者下一次运算的操作数。
static private Stack<Double> osValue = new Stack<>(); // 值 表操作数static private Stack<String> osChar = new Stack<>(); // 运算符static private void calculate(){ String b = osChar.pop(); double c = osValue.pop(); double d = osValue.pop(); double e; //结果 if (b.equals("+")) { e=d+c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("-")) { e=d-c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("*")) { e=d*c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("/")) { if(c==0) throw new ArithmeticException("除0错误!"); e=d/c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("%")) { if(c==0) throw new ArithmeticException("除0错误!"); else{ int c1=(int)c; int d1=(int)d;//化为整数 整数才能求余 if(c1==c&&d1==d){ e=d1%c1; osValue.push(e); } else throw new ArithmeticException("浮点数不能进行求余运算!"); } } else if(b.equals("^")){ int c1=(int)c; if(c1==c){ e=Math.pow(d, c); osValue.push(e); } else throw new ArithmeticException("幂方不能为浮点数!"); } else if(b.equals("e")){//科学计数法 int c1=(int)c; if(c1==c){ e=d*Math.pow(10,c1); osValue.push(e); } } }(2)提取数据和优先级设置
1.数据预处理:遍历字符串,当字符不是数字或小数点时(圆括号需要另算),可以截取一个操作数(字符串形式)和一个操作符。
2.优先级设置:将操作数转为Double类型推入osValue栈中,将操作符推入osChar中,为实现优先级声明,利用哈希表(HashMap<String, Integer> operator)实现操作符和优先级的映射关系。操作符推入规则:优先级为0,一定可以推入,优先级不为0,大于当前osChar栈顶元素优先级才可以插入。
static private Double calculate(String text){//数据处理、数据获取 HashMap<String, Integer> operator = new HashMap<>();//字典、映射关系 osValue.push(0.0); //设置一个操作数的初值为0 operator.put("(",0); operator.put(")",0); operator.put("e",2); operator.put("^",2); operator.put("/",2); operator.put("*",2); operator.put("%",2); operator.put("-",1); operator.put("+",1); operator.put("#",0); //设置优先级 osChar.push("#");//结束标记 int flag = 0;//记录操作数的头 int n = text.length(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { String a = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i)); //一个字符一个字符的进行查找 (导致只能使用单字符符号)不能用sin那些 if (!a.matches("[0-9.]")) {//当a不是数字或者.时 if(!operator.containsKey(a)) throw new ArithmeticException("计算式错误");//避免非法字符输入 if(i<n-1&& operator.get(a)>1){ String b = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i+1)); if(!b.matches("[0-9.]")&&operator.get(b)>0) throw new ArithmeticException("计算式错误"); } if(flag != i) { osValue.push(Double.parseDouble(text.substring(flag, i)));//将操作数推入osValue中 } flag = i + 1; while(!(a.equals("#") && osChar.peek().equals("#"))) { // peek 返回栈顶元素,不删除 (如果遍历到等号 以及 存放操作符号的栈也到#) if(operator.get(a) > operator.get(osChar.peek()) || a.equals("(")) { osChar.push(a); // 加入操作符 break; } else { if(a.equals(")")) { while(!osChar.peek().equals("(")) calculate(); osChar.pop(); break; } calculate(); } } } } return osValue.pop(); }(3)输出结果
根据上面两步,我们只需要调用calculate(text.getText())即可获得运算结果,但是运算结果该怎么输出?如何把功能添加到计算器中呢?
我们所设置 的方法是,当计算器的‘=’按钮被点击时进行计算,即在‘=’监听器中调用calculate(text.getText()+‘#’)获取运算结果清空文本区,再将结果转化为字符串类型,放入文本区中,实现调用与输出显示。
an[look_s(s, "=")].addActionListener(e->{ try{ System.out.println(text.getText());//输出text中的数 double x = calculate(text.getText()+"#"); //加“#”使无运算符时 可以正常输出当前结果 text.setText("");//清空文本 text.append(String.valueOf(x)); //输入结果 }catch(Exception cw){ //运算过程可能会出错(需要捕捉错误) if(cw.getMessage()==null) { text.setText("计算错误!"); } else text.setText(cw.getMessage()); } }); 2.4判错、处理异常:
根据以上代码我们可以发现其中有很多if判断语句去做 throw new ArithmeticException(),其目的是为了避免因为用户的非法输入导致程序异常,不对用户操作反应。以下是本程序支持的几种异常处理。
1.输入非法处理
当连续有两个操作符输入(除括号和等号)或者输入非键盘字符时运算式错误,对获取字符串进行判断,方法如下
//下列变量 text表示从文本区中获取的字符串for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { String a = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i)); //一个字符一个字符的进行查找 (导致只能使用单字符符号)不能用sin那些 if (!a.matches("[0-9.]")) {//当a不是数字或者.时 //情况1:当字符也不在操作字符的哈希表中 if(!operator.containsKey(a)) throw new ArithmeticException("计算式错误");//避免非法字符输入 //情况2:当字符串中有两个连续的操作符时 if(i<n-1&& operator.get(a)>1){ String b = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i+1)); if(!b.matches("[0-9.]")&&operator.get(b)>0) throw new ArithmeticException("计算式错误"); } }}2.运算异常处理
处理除法的除数不能为0以及求余时不能用浮点数进行运算的错误处理
(1).处理除法异常
if (b.equals("/")) { if(c==0) throw new ArithmeticException("除0错误!"); e=d/c; osValue.push(e); } (2).处理求余异常
//b表示osChar栈中pop出来的操作符//求余的异常处理 if (b.equals("%")) { if(c==0) //求余不能为0 throw new ArithmeticException("除0错误!"); else{ int c1=(int)c; int d1=(int)d; if(c1==c&&d1==d){//化为整数 整数才能求余 e=d1%c1; osValue.push(e); } else throw new ArithmeticException("浮点数不能进行求余运算!"); }}3.处理其他错误处理和异常的输出(可视化)
还有一些少见的错误,暂时想不到了,但是也不要忽略了,也应该对他们进行处理,实现如下
an[look_s(s, "=")].addActionListener(e->{ try{ System.out.println(text.getText());//输出text中的数 double x = calculate(text.getText()+"#"); //加“#”使无运算符时 可以正常输出当前结果 text.setText("");//清空文本 text.append(String.valueOf(x)); //输入结果 }catch(Exception cw){ //运算过程可能会出错(需要捕捉错误) if(cw.getMessage()==null) { text.setText("计算错误!"); } else text.setText(cw.getMessage()); } }); 3.代码展示
本次程序完整的代码,如下所示
import javax.swing.*;import java.awt.*;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Stack;/* *计算器 * 一个死板的,全部放主类中 */public class calculation_make extends JFrame {//进行数据运算 static private Stack<Double> osValue = new Stack<>(); // 值 表操作数 static private Stack<String> osChar = new Stack<>(); // 运算符 static public int R=255,B=255,G=255;//设置颜色 static private void calculate(){ String b = osChar.pop(); double c = osValue.pop(); double d = osValue.pop(); double e; //结果 if (b.equals("+")) { e=d+c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("-")) { e=d-c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("*")) { e=d*c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("/")) { if(c==0) throw new ArithmeticException("除0错误!"); e=d/c; osValue.push(e); } else if (b.equals("%")) { if(c==0) throw new ArithmeticException("除0错误!"); else{ int c1=(int)c; int d1=(int)d;//化为整数 整数才能求余 if(c1==c&&d1==d){ e=d1%c1; osValue.push(e); } else throw new ArithmeticException("浮点数不能进行求余运算!"); } } else if(b.equals("^")){ int c1=(int)c; if(c1==c){ e=Math.pow(d, c); osValue.push(e); } else throw new ArithmeticException("幂方不能为浮点数!"); } else if(b.equals("e")){//科学计数法 int c1=(int)c; if(c1==c){ e=d*Math.pow(10,c1); osValue.push(e); } } } static private Double calculate(String text){//数据处理、数据获取 HashMap<String, Integer> operator = new HashMap<>();//字典、映射关系 osValue.push(0.0); //设置一个操作数的初值为0 operator.put("(",0); operator.put(")",0); operator.put("e",2); operator.put("^",2); operator.put("/",2); operator.put("*",2); operator.put("%",2); operator.put("-",1); operator.put("+",1); operator.put("#",0); //设置优先级 osChar.push("#");//结束标记 int flag = 0;//记录操作数的头 int n = text.length(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { String a = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i)); //一个字符一个字符的进行查找 (导致只能使用单字符符号)不能用sin那些 if (!a.matches("[0-9.]")) {//当a不是数字或者.时 if(!operator.containsKey(a)) throw new ArithmeticException("计算式错误");//避免非法字符输入 if(i<n-1&& operator.get(a)>1){ String b = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i+1)); if(!b.matches("[0-9.]")&&operator.get(b)>0) throw new ArithmeticException("计算式错误"); } if(flag != i) { osValue.push(Double.parseDouble(text.substring(flag, i)));//将操作数推入osValue中 } flag = i + 1; while(!(a.equals("#") && osChar.peek().equals("#"))) { // peek 返回栈顶元素,不删除 (如果遍历到等号 以及 存放操作符号的栈也到#) if(operator.get(a) > operator.get(osChar.peek()) || a.equals("(")) { osChar.push(a); // 加入操作符 break; } else { if(a.equals(")")) { while(!osChar.peek().equals("(")) calculate(); osChar.pop(); break; } calculate(); } } } } return osValue.pop(); } calculation_make() { //使用重构的方法 构建计算器 JFrame f =new JFrame("my calulation(我的计算器)"); f.setSize(350,400); Font font = new Font("STCAIYUN", Font.PLAIN, 12); // 12是字体大小,可以根据需要调整 (字体名字可以去C:/Fonts中找到) font = font.deriveFont(font.getSize() * (float) 2.5);// 设置行高为1.5倍字体大小 (设置文字的一种格式) //板块1 菜单栏 JMenuBar menu=new JMenuBar(); //菜单条 JMenu jMenu0=new JMenu("设置"); JMenuItem tc=new JMenuItem("退出"); tc.addActionListener(e->{System.exit(0);}); //设置退出 jMenu0.add(tc); JMenuItem hf=new JMenuItem("恢复默认设置"); jMenu0.add(hf); menu.add(jMenu0); JMenu jMenu1=new JMenu("设置颜色"); JMenuItem item1=new JMenuItem("纸张模式"); JMenuItem item2=new JMenuItem("白天模式"); JMenuItem item3=new JMenuItem("夜晚模式"); jMenu1.add(item1); jMenu1.add(item2); jMenu1.add(item3); menu.add(jMenu1); JMenu jMenu2=new JMenu("设置字体"); JMenuItem Font1=new JMenuItem("字体1"); JMenuItem Font2=new JMenuItem("字体2"); JMenuItem Font3=new JMenuItem("字体3"); jMenu2.add(Font1); jMenu2.add(Font2); jMenu2.add(Font3); menu.add(jMenu2); f.setJMenuBar(menu); //板块2 文本框 JTextArea text=new JTextArea(100,10); text.setLineWrap(true); //相当于自动换行(取消横向方向的滚动条) text.setFont(font); text.setCaretPosition(text.getDocument().getLength()); JScrollPane m0 = new JScrollPane(text); //带滚动条的面板(JPanel) m0.setBounds(0,0,f.getWidth()-12, 100);//绝对地址+尺寸 (但好像xy的值不会影响成果) f.add(m0); //板块3 数字框 + 运算符 JPanel m1=new JPanel(); m1.setLayout(new GridLayout(0, 4)); //设置面板每列的按钮个数 (实现分层) String[] s={ "C","(",")","Del", "e","^","%","/", "7","8","9","*", "4","5","6","-", "1","2","3","+", "+/-","0",".","=" }; JButton[] an=new JButton[s.length]; for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++) { an[i]= new JButton(s[i]);// 宽度100像素, 高度50像素 an[i].setFont(font); m1.add(an[i]); } an[s.length-1].setBackground(Color.lightGray); f.getContentPane().add(m1,BorderLayout.SOUTH); //表方位,一定要加,否则会覆盖 //板块4 设置功能 for(int i=1;i<s.length-1;i++) //取消=的插入 {//用鼠标把数据放到text中 if(i==20 || i==3) continue; int j=i; an[i].addActionListener(e->text.append(s[j])); //必须用j=i来给text末尾加上数字 直接用i行不通 } //特殊功能按钮设置 an[look_s(s,"C")].addActionListener(e->{ text.setText("");//把文本框清空 osChar.clear(); osValue.clear();//把所有的东西都清空 }); //取相反数 an[look_s(s,"+/-")].addActionListener(e->{ String t1=text.getText(); if(t1.startsWith("-"))//表判断是不是以"-"开头 要和运算中的减号区分开 不然总是说运算出差 text.setText(text.getText().substring(1,text.getText().length()));//截取1到最后(去掉-号) else text.setText("-"+text.getText()); }); an[look_s(s, "Del")].addActionListener(e->{ try { text.setText(text.getText().substring(0,text.getText().length()-1)); } catch (Exception cw) { } }); an[look_s(s, "=")].addActionListener(e->{ try{ System.out.println(text.getText());//输出text中的数 double x = calculate(text.getText()+"#"); //加“#”使无运算符时 可以正常输出当前结果 text.setText("");//清空文本 text.append(String.valueOf(x)); //输入结果 }catch(Exception cw){ //运算过程可能会出错(需要捕捉错误) if(cw.getMessage()==null) { text.setText("计算错误!"); } else text.setText(cw.getMessage()); } }); /* 设置快捷键,但是没起效 KeyStroke clear_text = KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_C,InputEvent.CTRL_MASK);//设置一个快捷键(ctrl+c)清空text中的文字 text.getInputMap().put(clear_text, an[look_s(s, "C")]); */ //板块5 菜单功能设置 SetColor(m0,text,an,50); hf.addActionListener(e->{ R=G=B=255; SetColor(m0,text,an,50); SetFont(text, an,2); }); item1.addActionListener(e->{ R=240;G=230;B=140;//设置黄色 SetColor(m0,text,an,20); }); item2.addActionListener(e->{ R=G=B=255;//设置白色 SetColor(m0,text,an,50); }); item3.addActionListener(e->{ R=G=B=70;//夜间模式-->黑色 SetColor(m0,text,an,10); }); Font1.addActionListener(e->{ SetFont(text,an,0); }); Font2.addActionListener(e->{ SetFont(text,an,1); }); Font3.addActionListener(e->{ SetFont(text,an,2); }); //板块6 设置窗口属性(与可见) //f.pack();//显示已经有的,多的隐藏 (设置了会直接打开所有,没有小窗口) f.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE); //和窗口的布局有关 f.setVisible(true); } static public void SetColor(JScrollPane m,JTextArea a,JButton an[],int n){//颜色设置子函数 m.setBackground(new Color(R,G,B)); a.setBackground(new Color(R,G,B)); for (int i =0;i<an.length;i++){ if("="==an[i].getText()) an[i].setBackground(new Color(R-n,G-n,B-n)); else an[i].setBackground(new Color(R,G,B)); } } static public void SetFont(JTextArea a,JButton an[],int n){//字体设置子函数 String[] s={"STHUPO","STXINWEI","STCAIYUN"}; Font font = new Font(s[n], Font.PLAIN, 12); font = font.deriveFont(font.getSize() * (float) 2.5);// 设置行高为2.5倍字体大小 (设置文字的一种格式) a.setFont(font); for (int i =0;i<an.length;i++) { an[i].setFont(font); an[i].setSize(50,50); } } static public int look_s(String[] s,String s1){ int i=0; for(i=0;i<s.length;i++) { if(s[i].equals(s1)) return i; } return -1; } static public void main(String[] arg) { calculation_make a=new calculation_make(); } }4.参考文章
参考文章:【课程设计】Java 计算器实现(源码 + 详解)_java课程设计-CSDN博客