IOC操作Bean管理(基于xml方式)
前言一、基于 xml 方式创建对象二、基于 xml 方式注入属性1. 使用 set 方法进行属性注入2. 使用有参数构造进行属性注入3. p 名称空间注入简化操作(了解) 三、xml 注入其它类型属性1. 字面量2. 注入属性-外部 bean3. 注入属性-内部 bean4. 注入属性-级联赋值 四、xml 注入集合属性1. 注入数组类型属性2. 注入 List 集合类型属性3. 注入 Map 集合类型属性4. 在集合里面设置对象类型值5. 把集合注入部分提取出来 五、bean作用域六、bean 生命周期七、xml 自动装配八、外部属性文件九、FactoryBean
前言
本博主将用CSDN记录软件开发求学之路上亲身所得与所学的心得与知识,有兴趣的小伙伴可以关注博主!也许一个人独行,可以走的很快,但是一群人结伴而行,才能走的更远!让我们在成长的道路上互相学习,欢迎关注!
一、基于 xml 方式创建对象
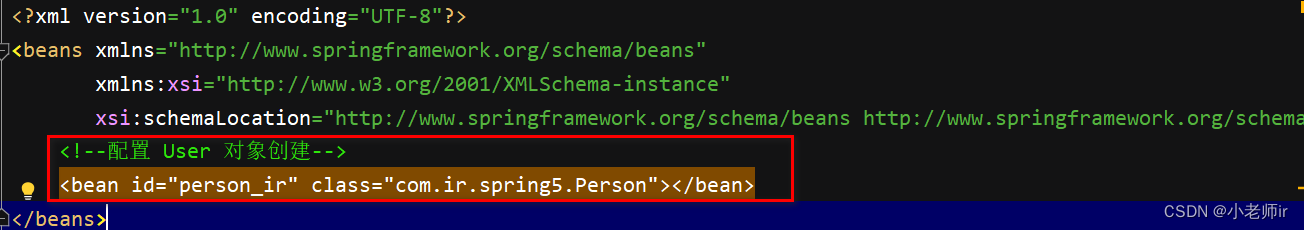
⭕在 spring 配置文件中,使用 bean 标签,标签里面添加对应属性,就可以实现对象创建
⭕在 bean 标签有很多属性,介绍常用的属性
id 属性:唯一标识class 属性:类全路径(包类路径)name属性:作用与id属性一致,区别是name属性里面可以用特殊字符,但现在很少用name属性了 ⭕创建对象时候,默认也是执行无参数构造方法完成对象创建,如果在类里用有参构造器覆盖无参构造器,运行时则会报错。
二、基于 xml 方式注入属性
DI:依赖注入,就是注入属性
1. 使用 set 方法进行属性注入
① 创建类,定义属性和对应的 set 方法
//演示使用 set 方法进行注入属性public class Person { private String name; private String food; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setFood(String food) { this.food = food; } public void eat(){ System.out.println(this.name+"吃"+this.food); }}② 在 spring 配置文件配置对象创建,配置属性注入
<!--配置 Person 对象创建--> <bean id="person_ir" class="com.ir.spring5.Person"> <!--使用 property 完成属性注入 name:类里面属性名称 value:向属性注入的值 --> <property name="name" value="小老师ir"></property> <property name="food" value="java"></property> </bean>property标签中的属性name是相应的类中的属性名,value是指要赋予属性的值
③ 测试代码:
@Test public void testEat(){ //1.加载spring配置文件 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("person1.xml"); //2. 获取配置创建的对象 Person person = context.getBean("person_ir",Person.class); //3. 测试 System.out.println(person);//com.ir.spring5.Person@1b26f7b2 person.eat(); //[小老师ir]吃java } 2. 使用有参数构造进行属性注入
① 创建类,定义属性,创建属性对应有参数构造方法
package com.ir.spring5;public class Car { private String number; private String speed; public Car(String number, String speed) { this.number = number; this.speed = speed; } public void run(){ System.out.println(number+"::"+speed); }}② 在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<!--配置 Car 对象创建--> <bean id="car_ir" class="com.ir.spring5.Car"> <!--有参数构造注入属性--> <!--方式1:通过name属性来确定类中的属性名--> <constructor-arg name="number" value="01"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="speed" value="200"></constructor-arg> <!--方式2:通过索引来确定属性名--><!-- <constructor-arg index="0" value="01"></constructor-arg>--><!-- <constructor-arg index="1" value="200"></constructor-arg>--> </bean>测试:
@Test public void testCar(){ //1.加载配置文件 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); //2.获取配置文件创建的对象 Car car = context.getBean("car_ir",Car.class); //3.测试 System.out.println(car);//com.ir.spring5.Car@a74868d car.run();//01::200 } 3. p 名称空间注入简化操作(了解)
使用 p 名称空间注入,可以简化基于 xml 配置方式
① 添加 p 名称空间在配置文件中
② 进行属性注入,在 bean 标签里面进行操作
<bean id="person_ir" class="com.ir.spring5.Person" p:name="小老师ir" p:food="c++"></bean>三、xml 注入其它类型属性
1. 字面量
⭕ null 值
<bean id="person_ir" class="com.ir.spring5.Person"> <property name="name" > <null/> </property> <property name="food" value="java"></property> </bean>@Test public void testEat(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); Person person = context.getBean("person_ir",Person.class); System.out.println(person);//com.ir.spring5.Person@1b26f7b2 person.eat(); //[null]吃java ⭕ 属性值包含特殊符号
● 方法一:把<>进行转义 < >
<bean id="person_ir" class="com.ir.spring5.Person"> <property name="name" value="<小老师ir>"></property> <property name="food" value="java"></property> </bean>@Test public void testEat(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); Person person = context.getBean("person_ir",Person.class); System.out.println(person);//com.ir.spring5.Person@a74868d person.eat(); //<小老师ir>吃java ● 方法二:把带特殊符号内容写到 CDATA
<bean id="person_ir" class="com.ir.spring5.Person"> <property name="name" > <value> <![CDATA[<<小老师ir>>]]> </value> </property> <property name="food" value="java"></property> </bean>@Test public void testEat(){ //1.加载spring配置文件 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); //2. 获取配置创建的对象 Person person = context.getBean("person_ir",Person.class); //3. 测试 System.out.println(person);//com.ir.spring5.Person@a74868d person.eat(); //[<<小老师ir>>]吃java 2. 注入属性-外部 bean
演示步骤:
① 创建两个类 service 类和 dao 类
② 在 service 调用 dao 里面的方法
UserDao
package Dao;/** * @author shkstart * @create 2022-05-07 23:08 */public interface UserDao { public void update();}UserService
package Service;import Dao.UserDao;/** * @author shkstart * @create 2022-05-07 23:08 */public class UserService { //创建 UserDao 类型属性,生成 set 方法 private UserDao userDao; public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } public void add() { System.out.println("service add..............."); userDao.update(); }}UserDaoImpl
package Dao;/** * @author shkstart * @create 2022-05-07 23:08 */public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ @Override public void update() { System.out.println("dao update..........."); }}③ 在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd"> <!--创建 UserService 对象--> <bean id="userservice" class="Service.UserService"> <!--注入 userDao 对象 name 属性:类里面属性名称 ref 属性:创建 userDao 对象 bean 标签 id 值 --> <property name="userDao" ref="userdaoimpl"></property> </bean> <!--创建 UserDaoImpl 对象--> <bean id="userdaoimpl" class="Dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean></beans>测试:
@Test public void testBean(){ ApplicationContext context1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService)context1.getBean("userservice"); System.out.println(userService);//Service.UserService@eafc191 userService.add();// service add...............// dao update........... }3. 注入属性-内部 bean
① 一对多关系:部门和员工,一个部门有多个员工,一个员工属于一个部门,部门是一,员工是多
② 在实体类之间表示一对多关系,员工表示所属部门,使用对象类型属性进行表示
部门类
package Bean;public class Dept { private String dname; public void setDname(String dname) { this.dname = dname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dept{" + "dname='" + dname + '\'' + '}'; }}员工类
package Bean;public class Emp { private String ename; private String gender; //员工属于某一个部门,使用对象形式表示 private Dept dept; public void setDept(Dept dept) { this.dept = dept; } public void setEname(String ename) { this.ename = ename; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public void add() { System.out.println(ename+"::"+gender+"::"+dept); }}③ 在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<!--内部bean--> <bean id="emp" class="Bean.Emp"> <!--设置两个属性--> <property name="ename" value="小老师ir"></property> <property name="gender" value="女"></property> <!--设置对象类型属性--> <property name="dept"> <bean id="dept" class="Bean.Dept"> <property name="dname" value="安保部"></property> </bean> </property> </bean>测试
@Test public void testEmp(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean3.xml"); Emp emp = (Emp)context.getBean("emp"); System.out.println(emp);//Bean.Emp@69b0fd6f emp.add();//小老师ir::女::Dept{dname='安保部'} }4. 注入属性-级联赋值
方式一:
在 spring 配置文件bean4.xml中进行配置
<!--级联赋值--> <bean id="emp" class="Bean.Emp"> <!--设置两个普通属性--> <property name="ename" value="小老师ir"></property> <property name="gender" value="女"></property> <!--级联赋值--> <property name="dept" ref="dept"></property> </bean> <bean id="dept" class="Bean.Dept"> <property name="dname" value="技术部"></property> </bean>测试:
@Test public void testEmp2(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml"); Emp emp = (Emp)context.getBean("emp"); System.out.println(emp);//Bean.Emp@462d5aee emp.add();//小老师ir::女::Dept{dname='技术部'} }方式二:员工属于某一个部门,使用对象形式表示
<!--级联赋值--> <bean id="emp" class="Bean.Emp"> <!--设置两个普通属性--> <property name="ename" value="小老师ir"></property> <property name="gender" value="女"></property> <!--级联赋值--> <property name="dept" ref="dept"></property> <property name="dept.dname" value="技术部"></property> </bean> <bean id="dept" class="Bean.Dept"></bean>测试:
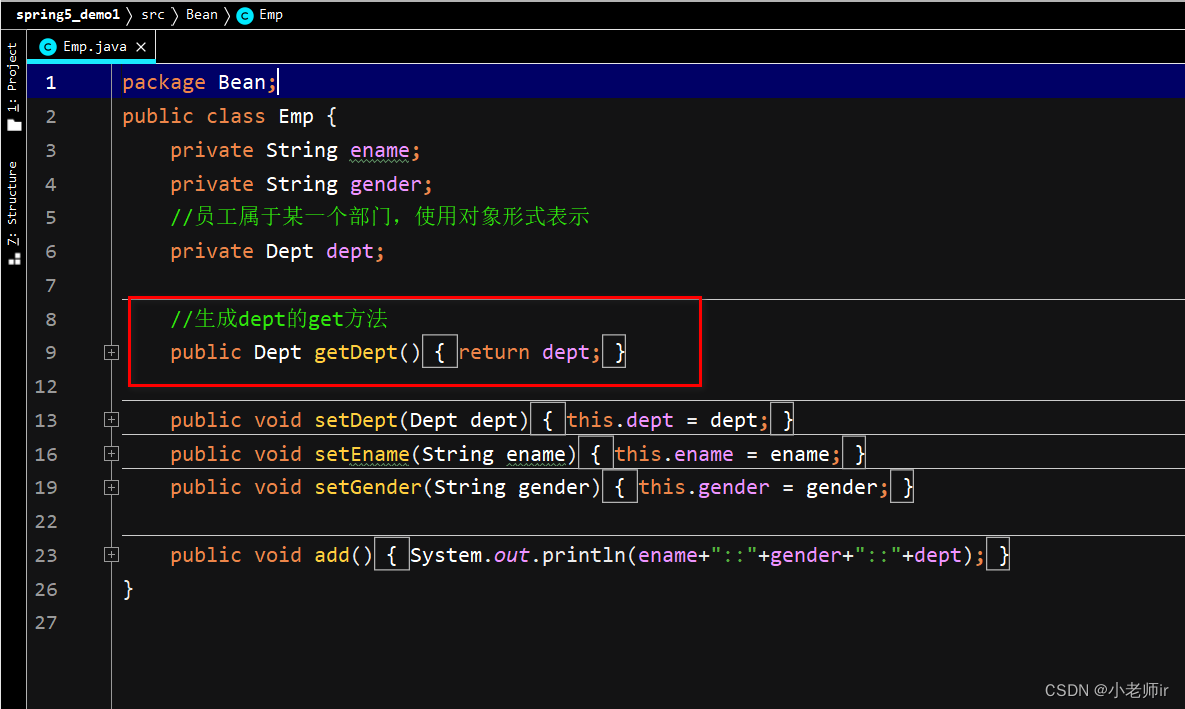
@Test public void testEmp3(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml"); Emp emp = (Emp)context.getBean("emp"); System.out.println(emp);//Bean.Emp@757942a1 emp.add();//小老师ir::女::Dept{dname='技术部'} }注意:此种方法中,Emp类中必须有getDept( )方法
四、xml 注入集合属性
1. 注入数组类型属性
2. 注入 List 集合类型属性
3. 注入 Map 集合类型属性
步骤:
① 创建类,定义数组、list、map、set 类型属性,生成对应 set 方法
Stu类
public class Stu { //1 数组类型属性 private String[] courses; //2 list集合类型属性 private List<String> list; //3 map集合类型属性 private Map<String,String> maps; //4 set集合类型属性 private Set<String> sets; public void setSets(Set<String> sets) { this.sets = sets; } public void setCourses(String[] courses) { this.courses = courses; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) { this.maps = maps; } @Override public String toString() { return "Stu{" + "courses=" + Arrays.toString(courses) + ", list=" + list + ", maps=" + maps + ", sets=" + sets + '}'; }}② 在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<bean id="student" class="collectiontest.Stu"> <!--注入数组属性--> <property name="courses"> <array > <value>Java</value> <value>C++</value> </array> </property> <!--注入list属性--> <property name="list"> <list> <value>Python</value> <value>Go</value> </list> </property> <!--注入map属性--> <property name="maps"> <map> <entry key="小老师ir" value="Java"></entry> <entry key="小老师ir" value="C++"></entry> </map> </property> <!--注入set属性--> <property name="sets"> <set> <value>喜羊羊</value> <value>美羊羊</value> </set> </property> </bean>测试:
@Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); Stu student = context.getBean("student",Stu.class); System.out.println(student);//Stu{courses=[Java, C++], list=[Python, Go], maps={小老师ir=C++}, sets=[喜羊羊, 美羊羊]} }4. 在集合里面设置对象类型值
Stu类
public class Stu { //1 数组类型属性 private String[] courses; //2 list集合类型属性 private List<String> list; //3 map集合类型属性 private Map<String,String> maps; //4 set集合类型属性 private Set<String> sets; //学生所学多门课程 private List<Course> courseList; public void setCourseList(List<Course> courseList) { this.courseList = courseList; } public void setSets(Set<String> sets) { this.sets = sets; } public void setCourses(String[] courses) { this.courses = courses; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) { this.maps = maps; } @Override public String toString() { return "Stu{" + "courses=" + Arrays.toString(courses) + ", list=" + list + ", maps=" + maps + ", sets=" + sets + ", courseList=" + courseList + '}'; }}Course类
//课程类public class Course { private String cname; //课程名称 public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Course{" + "cname='" + cname + '\'' + '}'; }}在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<!--创建多个 course 对象--> <bean id="course1" class="collectiontest.Course"> <property name="cname" value="英语课"></property> </bean> <bean id="course2" class="collectiontest.Course"> <property name="cname" value="语文课"></property> </bean> <bean id="course3" class="collectiontest.Course"> <property name="cname" value="数学课"></property> </bean> <!--创建Stu对象--> <bean id="student1" class="collectiontest.Stu"> <!--注入 list 集合类型,值是对象--> <property name="courseList"> <list> <ref bean="course1"></ref> <ref bean="course2"></ref> <ref bean="course3"></ref> </list> </property> </bean>测试
@Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); Stu student = context.getBean("student1",Stu.class); System.out.println(student);//Stu{courses=null, list=null, maps=null, sets=null, courseList=[Course{cname='英语课'}, Course{cname='语文课'}, Course{cname='数学课'}]} }5. 把集合注入部分提取出来
Book类·
public class Book { private List<String> list; public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "list=" + list + '}'; }}步骤:
① 在 spring 配置文件中引入名称空间 util
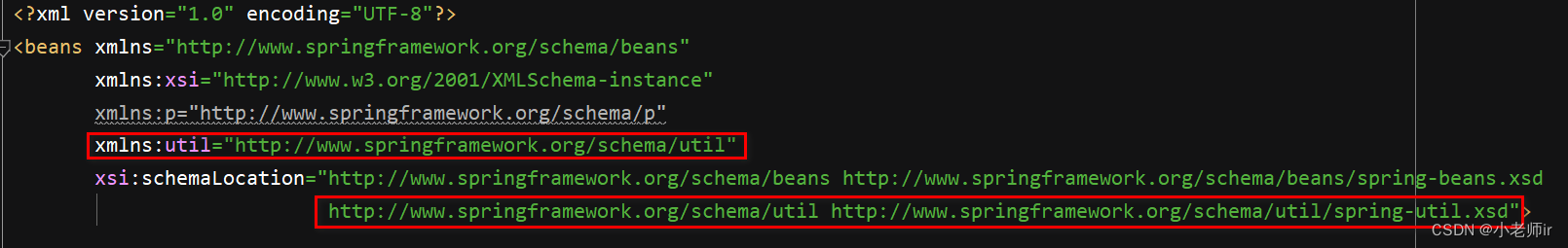
② 在 spring 配置文件进行配置,使用 util 标签完成 list 集合注入提取
<!--1 提取list集合类型属性注入--> <util:list id="bookList"> <value>java</value> <value>c++</value> <value>python</value> </util:list> <!--2 提取list集合类型属性注入使用--> <bean id="book" class="collectiontest.Book" scope="prototype"> <property name="list" ref="bookList"></property> </bean>测试
@Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml"); Book book= context.getBean("book", Book.class); System.out.println(book);//Book{list=[java, c++, python]} }五、bean作用域
⭕ 在 Spring 里面,设置创建 bean 实例是单实例还是多实例 ?
⭕在 Spring 里面,默认情况下,bean 是单实例对象
Book类
public class Book { private List<String> list; public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; }}在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<!--1 提取list集合类型属性注入--> <util:list id="bookList"> <value>java</value> <value>c++</value> <value>python</value> </util:list> <!--2 提取list集合类型属性注入使用--> <bean id="book" class="collectiontest.Book" > <property name="list" ref="bookList"></property> </bean>测试:
@Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml"); Book book1= context.getBean("book", Book.class); Book book2= context.getBean("book", Book.class); System.out.println(book1);//collectiontest.Book@27d415d9 System.out.println(book2);//collectiontest.Book@27d415d9 }由以上测试输出结果可知,创建的两个book对象地址相同,即为其实是同一个对象
⭕如何设置单实例还是多实例
● 在 spring 配置文件 bean 标签里面有属性(scope)用于设置单实例还是多实例
● scope 属性值,其中有两个常见的词
在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<!--1 提取list集合类型属性注入--> <util:list id="bookList"> <value>java</value> <value>c++</value> <value>python</value> </util:list> <!--2 提取list集合类型属性注入使用--> <bean id="book" class="collectiontest.Book" scope="prototype"> <property name="list" ref="bookList"></property>y </bean>测试:
@Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml"); Book book1= context.getBean("book", Book.class); Book book2= context.getBean("book", Book.class); System.out.println(book1);//collectiontest.Book@27d415d9 System.out.println(book2);//collectiontest.Book@5c18298f }由以上测试输出结果可知,创建的两个book对象地址不相同,即为是两个对象
⭕ singleton 和 prototype 区别
● singleton 单实例,prototype 多实例
● 设置 scope 值是 singleton 时候,加载 spring 配置文件时候就会创建单实例对象
● 设置 scope 值是 prototype 时候,不是在加载 spring 配置文件时候创建 对象,而是在调用getBean 方法时候创建多实例对象
六、bean 生命周期
⭕ 生命周期:从对象创建到对象销毁的过程
⭕ bean 生命周期
(1)通过构造器创建 bean 实例(无参数构造)
(2)为 bean 的属性设置值和对其他 bean 引用(调用set 方法)
(3)调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
(4)bean 可以使用了(对象获取到了)
(5)当容器关闭时候,调用 bean 的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
⭕ 演示 bean 生命周期
Order类
public class Order { private String name; public Order() { System.out.println("第一步:执行无参构造器创建对象"); } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; System.out.println("第二步:调用set()方法设置属性值"); } public void initMethod(){ System.out.println("第三步:执行初始化方法"); } public void destroyMethod(){ System.out.println("第五步:执行销毁的方法"); }}在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<bean id="order" class="collectiontest.Order" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod"> <property name="name" value="电脑订单"></property></bean>测试:
@Test public void test(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml"); Order order= context.getBean("order", Order.class); System.out.println("第四步:获取创建 bean 实例对象"); System.out.println(order); context.close();// 第一步:执行无参构造器创建对象// 第二步:调用set()方法设置属性值// 第三步:执行初始化方法// 第四步:获取创建 bean 实例对象// collectiontest.Order@4a87761d// 第五步:执行销毁的方法 }⭕ bean 的后置处理器,bean 生命周期有七步
(1)通过构造器创建 bean 实例(无参数构造)
(2)为 bean 的属性设置值和对其他 bean 引用(调用 set 方法)
(3)把bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法 postProcessBeforeInitialization
(4)调用 bean 的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
(5)把 bean 实例传递 bean 后置处理器的方法postProcessAfterInitialization
(6)bean 可以使用了(对象获取到了)
(7)当容器关闭时候,调用bean 的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
⭕ 演示添加后置处理器效果
(1)创建类,实现接口 BeanPostProcessor,创建后置处理器
public class MyBeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("在初始化之前执行的方法"); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("在初始化之后执行的方法"); return bean; }}在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--配置order对象--> <bean id="order" class="bean.Order" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod"> <property name="name" value="电脑订单"></property> </bean> <!--配置后置处理器--> <bean id="mybeanpost" class="bean.MyBeanPost"></bean></beans>测试:
@Test public void test(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean4.xml"); Order order= context.getBean("order", Order.class); System.out.println("第四步:获取对象"); System.out.println(order); context.close();// 第一步:执行无参构造器创建对象// 第二步:调用set()方法设置属性值// 在初始化之前执行的方法// 第三步:执行初始化方法// 在初始化之后执行的方法// 第四步:获取对象// bean.Order@37374a5e// 第五步:执行销毁的方法 }七、xml 自动装配
⭕ 什么是自动装配?
根据指定装配规则(属性名称或者属性类型),Spring 自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
① bean 标签属性 autowire,配置自动装配
② autowire 属性常用两个值:
⭕演示自动装配过程
● 根据属性名称自动注入
Dept类
public class Dept { private String name; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dept{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; }}Emp类
public class Emp { private Dept dept; public void setDept(Dept dept) { this.dept = dept; } @Override public String toString() { return "Emp{" + "dept=" + dept + '}'; }}在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<!--创建emp对象--> <!--使用自动装配方式注入属性:通过属性名的方式--> <bean id="emp" class="bean.Emp" autowire="byName"> <!--使用手动方式注入属性--><!-- <property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>--> </bean><!--创建dept对象--> <bean id="dept" class="bean.Dept"> <property name="name" value="技术部"></property> </bean>测试:
@Test public void test() { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean5.xml"); Emp emp = context.getBean("emp", Emp.class); System.out.println(emp);//Emp{dept=Dept{name='技术部'}} }● 根据属性类型自动注入
<!--创建emp对象--> <!--使用自动装配方式注入属性:通过属性类型的方式--> <bean id="emp" class="bean.Emp" autowire="byType"> <!--使用手动方式注入属性--><!-- <property name="dept" ref="dept"></property>--> </bean><!--创建dept对象--> <bean id="dept" class="bean.Dept"> <property name="name" value="技术部"></property> </bean>测试:
@Test public void test() { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean5.xml"); Emp emp = context.getBean("emp", Emp.class); System.out.println(emp);//Emp{dept=Dept{name='技术部'}} }注意:通过属性类型的方式自动装配时,同一类型不能有多个bean对象,否则会报错
八、外部属性文件
⭕ 直接配置数据库信息
① 引入德鲁伊连接池依赖 jar 包
② 配置德鲁伊连接池
<!--创建数据库连接池对象--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <!--直接对连接池进行属性配置--> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userDb"></property> <property name="username" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> </bean>⭕ 引入外部属性文件配置数据库连接池
(1)创建外部属性文件,properties 格式文件,写数据库信息
jdbc.properties
prop.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverprop.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userDbprop.userName=rootprop.password=root(2)把外部 properties 属性文件引入到 spring 配置文件中
① 引入 context 名称空间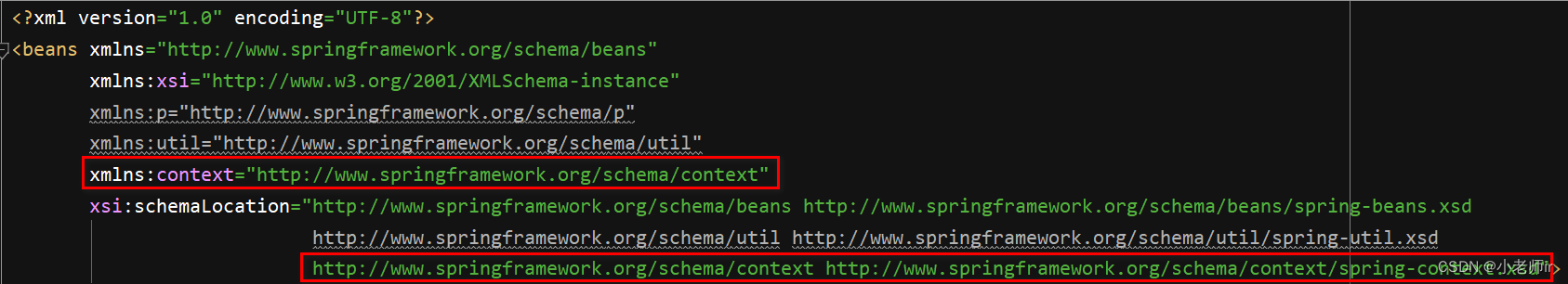
② 在 spring 配置文件使用标签引入外部属性文件
<!--引入外部属性文件--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/><!--创建数据库连接池对象--> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <!--对连接池进行属性配置--> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userDb"></property> <property name="username" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> </bean>九、FactoryBean
Spring 有两种类型 bean,一种普通 bean,另外一种工厂 bean(FactoryBean)
普通 bean:在配置文件中定义 bean 类型就是返回类型工厂 bean:在配置文件定义 bean 类型可以和返回类型不一样步骤:
① 创建类,让这个类作为工厂 bean,实现接口 FactoryBean
② 实现口里面的方法,在实现的方法中定义返回的bean 类型
Course类
public class Course { private String cname; //课程名称 public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } public String getCname(){ return this.cname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Course{" + "cname='" + cname + '\'' + '}'; }}public class MyBean implements FactoryBean<Course> { @Override public Course getObject() throws Exception { Course course = new Course(); course.setCname("Java"); return course; } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return null; }}③ 在 spring 配置文件进行配置
<!--创建MyBean对象--> <bean id="mybean" class="factorybean.MyBean"></bean>测试:
@Test public void test(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean3.xml"); Course course= context.getBean("mybean", Course.class); System.out.println(course.getCname());//Java }