提示1:参照本文,你可以快速搭建一个通讯交互实例,并完成一个项目演示用例。
提示2:如果你第一次来,请跳转到C#与西门子PLC通讯——新手快速入门了解背景信息。
关键词1:C#,.Net Core,S7 Net Plus,TIA Portal V17,PLCSIM Advanced V4,S7-1500。
关键词2:数据类型对照,DBX,DBB,DBW,DBD,面向对象编程,WinForm程序。
代码已同步至:
Gitee:https://gitee.com/lukailin/sim-s71500
Github:https://github.com/Millance/SimS71500
文章目录
前言一、PLC与C# 基础数据类型1.1 数据类型对照表1.2 C# 读写PLC数据1.2.1 Plc.Read方法源码浅析1.2.2 PLC 中增加数据类型1.2.3 C# 读取PLC中不同类型的数据1.2.4 读取的代码解析1.2.4.1 基本数据类型的读取方法1.2.4.2 大端存储和小端存储的问题1.2.4.3 C# 读取中文乱码的问题 1.2.5 C# 写入PLC中不同类型的数据1.2.6 写入的代码解析 二、自定义数据类型2.1 自定义数据类型的创建2.2 C#读写自定义数据类型2.3 C#面向对象的模式读写PLC的自定义数据类型 三、WinForm项目示例3.1 新建项目3.1.1 新建窗体项目3.1.2 项目中添加S7NetPlus NuGet包 3.2 PLC连接测试功能3.2.1 添加PLC连接用的控件3.2.2 创建一个单例模式的PLC控制对象3.2.3 窗体中的PLC控制类的调用 3.3 读写PLC指定地址功能3.3.1 继续添加控件3.3.2 增加读写反馈类3.3.3 PLC控制类中增加读写操作3.3.4 窗体功能中调用PLC控制类的读写操作 3.4 读写PLC自定义数据类型功能3.4.1 增加有立体效果的自定义控件3.4.2 继续添加其他控件3.4.3 添加自定义数据类型相应的对象3.4.5 窗体中自定义类的读写操作 3.5 最终运行效果 总结
前言
翌日,斯电气之士大喜,言已成通讯之试,访吾欲构一物。余默思片刻,书此以为之。
本文基于C# .Net Core和西门子博图TIA Portal V17搭建。由于手边没有西门子PLC实物,所以采用S7-PLCSIM Advanced V4.0作为模拟PLC,以实现0成本完成通讯测试实例。
在实际通讯中,往往需要先确定地址,数据类型和读写规则。因此本文将侧重分析数据类型的读写,以及处理读写过程中容易出现的问题,并且扩展了在交互过程中遇到陌生数据类型的处理方式。
最后本文以一个桌面小程序抛砖引玉,重点实现了熟手需要学习的面向对象编程、设计模式和界面设计。
一、PLC与C# 基础数据类型
1.1 数据类型对照表
这个对应关系主要取决于PLC与C#之间进行数据交换或通信时,确保数据的一致性和正确性。因此需要定义一种映射关系,以便在两个系统之间传递数据时能够正确地解释和处理数据。
常用的对照关系如下:
| PLC 数据类型 | C# 数据类型 | 字节数 |
|---|---|---|
| Bool | bool | 1/8 |
| Byte | byte | 1 |
| Char | char | 1 |
| Int | short | 2 |
| Word | ushort | 2 |
| DInt | int | 4 |
| DWord | uint | 4 |
| Real | float | 4 |
| LInt | long | 8 |
| LReal | double | 8 |
| LWord | ulong | 8 |
| String | string | 256 |
| Array[0…n] of Type | Type[n] | n × \times × Type |
不同数据类型在内存中占据不同的字节数。为了确保数据在两个系统之间传递时不会出现字节对齐、数据截断或者正负符号等问题,需要定义字节数对应关系。例如,一个PLC的Int类型在C#中被映射为short,因为它们都占据2个字节的内存空间。
Array[0…n] of Type中,需要根据Type的实际类型和数组长度n进行计算。
另外,其他的数据类型对照可以从字节数和有无符号的角度进行思考,字节数接近的可以进行尝试。
详细的PLC数据类型请参考西门子的在线帮助文档:基本数据类型以及char 和 string 的定义等。
或博图自带的帮助文档: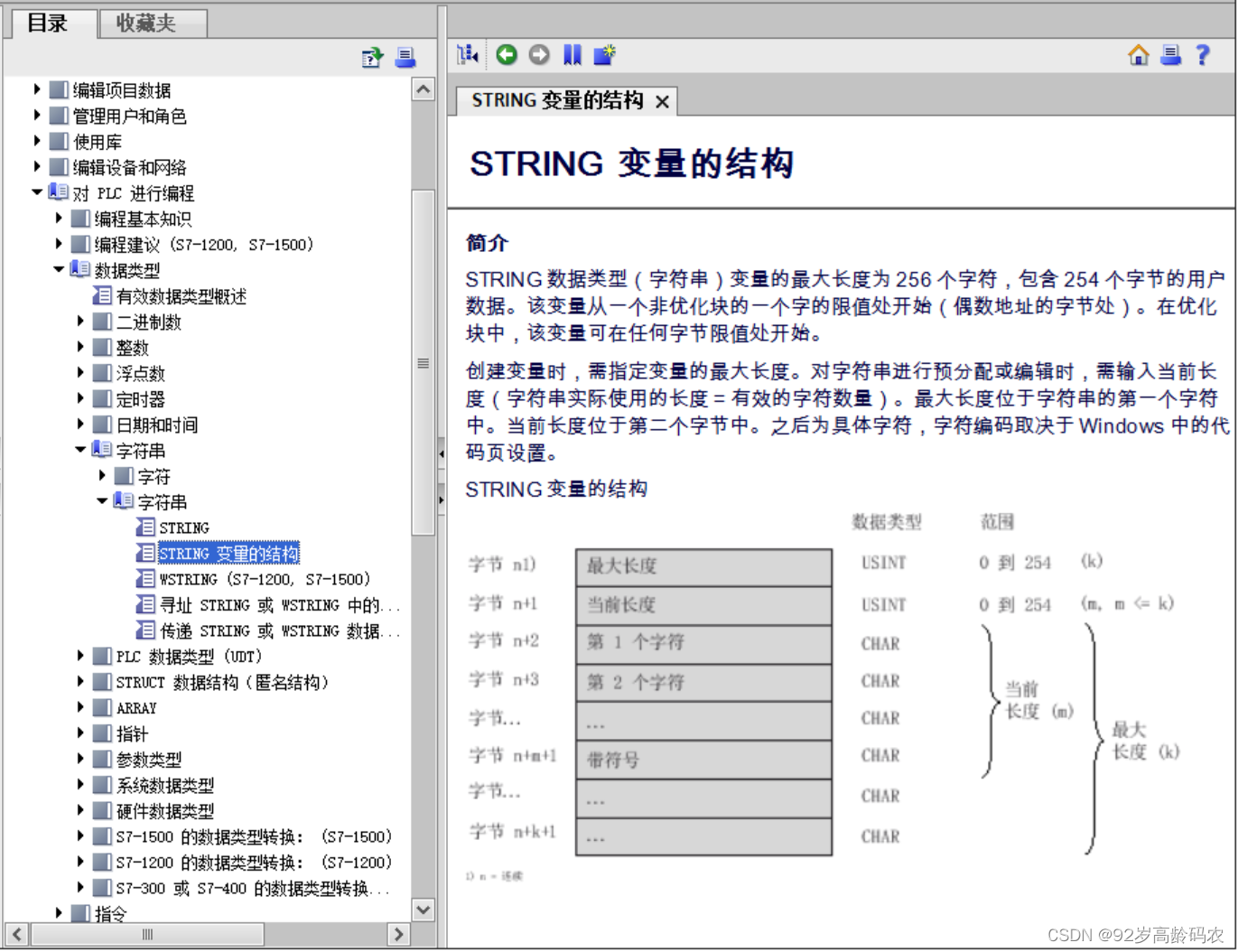
1.2 C# 读写PLC数据
1.2.1 Plc.Read方法源码浅析
先来扒一下S7 Net Plus源码。
调用plc.Read("DB1.DBX0.0")方法,会进行入下面的源码。
/// <summary>/// 从PLC读取单个变量,接受输入字符串如"DB1.DBX0.0","DB20.DBD200","MB20","T45"等。/// 如果读取不成功,请检查LastErrorCode或LastErrorString。/// </summary>/// <param name="variable">输入字符串如"DB1.DBX0.0","DB20.DBD200","MB20","T45"等。</param>/// <returns>返回包含值的对象。必须根据需要对该对象进行类型转换。如果没有读取到数据,将返回null。</returns>/// </summary>public object? Read(string variable){ var adr = new PLCAddress(variable); return Read(adr.DataType, adr.DbNumber, adr.StartByte, adr.VarType, 1, (byte)adr.BitNumber);}其中PLCAddress方法的代码如下:
namespace S7.Net{ internal class PLCAddress { ... public PLCAddress(string address) { Parse(address, out dataType, out dbNumber, out varType, out startByte, out bitNumber); } public static void Parse(string input, out DataType dataType, out int dbNumber, out VarType varType, out int address, out int bitNumber) { ... switch (input.Substring(0, 2)) { case "DB": string[] strings = input.Split(new char[] { '.' }); if (strings.Length < 2) throw new InvalidAddressException("To few periods for DB address"); dataType = DataType.DataBlock; dbNumber = int.Parse(strings[0].Substring(2)); address = int.Parse(strings[1].Substring(3)); string dbType = strings[1].Substring(0, 3); switch (dbType) { case "DBB": varType = VarType.Byte; return; case "DBW": varType = VarType.Word; return; case "DBD": varType = VarType.DWord; return; case "DBX": bitNumber = int.Parse(strings[2]); if (bitNumber > 7) throw new InvalidAddressException("Bit can only be 0-7"); varType = VarType.Bit; return; default: throw new InvalidAddressException(); } ... } } }}从PLCAddress的Parse方法可以看到,类似plc.Read("DB1.DBX0.0")、plc.Read("DB1.DBW2")这些读取指定地址的方法只能准确支持特定数据类型,如:Bit(DBX)、Byte(DBB)、Word(DBW)、DWord(DBD)。当数据类型的长度相同时,也可以支持相同长度的其他数据类型,但无法满足所有可能的情况。
Read方法还可以重载为:
/// <summary>/// 读取并解码提供的“VarType”指定字节数的数据。/// 可用于读取同一类型(如Word、DWord、Int等)的多个连续变量。/// 如果读取不成功,请检查LastErrorCode或LastErrorString。/// </summary>/// <param name="dataType">存储区域的数据类型,可以是DB、Timer、Counter、Merker(内存)、Input、Output。</param>/// <param name="db">存储区域的地址(如果要读取DB1,设置为1)。对于其他存储区域类型(计数器、定时器等),也必须设置此参数。</param>/// <param name="startByteAdr">起始字节地址。如果要读取DB1.DBW200,设置为200。</param>/// <param name="varType">要读取的变量类型</param>/// <param name="bitAdr">比特地址。如果要读取DB1.DBX200.6,将此参数设置为6。</param>/// <param name="varCount">变量的数量</param>/// </summary>/// <returns>返回包含值的对象。必须根据需要对该对象进行类型转换。</returns>public object? Read(DataType dataType, int db, int startByteAdr, VarType varType, int varCount, byte bitAdr = 0){ int cntBytes = VarTypeToByteLength(varType, varCount); byte[] bytes = ReadBytes(dataType, db, startByteAdr, cntBytes); return ParseBytes(varType, bytes, varCount, bitAdr);}同时,在public object? Read(string variable)中也可以看到,经过PLCAddress解析之后,也是调用的这个重载的Read方法。方法中的VarType可以选择众多类型,请自行探索。因此,一些无法用DBX、DBB、DBW和DBD进行读写的数据类型,可以用重载方法进行读写。
1.2.2 PLC 中增加数据类型
在博图软件中增加一些测试数据类型,如下: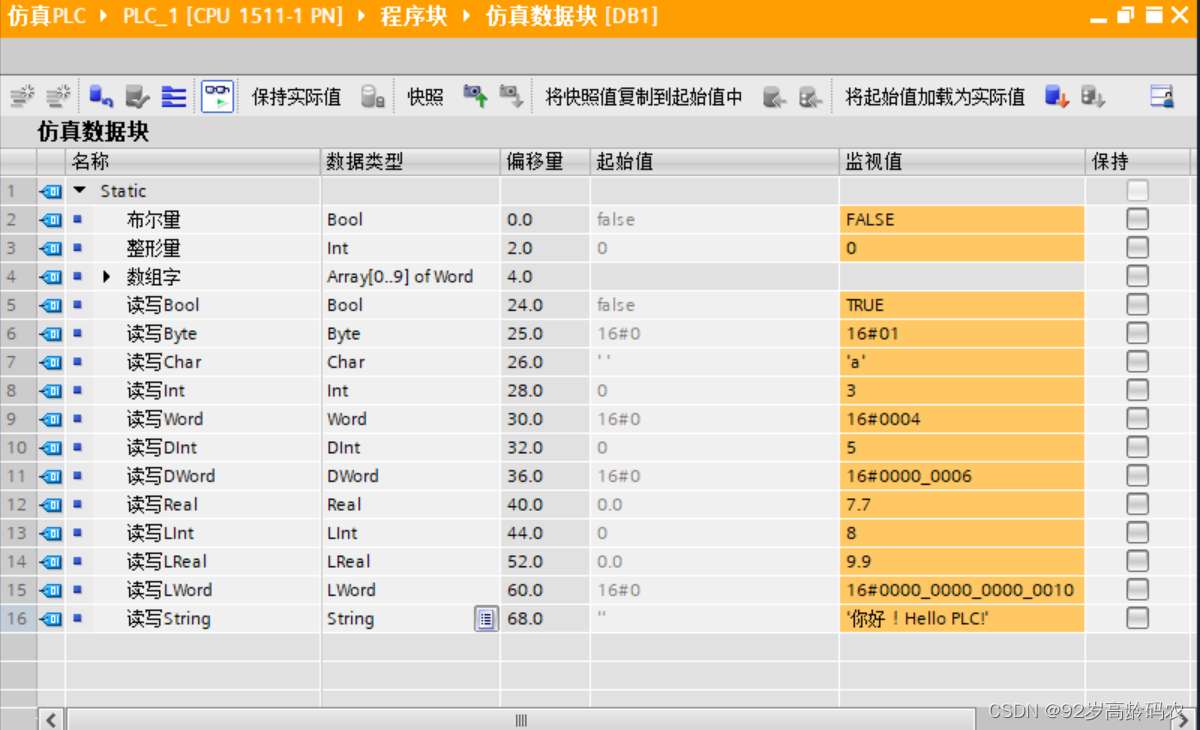
配置信息拷贝出来,方便参考:
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 偏移量 | 起始值 | 监视值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 布尔量 | Bool | 0.0 | false | FALSE |
| 整形量 | Int | 2.0 | 0 | 0 |
| 数组字 | Array[0…9] of Word | 4.0 | ||
| 读写Bool | Bool | 24.0 | false | TRUE |
| 读写Byte | Byte | 25.0 | 16#0 | 16#01 |
| 读写Char | Char | 26.0 | ’ ’ | ‘a’ |
| 读写Int | Int | 28.0 | 0 | 3 |
| 读写Word | Word | 30.0 | 16#0 | 16#0004 |
| 读写DInt | DInt | 32.0 | 0 | 5 |
| 读写DWord | DWord | 36.0 | 16#0 | 16#0000_0006 |
| 读写Real | Real | 40.0 | 0.0 | 7.7 |
| 读写LInt | LInt | 44.0 | 0 | 8 |
| 读写LReal | LReal | 52.0 | 0.0 | 9.9 |
| 读写LWord | LWord | 60.0 | 16#0 | 16#0000_0000_0000_0010 |
| 读写String | String | 68.0 | ‘’ | ‘你好!Hello PLC!’ |
这一步不会的,请跳转到C#与西门子PLC通讯——新手快速入门。
1.2.3 C# 读取PLC中不同类型的数据
我们继续改造新手入门的演示程序。
using S7.Net;using System.Text;namespace SimS71500{ internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 解决:“'GBK' is not a supported encoding name.”的方法 Encoding.RegisterProvider(CodePagesEncodingProvider.Instance); Plc plc = new Plc(CpuType.S71500, "192.168.0.100", 0, 1); plc.Open(); // 接收键入的值 string inputKey = ""; //存储区域的地址 int dbArea = 1; Task readPLCTask = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (plc.IsConnected && inputKey != "q") { Console.Clear(); // plc.Read 参数分别为数据块类型,数据块,偏移量,读取类型,读取长度 // 布尔量 Console.WriteLine("布尔量\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, VarType.Bit, 1)); // 整形量 Console.WriteLine("整形量\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 2, VarType.Int, 1)); // 数组字中的第一个元素 Console.WriteLine("数组字中的第一个元素\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, 1, 4, VarType.Word, 1)); // 数组字中的剩余元素 short[] remainArr = (short[])plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, 1, 6, VarType.Word, 9); Console.Write("数组字中的剩余元素\t"); for (int i = 0; i < remainArr.Length; i++) { Console.Write(remainArr[i] + "\t"); } Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("**************************************************************************************************"); // 读取Bool Console.WriteLine("读取Bool\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 24, VarType.Bit, 1)); // 读取Byte Console.WriteLine("读取Byte\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 25, VarType.Byte, 1)); // 读取Char Console.WriteLine("读取Char\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, VarType.String, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("读取Int \t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 28, VarType.Int, 1)); // 读取Word Console.WriteLine("读取Word\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 30, VarType.Word, 1)); // 读取DInt Console.WriteLine("读取DInt\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 32, VarType.DInt, 1)); // 读取DWord Console.WriteLine("读取DWord\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 36, VarType.DWord, 1)); // 读取Real Console.WriteLine("读取Real\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 40, VarType.Real, 1)); // 读取LInt byte[] dataLInt = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 44, 8); if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian) { Array.Reverse(dataLInt); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组 } Console.WriteLine("读取LInt\t" + BitConverter.ToInt64(dataLInt, 0)); // 读取LReal Console.WriteLine("读取LReal\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 52, VarType.LReal, 1)); // 读取LWord byte[] dataLWord = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 60, 8); if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian) { Array.Reverse(dataLWord); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组 } Console.WriteLine("读取LWord\t" + BitConverter.ToInt64(dataLWord, 0)); // 读取String byte[] dataS = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 68, 256); int stringLen = dataS[1]; string gbkString = Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetString(dataS, 2, stringLen); Console.WriteLine("读取String\t" + gbkString); Task.Delay(200).Wait(); } }); inputKey = Console.ReadLine(); plc.Close(); Task.WaitAll(readPLCTask); } }}下面是读取到的效果: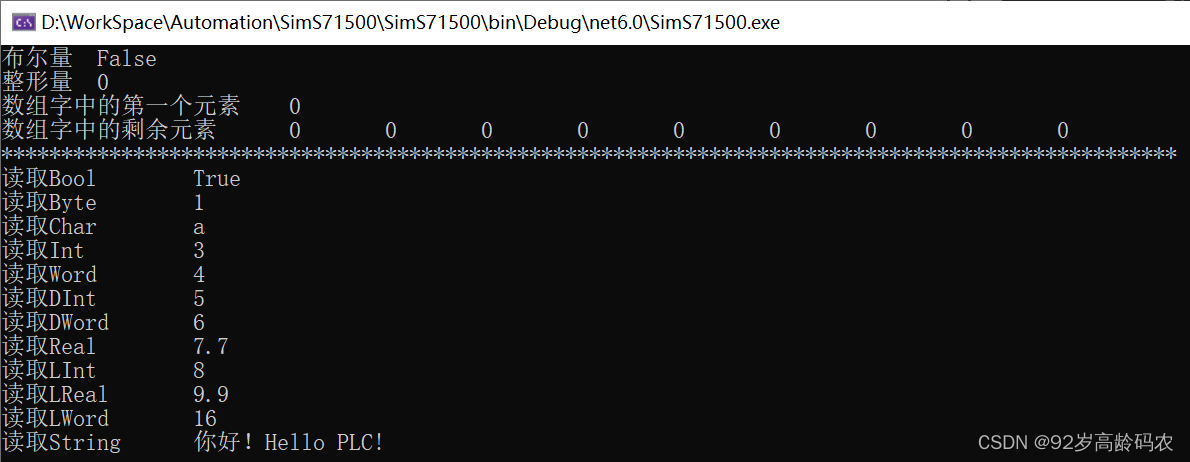
1.2.4 读取的代码解析
1.2.4.1 基本数据类型的读取方法
//存储区域的地址int dbArea = 1;plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, VarType.Bit, 1);其中,dbArea表示读取的数据块编号,即plc.Read("DB1.DBX0.0")中的DB1的1。VarType.Bit表示读取类型为Bit。
最后的1表示读取1个类型为VarType.Bit对应的长度。在比如:下面的9表示读取9个VarType.Word。
plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, 1, 6, VarType.Word, 9);1.2.4.2 大端存储和小端存储的问题
// 读取LIntbyte[] dataLInt = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 44, 8);if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian){ Array.Reverse(dataLInt); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组}Console.WriteLine("读取LInt\t" + BitConverter.ToInt64(dataLInt, 0));// 读取LWordbyte[] dataLWord = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 60, 8);if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian){ Array.Reverse(dataLWord); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组}Console.WriteLine("读取LWord\t" + BitConverter.ToInt64(dataLWord, 0));读取LInt和读取LWord比较特殊,VarType中没有对应的类型,因此需要手写byte[]转换方法。
同时,由于PLC采用大端存储,但是上位机一般采用小端存储,因此还需要反转一下byte数组。
1.2.4.3 C# 读取中文乱码的问题
Encoding.RegisterProvider(CodePagesEncodingProvider.Instance);解决:“System.ArgumentException:“‘GBK’ is not a supported encoding name. For information on defining a custom encoding, see the documentation for the Encoding.RegisterProvider method. Arg_ParamName_Name”” 的方法。
在Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetString()前任意位置执行即可。
它允许注册和使用其他字符编码提供程序,以便支持其他字符编码,例如 “GBK” 或 “GB2312”,这些编码不是.NET默认支持的。
一旦注册了字符编码提供程序,程序就可以使用所需的编码,例如 “GBK”,而不会遇到编码不支持的问题。这对于处理非标准字符编码的数据非常有用。
byte[] dataS = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 68, 256);int stringLen = dataS[1];string gbkString = Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetString(dataS, 2, stringLen);Console.WriteLine("读取String\t" + gbkString);其中,GetString(dataS, 2, stringLen)忽略前两个无法识别的字节。如果不使用2, stringLen这两个参数,则会在字符串前显示一个“?”。
具体解释参考西门子官方文档中关于string 在西门子 PLC 中的格式的解析。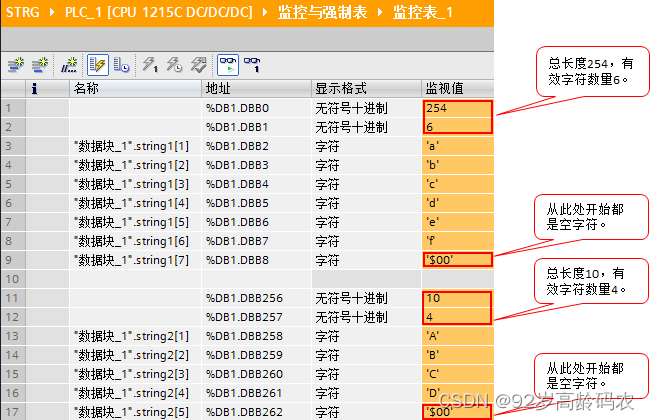
在我们的案例中,获取的byte数组为:
{254, 16, 196, 227, 186, 195, 163, 161, 72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 80, 76, 67, 33, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,…}
其中254表示String的长度,16表示字符数量(中文表示两个字符)。这两个字节是非文本数据或称为控制信息,而不是有效的字符数据。
因此,可以简化为直接从有效字符开始的偏移量读取中文,前提是要知道自己在干什么:
// 读取StringConsole.WriteLine("读取String\t" + Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetString(plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 70, 254)));1.2.5 C# 写入PLC中不同类型的数据
了解上面怎么读取的,那么写入的方法将非常易于理解:
using S7.Net;using System.Text;namespace SimS71500{ internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 解决:“'GBK' is not a supported encoding name.”的方法 Encoding.RegisterProvider(CodePagesEncodingProvider.Instance); Plc plc = new Plc(CpuType.S71500, "192.168.0.100", 0, 1); plc.Open(); // 接收键入的值 string inputKey = ""; bool boolFlag = false; short iCount = 1; //存储区域的地址 int dbArea = 1; Task readPLCTask = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (plc.IsConnected && inputKey != "q") { Console.Clear(); // plc.Read 参数分别为数据块类型,数据块,偏移量,读取类型,读取长度 // 布尔量 Console.WriteLine("布尔量\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, VarType.Bit, 1)); // 整形量 Console.WriteLine("整形量\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 2, VarType.Int, 1)); // 数组字中的第一个元素 Console.WriteLine("数组字中的第一个元素\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, 1, 4, VarType.Word, 1)); // 数组字中的剩余元素 short[] remainArr = (short[])plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, 1, 6, VarType.Word, 9); Console.Write("数组字中的剩余元素\t"); for (int i = 0; i < remainArr.Length; i++) { Console.Write(remainArr[i] + "\t"); } Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("**************************************************************************************************"); // 读取Bool Console.WriteLine("读取Bool\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 24, VarType.Bit, 1)); // 读取Byte Console.WriteLine("读取Byte\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 25, VarType.Byte, 1)); // 读取Char Console.WriteLine("读取Char\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, VarType.String, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("读取Int \t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 28, VarType.Int, 1)); // 读取Word Console.WriteLine("读取Word\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 30, VarType.Word, 1)); // 读取DInt Console.WriteLine("读取DInt\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 32, VarType.DInt, 1)); // 读取DWord Console.WriteLine("读取DWord\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 36, VarType.DWord, 1)); // 读取Real Console.WriteLine("读取Real\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 40, VarType.Real, 1)); // 读取LInt byte[] dataLInt = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 44, 8); if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian) { Array.Reverse(dataLInt); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组 } Console.WriteLine("读取LInt\t" + BitConverter.ToInt64(dataLInt, 0)); // 读取LReal Console.WriteLine("读取LReal\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 52, VarType.LReal, 1)); // 读取LWord byte[] dataLWord = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 60, 8); if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian) { Array.Reverse(dataLWord); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组 } Console.WriteLine("读取LWord\t" + BitConverter.ToInt64(dataLWord, 0)); // 读取String byte[] dataS = plc.ReadBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 68, 256); int stringLen = dataS[1]; string gbkString = Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetString(dataS, 2, stringLen); Console.WriteLine("读取String\t" + gbkString); Task.Delay(200).Wait(); } }); Random random = new Random(); Task writePLCTask = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (plc.IsConnected && inputKey != "q") { // 布尔量 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, boolFlag);//false表示写入的值 // 整形量 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 2, iCount); // 数组字中的第一个元素 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 4, (short)(iCount * 2)); // 数组字中的剩余元素 short[] arrValues = new short[9]; // 你要写入的新值数组 for (int i = 0; i < arrValues.Length; i++) { arrValues[i] = (short)(iCount * 2 + 1 + i); } plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 6, arrValues); // 写入Bool plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 24, boolFlag); // 写入Byte plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 25, (byte)(iCount + 2)); // 写入Char plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, ((char)random.Next(97, 123)).ToString()); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 28, (short)(iCount + 4)); // 写入Word plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 30, (ushort)(iCount + 5)); // 写入DInt plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 32, iCount + 6); // 写入DWord plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 36, iCount + 7); // 写入Real plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 40, (float)(random.NextDouble() * 10)); // 写入LInt // 生成两32位整数并合并为一个long long randomLInt = ((long)random.Next(int.MinValue, int.MaxValue) << 32) | (uint)random.Next(int.MinValue, int.MaxValue); byte[] dataLInt = BitConverter.GetBytes(randomLInt); if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian) { Array.Reverse(dataLInt); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组 } plc.WriteBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 44, dataLInt); // 写入LReal plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 52, random.NextDouble() * 100); // 写入LWord // 生成两32位整数并合并为一个long long randomLWord = ((long)random.Next(int.MinValue, int.MaxValue) << 32) | (uint)random.Next(int.MinValue, int.MaxValue); byte[] dataLWord = BitConverter.GetBytes(randomLWord); if (BitConverter.IsLittleEndian) { Array.Reverse(dataLWord); // 如果系统是小端序(Little Endian),需要反转字节数组 } plc.WriteBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 60, dataLWord); // 写入String string chineseString = boolFlag ? "你好!Hello PLC!" : "Hello PLC!"; // 编码为字节数组 byte[] chineseBytes = Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetBytes(chineseString); // 构建带控制信息的字节数组 byte[] dataString = new byte[chineseBytes.Length + 2]; // 加2是为了存储控制信息 // 添加控制信息 dataString[0] = 254; // 第一个字节固定为254 dataString[1] = (byte)(chineseBytes.Length); // 第二个字节表示字符长度 // 复制字符串数据到字节数组 Array.Copy(chineseBytes, 0, dataString, 2, chineseBytes.Length); // 将字节数组写入PLC plc.WriteBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 68, dataString); iCount++; boolFlag = !boolFlag; Task.Delay(200).Wait(); } }); inputKey = Console.ReadLine(); plc.Close(); Task.WaitAll(readPLCTask, writePLCTask); } }}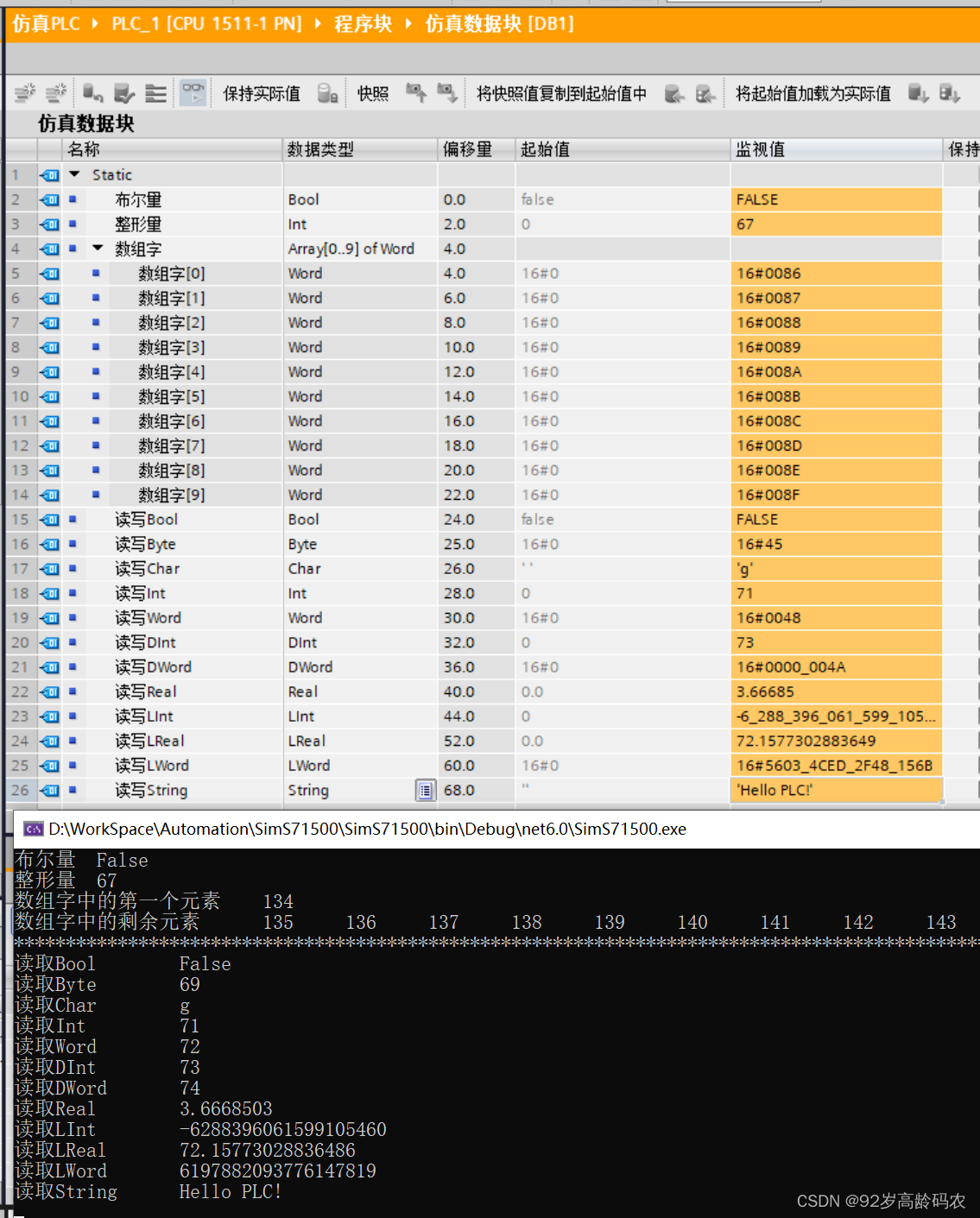
1.2.6 写入的代码解析
其中字符串的处理较为麻烦,需要在字符串字节数组前增加两个控制信息。
// 写入Stringstring chineseString = boolFlag ? "你好!Hello PLC!" : "Hello PLC!";// 编码为字节数组byte[] chineseBytes = Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetBytes(chineseString);// 构建带控制信息的字节数组byte[] dataString = new byte[chineseBytes.Length + 2]; // 加2是为了存储控制信息// 添加控制信息dataString[0] = 254; // 第一个字节固定为254dataString[1] = (byte)(chineseBytes.Length); // 第二个字节表示字符长度// 复制字符串数据到字节数组Array.Copy(chineseBytes, 0, dataString, 2, chineseBytes.Length);// 将字节数组写入PLCplc.WriteBytes(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 68, dataString);二、自定义数据类型
2.1 自定义数据类型的创建
一些厉害的电气工程师还会增加自定义的数据类型,以下是随意写的示例,不当之处欢迎批评。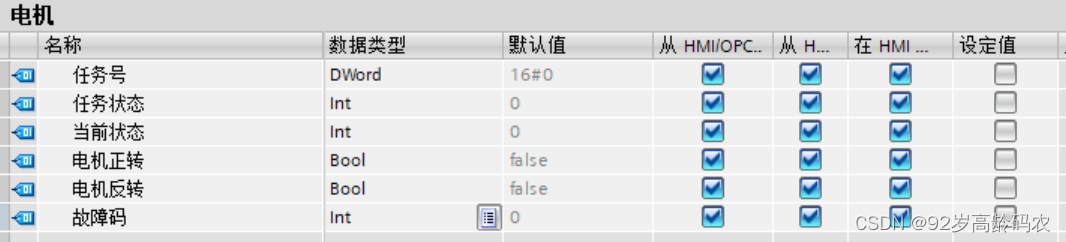
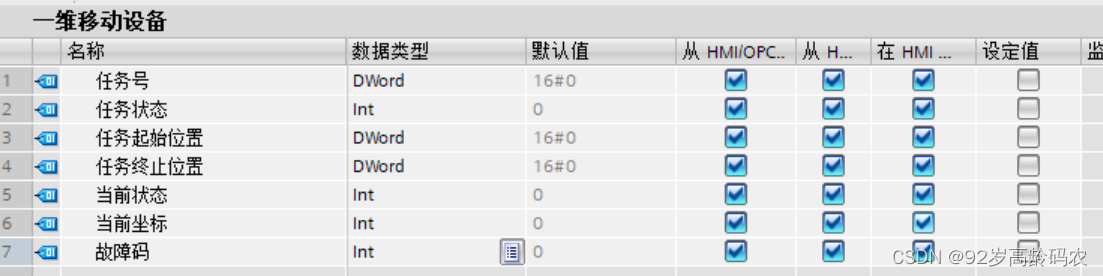
将两个自定义的数据类型加入到新的DB块中。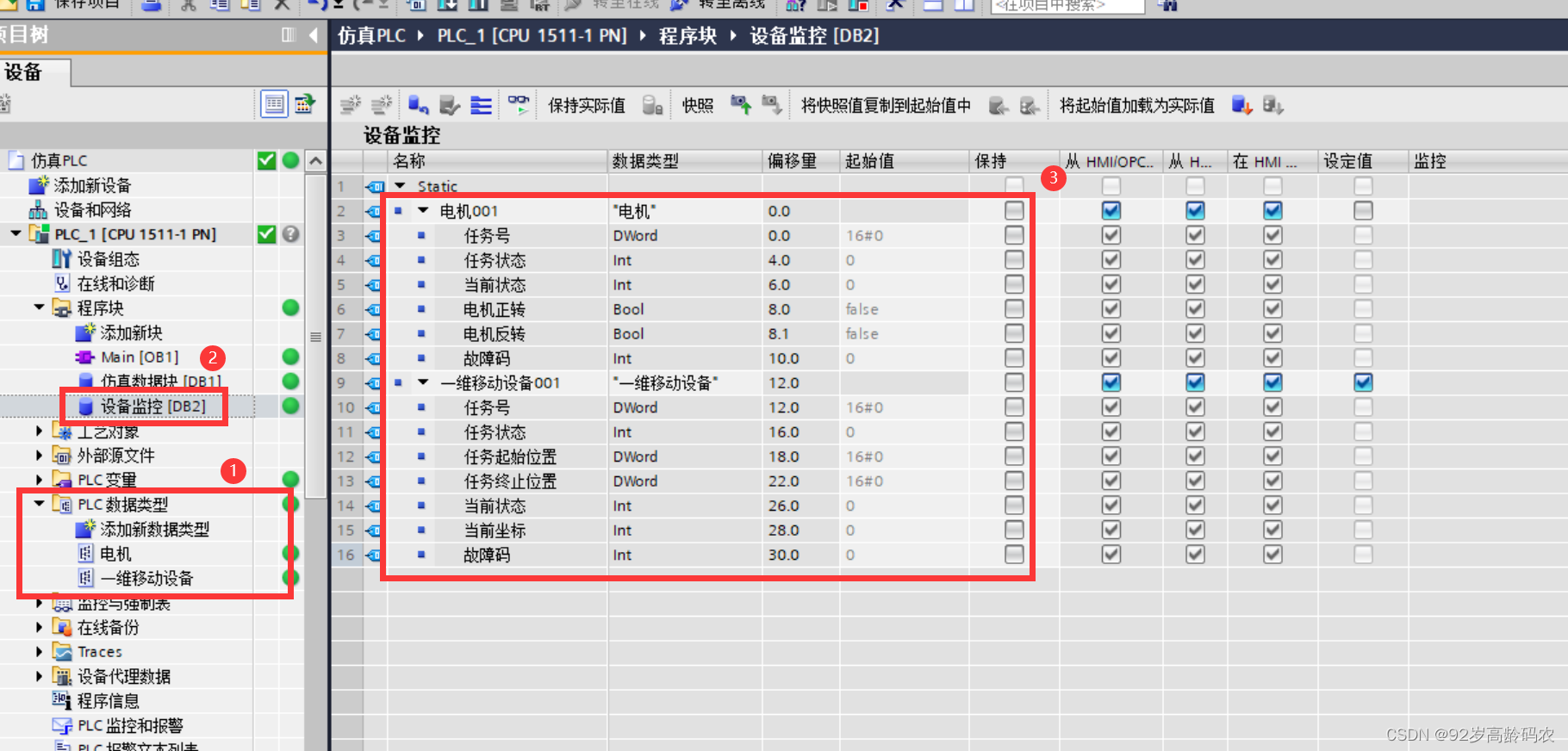
配置信息拷贝出来,方便参考:
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 偏移量 | 起始值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 电机001 | 电机 | 0 | |
| 任务号 | DWord | 0 | 16#0 |
| 任务状态 | Int | 4 | 0 |
| 当前状态 | Int | 6 | 0 |
| 电机正转 | Bool | 8 | FALSE |
| 电机反转 | Bool | 8.1 | FALSE |
| 故障码 | Int | 10 | 0 |
| 一维移动设备001 | 一维移动设备 | 12 | |
| 任务号 | DWord | 12 | 16#0 |
| 任务状态 | Int | 16 | 0 |
| 任务起始位置 | DWord | 18 | 16#0 |
| 任务终止位置 | DWord | 22 | 16#0 |
| 当前状态 | Int | 26 | 0 |
| 当前坐标 | Int | 28 | 0 |
| 故障码 | Int | 30 | 0 |
2.2 C#读写自定义数据类型
如果看懂了第一章的内容,这个地方看似简单,实则不难,直接贴代码:
using S7.Net;namespace SimS71500{ internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Plc plc = new Plc(CpuType.S71500, "192.168.0.100", 0, 1); plc.Open(); // 接收键入的值 string inputKey = ""; bool boolFlag = false; short iCount = 1; //存储区域的地址 int dbArea = 2; Task readPLCTask = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (plc.IsConnected && inputKey != "q") { Console.Clear(); // plc.Read 参数分别为数据块类型,数据块,偏移量,读取类型,读取长度 Console.WriteLine("*********************电机001*********************"); // 读取DWord Console.WriteLine("电机001-任务号 \t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, VarType.DWord, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("电机001-任务状态\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 4, VarType.Int, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("电机001-当前状态\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 6, VarType.Int, 1)); // 读取Bool Console.WriteLine("电机001-电机正转\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, VarType.Bit, 1)); // 读取Bool Console.WriteLine("电机001-电机反转\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, VarType.Bit, 1, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("电机001-故障码 \t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 10, VarType.Int, 1)); Console.WriteLine("****************一维移动设备001******************"); // 读取DWord Console.WriteLine("移动设备001-任务号 \t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 12, VarType.DWord, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("移动设备001-任务状态\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 16, VarType.Int, 1)); // 读取DWord Console.WriteLine("移动设备001-起始位置\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 18, VarType.DWord, 1)); // 读取DWord Console.WriteLine("移动设备001-终止位置\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 22, VarType.DWord, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("移动设备001-当前状态\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, VarType.Int, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("移动设备001-当前坐标\t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 28, VarType.Int, 1)); // 读取Int Console.WriteLine("移动设备001-故障码 \t" + plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 30, VarType.Int, 1)); Task.Delay(200).Wait(); } }); Task writePLCTask = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (plc.IsConnected && inputKey != "q") { // 写入DWord plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, iCount + 1); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 4, (short)(iCount + 2)); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 6, (short)(iCount + 3)); // 写入Bool plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, boolFlag); // 写入Bool plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, !boolFlag, 1); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 10, (short)(iCount + 4)); // 写入DWord plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 12, iCount + 5); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 16, (short)(iCount + 6)); // 写入DWord plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 18, iCount + 7); // 写入DWord plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 22, iCount + 8); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, (short)(iCount + 9)); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 28, (short)(iCount + 10)); // 写入Int plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 30, (short)(iCount + 11)); iCount++; boolFlag = !boolFlag; Task.Delay(200).Wait(); } }); inputKey = Console.ReadLine(); plc.Close(); Task.WaitAll(readPLCTask, writePLCTask); } }}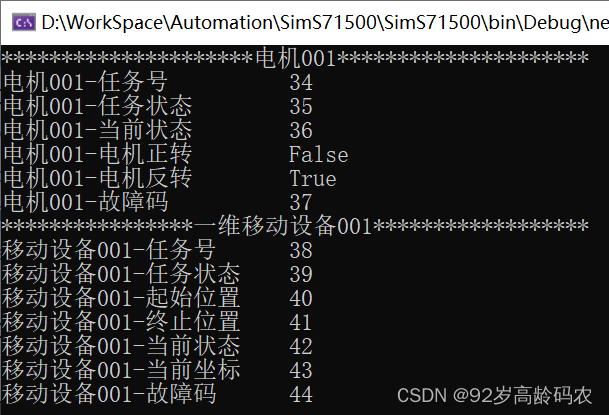
别忘了修改存储区域的地址!
//存储区域的地址int dbArea = 2;2.3 C#面向对象的模式读写PLC的自定义数据类型
现在学到了“一”是一横,“二”是二横,“三”是三横。请问“四”是亖横吗?
那么来挑战一下“四”怎么写。
using S7.Net;namespace SimS71500{ internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Plc plc = new Plc(CpuType.S71500, "192.168.0.100", 0, 1); plc.Open(); // 接收键入的值 string inputKey = ""; int dbArea = 2; Motor motor = new Motor("电机001", plc, dbArea); MobileDevice mobileDevice = new MobileDevice("一维移动设备001", plc, dbArea); // 使用 AutoResetEvent 进行任务协调 AutoResetEvent readComplete = new AutoResetEvent(false); AutoResetEvent writeComplete = new AutoResetEvent(true); bool needReadLock = false; // 控制是否需要读锁 Task readPLCTask = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (plc.IsConnected && inputKey != "q") { Console.Clear(); motor.ReadValues(); Console.WriteLine($"*********************{motor.Name}*********************"); Console.WriteLine($"{motor.TaskNumber} - {motor.TaskStatus} - {motor.CurrentStatus} - {motor.MotorForward} - {motor.MotorReverse} - {motor.FaultCode}"); mobileDevice.ReadValues(); Console.WriteLine($"****************{mobileDevice.Name}******************"); Console.WriteLine($"{mobileDevice.TaskNumber} - {mobileDevice.TaskStatus} - {mobileDevice.StartPosition} - {mobileDevice.EndPosition} - {mobileDevice.CurrentStatus} - {mobileDevice.CurrentCoordinate} - {mobileDevice.FaultCode}"); Task.Delay(200).Wait(); if (needReadLock) { writeComplete.Set(); // 通知写任务可以执行 readComplete.WaitOne(); // 等待写任务完成 } } }); bool boolFlag = false; short iCount = 1; Task writePLCTask = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { while (plc.IsConnected && inputKey != "q") { if (!needReadLock) { writeComplete.WaitOne(); // 等待读任务完成 needReadLock = true; // 设置需要读锁 } iCount++; motor.WriteValues((uint)(iCount + 1), (short)(iCount + 2), (short)(iCount + 3), boolFlag, !boolFlag, (short)(iCount + 4)); mobileDevice.WriteValues((uint)(iCount + 5), (short)(iCount + 6), (uint)(iCount + 7), (uint)(iCount + 8), (short)(iCount + 9), (short)(iCount + 10), (short)(iCount + 11)); boolFlag = !boolFlag; needReadLock = false; // 取消读锁 readComplete.Set(); // 通知读任务可以执行 Task.Delay(2000).Wait(); } }); inputKey = Console.ReadLine(); plc.Close(); Task.WaitAll(readPLCTask, writePLCTask); } internal class Motor { private Plc plc; private int dbArea; public Motor(string name, Plc plc, int dbArea) { this.Name = name; this.plc = plc; this.dbArea = dbArea; } // 字段属性 public string Name { get; private set; } public uint TaskNumber { get; private set; } // 任务号 public short TaskStatus { get; private set; } // 任务状态 public short CurrentStatus { get; private set; } // 当前状态 public bool MotorForward { get; private set; } // 电机正转 public bool MotorReverse { get; private set; } // 电机反转 public short FaultCode { get; private set; } // 故障码 // 读取PLC数据 public void ReadValues() { TaskNumber = (uint)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, VarType.DWord, 1); TaskStatus = (short)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 4, VarType.Int, 1); CurrentStatus = (short)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 6, VarType.Int, 1); MotorForward = (bool)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, VarType.Bit, 1); MotorReverse = (bool)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, VarType.Bit, 1, 1); FaultCode = (short)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 10, VarType.Int, 1); } // 写入PLC数据 public void WriteValues(uint taskNumber, short taskStatus, short currentStatus, bool motorForward, bool motorReverse, short faultCode) { Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 0, taskNumber); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 4, taskStatus); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 6, currentStatus); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, motorForward); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 8, motorReverse, 1); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 10, faultCode); } } internal class MobileDevice { private Plc plc; private int dbArea; public MobileDevice(string name, Plc plc, int dbArea) { this.Name = name; this.plc = plc; this.dbArea = dbArea; } // 字段属性 public string Name { get; private set; } public uint TaskNumber { get; private set; } // 任务号 public short TaskStatus { get; private set; } // 任务状态 public uint StartPosition { get; private set; } // 起始位置 public uint EndPosition { get; private set; } // 终止位置 public short CurrentStatus { get; private set; } // 当前状态 public short CurrentCoordinate { get; private set; } // 当前坐标 public short FaultCode { get; private set; } // 故障码 // 读取PLC数据 public void ReadValues() { TaskNumber = (uint)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 12, VarType.DWord, 1); TaskStatus = (short)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 16, VarType.Int, 1); StartPosition = (uint)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 18, VarType.DWord, 1); EndPosition = (uint)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 22, VarType.DWord, 1); CurrentStatus = (short)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, VarType.Int, 1); CurrentCoordinate = (short)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 28, VarType.Int, 1); FaultCode = (short)plc.Read(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 30, VarType.Int, 1); } // 写入PLC数据 public void WriteValues(uint taskNumber, short taskStatus, uint startPosition, uint endPosition, short currentStatus, short currentCoordinate, short faultCode) { Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 12, taskNumber); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 16, taskStatus); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 18, startPosition); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 22, endPosition); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, currentStatus); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 28, currentCoordinate); Thread.Sleep(100); // 添加一个延迟以验证效果 plc.Write(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 30, faultCode); } } }}这段代码中将两个PLC自定义数据类型转为了C#中的对象,通过对象的操作实现数据的读取。同时为了避免读的时候出现数据还没来得及写完的情况,加上了线程同步锁。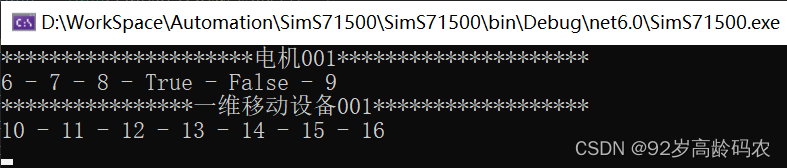
// 使用 AutoResetEvent 进行任务协调AutoResetEvent readComplete = new AutoResetEvent(false);AutoResetEvent writeComplete = new AutoResetEvent(true);// 读锁writeComplete.Set(); // 通知写任务可以执行readComplete.WaitOne(); // 等待写任务完成// 写锁writeComplete.WaitOne(); // 等待读任务完成readComplete.Set(); // 通知读任务可以执行如果将上面的线程同步锁去掉,会有几率读到还没写入完成的数据信息。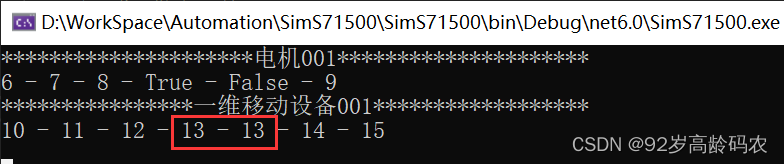
三、WinForm项目示例
尝试做一个WinForm程序测试程序。在这一章,你将体验到做成一个WinForm项目的完整流程,并且完成从新手到熟手的转变。
3.1 新建项目
3.1.1 新建窗体项目
右击【解决方案】- 点击【添加】- 点击【新建项目】。
选择【桌面】- 选择【Windows窗体应用】-【下一步】。
输入【项目名称】-【下一步】。
点击【创建】。
右击【新建的项目】-【设为启动项目】。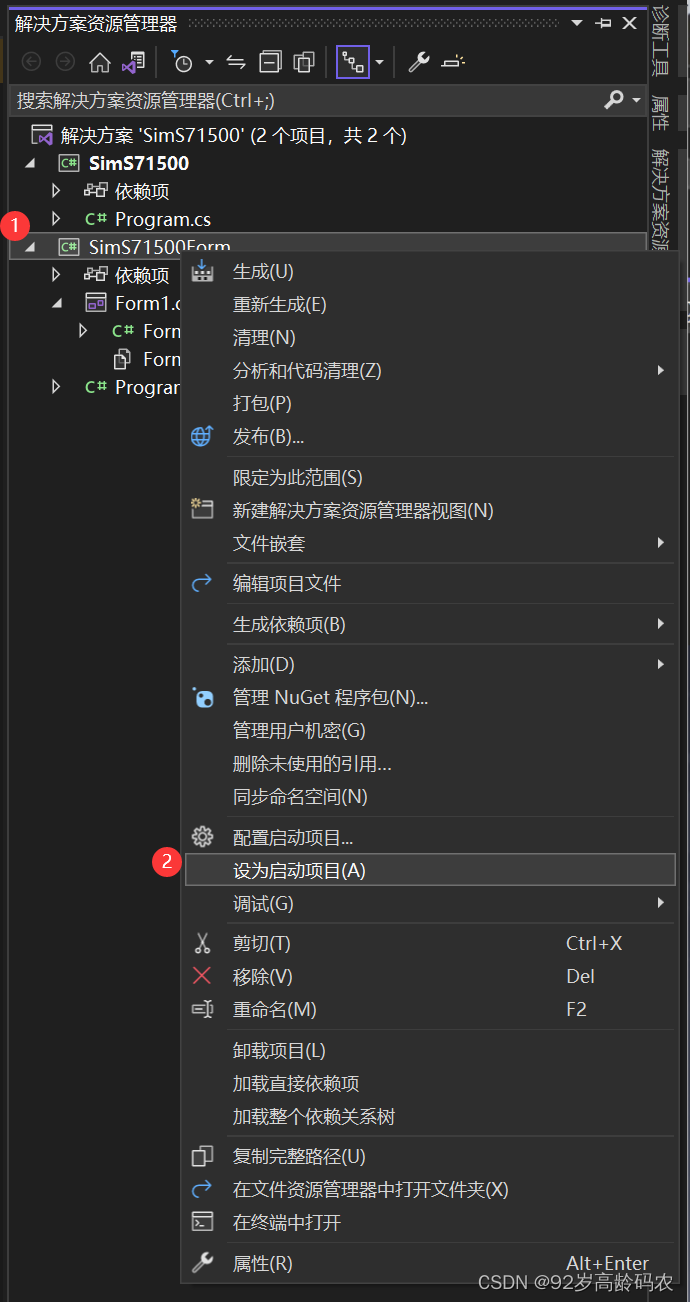
3.1.2 项目中添加S7NetPlus NuGet包
右击项目中的【依赖项】-【管控NuGet程序包】。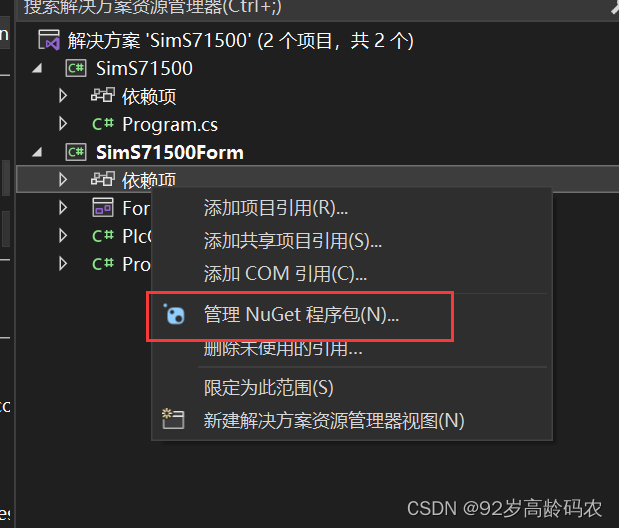 找到【S7netplus】-【安装】。
找到【S7netplus】-【安装】。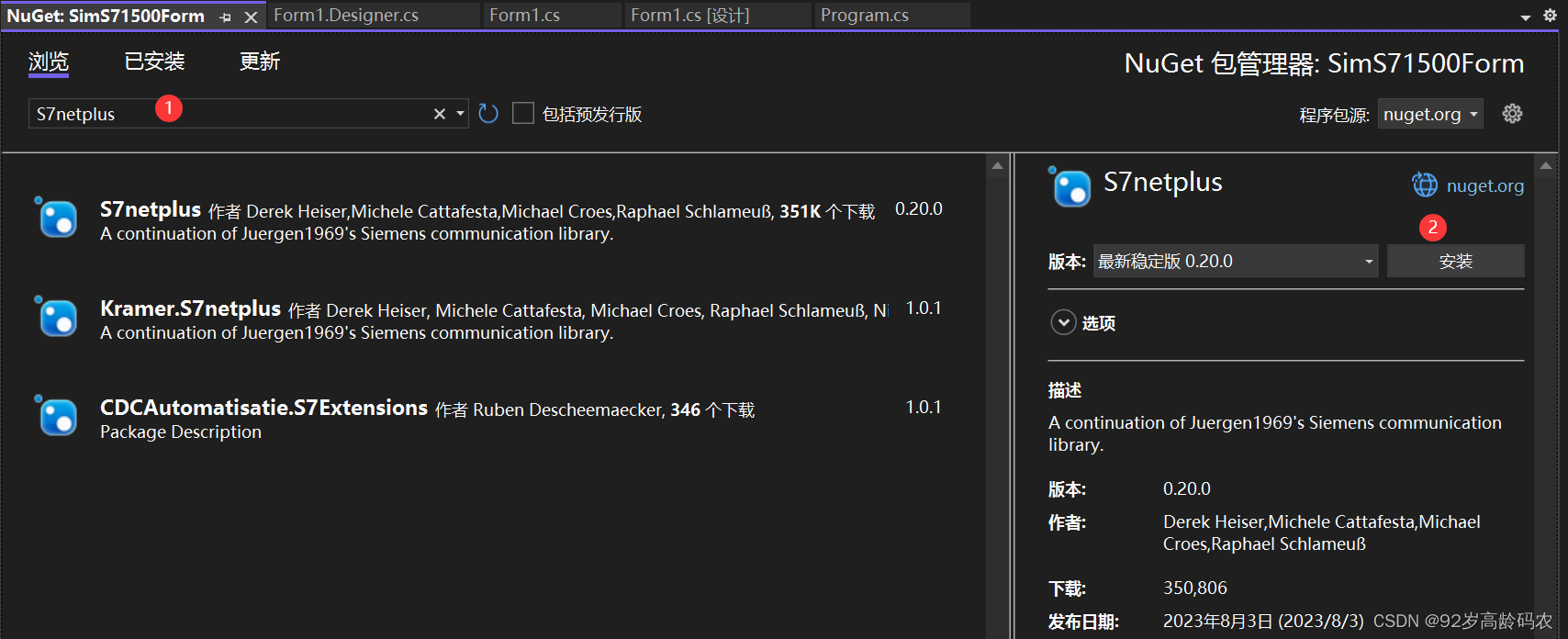 【OK】。
【OK】。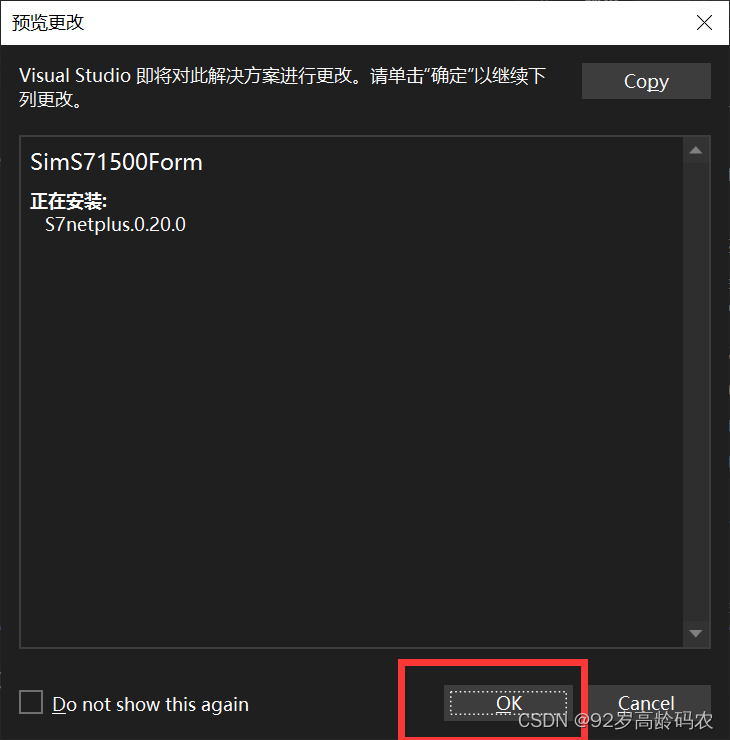 可以看到【依赖项】中,【包】增加了【S7netplus】库。
可以看到【依赖项】中,【包】增加了【S7netplus】库。
3.2 PLC连接测试功能
3.2.1 添加PLC连接用的控件
【可选】:如果没有在设计界面找到工具箱,请点击【视图】-【工具箱】。
随便选几个控件排版一下。
最终效果如下图所示: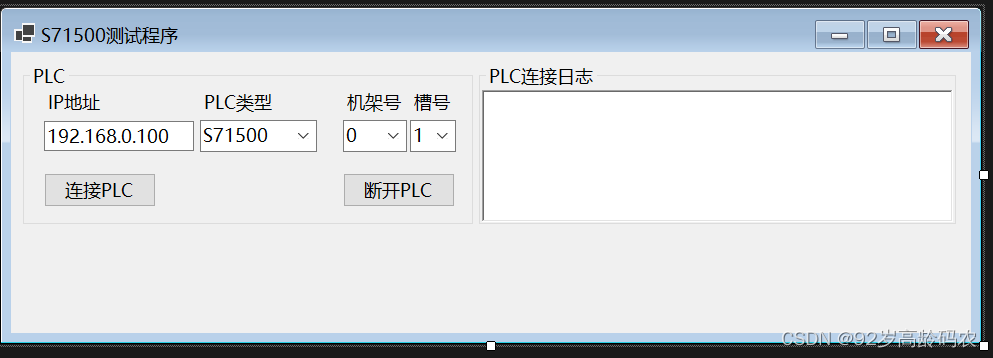
3.2.2 创建一个单例模式的PLC控制对象
创建PLC单例模式的主要目的是确保在应用程序中只有一个PLC连接实例。
以下是一些原因为什么要使用单例模式:
资源共享:在一个应用程序中,通常只需要一个PLC连接,多次创建连接实例会导致资源浪费,例如内存和网络资源。通过使用单例模式,可以确保只有一个连接实例,并共享这个实例。避免重复连接和断开:如果多个部分需要访问PLC,每次都创建和断开连接可能会导致不必要的连接和断开操作,这不仅浪费时间,还可能引发错误。单例模式确保在需要的时候可以共享已连接的PLC,而不需要重复连接和断开。维护一致性:PLC连接状态和属性应该在应用程序中保持一致。使用单例模式,可以确保应用程序中的所有部分都使用相同的连接实例,从而保持一致性。简化管理:通过将连接和相关的操作封装在单例类中,可以更容易地管理和维护PLC连接。在应用程序中只需关注一个连接点,而不是多个。线程安全性:单例模式可以用于确保在多线程环境中只有一个连接实例,从而避免竞态条件和其他与多线程相关的问题。总之,单例模式有助于管理资源、确保一致性、简化应用程序的结构和提高性能,特别是在需要共享和管理单个资源实例的情况下。
添加【类】 命名为【PlcController】。
命名为【PlcController】。 添加单例模式的PLC控制对象。
添加单例模式的PLC控制对象。 using S7.Net;namespace SimS71500Form{ public class PlcController { private static readonly PlcController myPlc = new PlcController(); private Plc? plc; // 饿汉式单例模式的私有构造函数 public static PlcController MyPlc { get { return myPlc; } }public async Task Connect(CpuType cpuType, string ipAddress, short rack, short slot){ // 检查PLC是否为null或未连接 if (plc == null || plc.IsConnected == false) { try { // 创建Ping对象以检查PLC的可达性 Ping ping = new Ping(); // 使用异步方式发送Ping请求 PingReply reply = await ping.SendPingAsync(ipAddress); // 如果Ping请求失败或PLC不可达,抛出异常 if (reply == null || reply.Status != IPStatus.Success) { throw new Exception("PLC通讯失败"); } // 初始化PLC连接 plc = new Plc(cpuType, ipAddress, rack, slot); // 异步方式打开PLC连接 await plc.OpenAsync(); } catch (Exception ex) { // 处理连接错误并抛出异常 throw new Exception("PLC连接错误: " + ex.Message); } }} public void Disconnect() { // 断开PLC连接 if (plc != null && plc.IsConnected) { plc.Close(); } } public bool IsConnected { get { if (plc != null) { return plc.IsConnected; } return false; } } }}3.2.3 窗体中的PLC控制类的调用
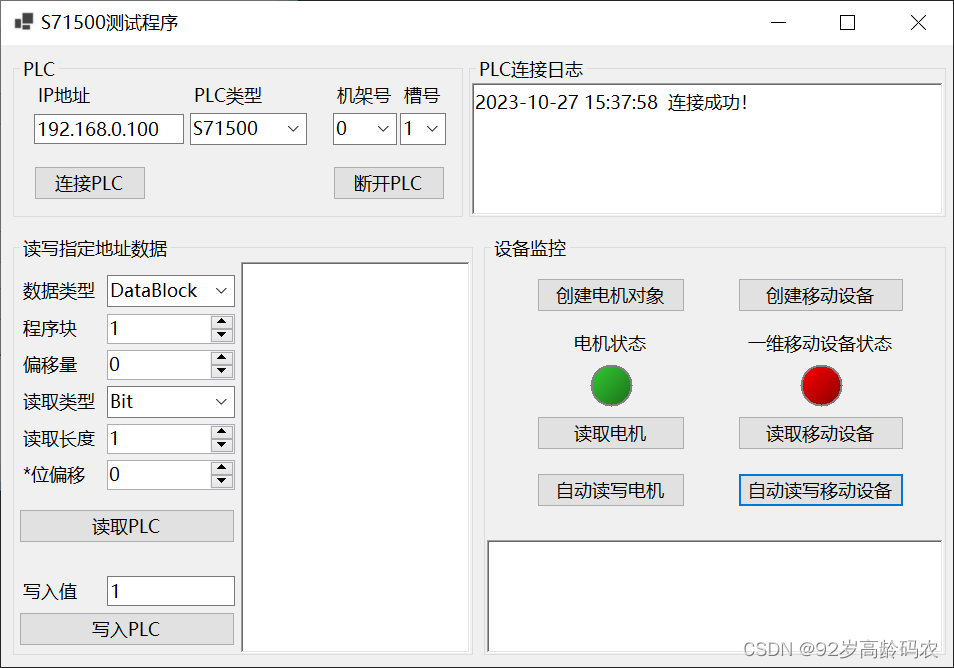
using S7.Net;namespace SimS71500Form{ public partial class MainForm : Form { public MainForm() { InitializeComponent(); } private void MainForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { string[] cpuTypeArr = Enum.GetNames(typeof(CpuType)); foreach (var item in cpuTypeArr) { cmbPLcType.Items.Add(item); } } private async void btnConnPlc_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { try { // 使用异步方法,防止WinForm界面卡顿(假死) await MyPlc.Connect( (CpuType)Enum.Parse(typeof(CpuType), cmbPLcType.Text), txtPlcIp.Text, Convert.ToInt16(cmbPlcRack.Text), Convert.ToInt16(cmbPlcSlot.Text) ); if (MyPlc.IsConnected) { txtConnLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")} 连接成功!\r\n"); } } catch (Exception ex) { // 处理读取错误 txtConnLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")} {ex.Message}\r\n"); } } private void btnDisConnPlc_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { try { PlcController.MyPlc.Disconnect(); if (PlcController.MyPlc.IsConnected == false) { txtConnLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")} 断开成功!\r\n"); } } catch (Exception ex) { // 处理读取错误 txtConnLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")} {ex.Message}\r\n"); } } }}成功!运行效果如下图所示: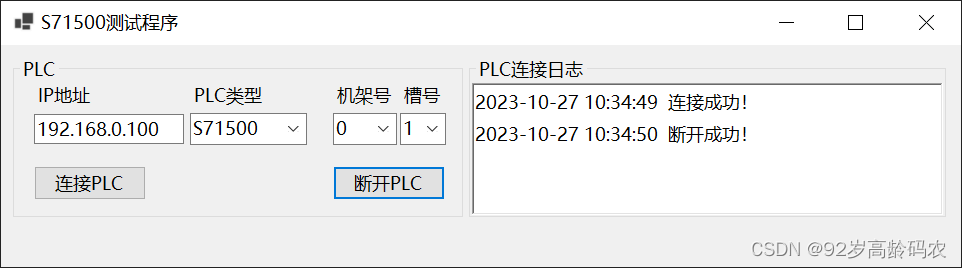
3.3 读写PLC指定地址功能
3.3.1 继续添加控件
需要注意的是,位偏移只有在类型为Bit时才会使用。
最终效果如下图所示: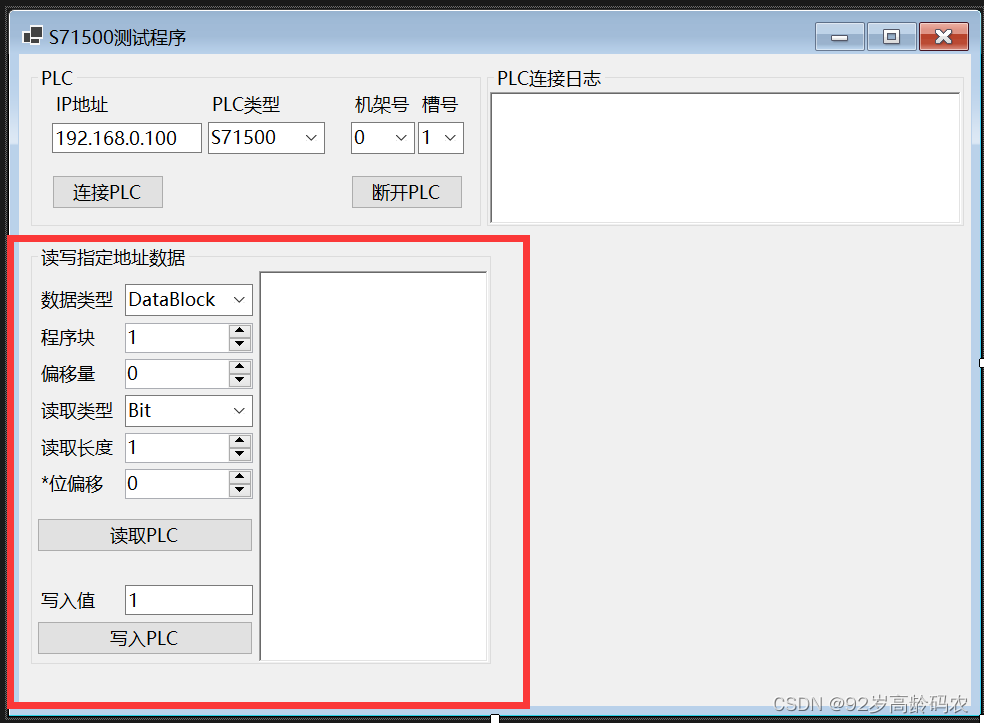
3.3.2 增加读写反馈类
这个类的主要目的是提供统一的反馈结果,以便在与PLC通信的过程中更容易处理结果和错误。
具体来说,这个代码段定义了以下类和属性:
PLCResponce类:
IsSuccess:布尔属性,指示操作是否成功。默认值为false,可以在操作成功时将其设置为true。
ReaponceMsg:字符串属性,用于存储操作的响应消息。默认为空字符串,可以在操作完成后将其设置为相关消息。
ReadResponce类(继承自PLCResponce):
Data:对象属性,用于存储从PLC读取的数据。这是一个通用属性,可以存储各种类型的数据,具体数据类型取决于从PLC读取的内容。
WriteResponce类(继承自PLCResponce):
这个类没有额外的属性,它继承了IsSuccess和ReaponceMsg属性,用于表示写入操作的结果和响应消息。
这些类的作用是将PLC操作的结果进行封装,包括成功与否的状态以及相关的响应消息。这可以有助于系统更容易地处理与PLC的通信,以及提供一致的反馈格式,以便进一步的错误处理和日志记录等操作。在实际应用中,使用这些类来封装PLC读取和写入操作的结果,并根据需要检查IsSuccess属性来确定操作是否成功,并访问Data属性来获取读取的数据。
namespace SimS71500Form{ public class Responses { public class PLCResponce { public bool IsSuccess { get; set; } = false; public string ReaponceMsg { get; set; } = ""; } /// <summary> /// 读取PLC后返回的数据结构 /// </summary> public class ReadResponce : PLCResponce { public object? Data { get; set; } } /// <summary> /// 写入PLC后返回的数据结构 /// </summary> public class WriteResponce : PLCResponce { } }}3.3.3 PLC控制类中增加读写操作
using static SimS71500Form.Responses;/// <summary>/// 读取指定地址的数据/// </summary>/// <param name="dataType">存储区域的数据类型</param>/// <param name="dbArea">存储区域的地址</param>/// <param name="startByteAdr">起始字节地址</param>/// <param name="varType">要读取的变量类型</param>/// <param name="varCount">变量的数量</param>/// <param name="bitAdr">比特地址</param>/// <returns></returns>/// <exception cref="Exception"></exception>public ReadResponce ReadVariable(DataType dataType, int dbArea, int startByteAdr, VarType varType, int varCount, byte bitAdr = 0){ ReadResponce responce = new ReadResponce(); try { if (plc == null || !plc.IsConnected) { responce.ReaponceMsg = "PLC未连接"; return responce; } switch (varType) { case VarType.Bit: responce.Data = plc.Read(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, VarType.Bit, varCount, bitAdr); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.Byte: case VarType.Word: case VarType.DWord: case VarType.Int: case VarType.DInt: case VarType.Real: case VarType.LReal: responce.Data = plc.Read(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, varType, varCount); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.String: byte[] dataS = plc.ReadBytes(dataType, dbArea, 68, 256); int stringLen = dataS[1]; string gbkString = Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetString(dataS, 2, stringLen); responce.Data = gbkString; responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.S7String: case VarType.S7WString: case VarType.Timer: case VarType.Counter: case VarType.DateTime: case VarType.DateTimeLong: responce.ReaponceMsg = "未处理相关逻辑,请自行探索"; break; default: break; } return responce; } catch (Exception ex) { // 处理读取错误 responce.ReaponceMsg = "PLC读取错误: " + ex.Message; return responce; }}/// <summary>/// 写入指定地址的数据/// </summary>/// <param name="dataType">存储区域的数据类型</param>/// <param name="dbArea">存储区域的地址</param>/// <param name="startByteAdr">起始字节地址</param>/// <param name="varType">要读取的变量类型</param>/// <param name="value">需要写入的值</param>/// <param name="bitAdr">比特地址</param>/// <returns></returns>public WriteResponce WriteVariable(DataType dataType, int dbArea, int startByteAdr, VarType varType, string value, int bitAdr = -1){ WriteResponce responce = new WriteResponce(); try { if (plc == null || !plc.IsConnected) { responce.ReaponceMsg = "PLC未连接"; return responce; } switch (varType) { case VarType.Bit: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToBoolean(value), bitAdr); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.Byte: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToByte(value)); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.Word: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToUInt16(value)); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.DWord: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToUInt32(value)); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.Int: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToInt16(value)); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.DInt: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToInt32(value)); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.Real: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToSingle(value)); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.LReal: plc.Write(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, Convert.ToDouble(value)); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.String: // 编码为字节数组 byte[] stringBytes = Encoding.GetEncoding("GBK").GetBytes(value); // 构建带控制信息的字节数组 byte[] dataString = new byte[stringBytes.Length + 2]; // 加2是为了存储控制信息 // 添加控制信息 dataString[0] = 254; // 第一个字节固定为254 dataString[1] = (byte)(stringBytes.Length); // 第二个字节表示字符长度 // 复制字符串数据到字节数组 Array.Copy(stringBytes, 0, dataString, 2, stringBytes.Length); // 将字节数组写入PLC plc.WriteBytes(dataType, dbArea, startByteAdr, dataString); responce.IsSuccess = true; break; case VarType.S7String: case VarType.S7WString: case VarType.Timer: case VarType.Counter: case VarType.DateTime: case VarType.DateTimeLong: responce.ReaponceMsg = "未处理相关逻辑,请自行探索"; break; default: break; } return responce; } catch (Exception ex) { // 处理读取错误 responce.ReaponceMsg = "PLC读取错误: " + ex.Message; return responce; }}3.3.4 窗体功能中调用PLC控制类的读写操作
private void btnReadPlc_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ ReadResponce responce = MyPlc.ReadVariable( (DataType)Enum.Parse(typeof(DataType), cmbDataType.Text), Convert.ToInt16(numDbArea.Value), Convert.ToInt16(numStartByteAdr.Value), (VarType)Enum.Parse(typeof(VarType), cmbVarType.Text), Convert.ToInt16(numVarCount.Value), Convert.ToByte(numBitAdr.Value) ); if (responce == null) { txtReadWriteLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} 读取失败!\r\n"); } else if (responce.IsSuccess == false) { txtReadWriteLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} 读取失败!{responce.ReaponceMsg}\r\n"); } else { txtReadWriteLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} {responce.Data}\r\n"); }}private void btnWritePlc_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ WriteResponce responce = MyPlc.WriteVariable( (DataType)Enum.Parse(typeof(DataType), cmbDataType.Text), Convert.ToInt16(numDbArea.Value), Convert.ToInt16(numStartByteAdr.Value), (VarType)Enum.Parse(typeof(VarType), cmbVarType.Text), txtInputData.Text, Convert.ToByte(numBitAdr.Value) ); if (responce == null) { txtReadWriteLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} 写入失败!\r\n"); } else if (responce.IsSuccess == false) { txtReadWriteLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} 写入失败!{responce.ReaponceMsg}\r\n"); } else { txtReadWriteLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} 写入成功!\r\n"); }}运行效果如下图所示: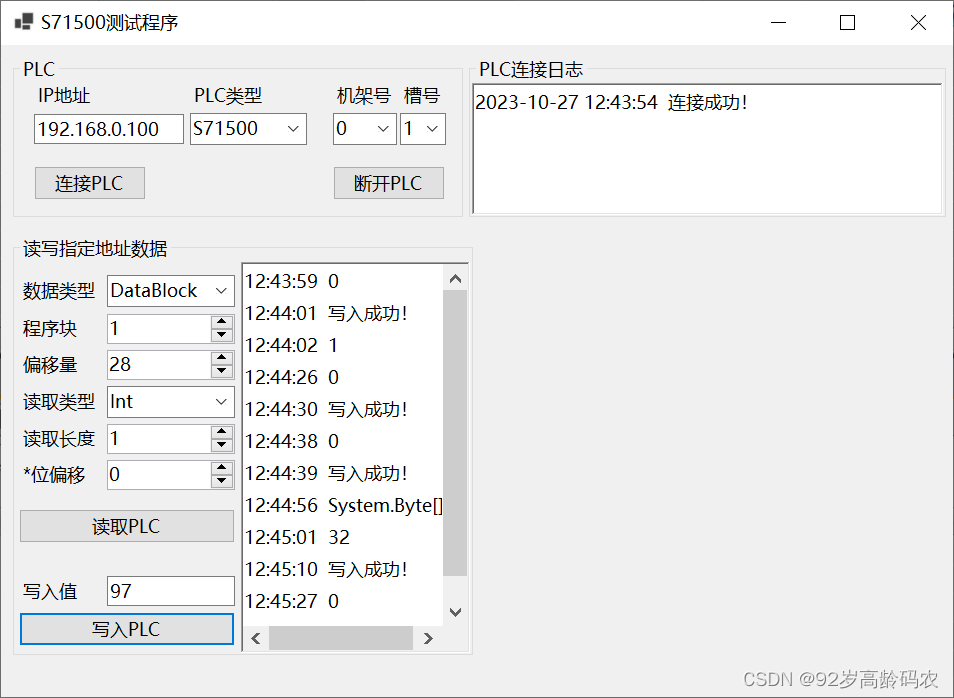
3.4 读写PLC自定义数据类型功能
3.4.1 增加有立体效果的自定义控件
既然数据类型都自定义了,那么控件也可以自定义一个。
右击【项目】-【添加】-【用户控件】。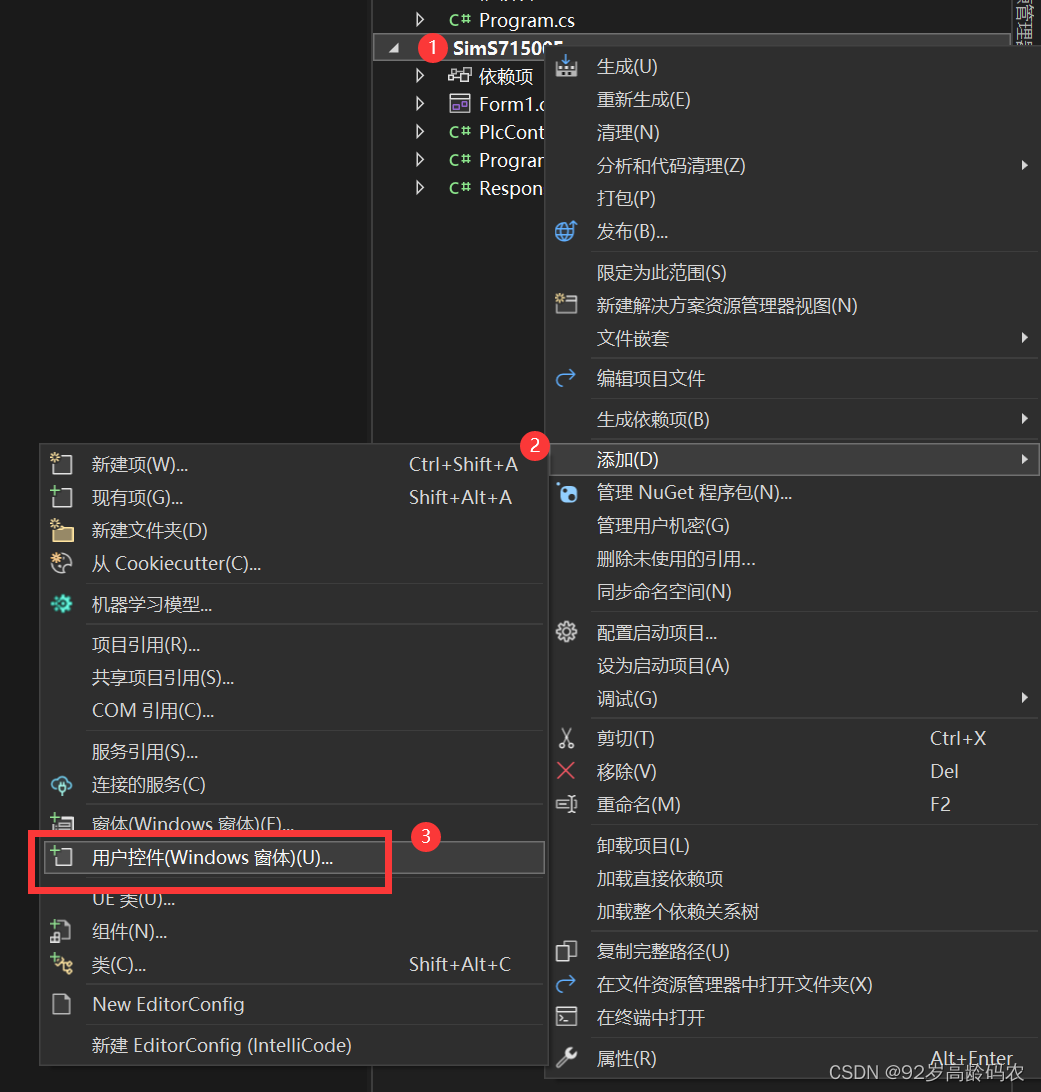
输入【名称】-【添加】。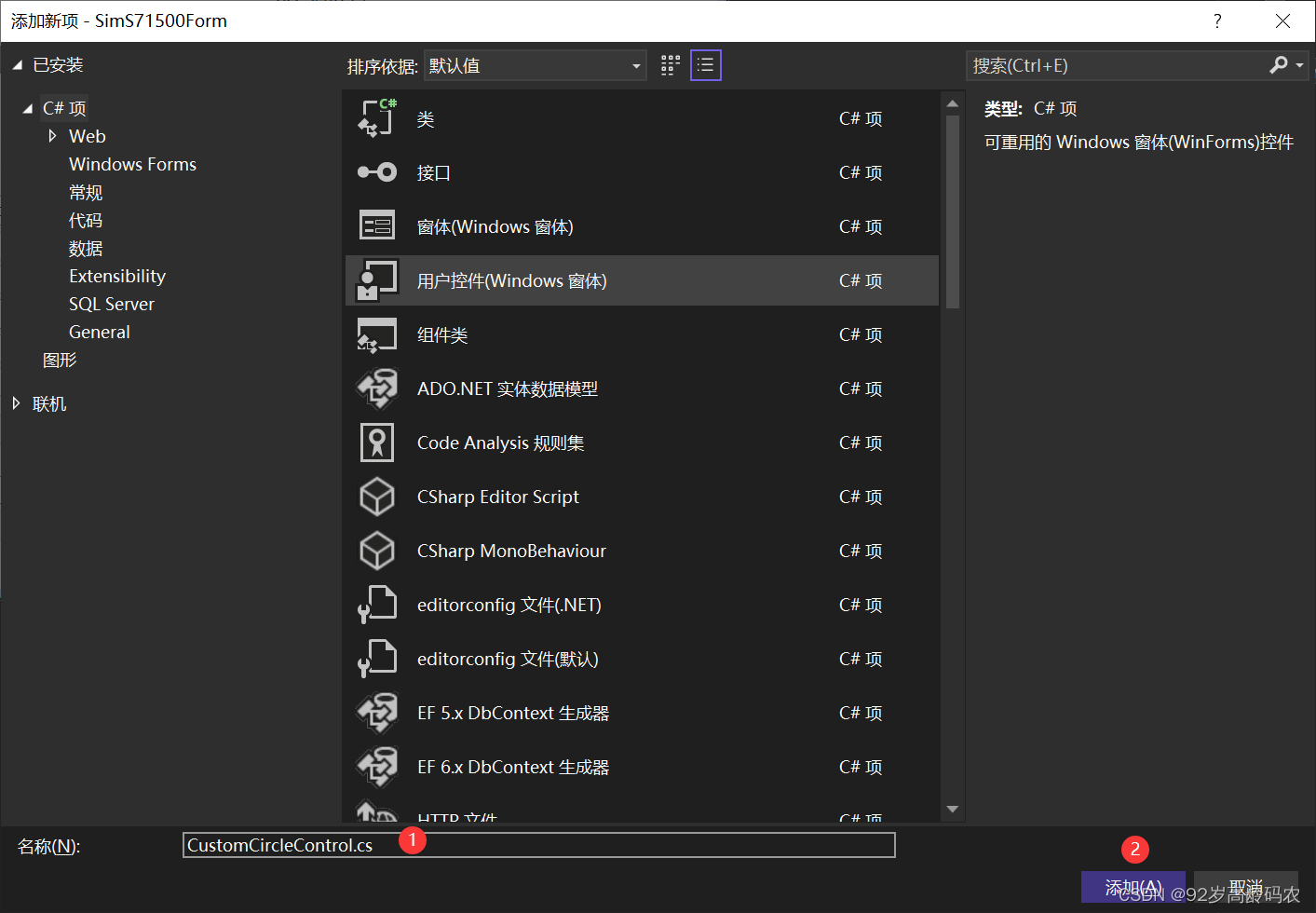
如果自定义控件类库没在工具箱出现,请右击【项目】-【重新生成】。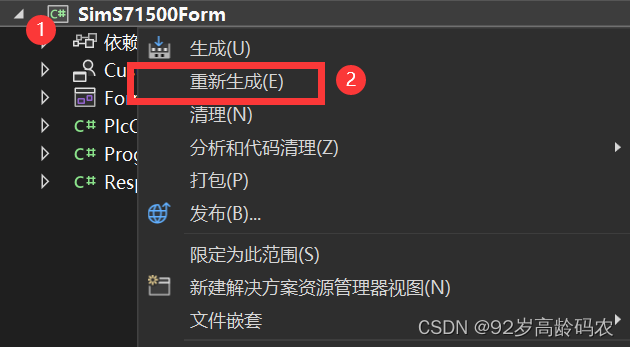
在自定义控件中添加代码。
using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;namespace SimS71500Form{ public partial class CustomCircleControl : UserControl { private Color statusColor = Color.Gray; public Color StatusColor { get { return statusColor; } set { statusColor = value; Invalidate(); // 强制重新绘制以显示新的颜色 } } public CustomCircleControl() { InitializeComponent(); DoubleBuffered = true; Size = new Size(50, 50); // 设置控件的大小 } protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e) { base.OnPaint(e); Color darkerColor = ControlPaint.Dark(statusColor, 0.2f); // 调整 0.2f 以控制加深的程度 int circleDiameter = Math.Min(Width, Height) - 10; int circleX = (Width - circleDiameter) / 2; int circleY = (Height - circleDiameter) / 2; // 创建一个线性渐变画刷 LinearGradientBrush gradientBrush = new LinearGradientBrush( new Rectangle(circleX, circleY, circleDiameter, circleDiameter), statusColor, // 渐变起始颜色 darkerColor, // 渐变结束颜色 LinearGradientMode.ForwardDiagonal); // 斜向45度的渐变 e.Graphics.FillEllipse(gradientBrush, circleX, circleY, circleDiameter, circleDiameter); // 创建一个灰色边框的画笔 Pen borderPen = new Pen(Color.Gray, circleDiameter / 15); e.Graphics.DrawEllipse(borderPen, circleX, circleY, circleDiameter, circleDiameter); } }}重新生成项目后,在工具栏中找到这个自定义控件,加入到窗体中。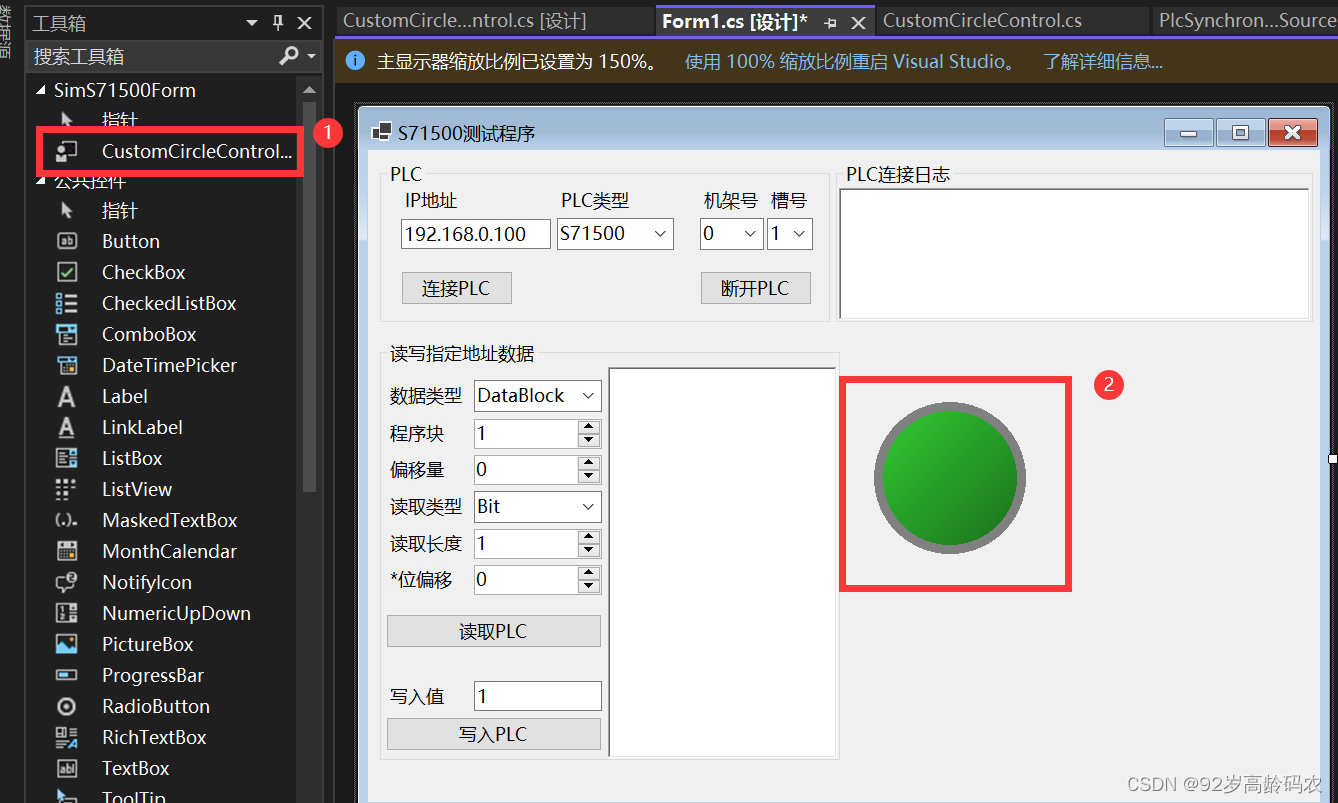
3.4.2 继续添加其他控件
最后布局如下图所示。注意:这里的自动读写的功能通过timer控件来实现。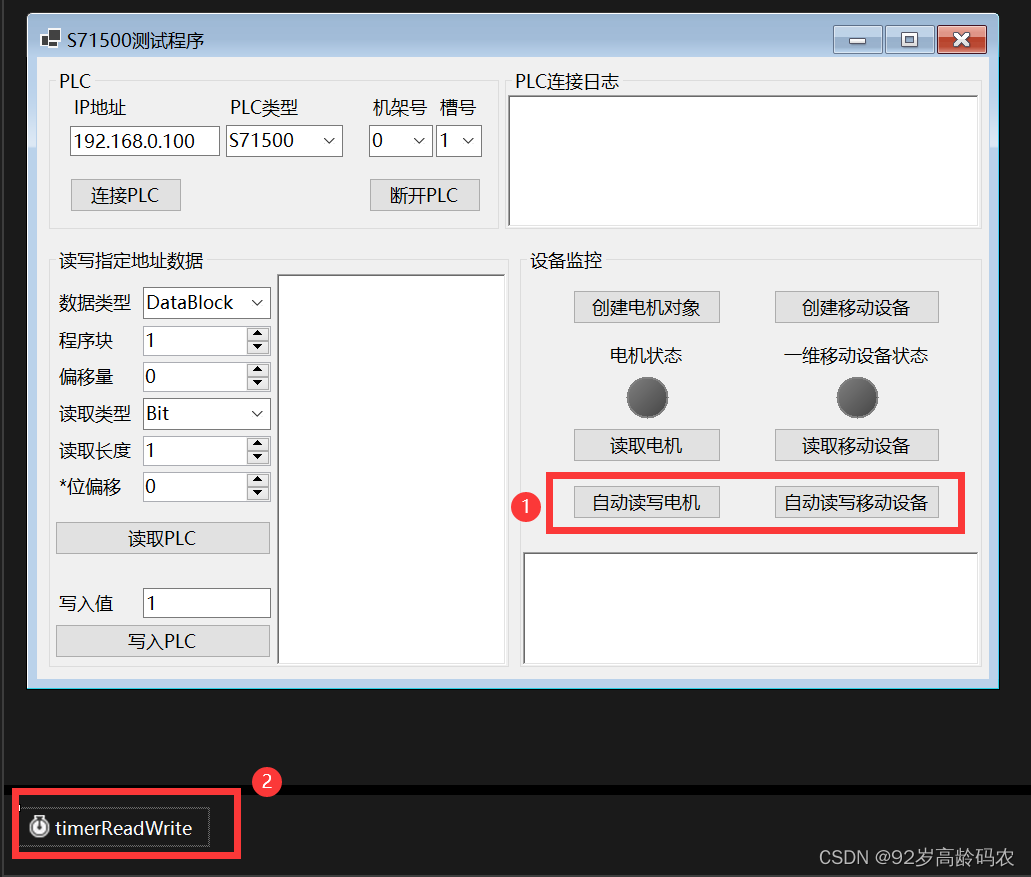
注意,timer控件需要设置如下属性,否则不会自动运行。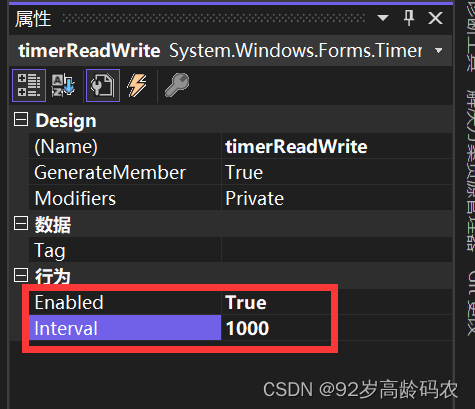
3.4.3 添加自定义数据类型相应的对象
创建一个Device类,代码中进行了简化,只读取当前状态,其他信息可以自行补充。
using S7.Net;using static SimS71500Form.Responses;namespace SimS71500Form{ public abstract class Device { public Device(string name, int dbArea) { this.Name = name; this.dbArea = dbArea; } public int dbArea { get; private set; } public string Name { get; private set; } public uint TaskNumber { get; private set; } // 任务号 public short TaskStatus { get; private set; } // 任务状态 public short CurrentStatus { get; private set; } // 当前状态 public short FaultCode { get; private set; } // 故障码 public void SetCurrentStatus(short newStatus) { // 提供一个方法在外部更改 CurrentStatus this.CurrentStatus = newStatus; } // 抽象的 Read 方法,返回ReadResponce public abstract ReadResponce Read(); // 抽象的 Write 方法,返回WriteResponce public abstract WriteResponce Write(short status); } public class Motor : Device { public Motor(string name, int dbArea) : base(name, dbArea) { } public bool MotorForward { get; private set; } // 电机正转 public bool MotorReverse { get; private set; } // 电机反转 public override ReadResponce Read() { ReadResponce responce = PlcController.MyPlc.ReadVariable(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 6, VarType.Int, 1); if (responce.IsSuccess && responce.Data != null) { SetCurrentStatus((short)responce.Data); } return responce; } public override WriteResponce Write(short status) { WriteResponce responce = PlcController.MyPlc.WriteVariable(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 6, VarType.Int, status.ToString()); return responce; } } public class MobileDevice : Device { public MobileDevice(string name, int dbArea) : base(name, dbArea) { } public uint StartPosition { get; private set; } // 起始位置 public uint EndPosition { get; private set; } // 终止位置 public short CurrentCoordinate { get; private set; } // 当前坐标 public override ReadResponce Read() { ReadResponce responce = PlcController.MyPlc.ReadVariable(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, VarType.Int, 1); if (responce.IsSuccess && responce.Data != null) { SetCurrentStatus((short)responce.Data); } return responce; } public override WriteResponce Write(short status) { WriteResponce responce = PlcController.MyPlc.WriteVariable(DataType.DataBlock, dbArea, 26, VarType.Int, status.ToString()); return responce; } }}3.4.5 窗体中自定义类的读写操作
Motor motor;private void btnCreateMotor_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ motor = new Motor("电机001", 2);}private void btnReadMotor_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ if (motor != null) { ReadResponce responce = motor.Read(); if (responce == null) { txtDeviceLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} {motor.Name}读取失败!\r\n"); } else if (responce.IsSuccess == false) { txtDeviceLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} {motor.Name}读取失败!{responce.ReaponceMsg}\r\n"); } else { if (motor.CurrentStatus == 0) { ledMotorState.StatusColor = Color.Gray; } else if (motor.CurrentStatus == 1) { ledMotorState.StatusColor = Color.LimeGreen; } else { ledMotorState.StatusColor = Color.Red; } } } else { txtDeviceLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} 电机未创建!\r\n"); }}MobileDevice mobileDevice;private void btnCreateMobile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ mobileDevice = new MobileDevice("一维移动设备001", 2);}private void btnReadMobile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ if (mobileDevice != null) { ReadResponce responce = mobileDevice.Read(); if (responce == null) { txtDeviceLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} {mobileDevice.Name}读取失败!\r\n"); } else if (responce.IsSuccess == false) { txtDeviceLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} {mobileDevice.Name}读取失败!{responce.ReaponceMsg}\r\n"); } else { if (mobileDevice.CurrentStatus == 0) { ledMobileDeviceState.StatusColor = Color.Gray; } else if (mobileDevice.CurrentStatus == 1) { ledMobileDeviceState.StatusColor = Color.LimeGreen; } else { ledMobileDeviceState.StatusColor = Color.Red; } } } else { txtDeviceLog.AppendText($"{DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm:ss")} 移动设备未创建!\r\n"); }}bool bAutoReadMotor = false;bool bAutoReadMobile = false;private void timerReadWrite_Tick(object sender, EventArgs e){ DateTime now = DateTime.Now; int data = now.Second % 3; if (bAutoReadMotor && motor != null) { btnReadMotor_Click(null, null); motor.Write((short)data); } if (bAutoReadMobile) { btnReadMobile_Click(null, null); data = 3 - data; mobileDevice.Write((short)data); }}private void btnAutoReadMotor_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ bAutoReadMotor = !bAutoReadMotor;}private void btnAutoReadMobile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){ bAutoReadMobile = !bAutoReadMobile;}其中,下面这两个变量用于分别控制自动读写的开关。只有开启的时候,才会自动进行读写。
bool bAutoReadMotor = false;bool bAutoReadMobile = false;下面这两行代码是直接调用点击按钮事件,减少重复的代码。
btnReadMotor_Click(null, null);btnReadMobile_Click(null, null);3.5 最终运行效果
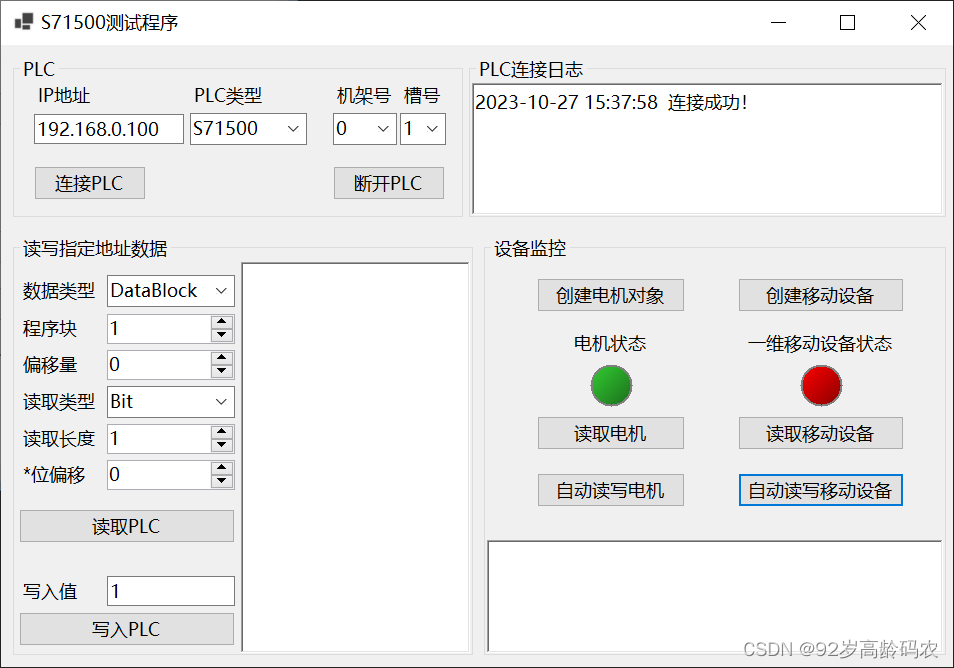
总结
这篇文档提供了一个关于如何使用C#与西门子PLC进行通讯的详细指南。
文档包含了以下主要内容:
非常感谢您能坚持看到这里。
欢迎交流!
终,电气问曰:「何能及君耶?」答曰:「无他,唯手熟尔。」