目录
一、Vuex是什么?
二、什么时候使用Vuex?
三、Vuex的核心概念和API
1.state
2.mutations
3. actions
4. getters
5. modules
四、Vuex的运作流程
五、应用举例
1.安装
2.创建store
3.在main.js文件中使用store
4.创建Home.vue组件
5.在App.vue中导入Home.vue
六、vuex中各种辅助函数的用法,可以使我们更加方便的运用vuex
1. …mapState
2. …mapGetters
3. …mapMutations:使用辅助函数后载荷的传参,直接在调用的地方进行传参便可
4. …mapActions
5. 修改后Home.vue组件
一、Vuex是什么?
Vuex在Vue项目开发时使用的状态管理工具。简单来说,就是对Vue的应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写)Vuex实现了一个单向数据流,在全局拥有一个State存放数据,当组件要更改State中的数据时,必须通过Mutation进行,Mutation同时提供了订阅者模式供外部插件调用获取State数据的更新。而当所有异步操作(常见于调用后端接口异步获取更新数据)或批量的同步操作需要走Action,但Action也是无法直接修改State的,还是需要通过Mutation来修改State的数据。最后,根据State的变化,渲染到视图上二、什么时候使用Vuex?
不适用场景:小型简单应用,用 Vuex 是繁琐冗余的,更适合使用简单的store模式适用场景: 构建一个中大型单页应用,可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,即多个组件共享状态多个视图依赖于同一状态:此时传参的方法对于多层嵌套的组件将会非常繁琐,并且对于兄弟组件间的状态传递无能为力。来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态:此时采用父子组件直接引用或者通过事件来变更和同步状态的多份拷贝,通常会导致无法维护的代码在这些情况下就适合用Vuex进行全局单例模式管理三、Vuex的核心概念和API
流程:View -> Actions -> Mutations -> State -> View
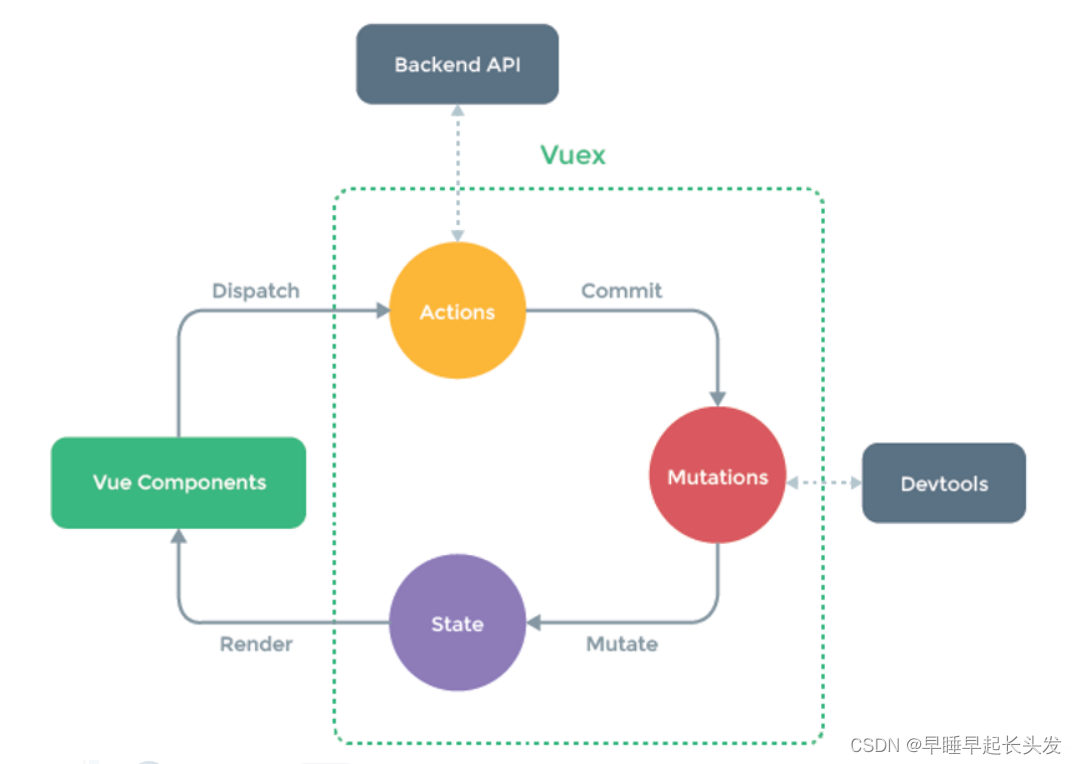
1.state
vuex 管理的状态对象它应该是唯一的 const state = {
xxx: initValue
}
2.mutations
包含多个直接更新 state 的方法(回调函数)的对象谁来触发: action 中的 commit(‘mutation 名称’)或者在组件中通过this.$store.commit(‘xxx’,params)使用。这个和组件中的自定义事件类似只能包含同步的代码, 不能写异步代码 const mutations = {
xxx(state, {data1}) {
// 更新 state 的某个属性
}
}
3. actions
提交 mutation,异步操作。包含多个事件回调函数的通过执行: commit()来触发 mutation 的调用, 间接更新 state谁来触发: 组件中通过this.$store.dispatch(‘action 名称’, data1)可以包含异步代码(axios) const actions ={
zzz ({commit, state}, data1)
commit(‘xxx’, {data1})
}
}
4. getters
对数据获取之前的再次编译,可以理解为state的计算属性谁来读取: 组件中: this.$store.getters.xxx const getters ={
xxx (state) {
return …
}
}
5. modules
包含多个 module:store的子模块,为了开发大型项目,方便状态管理而使用的,即将store分割为模块,使store对象不会太臃肿。一个 module 是一个 store 的配置对象与一个组件(包含有共享数据)对应 四、Vuex的运作流程
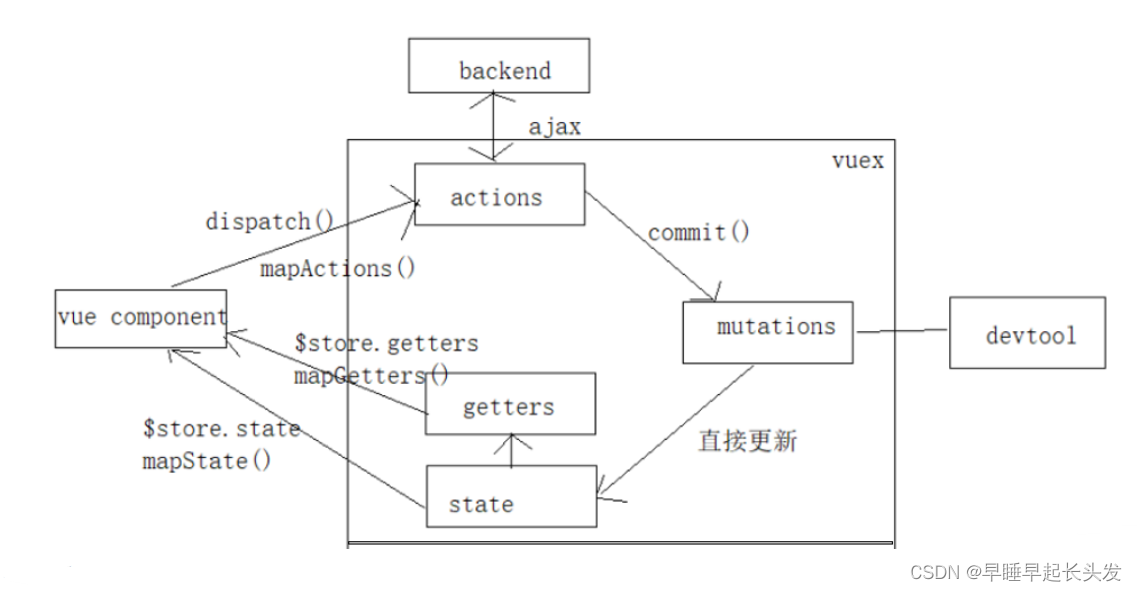
流程详解:
在组件(页面)中,通过dispatch()或mapActions()这个函数分发给actions的函数去处理。actions的函数可以与后台交互,也可以通过 commit() 提交给mutations去处理。mutations 可以直接与devtool(如本地存储工具 → 在实例代码中的utils里的storageUtils.js)交互与直接更新state(数据状态)。如果有计算属性(get函数写在getters里面),则状态通过getters的$store.getters()或mapGetters()来更新组件;反之就通过$store.state()或者mapState()的方式来更新组件。五、应用举例
1.安装
npm i vuex -S
2.创建store
store:src/store/index.js
import {createStore} from "vuex";export default createStore({ //state全局存储数据的对象 state:{ count:0, age:0 }, //计算属性(可选的):用于获取state属性的值。 //(1)若定义了getters:获取属性值的方法是$store.getters()或mapGetters() //(2)若没有定义getters,获取state属性值的方法是:$store.state()或者mapState() getters:{ getterAge:(state)=>{ //state是原来的状态 return state.age = 25 //return返回的是新的状态 } }, //mutations:用于修改state状态值,定义的函数必须是同步的 mutations:{ addCount(state,obj){ //state是原来的state,obj是调用该方法时传入的对象 return state.count += obj.num }, subCount(state,obj){ return state.count -=obj.num } },// actions:通过动作的提交,来调用mutations中方法,修改state属性 actions:{ // 异步加法函数 addCountAsyn(context){//context:表示上下文环境,就派发动作的对象(组件) setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('addCount',{ num:1 }) },3000) }, // 异步减法函数 subCountAsyn(context){ setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('subCount',{ num:1 }) },3000) } }})3.在main.js文件中使用store
import { createApp } from 'vue'import './style.css'import App from './App.vue'import store from './store/index'const app= createApp(App);app.use(store)app.mount('#app')4.创建Home.vue组件
<template> <div> <h2>通过getter获得计算后的年龄:{{ getterAge }}</h2> <p>Count:{{ count }}</p> <button @click="handlerAdd()">加1</button> <button @click="handlerSub()">减1</button> <button @click="handlerAddAnys()">异步增加(2s后执行)</button> <button @click="handlerSubAnys()">异步减少(2s后执行)</button> </div></template><script>export default { name: "Home", computed: { count(){ return this.$store.state.count }, getterAge(){ return this.$store.getters.getterAge } }, methods: { handlerAdd(){ this.$store.commit("addCount",{ num: 1 }) }, handlerSub(){ this.$store.commit("subCount",{ num: 1 }) }, handlerAddAnys(){ this.$store.dispatch('addCountAsyn') }, handlerSubAnys(){ this.$store.dispatch('subCountAsyn') } }}</script><style scoped></style>5.在App.vue中导入Home.vue
import Home from './components/Home.vue'<template> <img src="./assets/vue.svg" class="logo vue" alt="Vue logo" /> <Home/></template>六、vuex中各种辅助函数的用法,可以使我们更加方便的运用vuex
1. …mapState
count(){ return this.$store.state.count}, 等价于...mapState([ 'count']),2. …mapGetters
count(){ return this.$store.state.count}, 等价于...mapState([ 'count']),3. …mapMutations:使用辅助函数后载荷的传参,直接在调用的地方进行传参便可
handlerAdd(){ this.$store.commit("addCount",{ num: 1 })},handlerSub(){ this.$store.commit("subCount",{ num: 1 })},等价于...mapMutations({ handlerAdd: 'addCount', handlerSub: 'subCount'}) 4. …mapActions
handlerAddAnys(){ this.$store.dispatch('addCountAsyn')},handlerSubAnys(){ this.$store.dispatch('subCountAsyn')}等价于...mapActions({ handlerAddAnys: 'addCountAsyn', handlerSubAnys: 'subCountAsyn'})修改上例中的Home.vue组件

5. 修改后Home.vue组件
<template><div> <h3>通过Getters获取age:{{ getterAge }}</h3> <p>Count:{{ count }}</p> <button @click="handlerAdd({num:1})">同步加一</button> <button @click="handlerSub({num:1})">同步减一</button> <button @click="handlerAddAsyn">异步加一(3s后执行)</button> <button @click="handlerSubAsyn">异步减一(3s后执行)</button></div></template><script>import { mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions } from 'vuex'export default { name: "Home", computed: { // count() { //使用非getters方法获取state的count属性值 // return this.$store.state.count // }, ...mapState(['count']), // getterAge() {//使用getters方法获取state的age属性 // return this.$store.getters.getterAge // } ...mapGetters(['getterAge']) }, methods: { // handlerAdd() {//同步加一 // this.$store.commit('addCount', {num: 1});//通过commit提交动作:addCount,给mutation // }, // handlerSub() {//同步减一 // this.$store.commit('subCount', {num: 1}) // }, ...mapMutations({ handlerAdd:'addCount', handlerSub:'subCount' }), // handlerAddAsyn() {//异步加一 // this.$store.dispatch('addCountAsyn');//通过dispatch方法将动作派发给action,再由action提交给mutation // }, // handlerSubAsyn() {//异步加一 // this.$store.dispatch('subCountAsyn');//通过dispatch方法将动作派发给action,再由action提交给mutation // } ...mapActions({ handlerAddAsyn:'addCountAsyn', handlerSubAsyn:'subCountAsyn' }) }}</script><style scoped></style>