文章目录
1、简介2、安装3、基本测试3.1 入门代码3.2 组件属性3.3 多个输入和输出组件3.4 图像示例3.5 聊天机器人3.6 模块:更灵活、更可控3.7 进度条 结语
1、简介
https://www.gradio.app/
Gradio是用友好的网络界面演示机器学习模型的最快方法,因此任何人都可以在任何地方使用它!
Gradio与他人共享机器学习模型、API或数据科学工作流程的最佳方法之一是创建一个交互式应用程序,允许您的用户或同事在浏览器中尝试演示。
Gradio允许您构建演示并共享它们,所有这些都使用Python。通常只需几行代码!让我们开始吧。
使用gradio,只需在原有的代码中增加几行,就能自动化生成交互式web页面,并支持多种输入输出格式,比如图像分类中的图>>标签,超分辨率中的图>>图等。
2、安装
Gradio requires Python 3.8 or higher, that’s all!
pip install gradio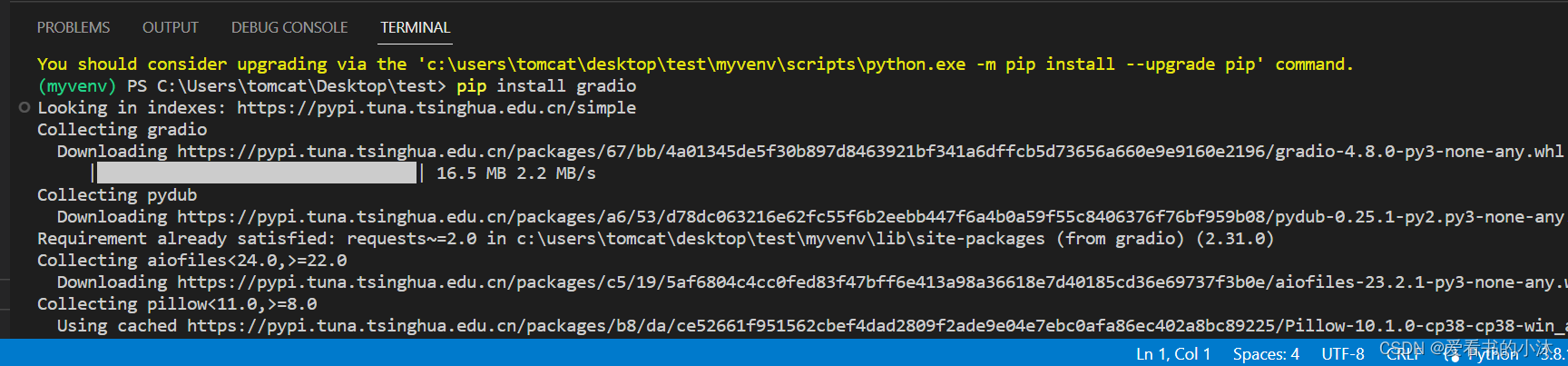
3、基本测试
3.1 入门代码
Run the code below as a Python script or in a Jupyter Notebook (or Google Colab):
import gradio as grdef greet(name): return "小沐: " + name + "!"demo = gr.Interface(fn=greet, inputs="text", outputs="text") if __name__ == "__main__": demo.launch(show_api=False) 浏览器访问:
http://127.0.0.1:7860/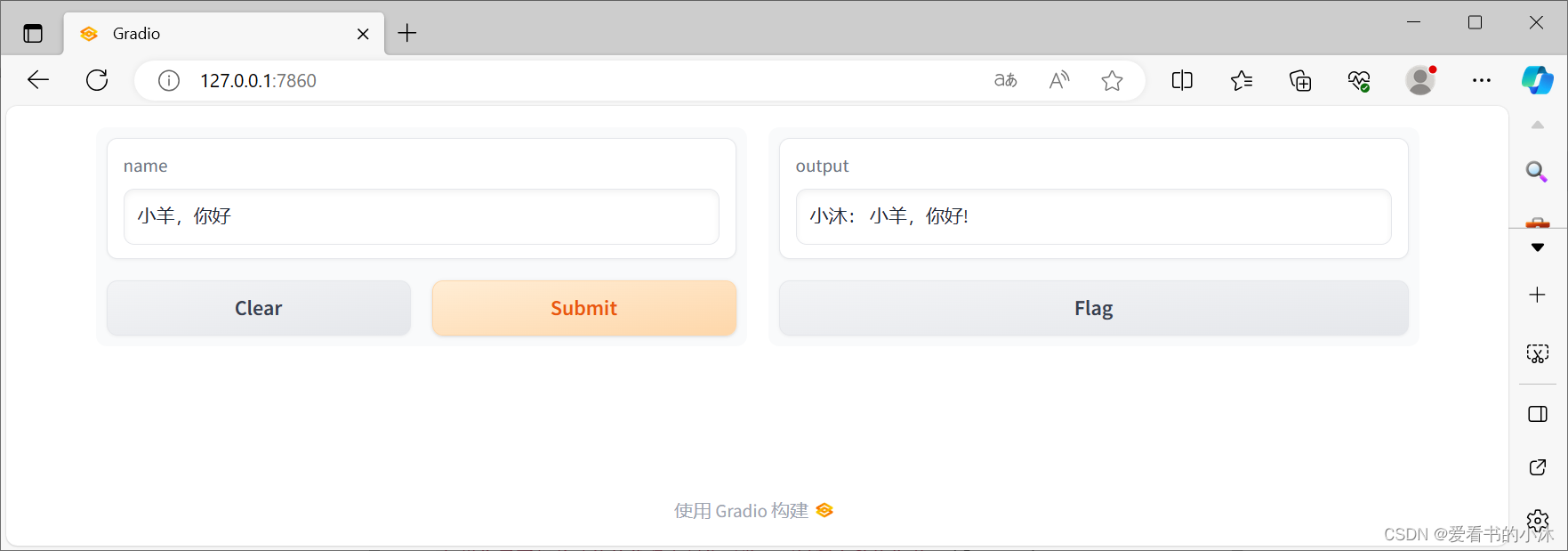
在本地开发时,如果要将代码作为 Python 脚本运行,可以使用 Gradio CLI 以重新加载模式启动应用程序,这将提供无缝和快速的开发。
gradio test.py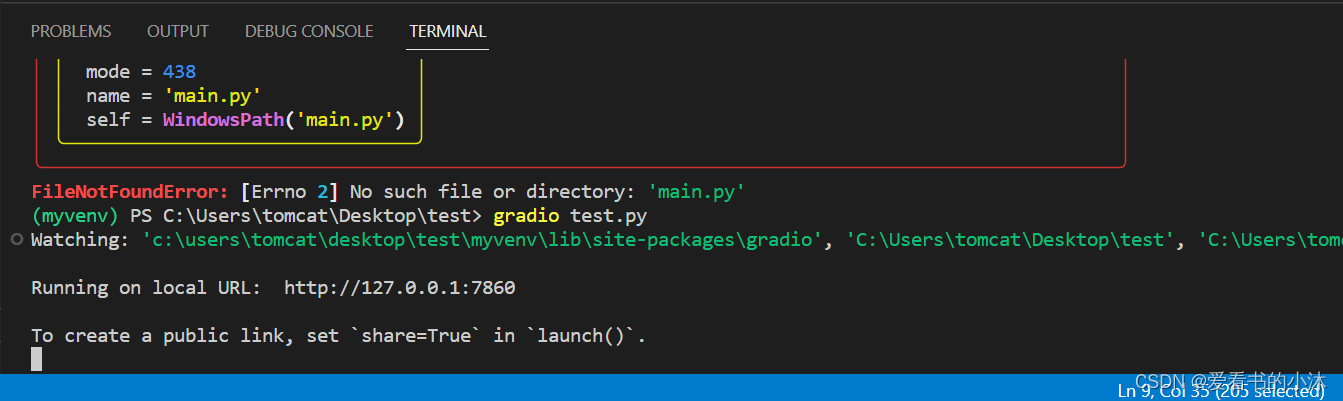
注意:你也可以这样做,但它不会提供自动重新加载机制。python test.py
3.2 组件属性
假设您要自定义输入文本字段,例如,您希望它更大并具有文本占位符。
import gradio as grdef greet(name): return "小沐: " + name + "!"demo = gr.Interface( fn=greet, inputs=gr.Textbox(lines=2, placeholder="Name Here..."), outputs="text",)demo.launch()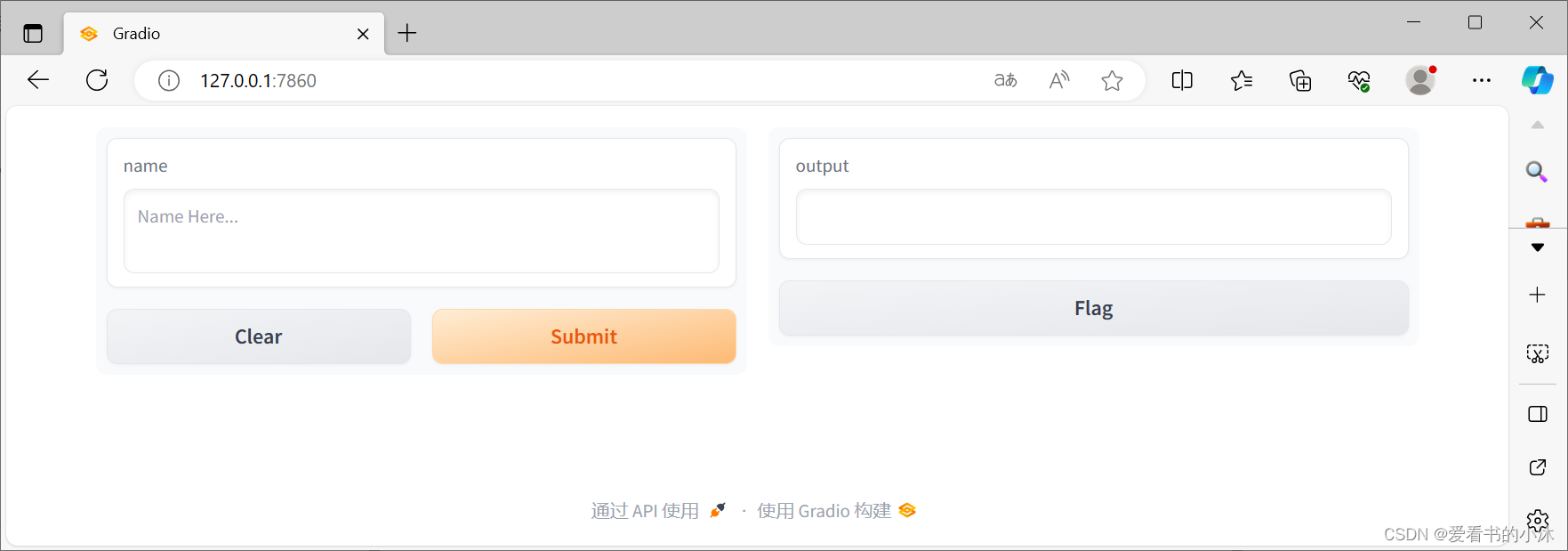
3.3 多个输入和输出组件
假设您有一个更复杂的函数,具有多个输入和输出。在下面的示例中,我们定义了一个函数,该函数接受字符串、布尔值和数字,并返回字符串和数字。看看如何传递输入和输出组件列表。
import gradio as grdef greet(name, is_morning, temperature): salutation = "Good morning" if is_morning else "Good evening" greeting = f"{salutation} {name}. It is {temperature} degrees today" celsius = (temperature - 32) * 5 / 9 return greeting, round(celsius, 2)demo = gr.Interface( fn=greet, inputs=["text", "checkbox", gr.Slider(0, 100)], outputs=["text", "number"],)demo.launch()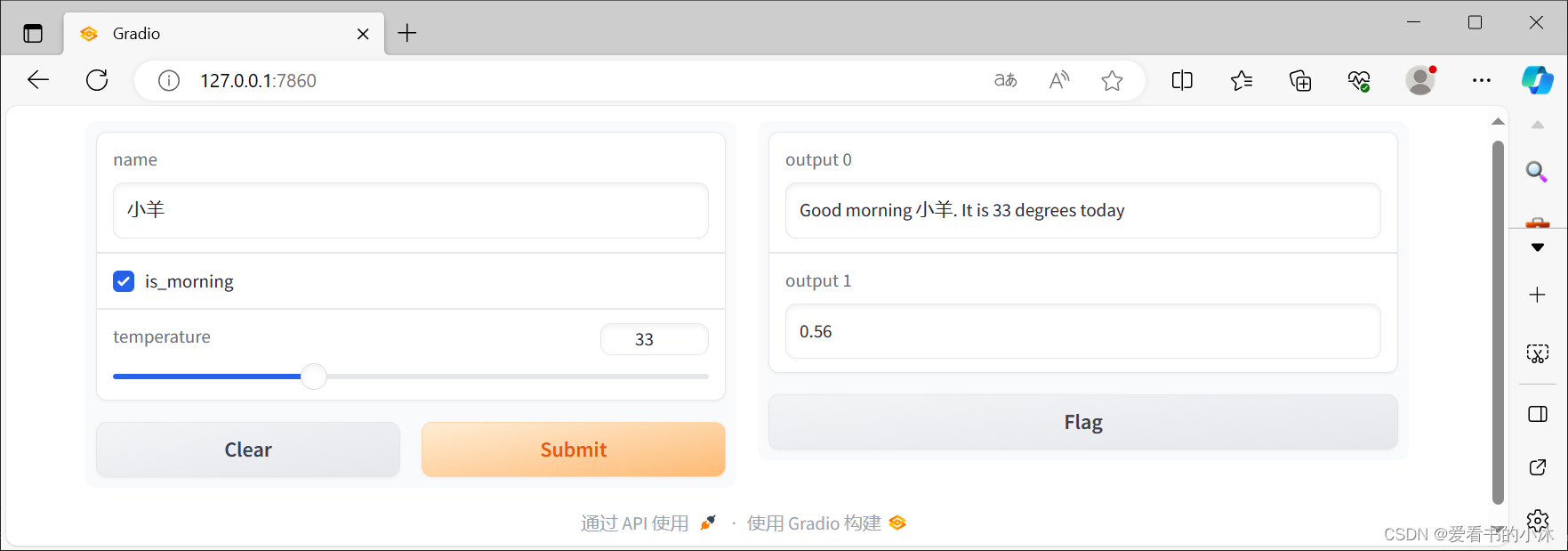
3.4 图像示例
Gradio 支持多种类型的组件,例如 、 、 或 。让我们尝试一个图像到图像功能来感受这些!
import numpy as npimport gradio as grdef sepia(input_img): sepia_filter = np.array([ [0.393, 0.769, 0.189], [0.349, 0.686, 0.168], [0.272, 0.534, 0.131] ]) sepia_img = input_img.dot(sepia_filter.T) sepia_img /= sepia_img.max() return sepia_imgdemo = gr.Interface(sepia, gr.Image(), "image")demo.launch()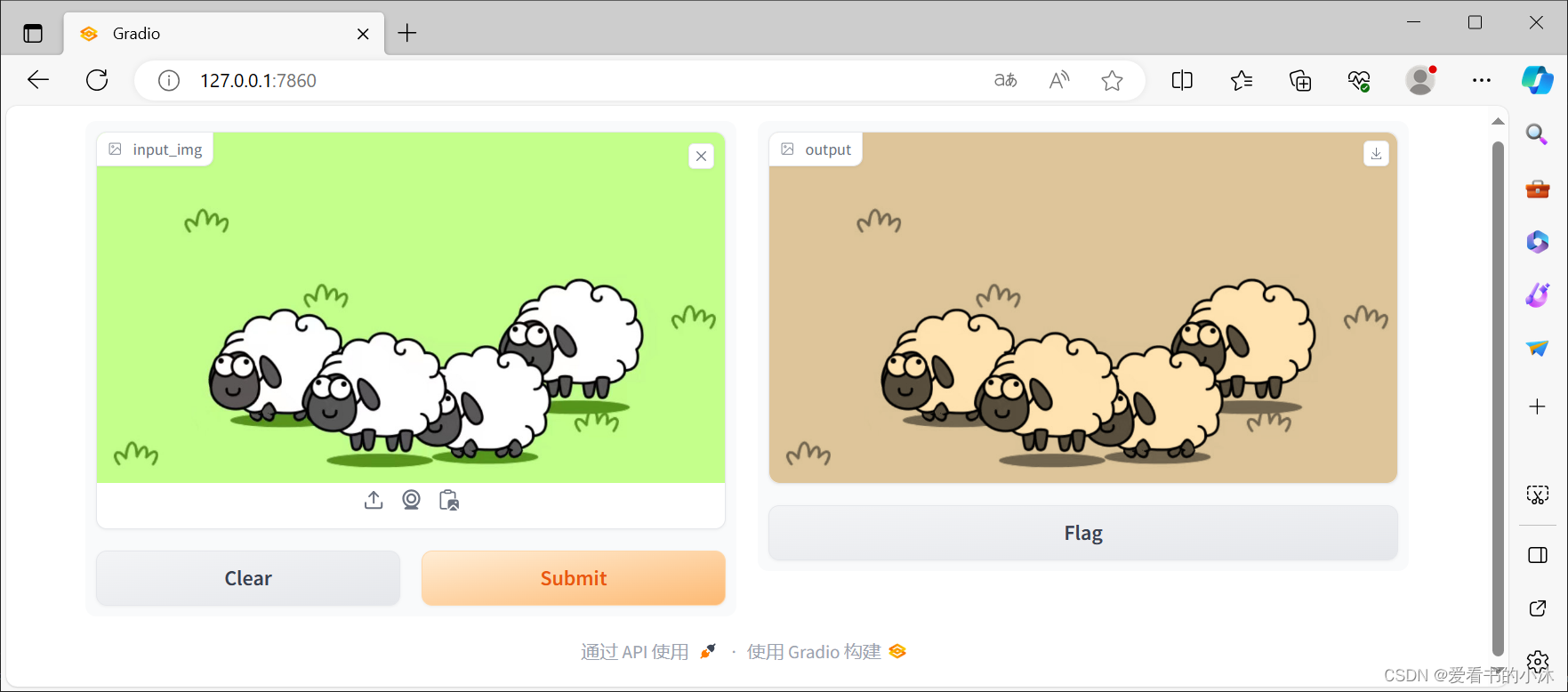
3.5 聊天机器人
Gradio 包含一个高级类,它类似于 ,但专为聊天机器人 UI 设计。该类还包装一个函数,但此函数必须具有特定的签名。该函数应该接受两个参数:然后(参数可以命名为任何名称,但必须按此顺序命名).
gr.ChatInterfacegr.Interfacegr.ChatInterfacemessagehistory:
message:a 表示用户的输入strhistory:a 表示在此之前的对话。每个内部列表由两个表示一对组成:。listliststr[user input, bot response]import randomimport gradio as grdef random_response(message, history): return random.choice(["Yes", "No"])demo = gr.ChatInterface(random_response)demo.launch()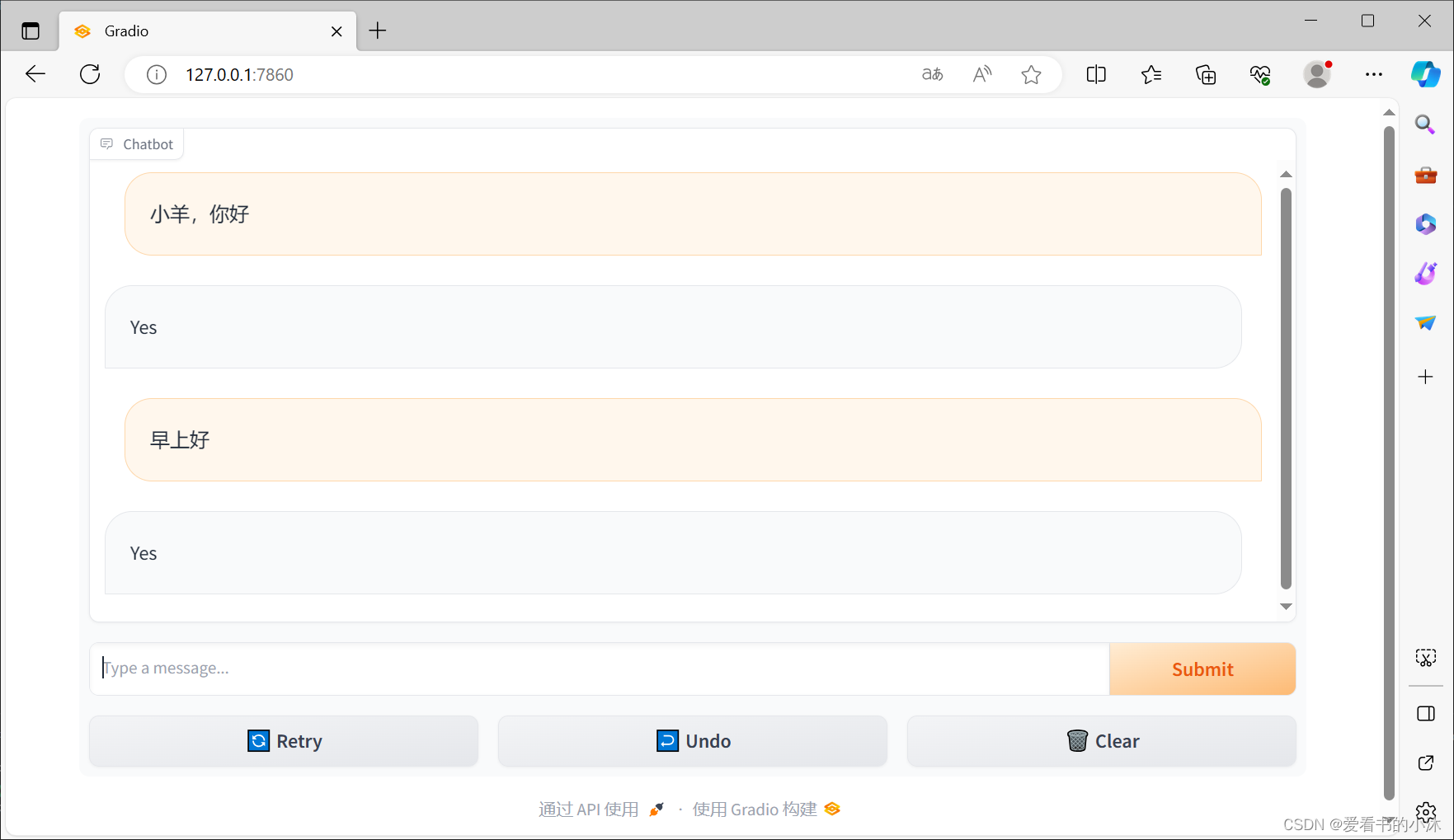
3.6 模块:更灵活、更可控
Gradio提供了两种构建应用程序的方法:
Interface 和 ChatInterface,它们为创建我们目前一直在讨论的演示提供了高级抽象。Blocks,一个低级 API,用于设计具有更灵活布局和数据流的 Web 应用程序。Blocks 允许您执行诸如具有多个数据流和演示、控制组件在页面上的显示位置、处理复杂的数据流(例如,输出可以作为其他函数的输入)以及基于用户交互更新组件的属性/可见性等操作——所有这些都在 Python 中。import gradio as grdef greet(name): return "Hello " + name + "!"with gr.Blocks() as demo: name = gr.Textbox(label="Name") output = gr.Textbox(label="Output Box") greet_btn = gr.Button("Greet") greet_btn.click(fn=greet, inputs=name, outputs=output, api_name="greet")demo.launch()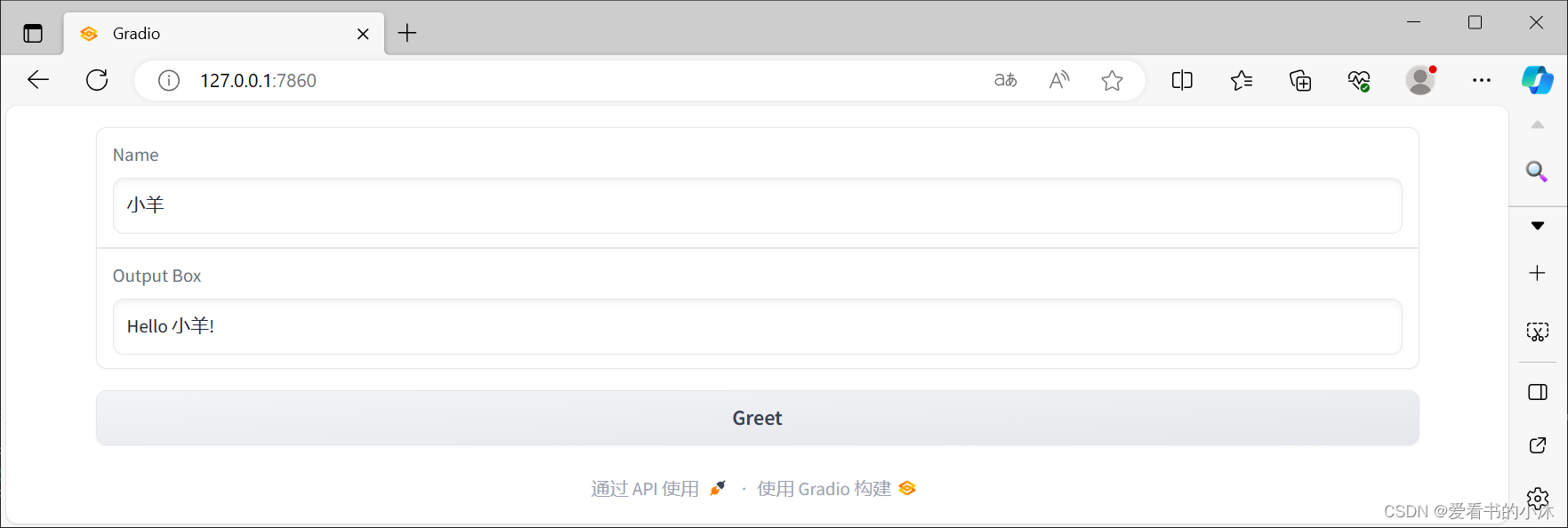
这里有一个应用程序,可以让你体验到什么是可能的:Blocks
import numpy as npimport gradio as grdef flip_text(x): return x[::-1]def flip_image(x): return np.fliplr(x)with gr.Blocks() as demo: gr.Markdown("Flip text or image files using this demo.") with gr.Tab("Flip Text"): text_input = gr.Textbox() text_output = gr.Textbox() text_button = gr.Button("Flip") with gr.Tab("Flip Image"): with gr.Row(): image_input = gr.Image() image_output = gr.Image() image_button = gr.Button("Flip") with gr.Accordion("Open for More!"): gr.Markdown("Look at me...") text_button.click(flip_text, inputs=text_input, outputs=text_output) image_button.click(flip_image, inputs=image_input, outputs=image_output)demo.launch()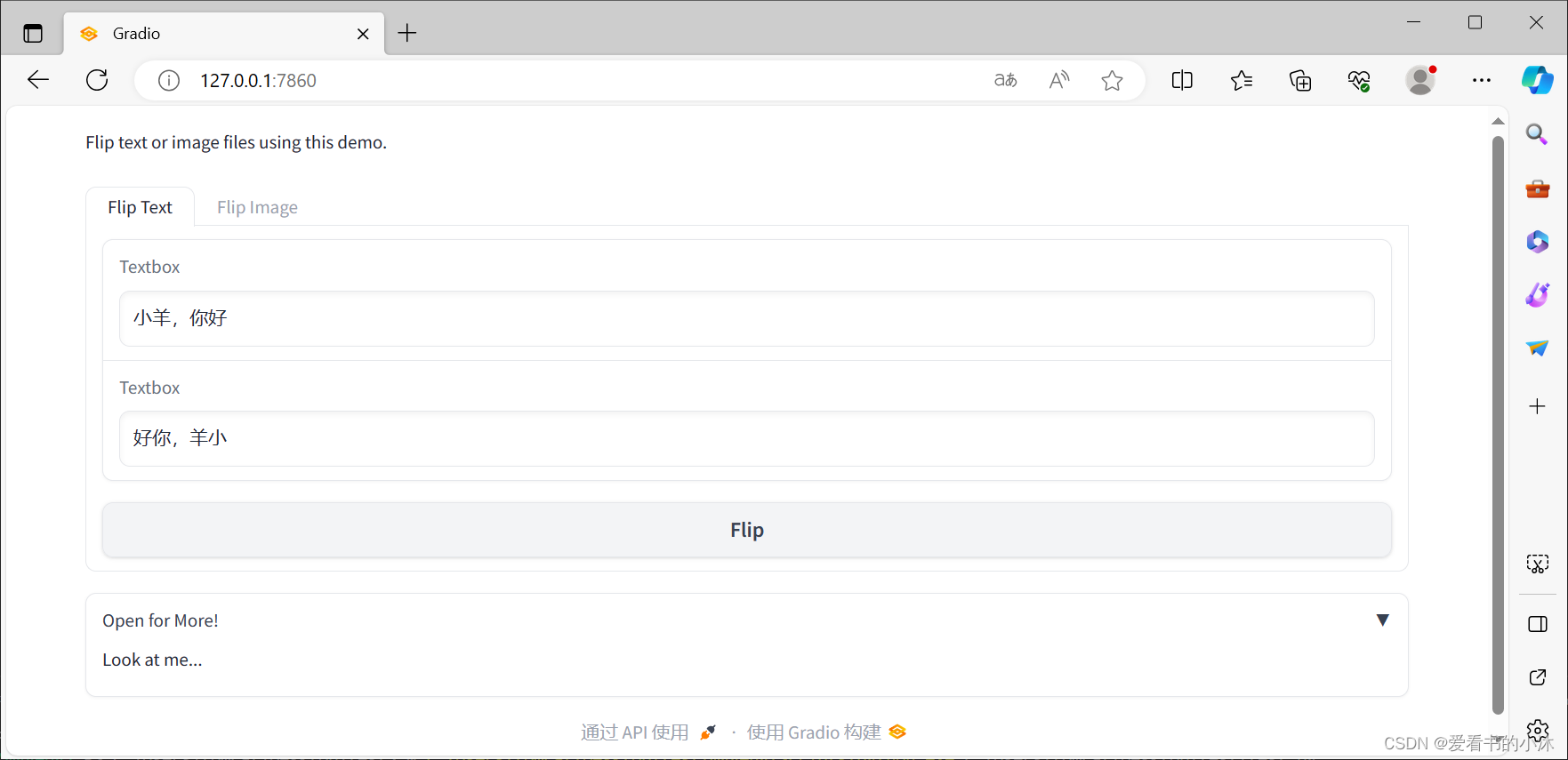
3.7 进度条
import gradio as grimport timedef slowly_reverse(word, progress=gr.Progress()): progress(0, desc="Starting") time.sleep(1) progress(0.05) new_string = "" for letter in progress.tqdm(word, desc="Reversing"): time.sleep(0.25) new_string = letter + new_string return new_stringdemo = gr.Interface(slowly_reverse, gr.Text(), gr.Text())demo.launch()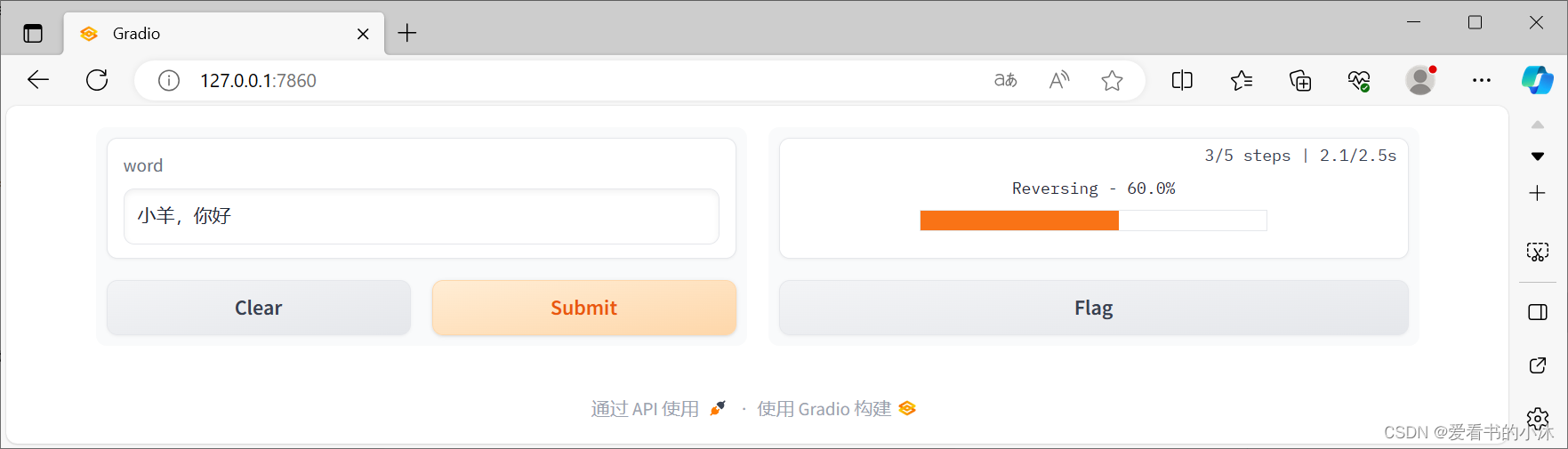
结语
如果您觉得该方法或代码有一点点用处,可以给作者点个赞,或打赏杯咖啡;╮( ̄▽ ̄)╭如果您感觉方法或代码不咋地//(ㄒoㄒ)//,就在评论处留言,作者继续改进;o_O???如果您需要相关功能的代码定制化开发,可以留言私信作者;(✿◡‿◡)感谢各位大佬童鞋们的支持!( ´ ▽´ )ノ ( ´ ▽´)っ!!!