文章目录
二叉树链式结构的实现前序遍历中序遍历后序遍历层序遍历树节点个数树的深度第K层节点个数 查找二叉树中的元素
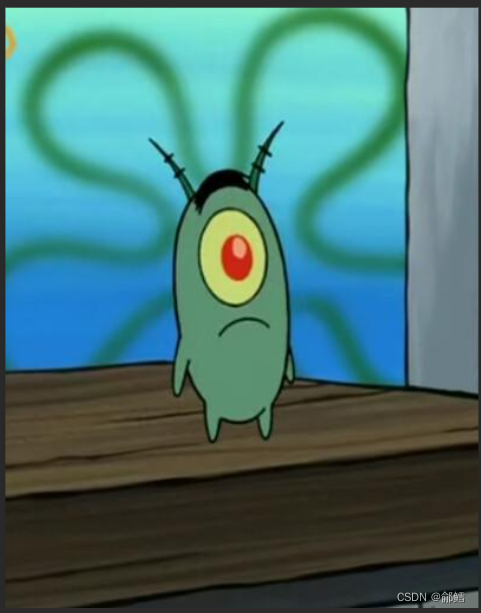

二叉树链式结构的实现
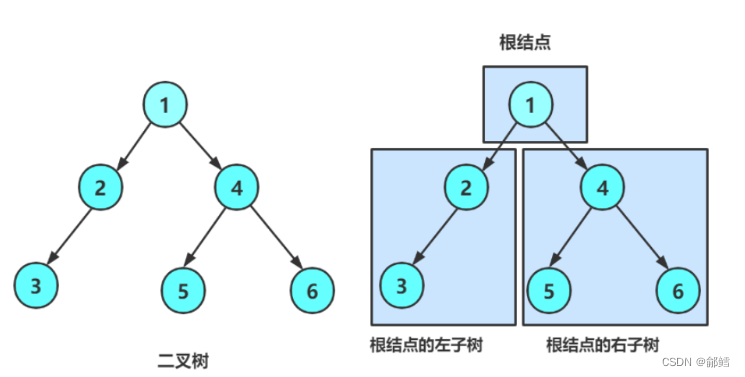
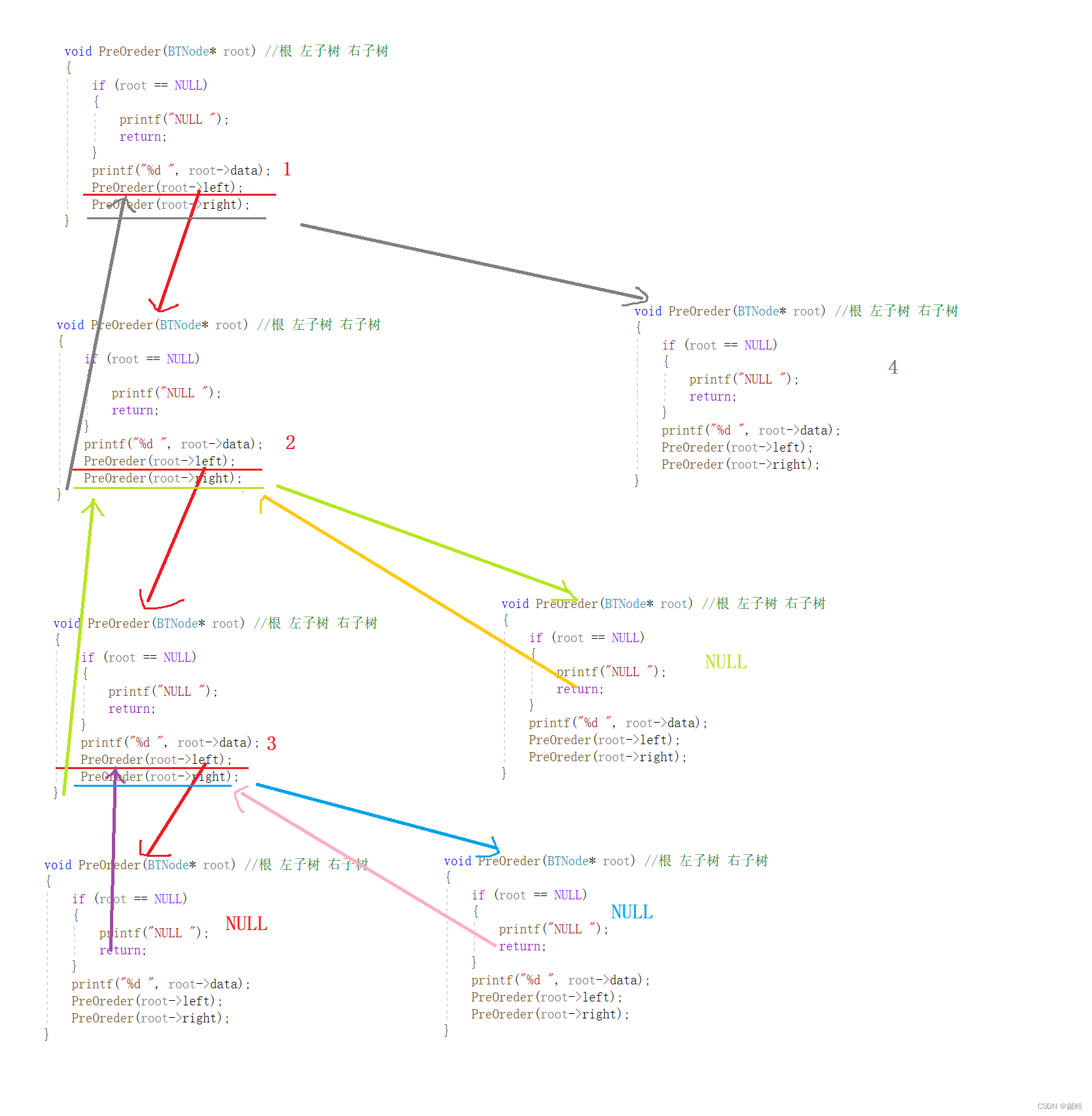
typedef int BinartTreeType;typedef struct BinarytTreeNode{BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子}BTNode;前序遍历
访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前
简单来说就是 根节点 左子树 右子树
1 2 3 NULL NULL NULL 4 5 NULL NULL 6 NULL NULL
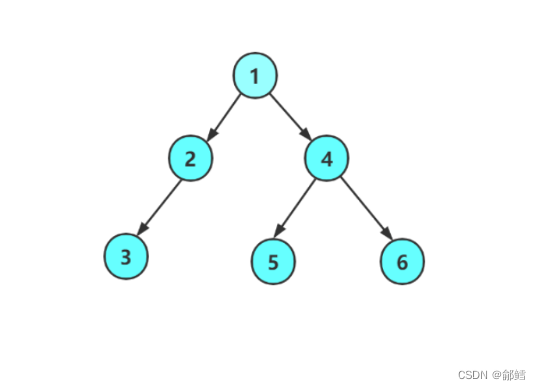
BTNode* CreateTree() { BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1); BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2); BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3); BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4); BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5); BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6); BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7); node1->left = node2; node1->right = node4; node2->left= node3; node4->left = node5; node4->right = node6; //node3->right = node7; return node1; } void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树 { if (root == NULL) { printf("NULL "); return; } printf("%d ", root->data); PreOreder(root->left); PreOreder(root->right); } int main() { BTNode* root = CreateTree(); PreOreder(root); return 0; }从根节点1开始遍历 , 遍历完1这个根节点 ,然后去遍历1这个根节点的左子树(2) ,遍历到节点2时 , 但是节点 2 又被分成根节点 (2)、左子树(3) 、右子树(NULL) 。遍历到节点3时 ,节点3又被分成根节点 (3)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,对于节点3而言 ,3的左子树(NULL)走完 ,就走节点3的右子树(NULL) , 3这一整棵树作为2的左子树 ,2的左子树走完了 ,就走2的右子树(NULL) , 2的整棵树作为1的左子树, ,2这一整棵树走完了, 就走到1的右子树4 ,但是节点 4 又被分成根节点 (4)、左子树(5) 、右子树(6) ,然后走到4的左子树5 ,但是节点 5 又被分成根节点 (5)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,5的整棵树作为4的左子树, ,5这一整棵树走完了,就来到了4的右子树(6),但是节点 6又被分成根节点 (6)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL), 4的左子树,右子树都遍历完了 ,4的这一整棵树也遍历完了,4这一整棵树是作为1的右子树 ,
前序遍历就是将每一个节点不断拆分成 根,左子树 ,右子树的一个过程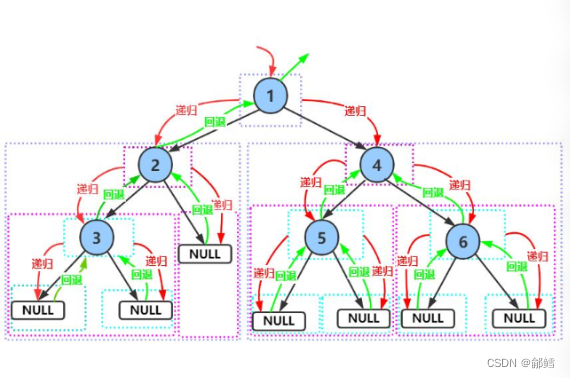
前序遍历递归展开图,以左子树为例,右子树并未画出
中序遍历
访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)
简单来说就是 左子树 根节点 右子树
NULL 3 NULL 2 NULL 1 NULL 5 NULL 4 NULL 6 NULL
节点 1被分成根节点 (1)、左子树(2) 、右子树(4) ,先遍历1的左子树2,遇到节点2不能直接访问,得继续拆分 , 节点 2被分成根节点 (2)、左子树(3) 、右子树(NULL) ,遇到节点3,节点3又被分成根节点 (3)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,那什么样的情况,能直接访问左子树? 遇到空树就可以直接访问,因为空树不能再被拆分,是最小规模的子问题 。 所以第一个访问的是节点3的左子树(NULL) ,再到根节点(3) ,再到3的右子树(NULL) 。3的整棵树作为2的左子树, ,3这一整棵树走完了。2的左子树访问完了 ,就可以访问根节点2了 ,然后到2的右子树(NULL),2的整棵树作为1的左子树, ,2这一整棵树走完了 ,就可以访问根节点1了 ,然后到1的右子树(4) ,遇到节点4不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 4 又被分成根节点 (4)、左子树(5) 、右子树(6),遇到节点5不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 5 又被分成根节点 (5)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,然后访问5的左子树(NULL) ,、5(根节点)、5的右子树(NULL),5这一整棵树走完了。4的左子树访问完了 ,就可以访问根节点4了 ,然后到4的右子树(6),遇到节点6不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 6又被分成根节点 (6)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,然后访问6的左子树(NULL) ,、6(根节点)、6的右子树(NULL),6这一整棵树走完了,4的右子树访问完了 , 4这一整棵树作为1的右子树也访问完了
中序遍历访问的第一个一定是NULL ,因为任何一个节点都可以被视作根节点 ,有些书上中序遍历访问的第一个不是NULL ,是因为书上省略了
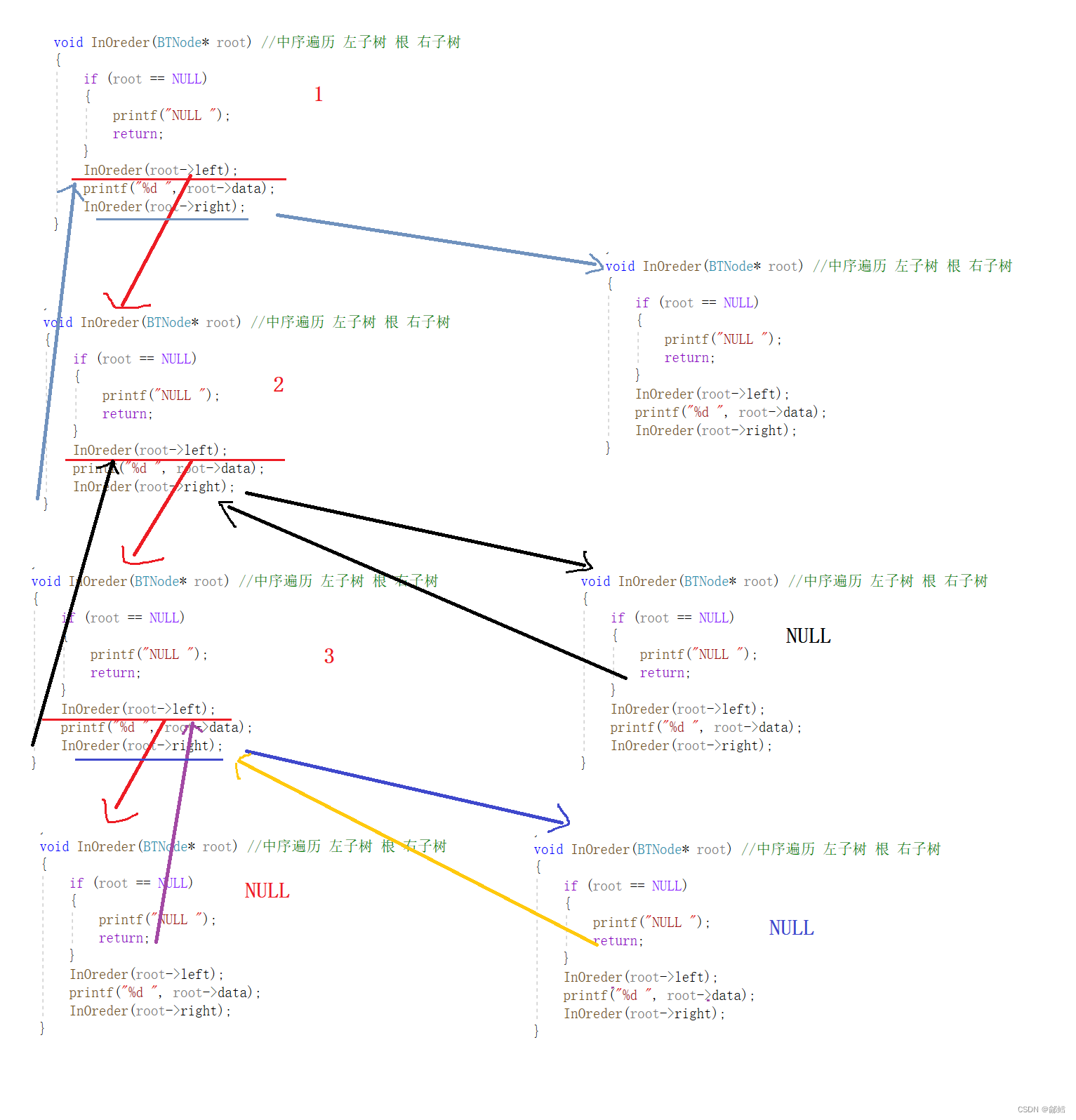
BTNode* CreateTree() { BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1); BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2); BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3); BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4); BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5); BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6); BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7); node1->left = node2; node1->right = node4; node2->left= node3; node4->left = node5; node4->right = node6; //node3->right = node7; return node1; } void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树 { if (root == NULL) { printf("NULL "); return; } printf("%d ", root->data); PreOreder(root->left); PreOreder(root->right); } void InOreder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历 左子树 根 右子树 { if (root == NULL) { printf("NULL "); return; } InOreder(root->left); printf("%d ", root->data); InOreder(root->right); } int main() { BTNode* root = CreateTree();/* PreOreder(root);*/ InOreder(root); PostOreder(root); return 0; }中序遍历递归展开图,以左子树为例,右子树并未画出
后序遍历
访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后
简单来说就是 左子树 右子树 根
NULL NULL 3 NULL 2 NULL NULL 5 NULL NULL 6 4 1
遇到节点1不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点1又被分成根节点 (1)、左子树(2) 、右子树(4) ,遇到节点2不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 2被分成根节点 (2)、左子树(3) 、右子树(NULL) ,遇到节点3不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点3又被分成根节点 (3)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL), 先访问3的左子树(NULL) ,再访问3的右子树(NULL) ,然后才到根节点(3),3这一整棵树走完了。2的左子树访问完了 ,再访问2的右子树(NULL)了,然后才到根节点(2)。2的整棵树作为1的左子树, ,2这一整棵树走完了 ,就走到节点1,但是遇到节点1不能直接访问,然后走到1的右子树(4),但是遇到节点4不能直接访问 得继续拆分,节点 4 又被分成根节点 (4)、左子树(5) 、右子树(6),来到4的左子树节点5,还是不能直接访问 ,得继续拆分,节点 5 又被分成根节点 (5)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL) ,先访问5的左子树(NULL) ,再访问5的右子树(NULL) ,然后才到根节点(5),5这一整棵树走完了。4的左子树访问完了 ,再访问4的右子树(6)了,遇到节点6不能直接访问,得继续拆分,节点 6又被分成根节点 (6)、左子树(NULL) 、右子树(NULL),先访问6的左子树(NULL) ,再访问6的右子树(NULL),然后才到根节点(6),6的整棵树作为4的右子树, ,6这一整棵树走完了 ,就走到节点4, 4的整棵树作为1的右子树, ,4这一整棵树走完了 ,就走到节点1
BTNode* CreateTree() { BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1); BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2); BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3); BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4); BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5); BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6); BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7); node1->left = node2; node1->right = node4; node2->left= node3; node4->left = node5; node4->right = node6; //node3->right = node7; return node1; } void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树 { if (root == NULL) { printf("NULL "); return; } printf("%d ", root->data); PreOreder(root->left); PreOreder(root->right); } void InOreder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历 左子树 根 右子树 { if (root == NULL) { printf("NULL "); return; } InOreder(root->left); printf("%d ", root->data); InOreder(root->right); } PostOreder(BTNode* root) // 后序遍历 左子树 右子树 根 { if (root == NULL) { printf("NULL "); return; } PostOreder(root->left); PostOreder(root->right); printf("%d ", root->data); } int main() { BTNode* root = CreateTree();/* PreOreder(root);*/ InOreder(root); PostOreder(root); return 0; }层序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6
层序遍历使用队列先进先出的特性,二叉树的上一层 出队,二叉树的下一层入队
根节点1入队 ,然后1节点出队 ,再把1节点的左孩子2 、右孩子4入队 , 再2节点出队 ,2的左孩子3入队 ,2的右孩子空树 ,空树就不入队了 ,4出队 ,4的左孩子5入队 ,右孩子6入队 ,
最后3出队 ,左右孩子都是空树就不入队了,5出队 ,左右孩子都是空树就不入队了,6出队 ,左右孩子都是空树就不入队了, 当所有节点出队也就结束了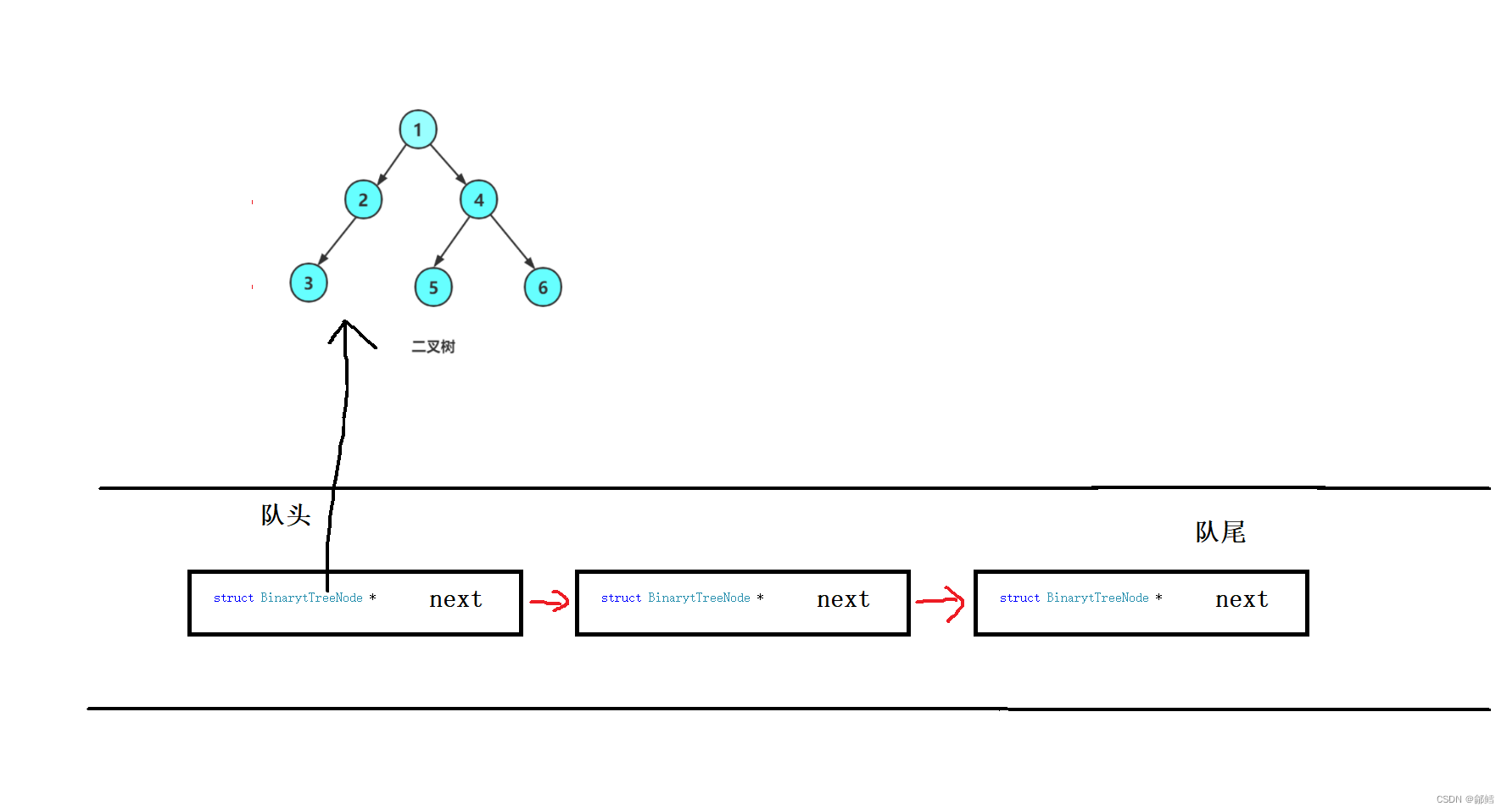
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root) //层序遍历 {Queue q;QueueInit(&q);//遍历 //不是空树 if (root)QueuePush(&q ,root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q) ){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%d ",front->data); if (front->left)//不是空树 入队{QueuePush(&q, front->left);}if (front->right) //不是空树 入队{QueuePush(&q, front->right);}}QueueDestory(&q);}树节点个数
采用分治方法
分治法的设计思想是:将一个难以直接解决的大问题,分割成一些规模较小的相同问题,以便各个击破,分而治之。
分治策略是:对于一个规模为n的问题,若该问题可以容易地解决(比如说规模n较小)则直接解决,否则将其分解为k个规模较小的子问题,这些子问题互相独立且与原问题形式相同,递归地解这些子问题,然后将各子问题的解合并得到原问题的解。这种算法设计策略叫做分治法。
typedef int BinartTreeType;typedef struct BinarytTreeNode{BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x){BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){printf("malloc fail");exit(-1);}//扩容成功node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;}BTNode* CreateTree(){BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;//node3->right = node7;return node1;}//int TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize)//{//if (root == NULL)//return;//(*psize)++;//TreeSize(root->left, psize);//TreeSize(root->right, psize);//}int TreeSize(BTNode* root) //分治思想{return root == NULL ? 0 :TreeSize(root->left ) +TreeSize(root->right)+ 1; // +1 是加上自己}int main(){BTNode* root = CreateTree();printf("%d ", TreeSize(root));return 0;}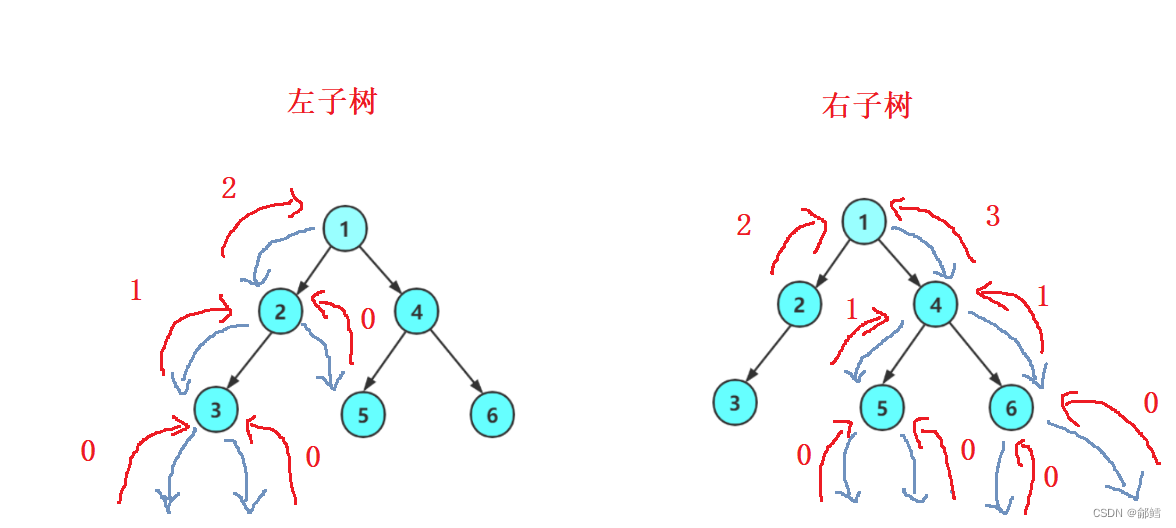
树的深度
采用分治思想 ,求出最长的那一条
当前树的高度 = 左右子树高度大的+1
typedef int BinartTreeType;typedef struct BinarytTreeNode{BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x){BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){printf("malloc fail");exit(-1);}//扩容成功node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;}BTNode* CreateTree(){BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;//node3->right = node7;return node1;}//int TreeHight(BTNode* root) //求整棵树的高度//{//if (root == NULL)//{//return 0;//}//return TreeHight(root->left) > TreeHight(root->right) //? TreeHight(root->left) + 1: TreeHight(root->right) + 1;//}int TreeHeight(BTNode* root){if( root == NULL)return 0; int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1: rightHeight + 1;}int main(){BTNode* root = CreateTree();printf("%d ", TreeHeight(root));return 0;}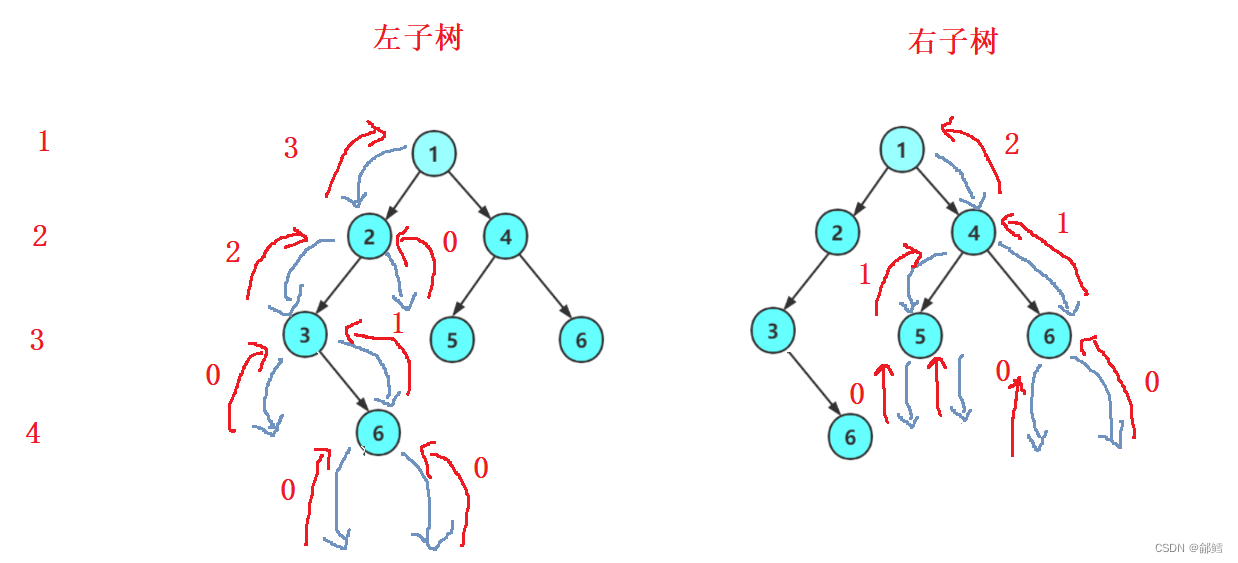
第K层节点个数
根的第K层节点个数 = 左子树的第K-1层个数 + 右子树的第K-1 层个数
typedef int BinartTreeType;typedef struct BinarytTreeNode{BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x){BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){printf("malloc fail");exit(-1);}//扩容成功node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;}BTNode* CreateTree(){BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;node3->right = node7;return node1;}int TreeKlevel(BTNode* root,int k) //第K层节点个数{if (root == NULL)return 0;if (k == 1) // 隐含root != NULL , 此时是第K层return 1;//左子树 K-1 个数 + 右子树K-1 个数 int leftKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->left, k - 1);int rightKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->right, k - 1);return leftKlevel + rightKlevel;}int main(){BTNode* root = CreateTree();int k = 3;printf("%d ", TreeKlevel(root,k));return 0;}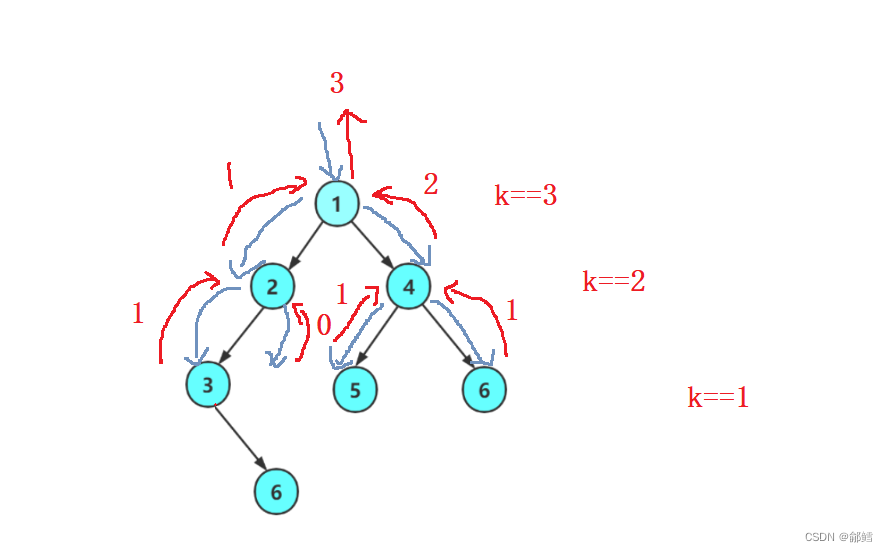
查找二叉树中的元素
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root , BinartTreeType x )//查找二叉树中的元素{//左子树 右子树 根if (root == NULL)return NULL;if (root->data == x)return root;//保存BTNode* lret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);if (lret)return lret;//保存BTNode* rret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);if (rret)return rret;//没有找到return NULL;}递归展开图:

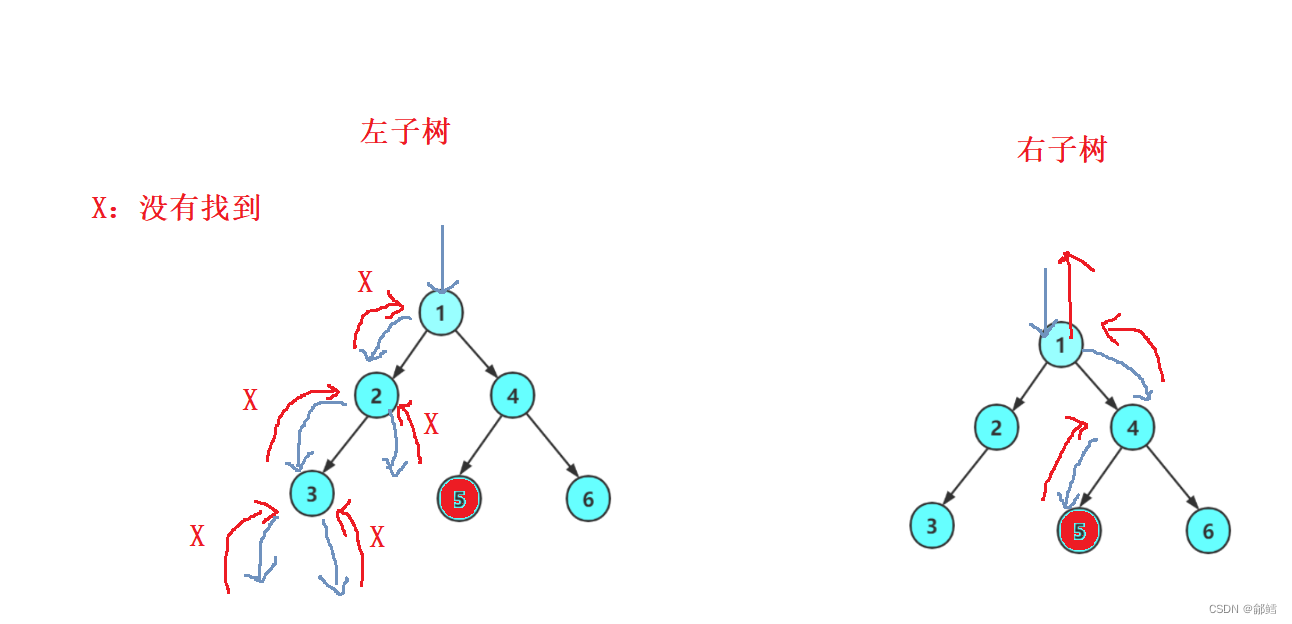
完整代码
Test.c
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<assert.h>#include"Queue.h"typedef int BinartTreeType;typedef struct BinarytTreeNode{BinartTreeType data;//节点存放的数据struct BinarytTreeNode* left; //指向当前节点的左孩子struct BinarytTreeNode* right;//指向当前节点的右孩子}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BinartTreeType x){BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){printf("malloc fail");exit(-1);}//扩容成功node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;}BTNode* CreateTree(){BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);BTNode* node7 = BuyNode(7);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;node3->right = node7;return node1;}//void PreOreder(BTNode* root) //根 左子树 右子树 //{//if (root == NULL)//{//printf("NULL ");//return;//}//printf("%d ", root->data);//PreOreder(root->left);//PreOreder(root->right);//}//void InOreder(BTNode* root) //中序遍历 左子树 根 右子树//{//if (root == NULL)//{//printf("NULL ");//return;//}//InOreder(root->left);//printf("%d ", root->data);//InOreder(root->right);//}////void PostOreder(BTNode* root) // 后序遍历 左子树 右子树 根//{//if (root == NULL)//{//printf("NULL ");//return;//}//PostOreder(root->left);//PostOreder(root->right);//printf("%d ", root->data);//}//int TreeSize(BTNode* root, int* psize)//{//if (root == NULL)//return;//(*psize)++;//TreeSize(root->left, psize);//TreeSize(root->right, psize);//}////int TreeSize(BTNode* root) //分治思想//{//return root == NULL ? 0 ://TreeSize(root->left)//+ TreeSize(root->right)//+ 1; // +1 是加上自己////}//int TreeHight(BTNode* root) //求整棵树的高度//{//if (root == NULL)//{//return 0;//}//return TreeHight(root->left) > TreeHight(root->right) //? TreeHight(root->left) + 1: TreeHight(root->right) + 1;//}//int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)//{//if( root == NULL)//return 0;// //int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);//int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);////return leftHeight > rightHeight //? leftHeight + 1//: rightHeight + 1;////}//int TreeKlevel(BTNode* root,int k) //第K层节点个数//{//if (root == NULL)//return 0;//if (k == 1) // 隐含root != NULL , 此时是第K层//return 1;////左子树 K-1 个数 + 右子树K-1 个数 //int leftKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->left, k - 1);//int rightKlevel = TreeKlevel(root->right, k - 1);//return leftKlevel + rightKlevel;////}BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root , BinartTreeType x )//查找二叉树中的元素{//左子树 右子树 根if (root == NULL)return NULL;if (root->data == x)return root;//保存BTNode* lret = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);if (lret)return lret;//保存BTNode* rret = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);if (rret)return rret;//没有找到return NULL;}void LevelOrder(BTNode* root) //层序遍历 {Queue q;QueueInit(&q);//遍历 //不是空树 if (root)QueuePush(&q ,root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q) ){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%d ",front->data); if (front->left)//不是空树 入队{QueuePush(&q, front->left);}if (front->right) //不是空树 入队{QueuePush(&q, front->right);}}QueueDestory(&q);}int main(){BTNode* root = CreateTree();/* PreOreder(root);*/ // InOreder(root); // PostOreder(root);//int size1 = 0;//TreeSize(root, &size1);//printf("%d ", size1);//printf("%d ", TreeSize(root));//printf("%d ", TreeHeight(root));/*int k = 3;printf("%d ", TreeKlevel(root,k));*//*printf("%p ", BinaryTreeFind(root, 2));*/LevelOrder(root);return 0;}Queue.h
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdbool.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<assert.h>typedef struct BinarytTreeNode * QueueNodeTypeData;typedef struct QueueNode{struct QueueNode* next;QueueNodeTypeData data;}QueueNodeType;typedef struct Queue{QueueNodeType * tail; // 队尾QueueNodeType * head; //队头int size; } Queue; // 链式结构:表示队列void QueueInit(Queue* pq); // 初始化 void QueueDestory(Queue* pq); //队列的销毁void QueuePush(Queue* pq , QueueNodeTypeData x ); // 队尾入队列void QueuePop(Queue* pq); //队头出队列int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//获取队列中有效元素个数bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); // 判断队列是否为空 QueueNodeTypeData QueueFront(Queue* pq); //获取队列头部元素QueueNodeTypeData QueueBack(Queue* pq); //获取队列尾部元素Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"void QueueInit(Queue* pq){assert(pq);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;}void QueueDestory(Queue* pq) //队列的销毁{assert(pq);QueueNodeType * cur = pq->head;//遍历 while (cur){QueueNodeType* next = cur->next; //保存下一个节点的地址free(cur); //释放当前节点cur = next; } pq->tail = pq->head = NULL;pq->size = 0;}void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QueueNodeTypeData x) // 入队 {assert(pq);QueueNodeType* newnode =(QueueNodeType*) malloc( sizeof(QueueNodeType) );if (newnode == NULL){printf(" malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;//扩容成功//第一次入队if ( pq->head == NULL){ assert(pq->tail == NULL); //pq->head ==NULL , pq->tail != NULL ,就是出问题了pq->tail = pq->head = newnode;}else //非第一次入队{pq->tail->next = newnode; // 类似尾插pq->tail = newnode; // 更新tail 指针}pq->size++;}void QueuePop(Queue* pq) //队头出队列{assert(pq);assert(pq->head != NULL); //只有一个节点if (pq->head->next == NULL) {free(pq->tail); //出队pq->tail = pq->head = NULL;}// 多个节点else{QueueNodeType* next = pq->head->next; // 保存下一个节点的地址 free(pq->head); // 出队pq->head = NULL;pq->head = next; //更新pq->head ,往后走 }pq->size--;}int QueueSize(Queue* pq)//获取队列中有效元素个数{assert(pq);return pq->size;}//bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) // 判断队列是否为空 //{//assert(pq);////if (pq->head == 0)//{//return true;//}//else//{//return false;//}//}bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq){assert(pq);return pq->size == 0;}QueueNodeTypeData QueueFront(Queue* pq) //获取队列头部元素{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); //防止队列为空return pq->head->data;}QueueNodeTypeData QueueBack(Queue* pq) //获取队列尾部元素{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); //防止队列为空return pq->tail->data;}
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,不妨动动手指给点赞收藏加转发,给鄃鳕一个大大的关注
你们的每一次支持都将转化为我前进的动力!!!