常用的库函数
一.前言二.内容1.sort()题目 2.upper_bound()与lower_bound()题目 3.to_string()4.string 内嵌的 find()函数 //注:vector无find()函数5.大小写转换 to_lower() to_upper() 以及transform()注意transform的用法题目(BFS[牛客网]) 6.unique()、erase()函数题目 7.isdigit()应用:快读快写的优化 8. nth_element()应用:第k小数 三.小声bb四.更新日志
一.前言
在刷题过程中,总能看到dl用一些库函数,简化算法,由此萌生慢慢学习整理常用的库函数的想法,本文目前仅为了自用而整理,欢迎指正。
(整理顺序按学习顺序,后续可能会调整 3.27 )
二.内容
1.sort()
作用描述: 对给定区间的所有元素进行排序,默认为升序,也可进行降序排序。
时间复杂度: n*logn (高于冒泡排序)
头文件: < algorithm >
函数声明:void sort(start,end,cmp)
说明:
start:排序的起始地址
end:数组结束地址的下一位
cmp:用于规定排序的方法(可不填,默认升序)
如果cmp返回结果为假, 那么函数就会将他们互换位置;
如果cmp返回结果为真,就会保持原来位置不变。
补充:(其余sort类函数)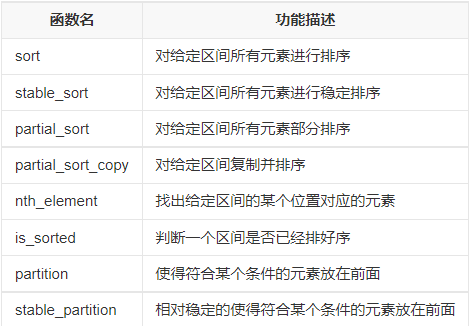
实例:
1.不加cmp,默认升序(从小到大)
#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int main(){int a[7] = { 2,6,9,8,4,3,2 };for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)cout << a[i] << " ";sort(a, a + 7);cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)cout << a[i] << " ";return 0;}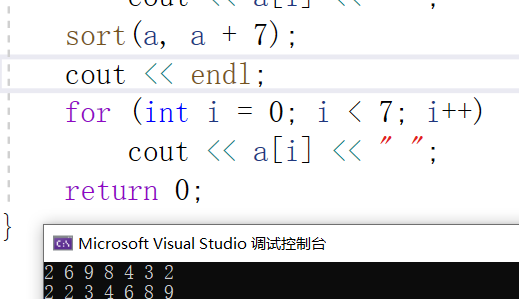
2.加上cmp,实现从大到小排序
#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;bool cmp(int a, int b){return a > b; //返回值为假,说明a<=b,交换,使其从大到小排序}int main(){int a[7] = { 2,6,9,8,4,3,2 };for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)cout << a[i] << " ";sort(a, a + 7,cmp);cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)cout << a[i] << " ";return 0;}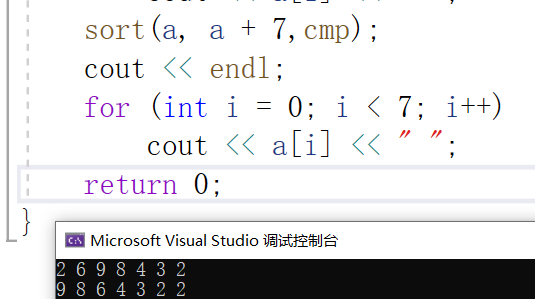
3.结构体排序(已更新)
//实现目标:将a按升序排序,如果a相同再按b降序排序,b相同,则按c降序排列
#include <iostream>using namespace std; //结构体sort()排序#include <algorithm>struct Node{int a;int b;double c;};bool cmp(Node x, Node y){if (x.a != y.a)return x.a < y.a;if (x.b != y.b)return x.b > y.b;return x.c > y.c;}int main() {struct Node arr[4];arr[0] = { 3,4,3.15 };arr[1] = { 7,8,3.26 };arr[2] = { 5,9,3.8 };arr[3] = { 4,9,3.7 };for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)cout << arr[i].a << " " << arr[i].b << " " << arr[i].c << endl;sort(arr, arr + 4, cmp);cout << "排序后:" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)cout << arr[i].a << " " << arr[i].b << " " << arr[i].c << endl;return 0;}
题目
题目跳转链接:比赛谁更快
2.upper_bound()与lower_bound()
作用:
upper_bound()可以在有序序列中找到大于val的位置
lower_bound()可以在有序序列中找到大于等于val的位置
(val即要查找的数据)
函数头文件:< algorithm >
函数声明:
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,const T& val, Compare comp);
说明:
个人理解的函数声明:
iterator upper_bound(fisrt,last,const &val,cmp)
The range used is [first,last), which contains all the elements between first and last, including the element pointed by first but not the element pointed by last.
(必须是已经排好序的序列,范围是从[first,last)的左闭右开区间查找)
查找val的规则:
Unlike lower_bound, the value pointed by the iterator returned by this function cannot be equivalent to val, only greater.
(upper_bound()找到严格大于val的位置,lower_bound()找到大于等于val的位置)
返回值:
An iterator to the upper bound position for val in the range.
If no element in the range compares greater than val, the function returns last.
(如果找不到比val大的数据,则返回last的位置)
注意:返回值的类型是迭代器(理解为指针即可)
题目
题目跳转链接:P1102 A-B 数对
3.to_string()
作用: 将整型转换为 string 类型
函数头文件: < sstream >
举例:
#include <iostream>#include <sstream>using namespace std;int main(){int a = 1048784848;string s = to_string(a);cout << s;return 0;}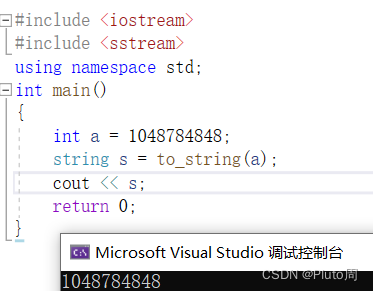
4.string 内嵌的 find()函数 //注:vector无find()函数
**作用:**找到字符串str在字符串s中(第一次)出现的位置
用法: s.find(str) [s str 均为 string类型]
返回值: str在s中出现的位置,如果匹配不到,则返回标记 npos (4294967295 亦即 int 类型的 -1)
举例:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){string s = "abcabcd";cout << s.find("ca") << endl;cout << s.find("ef") << endl;cout <<(int)s.find("ef") << endl;if (s.find("ef") == s.npos)cout << "没找到,返回标记 npos" << endl;return 0;}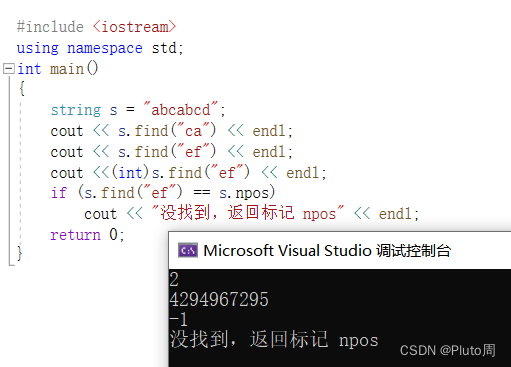
区分find()与find_first_of()
差别在于:find 必须匹配完整的字符串,find_first_of只需要匹配部分~
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){string s = "abcabcd";cout << s.find_first_of("bzzzzz") << endl;return 0;}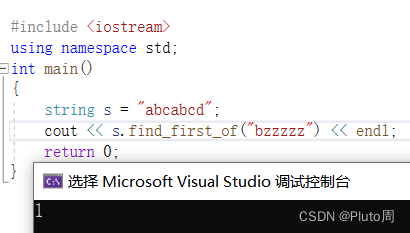
5.大小写转换 to_lower() to_upper() 以及transform()
to_lower() 、 to_upper()为C库中的
transform()可以调用to_lower ()、 to_upper()实现大小写的转换
函数声明:transform (const_inlt_First,const_inlt_Last,des,func)
四个参数:
字符串首地址,字符串末尾地址,转换后存储的字符串,所调用的函数
举例:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include <algorithm>int main(){string s = "ad SaF";/*for (auto x : s) if (x >= 'A' && x <= 'Z') //x是临时变量,无法通过x改变原来的值x = x - 'A' + 'a';*/for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)if (s[i] >= 'A' && s[i] <= 'Z') //实现过程s[i] = s[i]- 'A' + 'a';cout << s << endl;transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),toupper); //大小写转换cout << s;return 0;}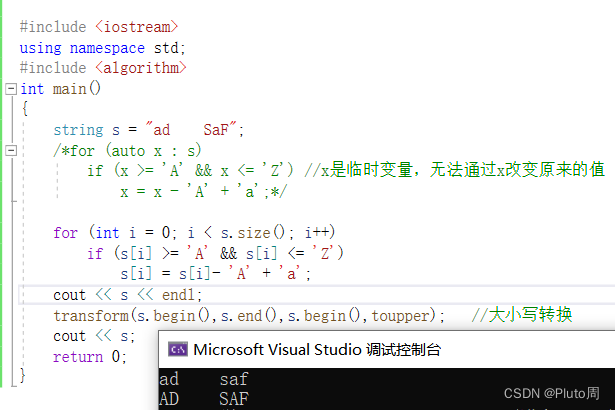
注意transform的用法
如果这样写不可以
transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),toupper); //大小写转换则可能是兼容性问题,改为以下写法即可
std::transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),::toupper);//或者transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),toupper);题目(BFS[牛客网])
6.unique()、erase()函数
作用:去除重复的元素,只保留1个(将重复元素放到元素的后面)
uique(begin,last) 左闭右开区间
返回值:指向非重复元素最后一位的后一位
题目
P1059 [NOIP2006 普及组] 明明的随机数
//方法1:#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include <algorithm>const int N = 1e3 + 10;int a[N];int main(){int n;cin >> n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)scanf("%d", &a[i]);sort(a, a + n);int* p = unique(a, a + n);cout << p - a << endl;for (int* q = a; q < p; q++)cout << *q << ' ';return 0;}//方法2:#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include <algorithm>#include <vector>int main(){vector <int> res;int n;cin >> n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int x;scanf("%d", &x);res.push_back(x);}sort(res.begin(), res.end());res.erase(unique(res.begin(), res.end()), res.end());cout << res.end() - res.begin() << endl;for (auto x : res)cout << x << ' ';return 0;}7.isdigit()
作用:可用于检查传递的字符是否为数字字符[即 ‘0’ 到 ‘9’ ]
头文件:cstdio
函数声明:isdigit(int arg)
参数:arg 整数形式的单个参数
[备注:即使isdigit()接受整数作为参数,若传递为字符,则该字符也会传递给函数。在内部,该字符将转换为其ASCII值以进行检查。]
返回值:如果参数是数字字符,则返回非零值(真值),否则返回零(假值)。
实例:
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(){char a = '6', b = 7, c = 'p';//a为数字字符,b、c不是cout << isdigit(a) << " " << isdigit(b) << " " << isdigit(c);return 0;}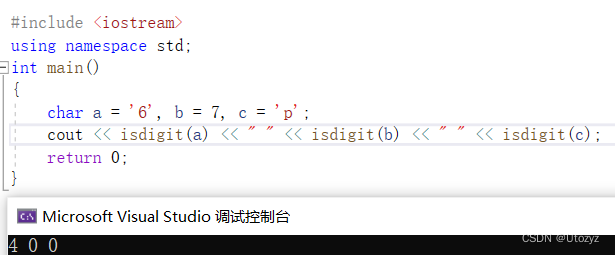
应用:快读快写的优化
跳转至 快读快写的优化
8. nth_element()
功能:
当采用默认的升序排序规则(std::less)时,该函数可以从某个序列中找到第 n 小的元素 K ,并将 K 移动到序列中第 n 的位置处。不仅如此,整个序列经过 nth_element() 函数处理后,所有位于 K 之前的元素都比 K 小,所有位于 K 之后的元素都比 K 大。
注意:但并不一定保证调用后,所有元素升序排列
eg: 2 4 6 8 第0小:2第1小:4第2小:6头文件: algorithm
函数声明: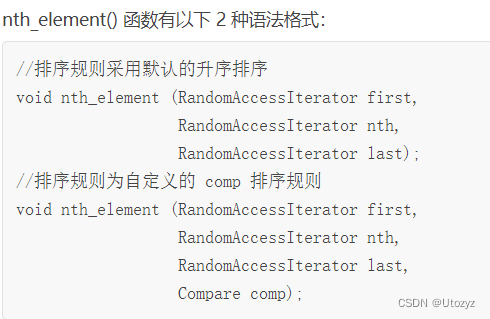
参数:
first 和 last: 都是随机访问迭代器,[first, last) 用于指定该函数的作用范围(即要处理哪些数据);
nth: 也是随机访问迭代器,其功能是令函数查找“第 nth 大”的元素,并将其移动到 nth 指向的位置;
comp: 用于自定义排序规则。
实例:第k小[简化]
#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include <algorithm>int main(){int a[10] = { 9,5,3,11,0,46,21,3,8,12 };int k = 2; // "第2小"int n = 10;puts("调用函数前:");for (auto x : a)printf("%d ", x);puts("");nth_element(a, a + k, a + n);puts("调用函数后:");for (auto x : a)printf("%d ", x);puts("");printf("\"第2小:\" %d", a[k]);return 0;}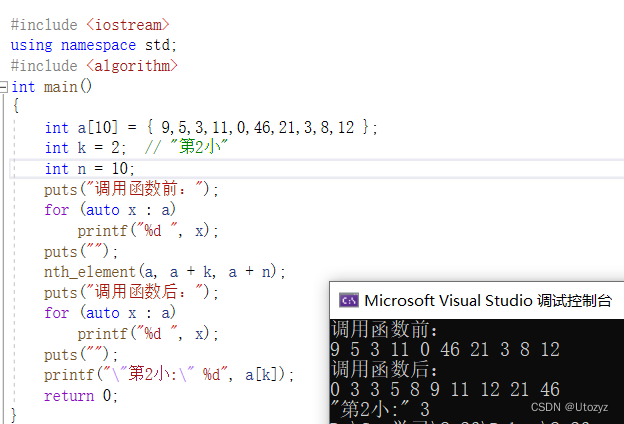
注意:重复数字也算
应用:第k小数
题目链接
三.小声bb
慢慢总结,慢慢进步~~
四.更新日志
2022.3.28 整理sort()及其题目
2022.6.27 整理大小写转换及transform()的注意事项
2022.8.6 isdigit()