✨个人主页: 熬夜学编程的小林
?系列专栏: 【C语言详解】 【数据结构详解】
目录
1、strncat 函数的使用
2、strncmp 函数的使用
3、strstr 函数的使用和模拟实现
4、strtok 函数的使用
5、strerror 函数的使用
6、perror 函数的使用
总结
1、strncat 函数的使用
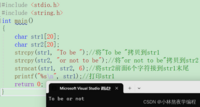
char * strncat ( char * destination, const char * source, size_t num );/* strncat example */#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main (){ char str1[20]; char str2[20]; strcpy (str1,"To be ");//将"To be "拷贝到str1 strcpy (str2,"or not to be");//将"or not to be"拷贝到str2 strncat (str1, str2, 6);//将str2前面6个字符接到str1末尾 printf("%s\n", str1);//打印str1 return 0;}2、strncmp 函数的使用
int strncmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2, size_t num );#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main(){char str1[20];char str2[20];strcpy(str1, "abcdef");//将"abcdef"拷贝到str1strcpy(str2, "abc");//将"abc"拷贝到str2int ret=strncmp(str1, str2, 4);//将返回值给赋值给retif (ret > 0)printf("str1 > str2\n");else if (ret < 0)printf("str1 < str2\n");elseprintf("str1 == str2\n");return 0;} 
3、strstr 函数的使用和模拟实现
char * strstr ( const char * str1, const char * str2);/* strstr example */#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main (){ char str[] ="This is a simple string"; char * pch; pch = strstr (str,"simple");//找到与simple相等的首地址赋值给pch strncpy (pch,"sample",6);//将sample前6个字符拷贝到pch 即修改str中的simple printf("%s\n", str);//打印str return 0;}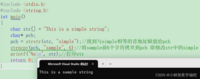 strstr的模拟实现:
strstr的模拟实现: char * strstr (const char * str1, const char * str2){ char *cp = (char *) str1;//str1为const修饰指针,需强制转化为可改指针 char *s1, *s2; if ( !*str2 )//str2为空返回str1首地址 return((char *)str1);//返回值为char*,需强转成char* while (*cp) { s1 = cp; s2 = (char *) str2; while ( *s1 && *s2 && !(*s1-*s2) )//*s1 s2不为'\0'且*s1==*s2, s1++, s2++; if (!*s2)//*s2为'\0'则返回cp return cp; cp++;//否则cp++ } return NULL;//没有找到则返回NULL}4、strtok 函数的使用
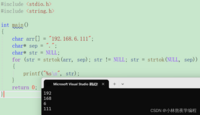
char * strtok ( char * str, const char * sep);#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main(){ char arr[] = "192.168.6.111"; char* sep = "."; char* str = NULL; for (str = strtok(arr, sep); str != NULL; str = strtok(NULL, sep)) { printf("%s\n", str); } return 0;}5、strerror 函数的使用
char * strerror ( int errnum );#include <errno.h>#include <string.h>#include <stdio.h>//我们打印⼀下0~10这些错误码对应的信息int main(){ int i = 0; for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++) { printf("%s\n", strerror(i)); } return 0;}Operation not permitted 不允许操作
No such file or directory 没有这样的文件或目录
No such process 没有这样的过程
Interrupted function call 中断的函数调用
Input/output error 输入/输出误差
No such device or address 没有这样的设备或地址
Arg list too long 参数列表太长
Exec format errorExec 格式错误
Bad file descriptor 错误的文件描述符
No child processes 无子进程 举例:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <errno.h>int main (){ FILE * pFile; pFile = fopen ("unexist.ent","r"); if (pFile == NULL) printf ("Error opening file unexist.ent: %s\n", strerror(errno)); return 0;} Error opening file unexist.ent: No such file or directory6、perror 函数的使用
void perror ( const char * str );#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <errno.h>int main (){ FILE * pFile; pFile = fopen ("unexist.ent","r"); if (pFile == NULL) perror("Error opening file unexist.ent"); return 0;}Error opening file unexist.ent: No such file or directory总结
本篇博客就结束啦,谢谢大家的观看,如果公主少年们有好的建议可以留言喔,谢谢大家啦!