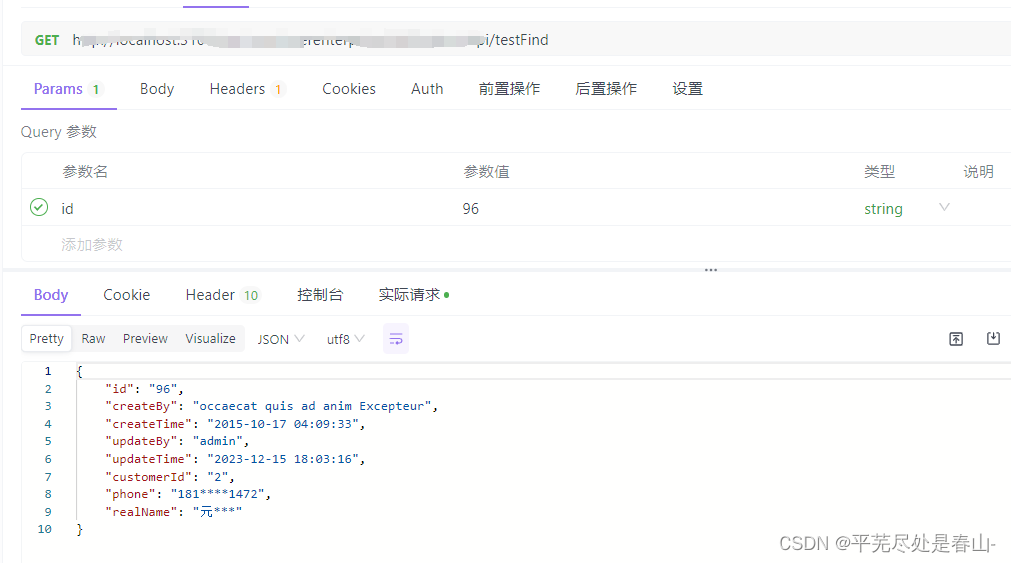
一、AES加密
1 加密工具类
使用KeyGenerator生成AES算法生成器
public class AESUtil { /** * 密钥长度: 128, 192 or 256 */ private static final int KEY_SIZE = 256; /** * 加密/解密算法名称 */ private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES"; /** * 随机数生成器(RNG)算法名称 */ private static final String RNG_ALGORITHM = "SHA1PRNG"; /** * 生成密钥的种子不可泄露 16位 */ public static final String KEY = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"; /** * 生成密钥对象 */ private static SecretKey generateKey(byte[] key) throws Exception { // 创建安全随机数生成器 SecureRandom random = SecureRandom.getInstance(RNG_ALGORITHM); // 设置 密钥key的字节数组 作为安全随机数生成器的种子 random.setSeed(key); // 创建 AES算法生成器 KeyGenerator gen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(ALGORITHM); // 初始化算法生成器 gen.init(KEY_SIZE, random); // 生成 AES密钥对象, 也可以直接创建密钥对象: return new SecretKeySpec(key, ALGORITHM); return gen.generateKey(); } /** * 数据加密: 明文 -> 密文 */ public static String encrypt(String content, byte[] key) throws Exception { // 生成密钥对象 SecretKey secKey; try { secKey = generateKey(key); // 获取 AES 密码器 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); // 初始化密码器(加密模型) cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secKey); // 加密数据, 返回密文 byte[] result = new byte[]{}; if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(content)){ byte[] plainBytes = content.getBytes("utf-8"); result = cipher.doFinal(plainBytes); } return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(result);//通过Base64转码返回 } catch (Exception e) { throw new Exception( "AES 加密失败:" + e.getMessage()); } } /** * 数据解密: 密文 -> 明文 */ public static String decrypt(String content, byte[] key) throws Exception { try { // 生成密钥对象 SecretKey secKey = generateKey(key); // 获取 AES 密码器 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); // 初始化密码器(解密模型) cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secKey); // 解密数据, 返回明文 byte[] result = new byte[]{}; if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(content)){ result = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(content)); } return new String(result, "utf-8"); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Exception("AES 解密失败:" + e.getMessage()); } } /** * 加密文件: 明文输入 -> 密文输出 */ public static void encryptFile(File plainIn, File cipherOut, byte[] key) throws Exception { aesFile(plainIn, cipherOut, key, true); } /** * 解密文件: 密文输入 -> 明文输出 */ public static void decryptFile(File cipherIn, File plainOut, byte[] key) throws Exception { aesFile(plainOut, cipherIn, key, false); } /** * AES 加密/解密文件 */ private static void aesFile(File plainFile, File cipherFile, byte[] key, boolean isEncrypt) throws Exception { // 获取 AES 密码器 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM); // 生成密钥对象 SecretKey secKey = generateKey(key); // 初始化密码器 cipher.init(isEncrypt ? Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE : Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secKey); // 加密/解密数据 InputStream in = null; OutputStream out = null; try { if (isEncrypt) { // 加密: 明文文件为输入, 密文文件为输出 in = new FileInputStream(plainFile); out = new FileOutputStream(cipherFile); } else { // 解密: 密文文件为输入, 明文文件为输出 in = new FileInputStream(cipherFile); out = new FileOutputStream(plainFile); } byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; // 循环读取数据 加密/解密 while ((len = in.read(buf)) != -1) { out.write(cipher.update(buf, 0, len)); } out.write(cipher.doFinal()); // 最后需要收尾 out.flush(); } finally { close(in); close(out); } } private static void close(Closeable c) { if (c != null) { try { c.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // nothing } } }}2、TypeHandler类型处理器
使用Mybatis中的TypeHandler类型处理器,定义一个实现自动加密解密的处理器
BaseTypeHandler背景
BaseTypeHandler是Mybatis中的一个基类,他的作用有如下几点:
类型处理器的基类Mybatis中的TypeHandler类型处理器,用于JavaType和jdbcType转换,用于 PreparedStatement 设置参数值和从 ResultSet 或 CallableStatement 中取出一个值。MyBatis 内置了很多TypeHandler可以实现BaseTypeHandler,自定义 TypeHandler
@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType.VARCHAR)public class AESEncryptHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Object> { @Override public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Object parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException { String content = (parameter == null) ? "" : parameter.toString(); try { ps.setString(i, AESUtil.encrypt(content, AESUtil.KEY.getBytes())); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public Object getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException { String columnValue = rs.getString(columnName); try { return AESUtil.decrypt(columnValue, AESUtil.KEY.getBytes()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public Object getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { String columnValue = rs.getString(columnIndex); try { return AESUtil.decrypt(columnValue, AESUtil.KEY.getBytes()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public Object getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { String columnValue = cs.getString(columnIndex); try { return AESUtil.decrypt(columnValue, AESUtil.KEY.getBytes()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } }}3、在实体Bean的字段上使用注解
/** * 手机号码 AES加密 */ @ApiModelProperty(value = "手机号码") @TableField(typeHandler = AESEncryptHandler.class) private java.lang.String phone;4、自定义SQL中使用resultMap
此时在mybatis plus中是可以正常使用的,但是当我们在xml中自定义SQL文件时无效,这时需要在xml中定义resultMap
(1) 在实体中设置:autoResultMap = true
@Data@NoArgsConstructor@AllArgsConstructor@TableName(value = "sys_user",autoResultMap = true)public class SysUser extends BaseBean implements Serializable {}(2)在xml中设置返回数据类型
<resultMap id="objectMap" type="com.depu.ems.bean.system.SysUser"> <id column="id" property="id" /> <result property="phone" column="phone" typeHandler="com.depu.ems.common.util.AESEncryptHandler"/> </resultMap> <select id="getObjectList" resultMap="objectMap">SELECT * FROM table_name </select>需要手机加密解密的使用场景:
1)xml中自定义sql 返回实体类不能解密,返回resultMap在map中配置typeHandler可以解密。
2)自带的wrappers更新不能加密,需要将数据加密后更新。
二、数据脱敏
1、引入hutool
<dependency> <groupId>cn.hutool</groupId> <artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId> <version>5.8.10</version></dependency>2、配合JackSon通过注解方式实现脱敏
(1)定义脱敏的枚举类
public enum DesensitizationTypeEnum { //自定义 MY_RULE, //用户id USER_ID, //中文名 CHINESE_NAME, //身份证号 ID_CARD, //座机号 FIXED_PHONE, //手机号 MOBILE_PHONE, //地址 ADDRESS, //电子邮件 EMAIL, //密码 PASSWORD, //中国大陆车牌,包含普通车辆、新能源车辆 CAR_LICENSE, //银行卡 BANK_CARD}(2)定义一个用于脱敏的 Desensitization 注解
/** * @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):运行时生效。 * @Target(ElementType.FIELD):可用在字段上。 * @JacksonAnnotationsInside:此注解可以点进去看一下是一个元注解,主要是用户打包其他注解一起使用。 * @JsonSerialize:上面说到过,该注解的作用就是可自定义序列化,可以用在注解上,方法上,字段上,类上,运行时生效等等,根据提供的序列化类里面的重写方法实现自定义序列化。 */@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@JacksonAnnotationsInside@JsonSerialize(using = DesensitizationSerialize.class)public @interface Desensitization { /** * 脱敏数据类型,在MY_RULE的时候,startInclude和endExclude生效 */ DesensitizationTypeEnum type() default DesensitizationTypeEnum.MY_RULE; /** * 脱敏开始位置(包含) */ int startInclude() default 0; /** * 脱敏结束位置(不包含) */ int endExclude() default 0;}(3)创建自定的序列化类
import cn.hutool.core.text.CharSequenceUtil;import cn.hutool.core.util.DesensitizedUtil;import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.BeanProperty;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonMappingException;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonSerializer;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializerProvider;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.ContextualSerializer;import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;import org.jeecg.common.constant.enums.DesensitizationTypeEnum;import org.jeecg.common.system.annotation.Desensitization;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Objects;/** * @description: 自定义序列化类 * @author: Zhangxue * @time: 2023/12/15 15:57 */@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic class DesensitizationSerialize extends JsonSerializer<String> implements ContextualSerializer { private DesensitizationTypeEnum type; private Integer startInclude; private Integer endExclude; @Override public void serialize(String str, JsonGenerator jsonGenerator, SerializerProvider serializerProvider) throws IOException { switch (type) { // 自定义类型脱敏 case MY_RULE: jsonGenerator.writeString(CharSequenceUtil.hide(str, startInclude, endExclude)); break; // userId脱敏 case USER_ID: jsonGenerator.writeString(String.valueOf(DesensitizedUtil.userId())); break; // 中文姓名脱敏 case CHINESE_NAME: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.chineseName(String.valueOf(str))); break; // 身份证脱敏 case ID_CARD: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.idCardNum(String.valueOf(str), 1, 2)); break; // 固定电话脱敏 case FIXED_PHONE: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.fixedPhone(String.valueOf(str))); break; // 手机号脱敏 case MOBILE_PHONE: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.mobilePhone(String.valueOf(str))); break; // 地址脱敏 case ADDRESS: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.address(String.valueOf(str), 8)); break; // 邮箱脱敏 case EMAIL: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.email(String.valueOf(str))); break; // 密码脱敏 case PASSWORD: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.password(String.valueOf(str))); break; // 中国车牌脱敏 case CAR_LICENSE: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.carLicense(String.valueOf(str))); break; // 银行卡脱敏 case BANK_CARD: jsonGenerator.writeString(DesensitizedUtil.bankCard(String.valueOf(str))); break; default: } } @Override public JsonSerializer<?> createContextual(SerializerProvider serializerProvider, BeanProperty beanProperty) throws JsonMappingException { if (beanProperty != null) { // 判断数据类型是否为String类型 if (Objects.equals(beanProperty.getType().getRawClass(), String.class)) { // 获取定义的注解 Desensitization desensitization = beanProperty.getAnnotation(Desensitization.class); // 为null if (desensitization == null) { desensitization = beanProperty.getContextAnnotation(Desensitization.class); } // 不为null if (desensitization != null) { // 创建定义的序列化类的实例并且返回,入参为注解定义的type,开始位置,结束位置。 return new DesensitizationSerialize(desensitization.type(), desensitization.startInclude(), desensitization.endExclude()); } } return serializerProvider.findValueSerializer(beanProperty.getType(), beanProperty); } return serializerProvider.findNullValueSerializer(null); }}3、使用
使用@Desensitization注解实现脱敏
/** * 手机号码 AES加密、脱敏 */ @ApiModelProperty(value = "手机号码") @TableField(typeHandler = AESEncryptHandler.class) @Desensitization(type = DesensitizationTypeEnum.MOBILE_PHONE) private java.lang.String phone;三、测试运行结果
1、增
测试程序: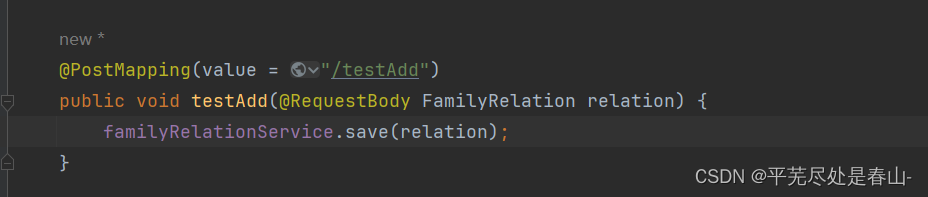
调用: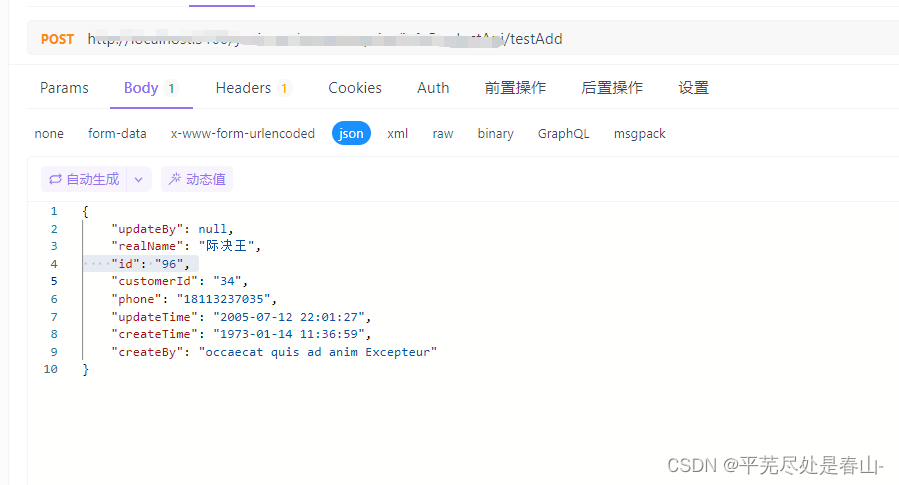
数据库中结果: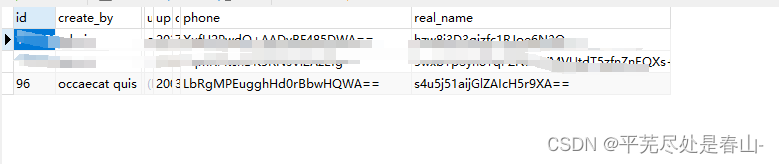
2、查
测试程序: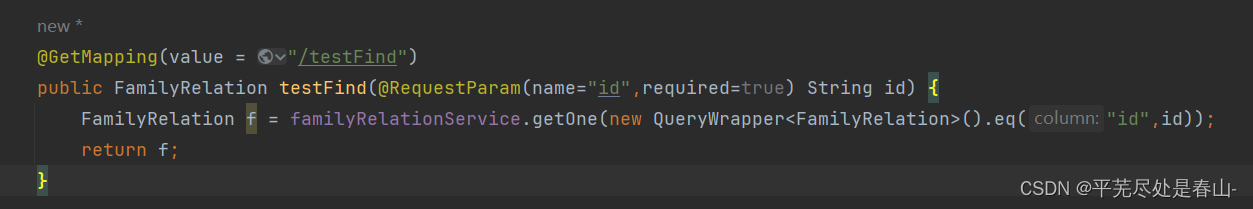
调用: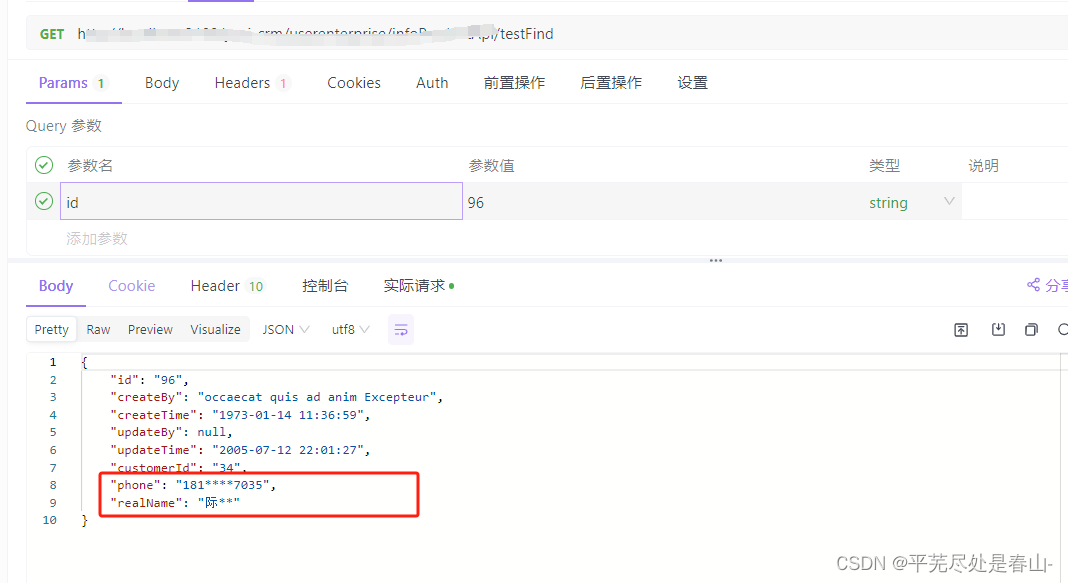
3、改
测试程序: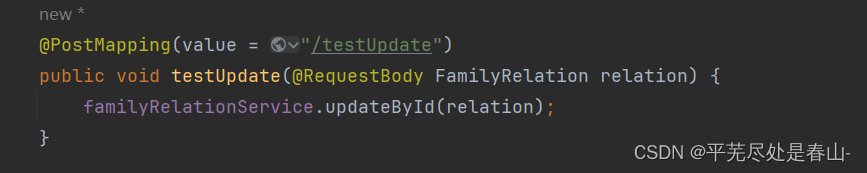
调用: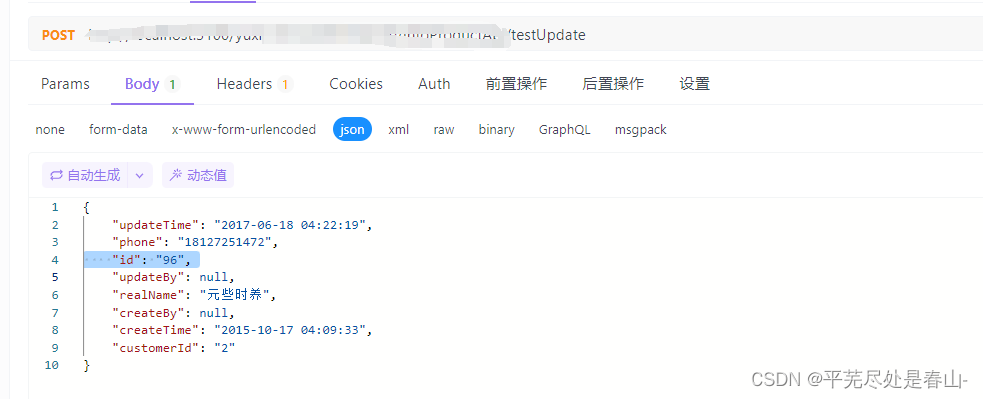
数据库结果: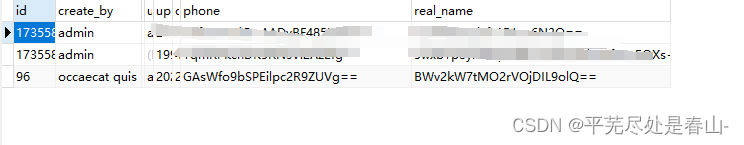
再次查询: