Function Calling是大模型连接外部世界的通道,目前出现的插件(Plugins )、OpenAI的Actions、各个大模型平台中出现的tools工具集,其实都是Function Calling的范畴。时下大火的OpenAI的GPTs,原理就是使用了Function Calling,例如联网检索、code interpreter。
本文带大家了解下Function calling,看它是如何让大模型能与外部世界连接的。
文章目录
0. 接口形式1. Function Calling在AI大模型应用中的位置 - 架构2. 大模型为什么需要连接外部世界3. 实战3.1 调用本地函数3.1.1 定义一个自定义的本地函数,也可以是现有的库中的函数3.1.2 告诉大模型这个函数的存在3.1.3 给一个需要使用该函数的Prompt3.1.4 解析函数名称和参数3.1.5 再次调用大模型获取最终结果3.1.6 完整代码 3.2 多Function的调用3.2.1 定义本地函数3.2.2 告诉大模型这两个函数的存在3.2.3 使用示例3.2.4 完整代码 4. 总结参考
0. 接口形式
写过程序的人可能都懂接口是什么,这里再简述一下接口的形式。
目前常见的接口形式:
命令行(Command Line Interface),简称 CLI(DOS、Unix/Linux shell, Windows Power Shell)图形界面(Graphical User Interface),简称 GUI(Windows、MacOS、iOS、Android)AI时代的接口形式:用户通过自然语言与软件或系统交互,不用再点击按钮,按标准流程操作软件
语言界面(Conversational User Interface),简称 CUI,或 Natural-Language User Interface,简称 LUI未来的接口形式:
脑机接口(Brain–Computer Interface),简称 BCI以前的接口调用,我们需要给定明确的接口名称和精确的参数。大模型时代的接口调用,我们只需要给出自然语言任务,大模型自动解析出参数和调用哪个接口。
1. Function Calling在AI大模型应用中的位置 - 架构
没有Function Calling的架构:
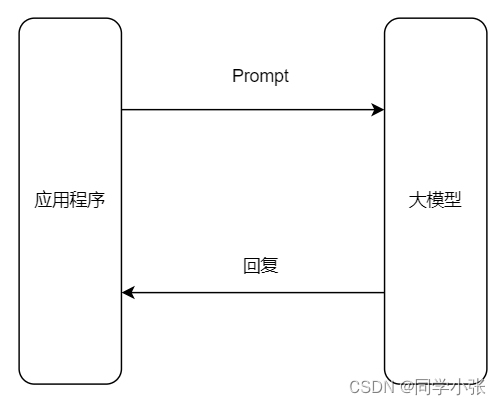
加入Function calling之后的架构:
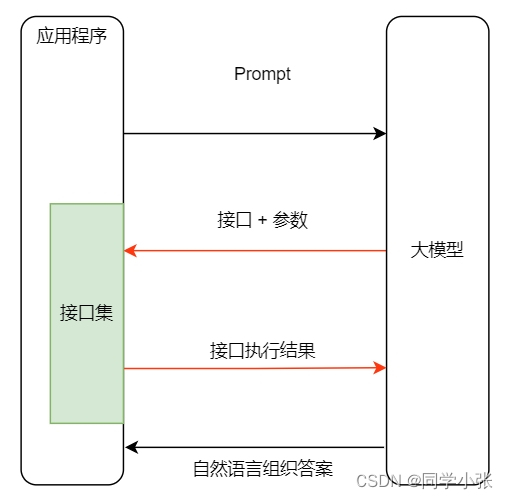
2. 大模型为什么需要连接外部世界
其实大模型也不是万能的,它有三大缺陷:
训练数据不可能涵盖所有信息。垂直、非公开数据必有欠缺。不知道最新信息。大模型的训练周期很长,且更新一次耗资巨大。所以它不可能实时训练。GPT-3.5 的知识截至 2022 年 1 月,GPT-4 是 2023 年 4 月。没有「真逻辑」。它表现出的逻辑、推理,是训练文本的统计规律,而不是真正的逻辑。也就是说,它的结果都是有一定不确定性的,这对于需要精确和确定结果的领域,如数学等,是灾难性的,基本是不可用的。比如算加法:
把 100 以内所有加法算式都训练给大模型,它就能回答 100 以内的加法算式如果问它更大数字的加法,就不一定对了因为它并不懂「加法」,只是记住了 100 以内的加法算式的统计规律
所以:大模型需要连接真实世界,并对接真逻辑系统,以此来控制大模型输出的不确定性和幻觉,达到我们想要的结果。
3. 实战
3.1 调用本地函数
3.1.1 定义一个自定义的本地函数,也可以是现有的库中的函数
以Python内置的sum函数为例,假设我们想让大模型使用这个函数。
sum函数介绍,接收一个列表、元组或集合: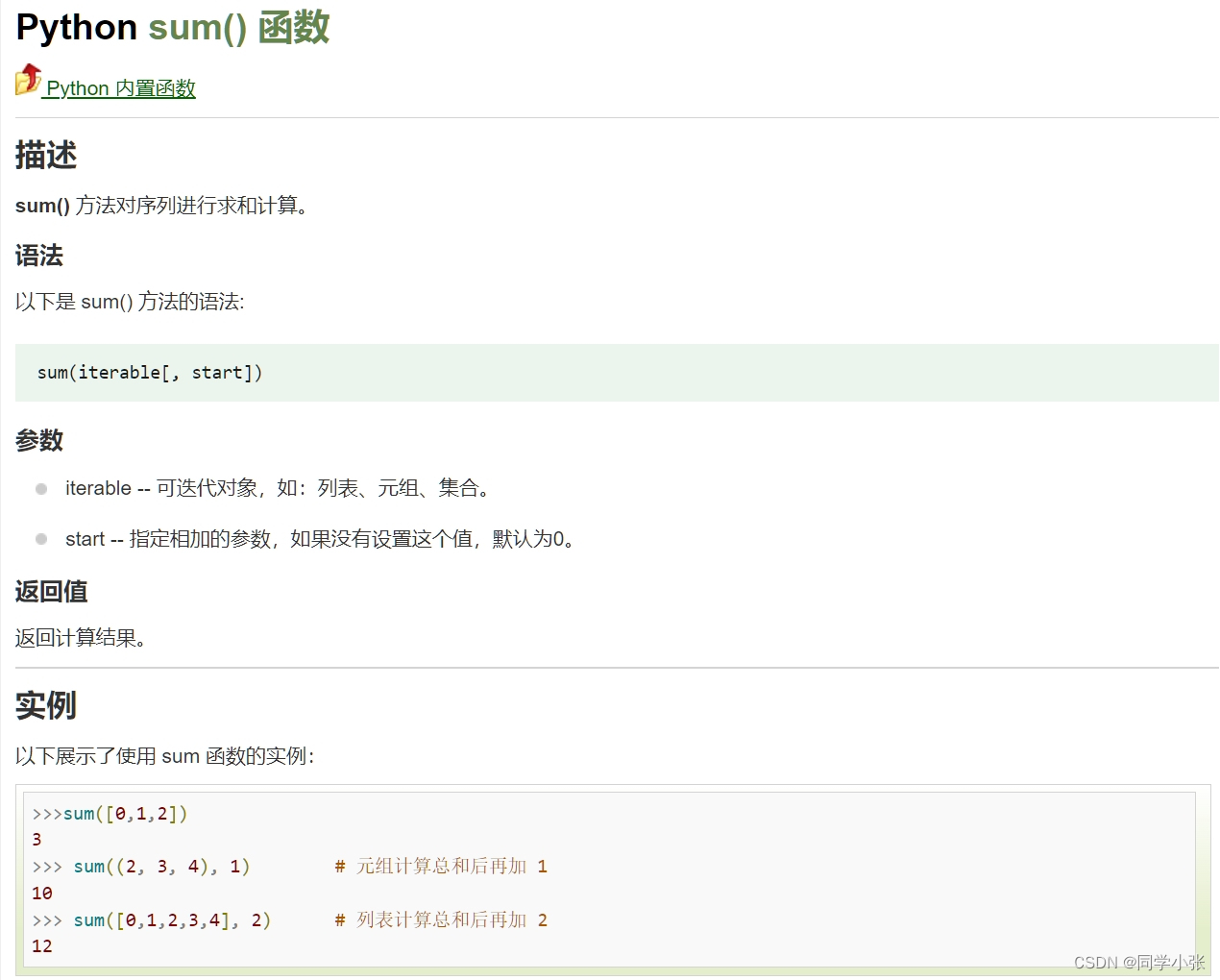
3.1.2 告诉大模型这个函数的存在
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-1106"): response = openai.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, max_tokens=1024, tools=[ { # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个。由大模型决定调用谁 "type": "function", "function": { "name": "sum", "description": "计算一组数的和", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "numbers": { "type": "array", "items": { "type": "number" } } } } } }, ] ) return response.choices[0].message代码解释:
还是我们熟悉的openai.chat.completions.create接口,这次我们需要使用的是tools参数将本地的函数用json描述,添加到tools参数中 注意:Function Calling 中的函数与参数的描述description也是一种 Prompt。这种 Prompt 也需要调优,否则会影响函数的召回、参数的准确性,甚至让 GPT 产生幻觉
3.1.3 给一个需要使用该函数的Prompt
我们用自然语言给一个做加法的需求:
prompt = "桌上有 2 个苹果,四个桃子和 3 本书,一共有几个水果?"messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个数学家,你可以计算任何算式。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt}]response = get_completion(messages)messages.append(response) # 注意这一句,必须加入到上下文中,否则报错print("=====GPT回复=====")print(response)运行看下这时候大模型的返回:
可以看到返回了函数的名称和函数的参数。
3.1.4 解析函数名称和参数
当大模型返回了需要调用的名称和参数之后,我们可以通过本地代码解析出来,然后再去调用相应函数。
if (response.tool_calls is not None): for tool_call in response.tool_calls: print(response.tool_calls) print(f"调用 {tool_call.function.name} 函数,参数是 {tool_call.function.arguments}") if tool_call.function.name == "sum": # 调用 sum 函数(本地函数或库函数,非chatgpt),打印结果 args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments) result = sum(args["numbers"]) print("=====函数返回=====") print(result)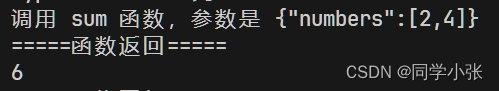
3.1.5 再次调用大模型获取最终结果
本地函数执行完得到结果后,再将这个结果给大模型,让大模型用自然语言组织起最终答案。
这里需要怎么给大模型呢?需要将函数调用结果,tool_call_id,role,name等一起加入到prompt中。
# 把函数调用结果加入到对话历史中messages.append( { "tool_call_id": tool_call.id, # 用于标识函数调用的 ID "role": "tool", "name": "sum", "content": str(result) # 数值result 必须转成字符串 })# 再次调用大模型print("=====最终回复=====")print(get_completion(messages).content)
经测试,tool_call_id和role是必须参数,name可以不要,但最好也加上。
3.1.6 完整代码
import jsonimport osfrom math import *import openai# 加载 .env 到环境变量from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-1106"): response = openai.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, max_tokens=1024, tools=[ { # 用 JSON 描述函数。可以定义多个。由大模型决定调用谁 "type": "function", "function": { "name": "sum", "description": "计算一组数的和", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "numbers": { "type": "array", "items": { "type": "number" } } } } } }, ] ) return response.choices[0].messageprompt = "桌上有 2 个苹果,四个桃子和 3 本书,一共有几个水果?"messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个数学家,你可以计算任何算式。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt}]response = get_completion(messages)# 把大模型的回复加入到对话历史中messages.append(response) # 注意这一句,必须加入到上下文中,否则报错print("=====GPT回复=====")print(response)# 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来if (response.tool_calls is not None): for tool_call in response.tool_calls: print(response.tool_calls) print(f"调用 {tool_call.function.name} 函数,参数是 {tool_call.function.arguments}") if tool_call.function.name == "sum": # 调用 sum 函数(本地函数或库函数,非chatgpt),打印结果 args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments) result = sum(args["numbers"]) print("=====函数返回=====") print(result) # 把函数调用结果加入到对话历史中 messages.append( { "tool_call_id": tool_call.id, # 用于标识函数调用的 ID "role": "tool", "name": "sum", "content": str(result) # 数值result 必须转成字符串 } ) # 再次调用大模型 print("=====最终回复=====") print(get_completion(messages).content)3.2 多Function的调用
这里以一个查询某个地点附近某些信息的需求为例。
3.2.1 定义本地函数
这里我们需要定义自己的本地函数,不再使用Python的库函数了。
下面的代码,我们定义了两个函数。
get_location_coordinate用于查询某个地点的地理坐标。search_nearby_pois用于查询地理坐标附近的某些信息(取决于用户输入的Keyword)def get_location_coordinate(location, city="北京"): url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/text?key={amap_key}&keywords={location}®ion={city}" print(url) r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: return result["pois"][0] return Nonedef search_nearby_pois(longitude, latitude, keyword): url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/around?key={amap_key}&keywords={keyword}&location={longitude},{latitude}" print(url) r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() ans = "" if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: for i in range(min(3, len(result["pois"]))): name = result["pois"][i]["name"] address = result["pois"][i]["address"] distance = result["pois"][i]["distance"] ans += f"{name}\n{address}\n距离:{distance}米\n\n" return ans这是用的高德地图的开放接口,在使用本例之前,你需要先去高德地图开放接口的官网申请一个key,免费的。这里就不过多介绍了。
3.2.2 告诉大模型这两个函数的存在
def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-1106"): response = openai.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, max_tokens=1024, tools=[{ "type": "function", "function": { "name": "get_location_coordinate", "description": "根据POI名称,获得POI的经纬度坐标", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "POI名称,必须是中文", }, "city": { "type": "string", "description": "POI所在的城市名,必须是中文", } }, "required": ["location", "city"], } } }, { "type": "function", "function": { "name": "search_nearby_pois", "description": "搜索给定坐标附近的poi", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "longitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的经度", }, "latitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的纬度", }, "keyword": { "type": "string", "description": "目标poi的关键字", } }, "required": ["longitude", "latitude", "keyword"], } } }] ) return response.choices[0].message3.2.3 使用示例
prompt = "北京三里屯附近的咖啡"messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个地图通,你可以找到任何地址。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt}]response = get_completion(messages)if (response.content is None): # 解决 OpenAI 的一个 400 bug response.content = ""messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中print("=====GPT回复=====")print(response)# 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来while (response.tool_calls is not None): # 1106 版新模型支持一次返回多个函数调用请求 for tool_call in response.tool_calls: args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments) print(args) if (tool_call.function.name == "get_location_coordinate"): print("Call: get_location_coordinate") result = get_location_coordinate(**args) elif (tool_call.function.name == "search_nearby_pois"): print("Call: search_nearby_pois") result = search_nearby_pois(**args) print("=====函数返回=====") print(result) messages.append({ "tool_call_id": tool_call.id, # 用于标识函数调用的 ID "role": "tool", "name": tool_call.function.name, "content": str(result) # 数值result 必须转成字符串 }) response = get_completion(messages) if (response.content is None): # 解决 OpenAI 的一个 400 bug response.content = "" messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中print("=====最终回复=====")print(response.content)看下执行过程和结果: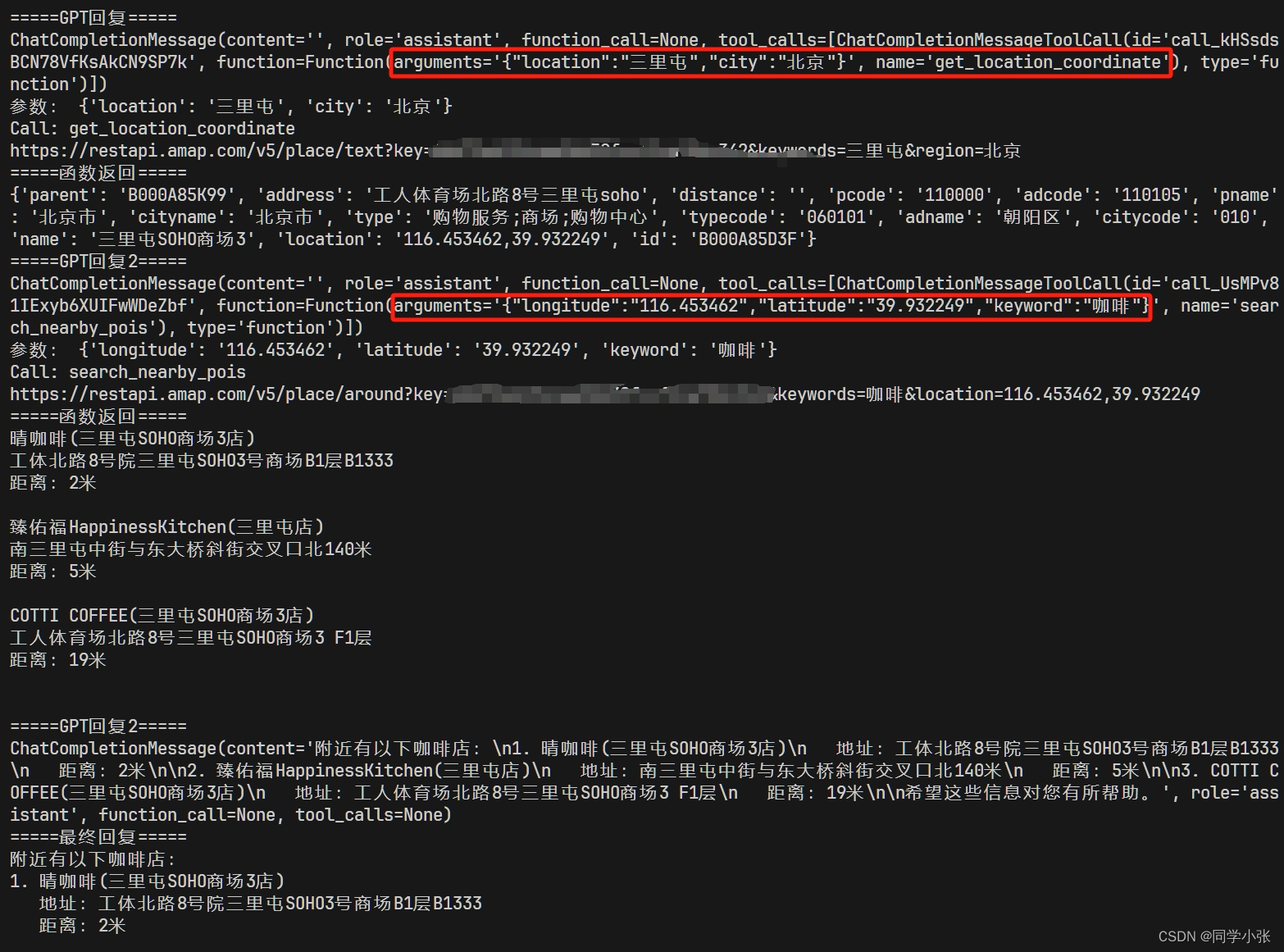
(1)首先大模型识别到应该先调用get_location_coordinate函数获取经纬度。
(2)get_location_coordinate执行结果给到大模型,大模型识别到下一步应该调用search_nearby_pois
(3)search_nearby_pois执行结果给到大模型,大模型识别到不需要调用其它函数,用自然语言组织了最终答案。
3.2.4 完整代码
import jsonimport osimport openaiimport requests# 加载 .env 到环境变量from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())amap_key = os.getenv('AMAP_KEY')def get_completion(messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-1106"): response = openai.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=messages, temperature=0, max_tokens=1024, tools=[{ "type": "function", "function": { "name": "get_location_coordinate", "description": "根据POI名称,获得POI的经纬度坐标", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "POI名称,必须是中文", }, "city": { "type": "string", "description": "POI所在的城市名,必须是中文", } }, "required": ["location", "city"], } } }, { "type": "function", "function": { "name": "search_nearby_pois", "description": "搜索给定坐标附近的poi", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "longitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的经度", }, "latitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的纬度", }, "keyword": { "type": "string", "description": "目标poi的关键字", } }, "required": ["longitude", "latitude", "keyword"], } } }] ) return response.choices[0].messagedef get_location_coordinate(location, city="北京"): url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/text?key={amap_key}&keywords={location}®ion={city}" print(url) r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: return result["pois"][0] return Nonedef search_nearby_pois(longitude, latitude, keyword): url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v5/place/around?key={amap_key}&keywords={keyword}&location={longitude},{latitude}" print(url) r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() ans = "" if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: for i in range(min(3, len(result["pois"]))): name = result["pois"][i]["name"] address = result["pois"][i]["address"] distance = result["pois"][i]["distance"] ans += f"{name}\n{address}\n距离:{distance}米\n\n" return ans prompt = "北京三里屯附近的咖啡"messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "你是一个地图通,你可以找到任何地址。"}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt}]response = get_completion(messages)if (response.content is None): # 解决 OpenAI 的一个 400 bug response.content = ""messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中print("=====GPT回复=====")print(response)# 如果返回的是函数调用结果,则打印出来while (response.tool_calls is not None): # 1106 版新模型支持一次返回多个函数调用请求 for tool_call in response.tool_calls: args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments) print("参数:", args) if (tool_call.function.name == "get_location_coordinate"): print("Call: get_location_coordinate") result = get_location_coordinate(**args) elif (tool_call.function.name == "search_nearby_pois"): print("Call: search_nearby_pois") result = search_nearby_pois(**args) print("=====函数返回=====") print(result) messages.append({ "tool_call_id": tool_call.id, # 用于标识函数调用的 ID "role": "tool", "name": tool_call.function.name, "content": str(result) # 数值result 必须转成字符串 }) response = get_completion(messages) if (response.content is None): # 解决 OpenAI 的一个 400 bug response.content = "" print("=====GPT回复2=====") print(response) messages.append(response) # 把大模型的回复加入到对话中print("=====最终回复=====")print(response.content)4. 总结
通过本文的两个实战示例,是否已经对Function calling有了一个初步的认识?
其实就是将函数说明组织成json形式告诉大模型。其中最重要的函数和参数描述,是该函数的prompt,大模型通过这个描述来确定用户的输入是否匹配该函数,是否召回该函数。大模型如果召回了某个函数,那么我们就可以在本地去解析函数名和参数去使用,从而完成大模型与外部世界的连接。参考
OpenAI官方Function Calling教程: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling欢迎 点赞 + 关注 ?,促使我持续学习,持续干货输出。+v: jasper_8017 一起交流?,一起进步?。