关于Java语言当中的this关键字:
1、this是一个关键字,翻译为:这个。
2、this是一个引用,this是一个变量,this变量中保存了内存地址指向了自身,this存储在JVM堆内存中Java对象的内部。
3、创建100Java对象,每一个对象都有this,也就是说有100个不同的this。
4、this可以出现在“实例方法”当中,(this指向)代表当前正在执行这个动作的对象。(this代表当前的对象“张三”)。
重点:没有static关键字的方法称为“实例方法”。实例方法访问: “ 引用. ”
重点:没有static关键字的变量称为“实例变量”。
注意:当一个行为/动作执行的过程当中是需要对象参与的,那么这个方法一定要定义为“实例方法”,不要带static关键字
(此图非常关键)
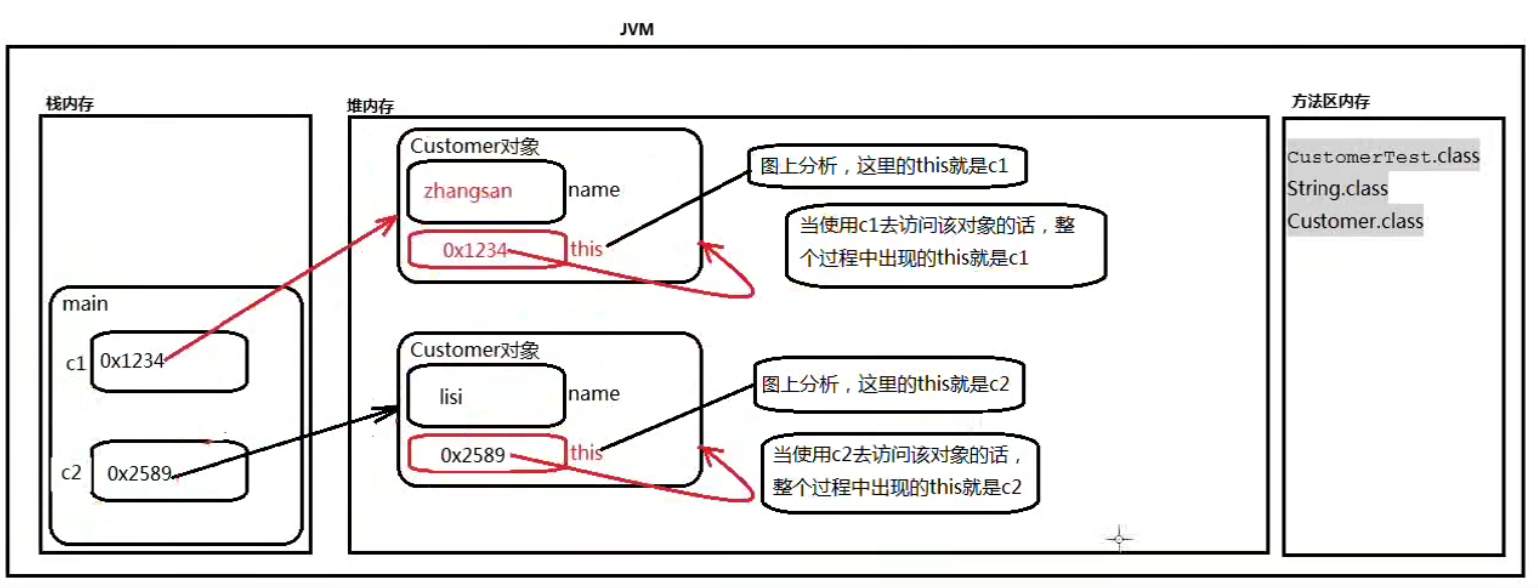
public class Customer {//姓名String name;//构造方法public Customer() {super();}//不带有static关键字的方法//顾客购物的行为//没有static关键字的方法称为“实例方法”public void shopping() {//由于name是一个实例变量,所以这个name访问的时候一定是访问当前对象的name//所以多数情况下“this.”是可以省略的。//System.out.println(name + "在购物!");//完整写法:引用.实例变量(c1.name + " is shopping!")System.out.println(this.name + "在购物!");//this <=> c1/c2}}由于name是一个实例变量,所以这个name访问的时候一定是访问当前对象的name,所以多数情况下“this.”是可以省略的。
public class CustomerTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建对象Customer c1 = new Customer();c1.name = "zhangsan";c1.shopping();//zhangsan在购物!Customer c2 = new Customer();c2.name = "lisi";c2.shopping();//lisi在购物!}}
public class ThisTest {int num = 10;//实例变量(引用.的方式访问)public static void main(String[] args) {//编译错误,没有当前对象this//System.out.println(num);//System.out.println(this.num);}}上述这两种访问方式均编译错误,那如何访问num?——创建对象,通过对象访问
ThisTest tt = new ThisTest();System.out.println(tt.num);辨析:
package This;public class ThisTest {//带有staticpublic static void main(String[] args) {//调用doSomeThisTest.doSome();//调用doSomedoSome();//调用doOtherThisTest tt = new ThisTest();tt.doOther();tt.run();}//带有staticpublic static void doSome() {System.out.println("Do Some!");}//不带有static,实例方法public void doOther() {//this表示当前对象System.out.println("Do Other!");}public void run() {//run是实例方法,调用run方法的一定有对象存在。System.out.println("Run!");doOther();//完整写法:this.doOther();}}最终结论:在带有static的方法当中,不能“直接”访问实例变量和实例方法。
因为实例变量和实例方法都需要对象的存在(new)。
而static方法当中是没有this的,也就是说当前对象是不存在的。自然也是无法直接访问当前对象的实例变量和实例方法。
This什么情况不能省略
public class User {//属性private int id;private String name;//构造函数//setter and getter/*public void setId(int a) {id = a;}这个 "a" 看着别捏*/public void setId(int id) {//等号后面的id是局部变量id//等号前面的this.id是实例变量idthis.id = id;}}结论:用来区分实例变量和局部变量的时候," this. "不能省略(90%可以省略)。
//自定义日期类型public class Date {//属性private int year; private int month; private int day;//构造函数//有参数public Date(int year, int month, int day) {this.year = year;this.month = month;this.day = day;} /** *需求:当程序员调用以下无参数构造方法时,默认创建日期是1970-1-1 * *///无参数public Date() {this.year = 1970;this.month = 1;this.day = 1;}//setter and getter存在问题:无参数构造方法和有参数构造方法中内容重复,如果内部属性多,则要重复编写大量代码。
改进方案:
/* this.year = 1970;
this.month = 1;
this.day = 1;*/
以上代码可以通过调用另一个构造方法来完成,但前提是不能创建新的对象
public Date() {this(1970,1,1);}这种方法不会创建新的Java对象,同时也可达到调用其他构造方法。
总结: this可以用在哪里:
1、可以使用在实例方法当中,代表当前对象。【语法格式:this.】
2、可以使用在构造方法当中,通过当前的构造方法调用其他的构造方法
【语法格式:this(实参)】。
重点【记忆】:this() 这种语法只能出现在构造方法中的第一行。