1、SpringBoot+老杜MyBatis
一、简单回顾一下MyBatis
二、快速入门
三、简易插入删除更改
四、查询
①、按其中一个字段查询
②、按所有字段进行查询
五、详解MyBatis核心配置(复习)
六、结合Web及SpringMVC
2、MyBatis小技巧
一、#{}与${}及模糊查询
二、别名机制与mapper标签
三、插入使用生成的主键值
3、MyBatis参数处理
一、单个简单类型参数
二、Map参数
①、插入信息
②、查询单个汽车信息
③、返回多个Map
④、返回Map,map>
三、实体类参数
四、多参数(@Param)
五、resultMap结果映射
①、使用resultMap进行结果映射(常用)
②、开启驼峰命名规范自动映射
六、获取总记录条数
4、动态SQL(注:使用了驼峰命名规范)
一、if标签
二、where标签
三、trim标签
四、set标签
五、choose where otherwise
六、foreach标签
①批量删除
②批量添加
七、sql、include标签
5、高级映射及延迟加载
一、多对一
二、多对一延迟加载
三、一对多
四、一对多延迟加载
6、MyBatis缓存机制
一、一级缓存
二、二级缓存
7、MyBatis使用PageHelper
一、limit分页
二、PageHelper插件
舞台再大 你不上台 永远是个观众
平台再好 你不参与 永远是局外人
能力再大 你不行动 只能看别人成功
没有人会在乎你付出多少努力 撑得累不累 摔得痛不痛
他们只会看你最后站在什么位置 然后羡慕或鄙夷
1、SpringBoot+老杜MyBatis
一、简单回顾一下MyBatis
核心对象包括以下三个:
SqlSessionFactoryBulider
SqlSessionFactory
SqlSession
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder --> SqlSessionFactory --> SqlSession

关于MyBatis的事务管理机制(两种)
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/> JDBC表示事务管理器
<transactionManager type="MANAGED"/> MANAGED表示事务事务管理器
JDBC事务管理器: MyBatis框架自己管理事务,自己采用原生的JDBC代码去管理事务: conn.setAutoCommit(false); 开启事务。 ....业务处理... conn.commit(); 手动提交事务 使用JDBC事务管理器的话,底层创建的事务管理器对象:JdbcTransaction对象。
如果你编写的代码是下面的代码: SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); 表示没有开启事务。因为这种方式压根不会执行:conn.setAutoCommit(false); 在JDBC事务中,没有执行conn.setAutoCommit(false);那么autoCommit就是true。 如果autoCommit是true,就表示没有开启事务。只要执行任意一条DML语句就提交一次。
MANAGED事务管理器: MyBatis不再负责事务的管理了。事务管理交给其它容器来负责。例如:spring。 我不管事务了,你来负责吧。对于我们当前的单纯的只有mybatis的情况下,如果配置为:MANAGED 那么事务这块是没人管的。没有人管理事务表示事务压根没有开启。没有人管理事务就是没有事务。
JDBC中的事务: 如果你没有在JDBC代码中执行:conn.setAutoCommit(false);的话,默认的autoCommit是true。
重点: 以后注意了,只要你的autoCommit是true,就表示没有开启事务。 只有你的autoCommit是false的时候,就表示开启了事务。
在SpringBoot+MyBatis项目中就不用写事务相关的东西了,但是用到业务层Service就需要了
二、快速入门
第一步:引入依赖
<!--junit测试依赖--><dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <scope>test</scope></dependency><!--lombok依赖,是为了简化实体类的编写代码量--><dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency>第二步:编写yml配置文件(此处我将properties后缀改成了yml)
其中包含连接数据库以及MyBatis的核心配置信息(但在SpringBoot框架中无需用MyBatis原核心配置文件)
spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/powernode username: root password: rootmybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml #目的是为了省略resultType里的代码量 type-aliases-package: com.chf.pojo configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl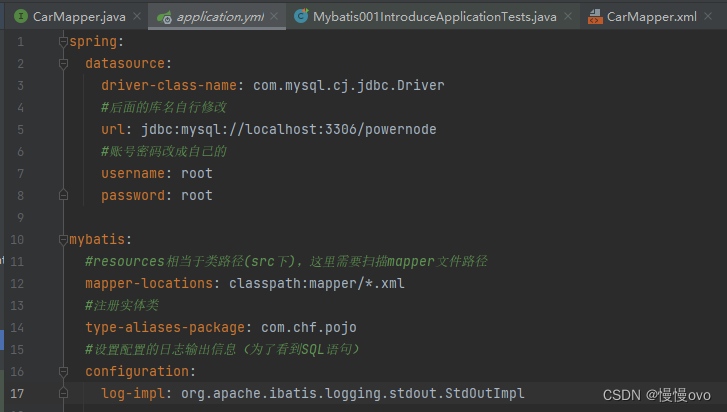
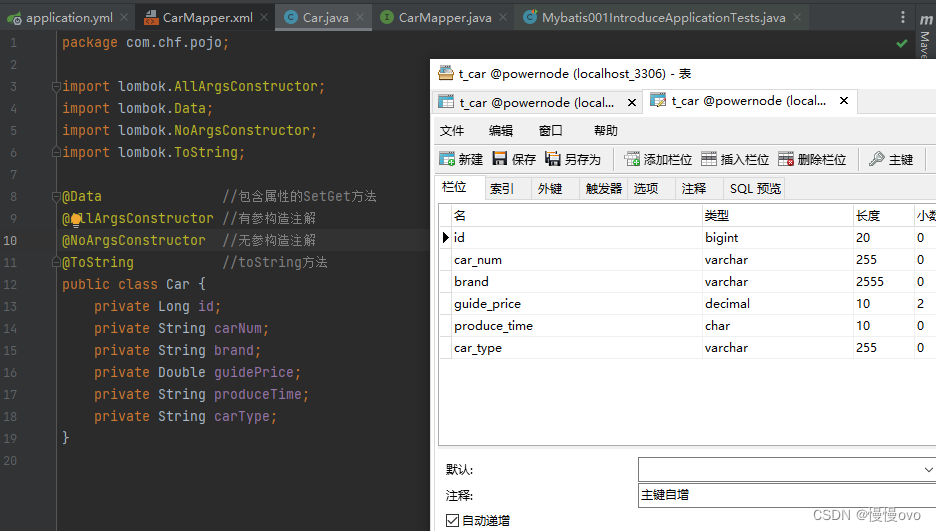
第三步:构建实体类(在pojo包下),与表中字段一一对应
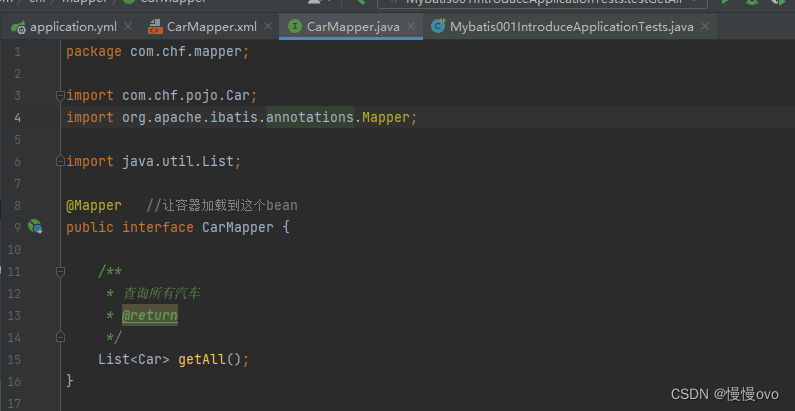
第四步:创建接口,用来写方法
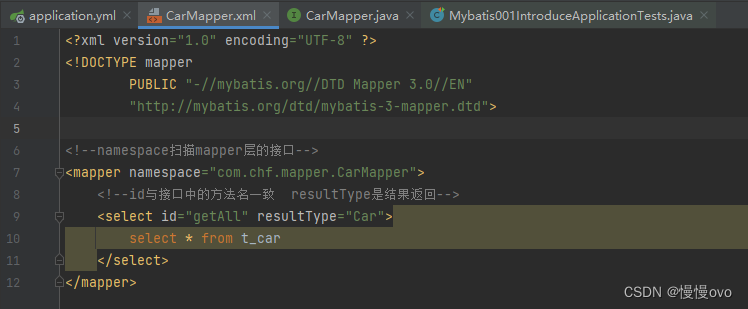
第五步:每一个实体类对应一个mapper映射文件,在resources的mapper包下写映射文件(SQL语句)
其实这里的Sql语句是有问题的,查询到控制台的有问题,这里做个伏笔后面会知道为什么。
第六步:先测试自己是否成功连接到了数据库,不然你不管怎么测试方法都不知道你为什么爆红
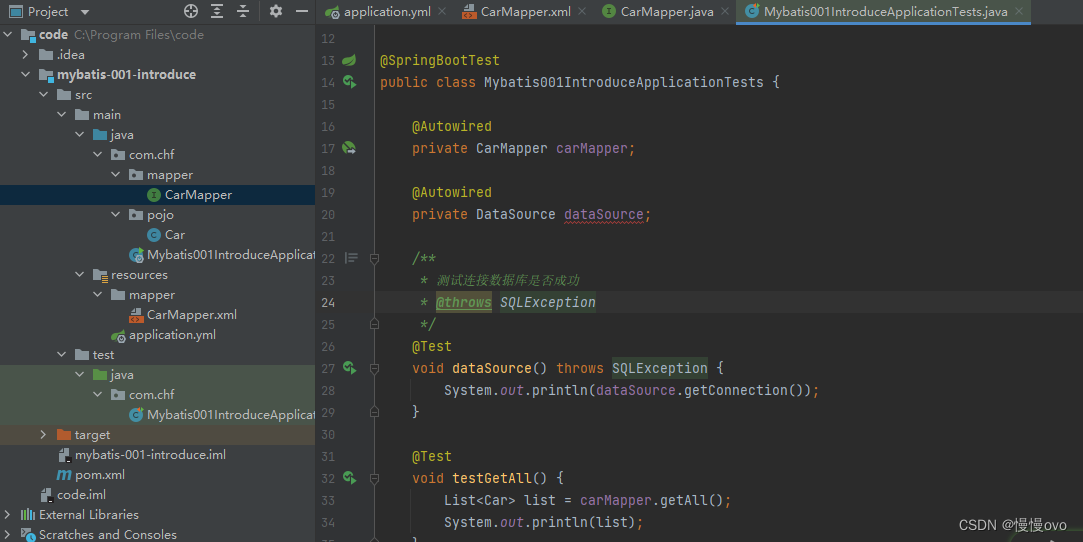
测试成功,开心开心(这里控制台输出的null是我埋下的伏笔,下面会讲)
 三、简易插入删除更改
三、简易插入删除更改
@Mapper public interface CarMapper { /** * 插入汽车 * @return * @param car */ int insert(Car car); /** * 按id删除车辆信息 * @param id * @return */ int delete(Long id); /** * 更新车辆信息 * @param car * @return */ int update(Car car);}<!--namespace和里面标签的id两者都是为了动态代理而需要的--><mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <!-- #{}对应的是pojo层实体类的属性名"abcDe"对应的"getAbcDe"的"abcDe"(驼峰命名规范) 想简单点,对应属性名就行,复杂可能会乱ovo --> <insert id="insert"> insert into t_car(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type) values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType}) </insert> <!--如果占位符只有一个,其实可以随便写里面的内容但不能不写,但最好见名知意,这次只是测试--> <delete id="delete"> delete from t_car where id = #{dasdad} </delete> <update id="update"> update t_car set car_num=#{carNum}, brand=#{brand}, guide_price=#{guidePrice}, produce_time=#{produceTime}, car_type=#{carType} where id=#{id} </update></mapper>@SpringBootTestpublic class Mybatis001IntroduceApplicationTests { @Autowired private CarMapper carMapper; @Test void testInsert(){ Car car = new Car(null,"111","奔驰",30.00,"2022-10-2","新能源"); int count = carMapper.insert(car); System.out.println((count == 1 ? "插入成功" : "插入失败")); } @Test void testDelete(){ int count = carMapper.delete(4L); System.out.println((count == 1 ? "删除成功" : "删除失败")); } @Test void testUpdate(){ Car car = new Car(6L,"1111","奔驰",30.00,"2022-10-2","新能源"); int count = carMapper.update(car); System.out.println((count == 1 ? "更新成功" : "更新失败")); }}四、查询
①、按其中一个字段查询
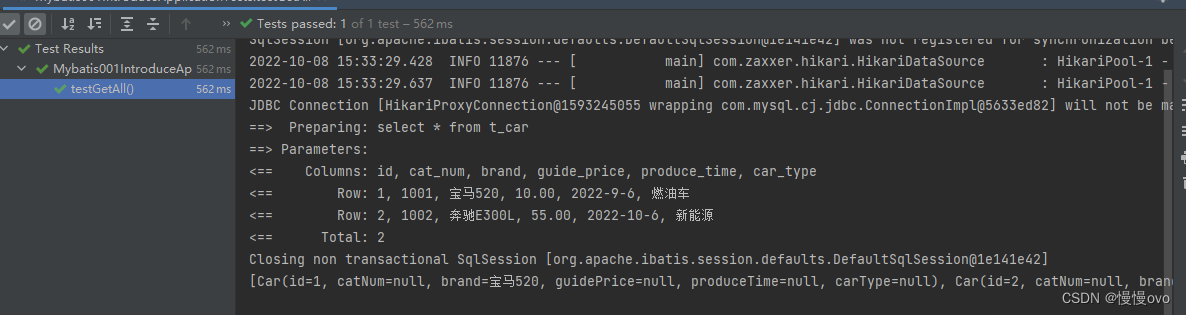
通过控制台你会仔细的发现:除了id和brand其他皆为null。
原因就在于:属性名与表名不一致造成的,所以我们应该编写Sql语句就可以完成查询
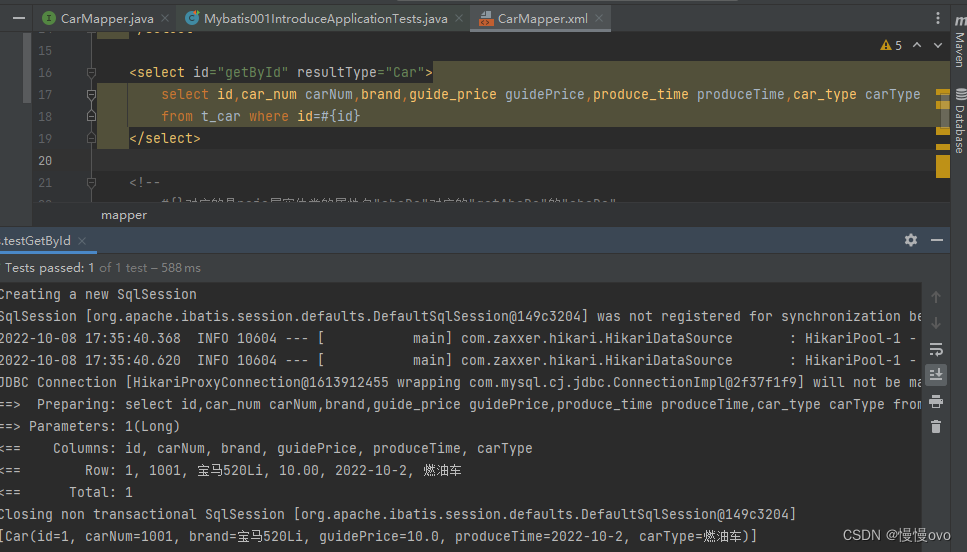
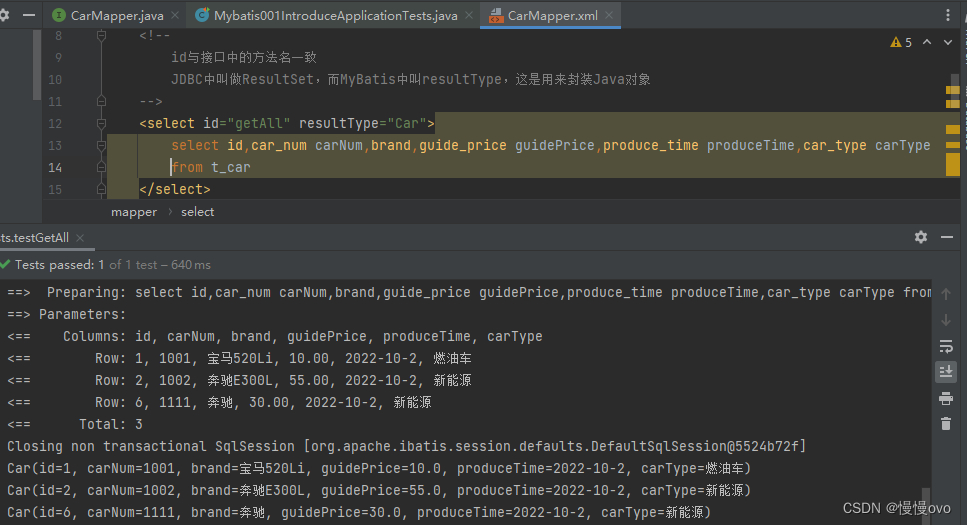
②、按所有字段进行查询
这也是我在快速入门那里留下的伏笔,其实那个select也要进行修改
 五、详解MyBatis核心配置(复习)
五、详解MyBatis核心配置(复习)
这里就当复习了,因为是看的老杜讲解的,更加细致。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration> <!--default表示默认使用的环境--> <environments default="development"> <!--其中的一个环境 连接的数据库是powernode一般一个数据库会对应一个SqlSessionFactory对象一个环境environment会对应一个SqlSessionFactory对象 --> <environment id="development"> <!--MyBatis事务管理器接口Transaction有两个实现类如果type="JDBC"那么底层会实例化JdbcTransaction对象如果type="MANAGED"那么底层会实例化ManagedTransaction对象--> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!--datasource配置:1、dataSource被称为数据源2、dataSource为程序提供Connection对象3、数据源实际上是一套规范,JDK中有这套规范:javax.sql.DataSource4、type有三种值可选其一:POOLED:使用MyBatis自己实现的数据库连接池UNPOOLED:不适用MyBatis的数据库连接池,每一次请求过来创建新的Connection对象JNDI:集成其它第三方的数据库连接池,这是一套规范,大部分Web容器都实现了此规范--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/powernode"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> <!--MyBatis另外一个环境,也就是连接的数据库是另一个数据库MyBatis--> <environment id="mybatisDB"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--通过此标签找到映射文件,实际在SpringBoot中的yml配置文件中变成:mybatis:mapper-locations--> <mappers> <package name="com.chf.mapper" /> </mappers></configuration>@SpringBootTestpublic class ConfigurationTest{@Testvoid testEnvironment() throws Exception{//获取SqlSessionFactory对象(采用默认方式获取)SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssf = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); //采用这种方式获取的就是默认的环境 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssf.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml")); //这种方式通过id获取的是指定的环境 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssf.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml"),"mybatisDB");}}六、结合Web及SpringMVC
这里老杜的是使用MVC架构模式,然后优化使用了动态代理写了两个工具类
但我是基于SpringBoot框架的基础上去复习老杜的MyBatis,所以会使用到SpringMVC去实现老杜的课程
一个项目从前往后写才知道具体需要实现的功能是什么(老杜教的)
修改成功和失败的页面就不截图展示了
项目目录如下以及超简易页面以及数据库表结构
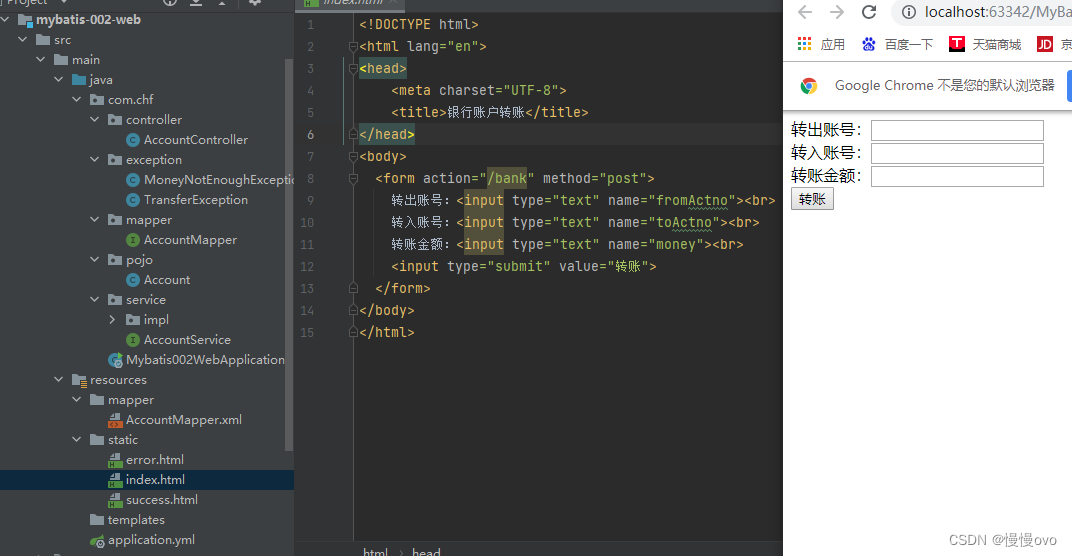
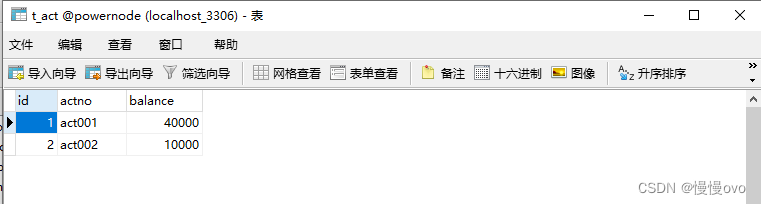 ①根据表结构去编写实体类做到与表中字段一一对应
①根据表结构去编写实体类做到与表中字段一一对应
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToStringpublic class Account { private Long id; private String actno; private Double balance;}②根据网页所知功能需求是银行转账,在Mapper接口编写方法
@Mapperpublic interface AccountMapper { /** * 根据账号查询账户信息 * @param actno * @return */ Account selectByActno(String actno); /** * 更新账户信息 * @param account * @return */ int updateByActno(Account account);}③根据Mapper接口的方法在映射文件中写Sql语句
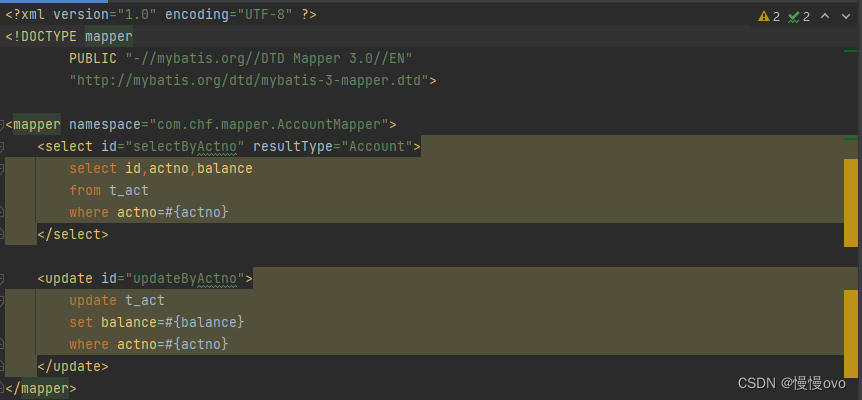
④根据Mapper接口所需方法在业务层中实现
public interface AccountService { /** * 根据账号查询账户信息 * @param actno * @return */ Account selectByActno(String actno); /** * 更新账户信息 * @param account * @return */ int updateByActno(Account account); /** * 账户转账业务。 * @param fromActno 转出账号 * @param toActno 转入账号 * @param money 转账金额 */ void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, TransferException;}@Servicepublic class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Autowired private AccountMapper accountMapper; @Override public Account selectByActno(String actno) { Account account = accountMapper.selectByActno(actno); return account; } @Override public int updateByActno(Account account) { int count = accountMapper.updateByActno(account); return count; } @Override @Transactional public void transfer(String fromActno,String toActno,double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException,TransferException { Account fromAct = selectByActno(fromActno); if(fromAct.getBalance() < money) throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足"); Account toAct = selectByActno(toActno); fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money); toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money); int count = updateByActno(fromAct); count += updateByActno(toAct); if(count != 2) throw new TransferException("转账异常,未知原因"); }}⑤根据想抛出的异常去编写异常类
public class MoneyNotEnoughException extends Exception{ public MoneyNotEnoughException(){} public MoneyNotEnoughException(String msg){ super(msg); }}public class TransferException extends Exception{ public TransferException(){} public TransferException(String msg){ super(msg); }}⑥数据层和业务层方法实现后在表示层编写
@Controllerpublic class AccountController { @Autowired private AccountService accountService; @PostMapping("/bank") public String transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) { double m = Double.parseDouble(String.valueOf(money)); try { accountService.transfer(fromActno,toActno,m); return "redirect:/success.html"; } catch (MoneyNotEnoughException | TransferException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return "redirect:/error.html"; } }}2、MyBatis小技巧
一、#{}与${}及模糊查询
这里就不多写了,详细可以看我博客另外一条文章:花了几天整理了学完的Mybatis框架(内含源码及面试题)_慢慢ovo的博客-CSDN博客
放一点笔记出来品品
<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <!-- 这里是不能使用#{} 否则会以字符串形式放在Sql语句当中 只能使用${} #{}是防止Sql注入风险的 是以值的方式放到Sql语句当中 如果需要的Sql语句的关键字(固定值)放到Sql语句当中只能使用${} --> <select id="selectAllByAscOrDesc" resultType="Car"> select id, car_num carNum, brand, guide_price guidePrice, produce_time produceTime, car_type carType from t_car order by produce_time ${ascOrDesc} </select> <select id="selectByCarType" resultType="Car"> select id, car_num carNum, brand, guide_price guidePrice, produce_time produceTime, car_type carType from t_car where car_type=#{carType} </select> <!--delete from t_car where id in (?,?)--> <delete id="deleteBatch"> delete from t_car where id in (${ids}) </delete> <select id="selectByBrandLike" resultType="Car"> select id, car_num carNum, brand, guide_price guidePrice, produce_time produceTime, car_type carType from t_car where <!--brand like '%${brand}%'--> <!--brand like concat('%',#{brand},'%')--> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </select></mapper>
二、别名机制与mapper标签
mybatis: #基于SpringBoot的mapper标签 mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml #基于SpringBoot的别名机制用于配合xml中的resultType type-aliases-package: com.chf.pojo configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl<!--MyBatis核心配置文件中的--><typeAliases> <!--别名自己指定的--> <typeAlias type="com.chf.pojo.Car" alias="aaa"/> <typeAlias type="com.chf.pojo.Log" alias="bbb"/> <!--采用默认的别名机制--> <typeAlias type="com.chf.pojo.Car"/> <typeAlias type="com.chf.pojo.Log"/> <!--包下所有的类自动起别名。使用简名作为别名。--> <package name="com.chf.pojo"/> </typeAliases><!-- 所有别名不区分大小写。 namespace不能使用别名机制。--> <mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/> <!--要求类的根路径下必须有:CarMapper.xml--> <mapper url="file:///d:/CarMapper.xml"/> <!--要求在d:/下有CarMapper.xml文件--> <mapper class="全限定接口名,带有包名"/><!-- mapper标签的属性可以有三个: resource:这种方式是从类的根路径下开始查找资源。采用这种方式的话,你的配置文件需要放到类路径当中才行。 url: 这种方式是一种绝对路径的方式,这种方式不要求配置文件必须放到类路径当中,哪里都行,只要提供一个绝对路径就行。这种方式使用极少,因为移植性太差。 class: 这个位置提供的是mapper接口的全限定接口名,必须带有包名的。 思考:mapper标签的作用是指定SqlMapper.xml文件的路径,指定接口名有什么用呢? <mapper class="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"/> 如果你class指定是:com.chf.mapper.CarMapper 那么mybatis框架会自动去com/chf/mapper目录下查找CarMapper.xml文件。 注意:也就是说:如果你采用这种方式,那么你必须保证CarMapper.xml文件和CarMapper接口必须在同一个目录下。并且名字一致。 CarMapper接口-> CarMapper.xml LogMapper接口-> LogMapper.xml ....-->三、插入使用生成的主键值
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper{/** * 插入车辆信息并且使用生成的主键值 * @param car * @return */ int insertCarUseGeneratedKeys(Car car);}
3、MyBatis参数处理
一、单个简单类型参数
简单类型包括:
七种数据类型(除了boolean)以及他们的包装类
String
java.util.Date
java.sql.Date
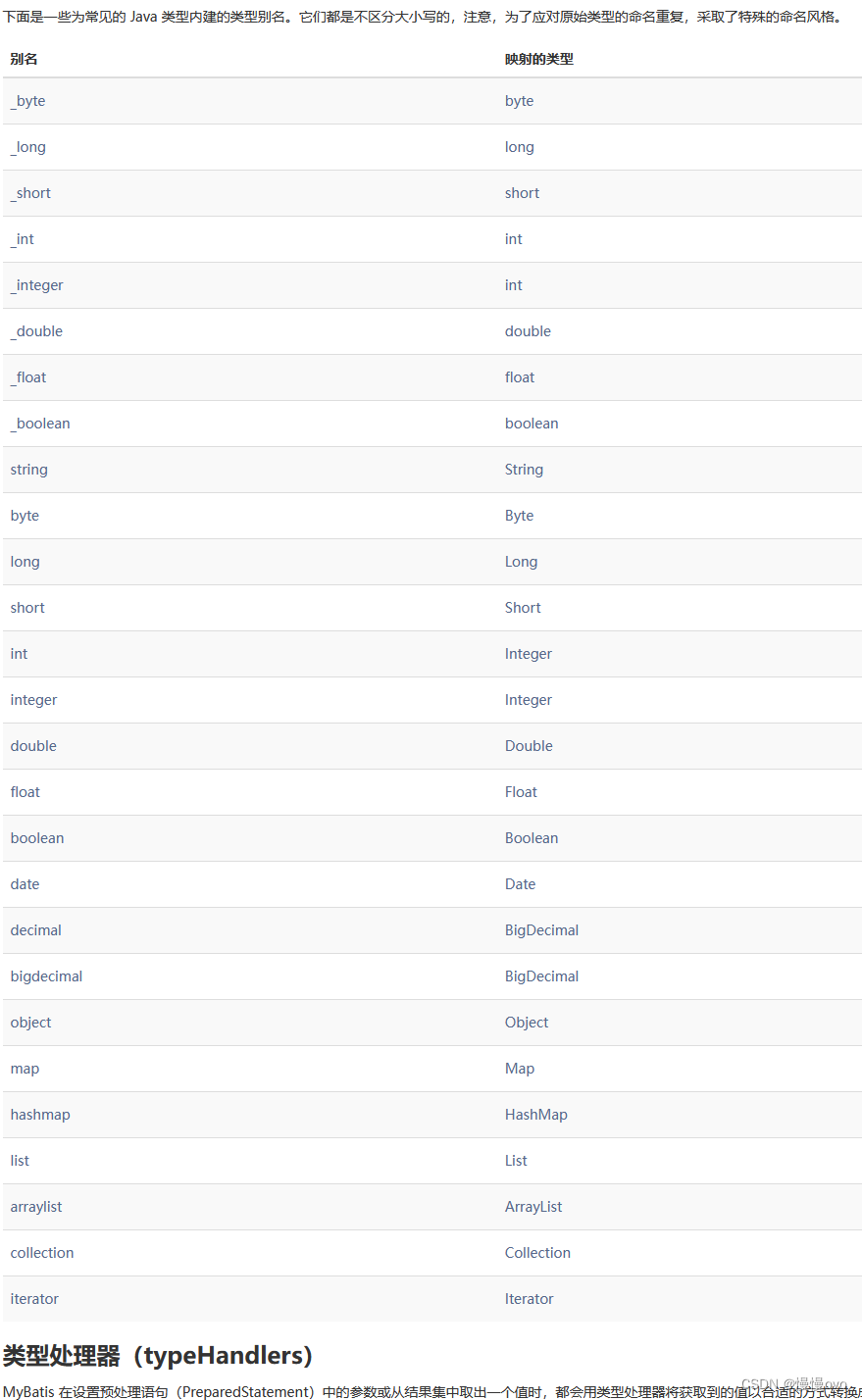
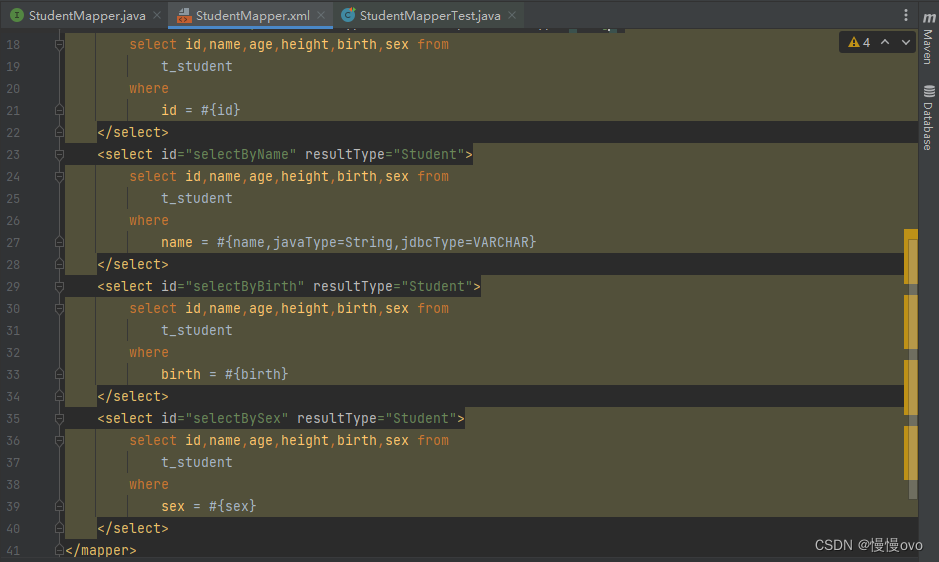
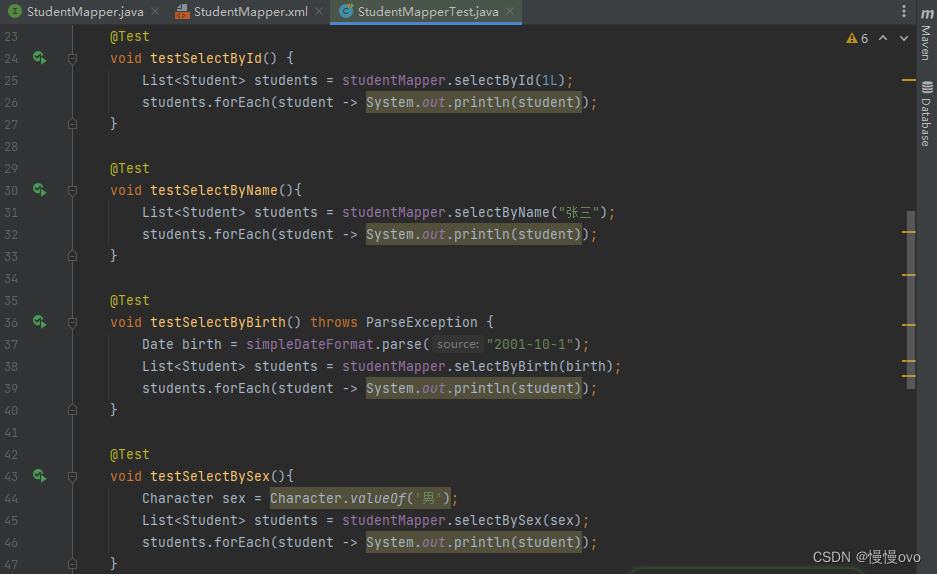
@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper { /** * 当接口的方法的参数只有一个,并且参数的数据类型都是简单类型 * 根据id、name、birth、sex查询 */ List<Student> selectById(Long id); List<Student> selectByName(String name); List<Student> selectByBirth(Date birth); List<Student> selectBySex(Character sex);}parameterType属性的作用: 告诉MyBatis框架这个方法的参数类型是什么类型 MyBatis框架自身带有类型自动推断机制,所以大部分情况下parameterType属性都是可以省略不写的
二、Map参数
①、插入信息
@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper{ /** * 保存学生信息,通过Map参数,以下是单个参数,但是参数的类型不是简单类型,是Map集合 * @param map * @return */ int insertStudentByMap(Map<String,Object> map);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper"><insert id="insertStudentByMap" parameterType="map"> insert into t_student values (null,#{姓名},#{年龄},#{身高},#{生日},#{性别}) </insert></mapper>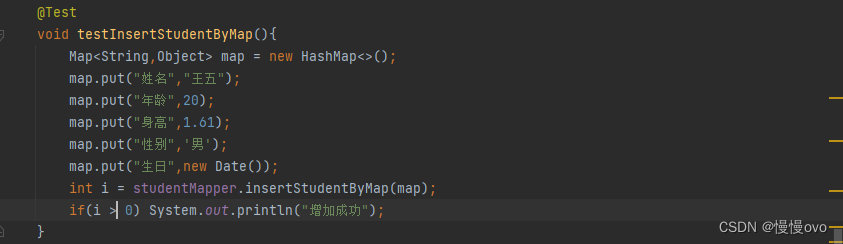
②、查询单个汽车信息
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper{ /** * 根据id获取汽车信息,将汽车信息放到Map集合中 * @param id * @return */ Map<String,Object> selectByIdRetMap(Long id);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"><select id="selectByIdRetMap" resultType="map"> select id, car_num carNum, brand, guide_price guidePrice, produce_time produceTime, car_type carType from t_car where id = #{id} </select></mapper>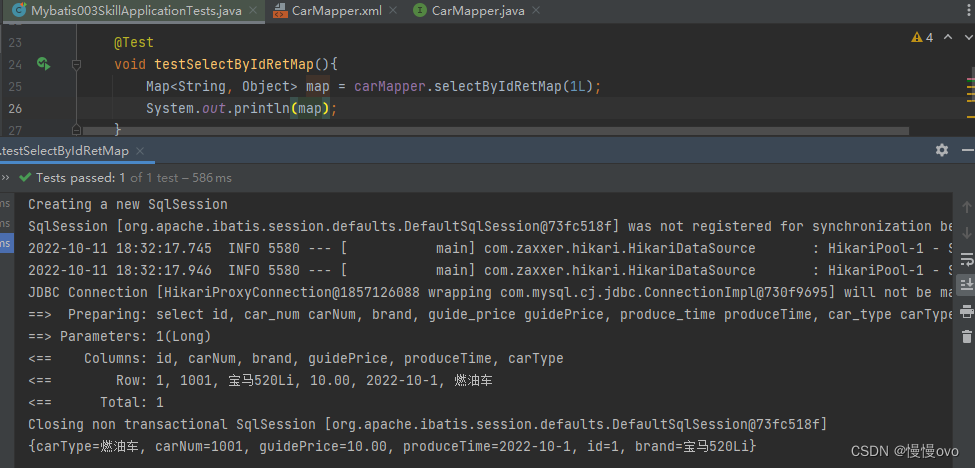
③、返回多个Map
查询结果大于等于1条数据,则可以返回一个存储Map集合的List集合,List<Map>等同于List<Car>
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper{ /** * 查询所有的Car信息返回一个放Map集合的List集合 * @return */ List<Map<String,Object>> selectAllRetListMap();}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"><!--注意:这个resultType是map不是list--> <select id="selectAllRetListMap" resultType="map"> select id, car_num carNum, brand, guide_price guidePrice, produce_time produceTime, car_type carType from t_car </select></mapper>④、返回Map<String,Map>
通过Car的id做Key,以后取出对应的Map集合时更方便
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper{ /** * 查询所有的Car返回一个大Map结合 * Map集合的key是每条记录的主键值 * Map集合的value的每条记录 * @return */ @MapKey("id") Map<Long,Map<String,Object>> selectAllRetMap();}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <select id="selectAllRetMap" resultType="map"> select id, car_num carNum, brand, guide_price guidePrice, produce_time produceTime, car_type carType from t_car </select></mapper>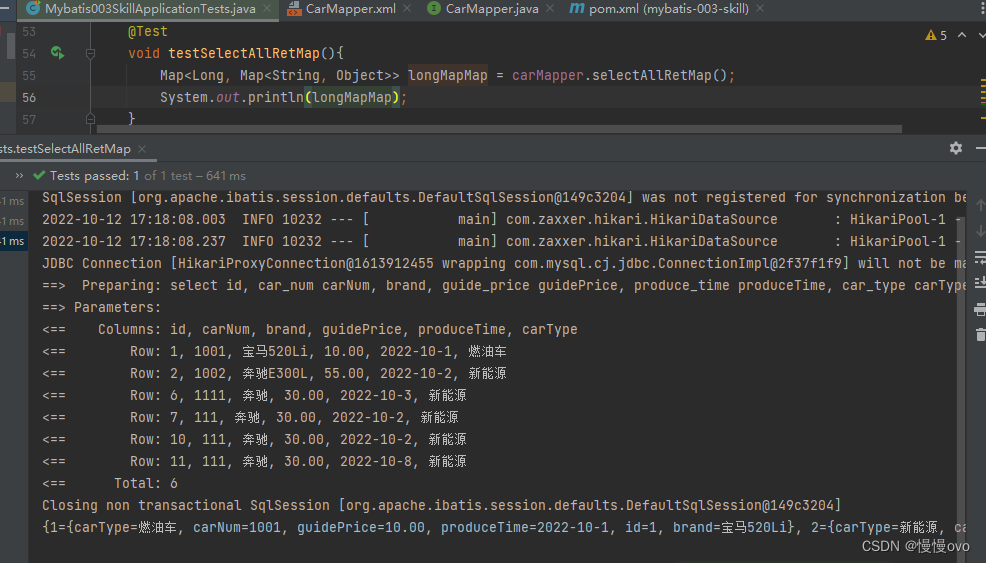
{
1={carType=燃油车, carNum=1001, guidePrice=10.00, produceTime=2022-10-1, id=1, brand=宝马520Li},
2={carType=新能源, carNum=1002, guidePrice=55.00, produceTime=2022-10-2, id=2, brand=奔驰E300L},
6={carType=新能源, carNum=1111, guidePrice=30.00, produceTime=2022-10-3, id=6, brand=奔驰},
7={carType=新能源, carNum=111, guidePrice=30.00, produceTime=2022-10-2, id=7, brand=奔驰},
10={carType=新能源, carNum=111, guidePrice=30.00, produceTime=2022-10-2, id=10, brand=奔驰},
11={carType=新能源, carNum=111, guidePrice=30.00, produceTime=2022-10-8, id=11, brand=奔驰}
}
三、实体类参数
@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper{ /** * 保存学生信息,通过POJO参数,Student是单个参数,但不是简单类型 * @param student * @return */ int insertStudentByPOJO(Student student);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper"><insert id="insertStudentByPOJO"> insert into t_student values (null,#{name},#{age},#{height},#{birth},#{sex}) </insert></mapper>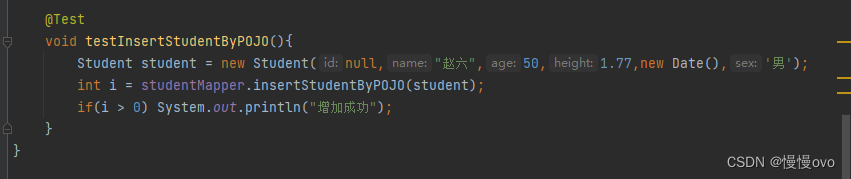
四、多参数(@Param)
不需要使用arg0、arg1、param1、param2等等,直接使用@Param注解增强可读性
需求:根据name和age查询学生信息
@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper{ /** * 这是多参数查询 * 根据name和sex查询Student信息 * 如果是多个参数的话,MyBatis框架底层的做法如下: * MyBatis框架会自动创建一个Map集合并且Map集合是以这种方式存储参数的 * map.put("arg0",name);/map.put("param1",name); * map.put("arg1",sex);/map.put("param2",sex); * * 使用Param注解指定Sql语句中的#{}命名 * @param name * @param sex * @return */ List<Student> selectByNameAndSex( @Param("nnn") String name, @Param("sss") Character sex);}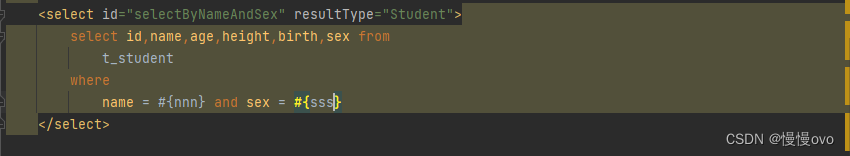
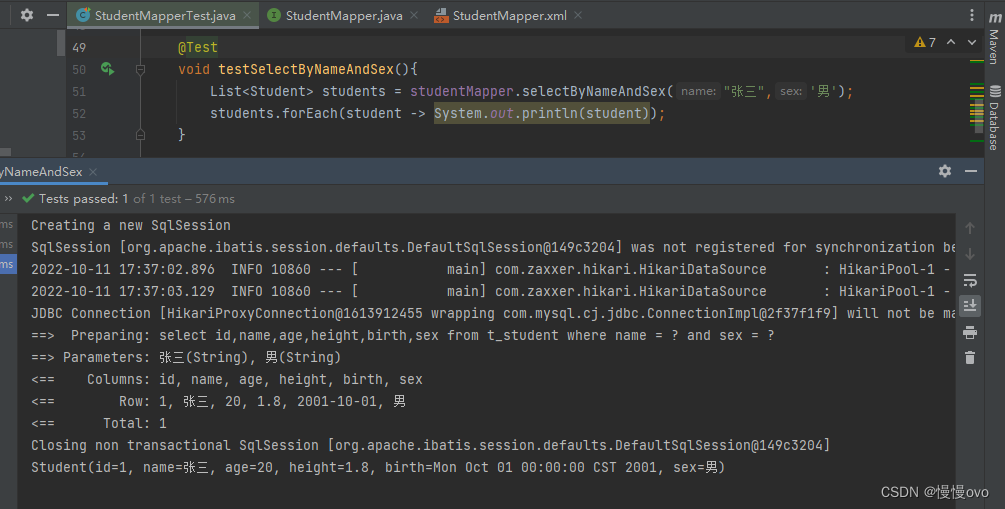
五、resultMap结果映射
①、使用resultMap进行结果映射(常用)
查询结果的列名和java对象的属性名对应不上的做法?
第一种方式:as 给列起别名 as可以省略不写,我们前面的做法就是如此
第二种方式:使用resultMap进行结果映射
第三种方式:是否开启驼峰命名自动映射(设置settings)
在一对标签中resultType和resultMap两者只能有一个 当查询要返回对象,
而且属性和字段不一致的时候用resultMap。
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper{ /** * 查询所有的Car信息,使用resultMap标签进行结果映射 * @return */ List<Car> selectAllByResultMap();}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"><!-- 1、专门定义一个结果映射,在这个结果映射当中指定数据库表的字段名和Java类的属性名的对应关系 2、type属性:用来指定POJO类的类名 3、id属性:指定resultMap的唯一标识,这个id将来要在select标签中使用 --> <resultMap id="carResultMap" type="Car"> <!--如果数据库表中有主键,一般都是有主键,要不然不符合数据库设计第一范式--> <!--如果有主键,建议这里配置一个id标签,这样的配置可以让MyBatis提高效率--> <id property="id" column="id" /> <!-- property后面填写的是POJO类的属性名 column后面填写数据库表的字段名 --> <result property="carNum" column="car_num" /> <result property="guidePrice" column="guide_price" /> <result property="produceTime" column="produce_time" /> <result property="carType" column="car_type" /> </resultMap> <!--select标签中的resultMap属性用来指定使用哪个结果映射,resultMap后面的值是resultMap的id--> <select id="selectAllByResultMap" resultMap="carResultMap"> select id, car_num, brand, guide_price, produce_time, car_type from t_car </select></mapper>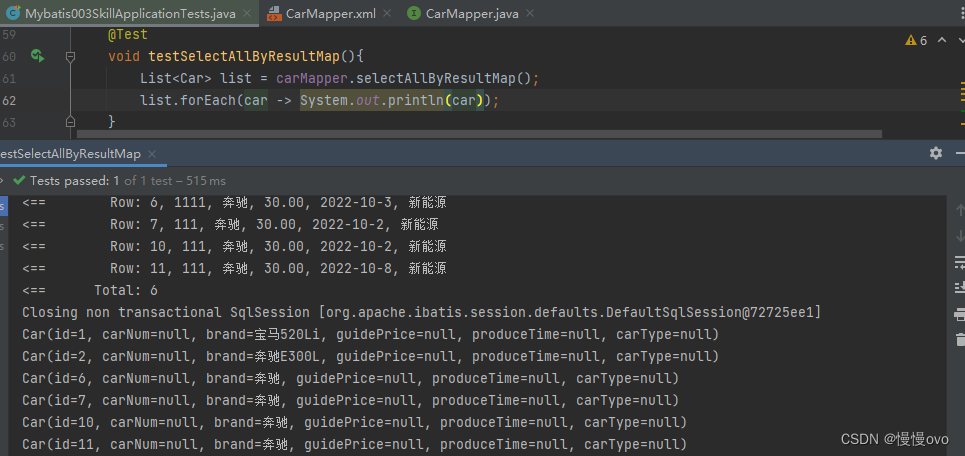
②、开启驼峰命名规范自动映射
使用这种方式的前提是:属性名遵循Java的命名规范,数据库表的列名遵循SQL的命名规范。
Java命名规范:首字母小写,后面每个单词首字母大写,遵循驼峰命名方式。
SQL命名规范:全部小写,单词之间采用下划线分割。
mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml type-aliases-package: com.chf.pojo configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #开启驼峰自动映射 map-underscore-to-camel-case: true@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper{ List<Car> selectAllByResultMapTwo();}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <select id="selectAllByResultMap" resultType="Car"> select id, car_num, brand, guide_price, produce_time, car_type from t_car </select></mapper>
六、获取总记录条数
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper{ /** * 获取Car的总记录条数 * @return */ Long selectTotal();}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <select id="selectTotal" resultType="long"> select count(*) from t_car </select></mapper>
4、动态SQL(注:使用了驼峰命名规范)
什么是动态SQL?
SQL的内容是变化的, 可以根据条件获取到不同的SQL语句 主要是where部分发生变化。 动态SQL的实现, 使用的是MyBatis提供的标签
为什么使用动态SQL
使用动态SQL可以解决某些功能的使用 例如使用条件查询某个商品 输入价格,地区等等进行筛选,如果使用静态SQL可能会查询出来的是一个空内容 但使用动态SQL可以很好的解决这种问题
动态SQL的标签:
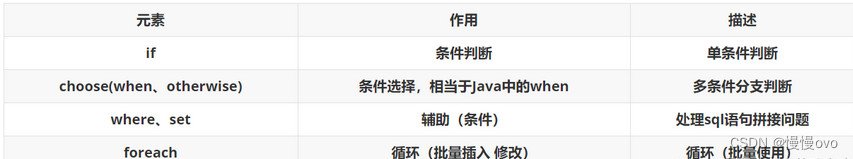
一、if标签
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 多条件查询 * @param brand 品牌 * @param guidePrice 指导价 * @param carType 汽车类型 * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiCondition(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <!-- 1、if标签中的test属性是必须的 2、if标签中test属性的值是false或者是true 3、如果为true,则if标签中的sql语句就会拼接。反之就不会拼接 4、test属性中可以使用的是: 当使用了@Param注解,那么test中要出现的是@Param注解指定的参数名。 当没有使用@Param注解,那么test中要出现的是:param1 param2 param3 ... 当使用了POJO,那么test中出现的是POJO类的属性名 5、在MyBatis的动态SQL中,不能使用&&,使用的是and 6、标签内与#{}内写的都是POJO属性名,其余是SQL的字段名 7、注意:这里我在yml文件配置了MyBatis的自动驼峰命名规范,所以不用使用as重新命名8、这个1 = 1是防止后面出现空传值导致SQL语句出现错误 --> <select id="selectByMultiCondition" resultType="Car"> select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car where 1 = 1 <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> and brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price >= #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type like "%"#{carType}"%" </if> </select></mapper>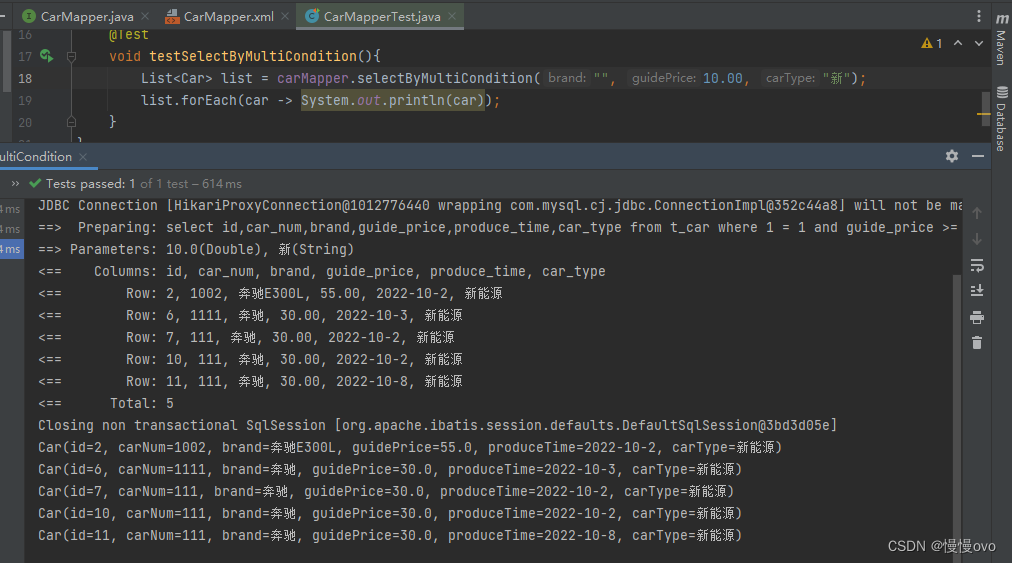
二、where标签
where标签的作用:让where子句更加动态智能。
所有条件都有空时,where标签保证不会生成where子句。
自动去除某些条件前面多余的and或or
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 使用where标签,让where子句更加的智能 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithWhere(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <!-- where标签是专门负责where子句动态生成的 这里将1 = 1去掉了并且第一个if标签语句还有"and"关键字 但丝毫不影响SQL查询语句 但要注意:不能在语句后面加"and"比如:and brand like "%"#{brand}"%" and --> <select id="selectByMultiConditionWithWhere" resultType="Car"> select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car <where> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> and brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> and guide_price >= #{guidePrice} </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> and car_type like "%"#{carType}"%" </if> </where> </select></mapper>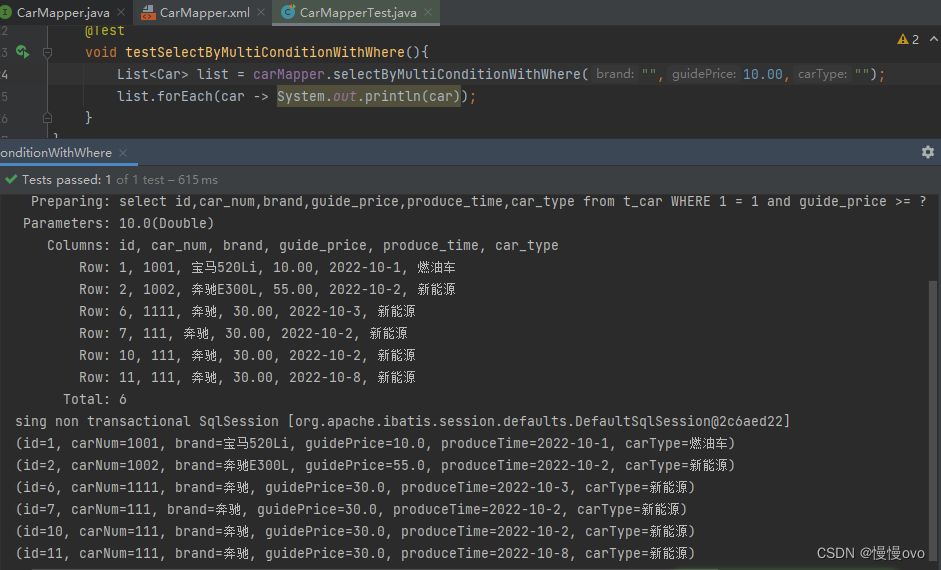
三、trim标签
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 使用trim标签 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithTrim(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <!-- prefix:加前缀 suffix:加后缀 prefixOverrides:删除前缀 suffixOverrides:删除后缀 以下表示在trim标签所有内容的前面添加where,后缀的and或者or去掉 --> <select id="selectByMultiConditionWithTrim" resultType="Car"> select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car <trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and|or"> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" and </if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> guide_price >= #{guidePrice} and </if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''"> car_type like "%"#{carType}"%" </if> </trim> </select></mapper>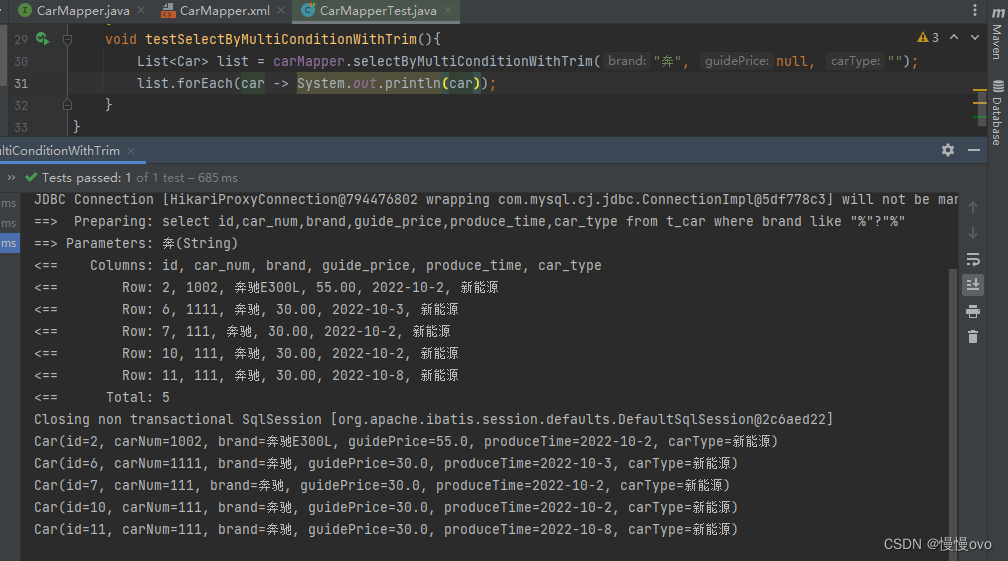
四、set标签
主要使用在update语句当中,用于生成set关键字,同时去掉最后多余的","
比如我们只更新提交的不为空的字段,如果提交的数据是空或者"",那么这个字段我们将不更新。
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 使用set标签进行更新 * @param car * @return */ int updateBySet(Car car);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <update id="updateBySet"> update t_car <set> <if test="carNum != null and carNum != ''">car_num = #{carNum},</if> <if test="brand != null and brand != ''">brand = #{brand},</if> <if test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''">guide_price = #{guidePrice},</if> <if test="produceTime != null and produceTime != ''">produce_time = #{produceTime},</if> <if test="carType != null and carType != ''">car_type = #{carType}</if> </set> where id = #{id} </update></mapper>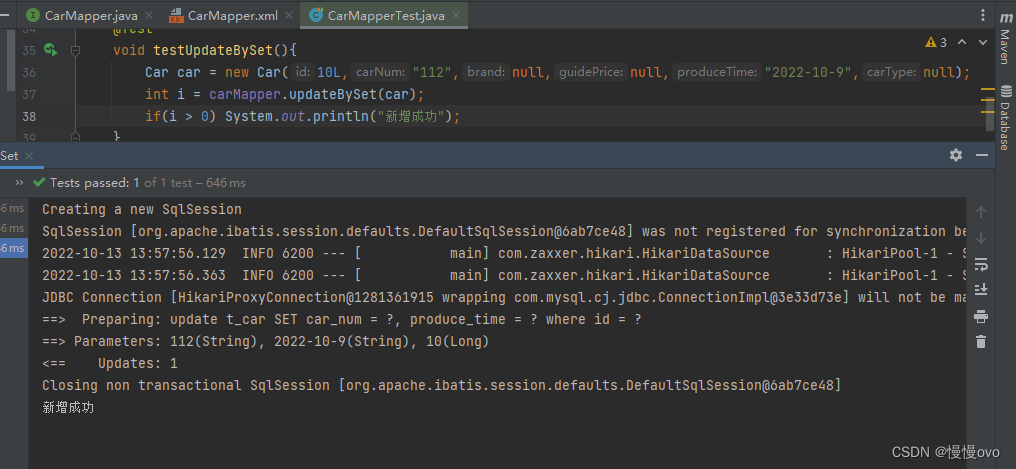
五、choose where otherwise
这三个标签是在一起使用的
Mapper映射语法格式:
<choose><when></when><when></when><otherwise></otherwise></choose>等同于Code语法格式:
if(){}else if(){}else if(){}else{}@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 使用choose when otherwise标签 * @param brand * @param guidePrice * @param carType * @return */ List<Car> selectByChoose(@Param("brand") String brand, @Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice, @Param("carType") String carType);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <select id="selectByChoose" resultType="Car"> select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car <where> <choose> <when test="brand != null and brand != ''"> brand like "%"#{brand}"%" </when> <when test="guidePrice != null and guidePrice != ''"> guide_price >= #{guidePrice} </when> <otherwise> car_type like "%"#{carType}"%" </otherwise> </choose> </where> </select></mapper>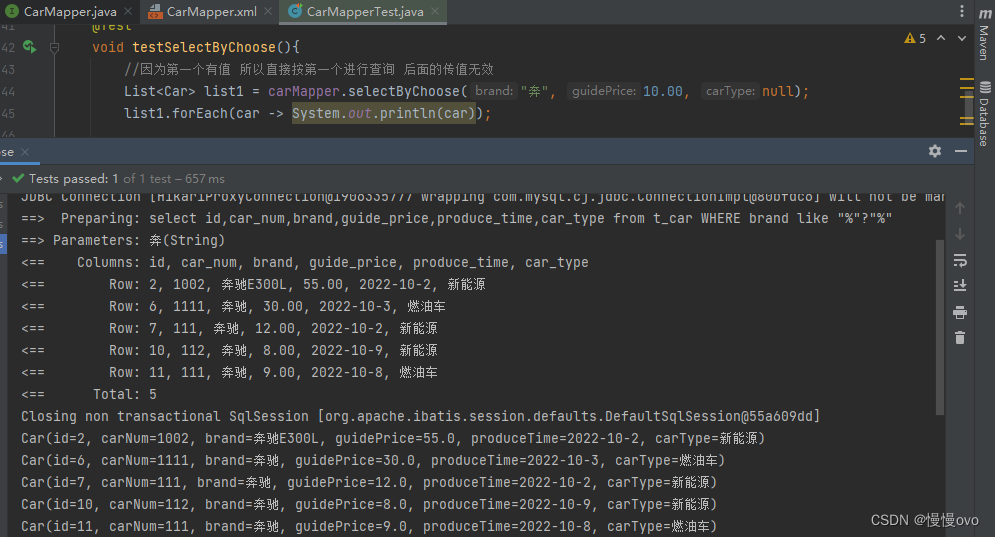
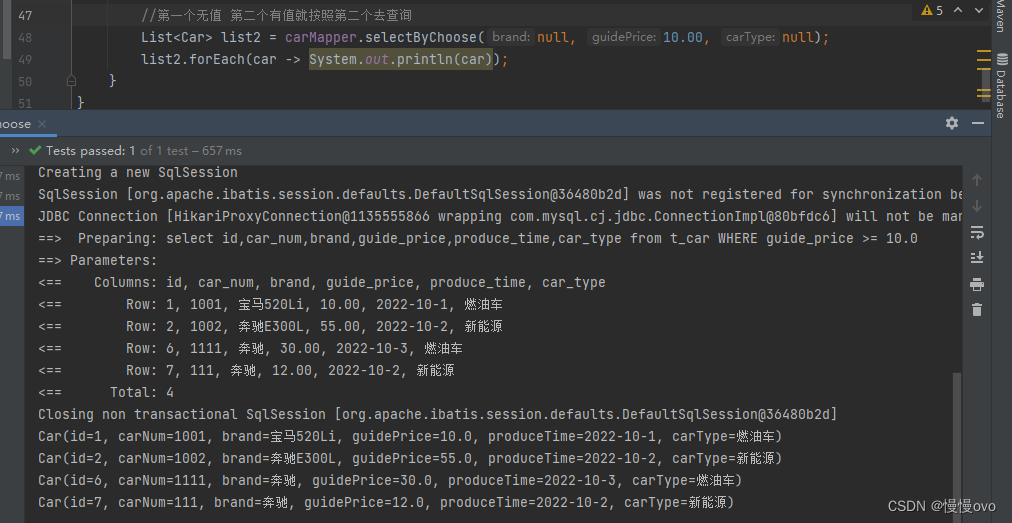
六、foreach标签
①批量删除
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 根据id批量删除 foreach * @param ids * @return */ int deleteByIds(@Param("ids") Long[] ids);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <!-- foreach标签的属性: collection:指定数组或者集合 item:代表数组或集合中的元素 separator:循环之间的分隔符 open:在标签先添加的符号 close:在标签后添加的符号 --> <update id="deleteByIds"> delete from t_car where id in <foreach collection="ids" item="aaa" separator="," open="(" close=")"> #{aaa} </foreach> </update></mapper>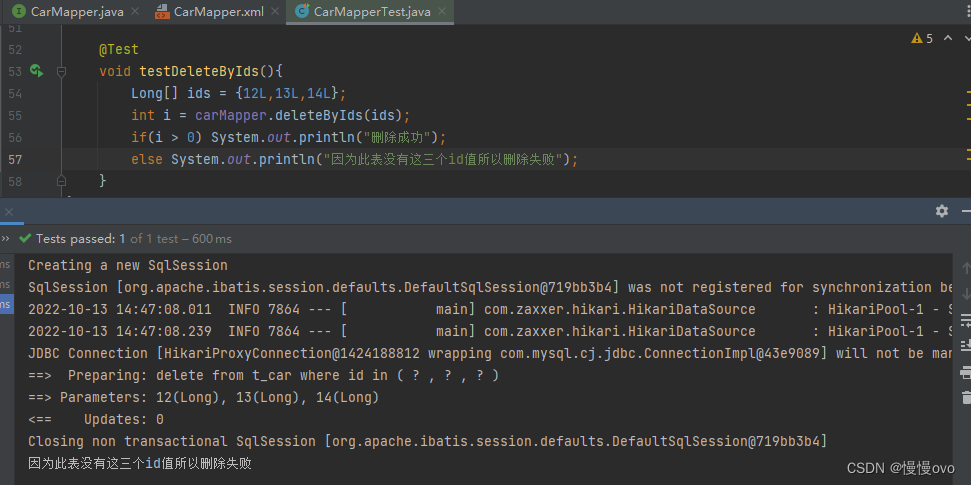
②批量添加
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 批量插入,一次插入多条Car信息 * @param cars * @return */ int insertBatch(@Param("cars") List<Car> cars);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <insert id="insertBatch"> insert into t_car values <foreach collection="cars" item="car" separator=","> (null,#{car.carNum},#{car.brand},#{car.guidePrice},#{car.produceTime},#{car.carType}) </foreach> </insert></mapper>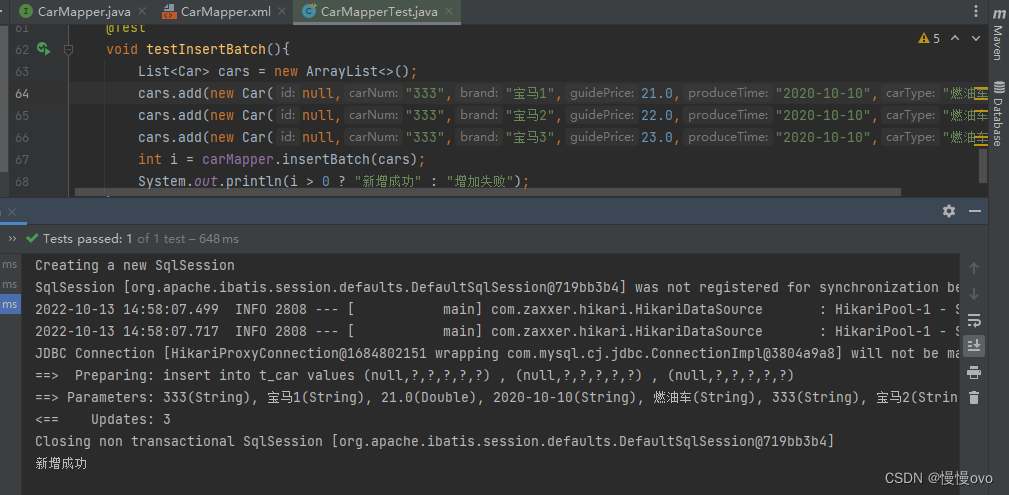
七、sql、include标签
sql标签用来声明sql片段
include标签用来将声明的sql片段包含到某个sql语句当中
作用:代码复用、易维护
在我跟着老杜学的MyBatis中。他提过一句查询语句最好不要使用星号,因为这会使MySQL索引失效从而导致查询性能下降。所以我上面的笔记没有使用到星号,都是用具体字段进行查询。
<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <!--声明一个SQL片段--> <sql id="carColumnNameSql"> id, car_num, brand, guide_price, produce_time, car_type </sql> <!--将声明的SQL片段包含进来--> <select id="selectAll" resultType="Car"> select <include refid="carColumnNameSql" /> from t_car </select></mapper>5、高级映射及延迟加载
一、多对一
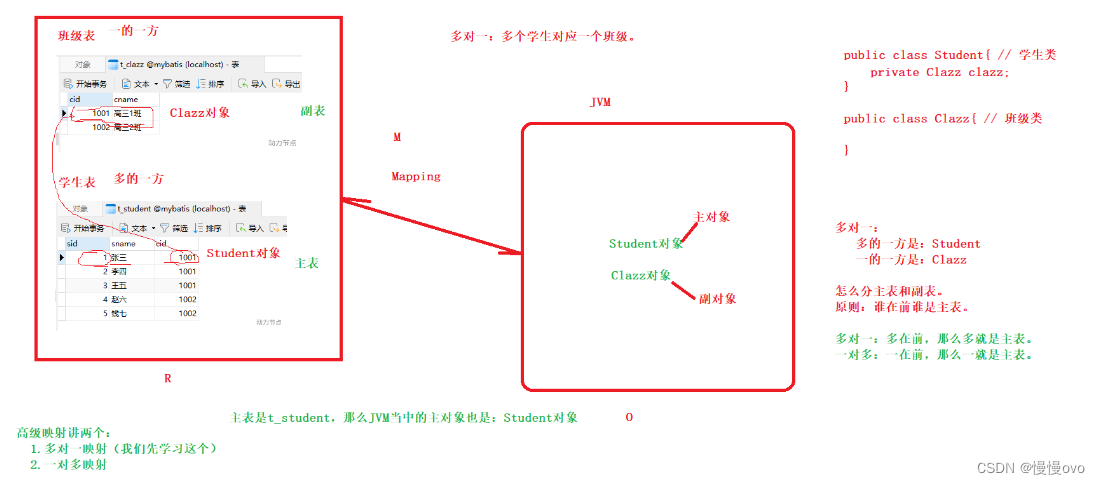
多种方式,常见的包括三种:
第一种方式:一条SQL语句,级联属性映射
第二种方式:一条SQL语句,association
第三种方式(常用):两条SQL语句,分步查询。 优点:可复用、支持懒加载
表的结构如下:
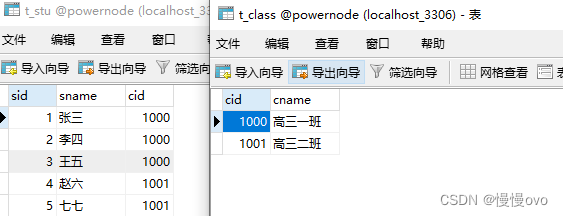
两个实体类如下:
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToStringpublic class Student { //Student是多的一方 private Integer sid; private String sname; private Class clazz; //clazz是一的一方}@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToStringpublic class Class { //教室类 private Integer cid; private String cname;}第一种方式:级联属性映射
@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper { /** * 根据id获取学生信息,同时获取学生关联的班级信息 * @param id 学生的id * @return 学生对象,但是学生对象当中含有班级对象 */ Student selectById(Integer id);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper"> <!--记住:前者是属性名,后者是字段名 前面了解过 这里再复习一下--> <!--多对一映射的第一种方式:一条SQL语句,级联属性映射--> <resultMap id="studentResultMap" type="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid" /> <result property="sname" column="sname" /> <result property="clazz.cid" column="cid" /> <result property="clazz.cname" column="cname" /> </resultMap> <select id="selectById" resultMap="studentResultMap"> select s.sid,s.sname,c.cid,c.cname from t_stu s left join t_class c on s.cid = c.cid where s.sid = #{sid} </select></mapper>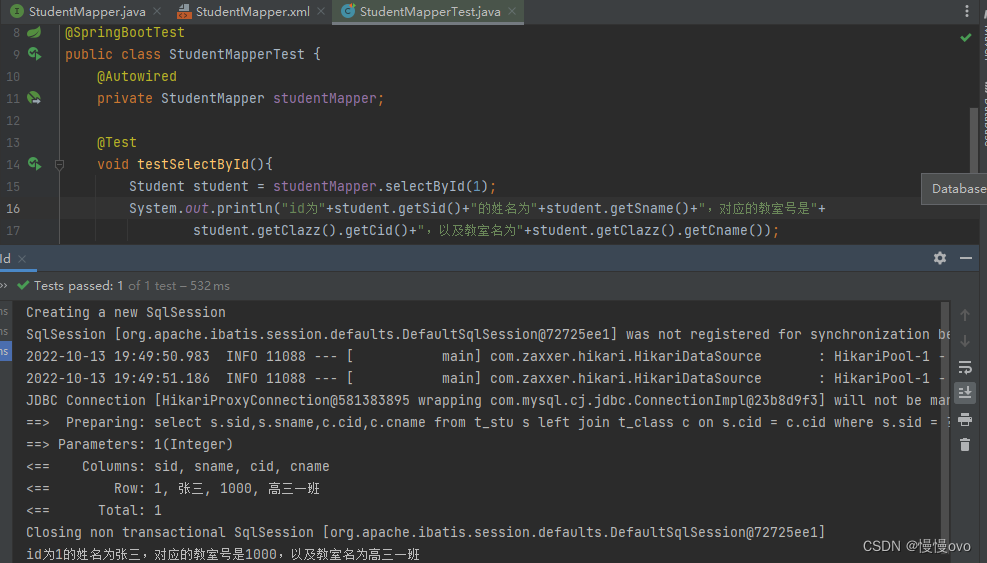
第二种方式:association
@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper { /** * 一条SQL语句,association * @param id * @return */ Student selectByIdAssociation(Integer id);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper"> <!-- association翻译为关联,一个Student对象关联一个Class对象 property:提供要映射的POJO的参数名 javaType:用来指定要映射的java类型 --> <resultMap id="studentResultMapAssociation" type="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid" /> <result property="sname" column="sname" /> <association property="clazz" javaType="Class"> <id property="cid" column="cid" /> <result property="cname" column="cname" /> </association> </resultMap> <select id="selectByIdAssociation" resultMap="studentResultMapAssociation"> select s.sid,s.sname,c.cid,c.cname from t_stu s left join t_class c on s.cid = c.cid where s.sid = #{sid} </select></mapper>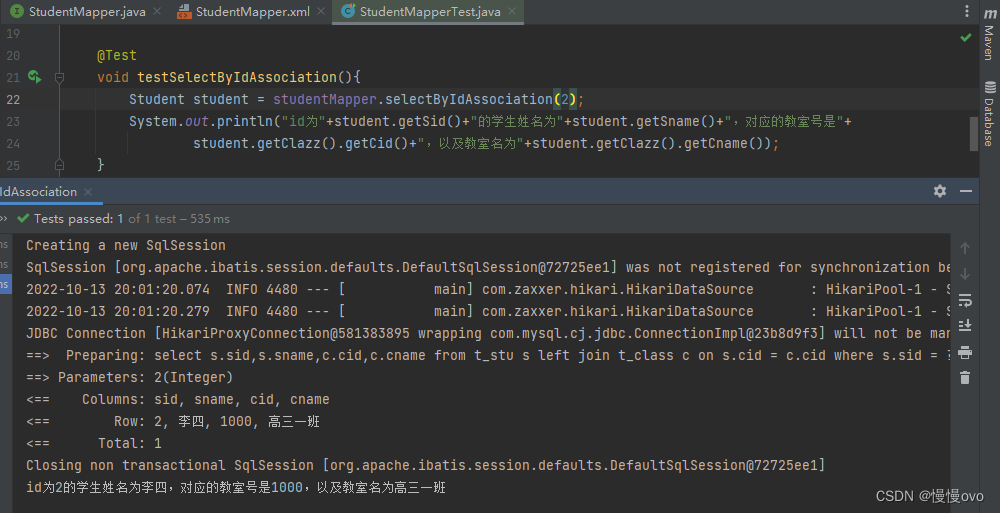
第三种方式:分步查询
@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper { /** * 分步查询第一步:先根据学生的sid查询学生的信息 * @param id * @return */ Student selectByIdStep1(Integer id);}@Mapperpublic interface ClassMapper { /** * 分步查询第二步:根据cid获取班级信息 * @param id * @return */ Class selectByIdStep2(Integer id);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper"> <!--分步查询的有点:第一:复用性增强。可以重复利用(大步分成小步,每一小步更加可以重新利用)第二:可以充分利用他们的延迟加载/懒加载机制--> <!--两条SQL语句,完成多对一的多步查询--> <!--这里是第一步:根据学生的id查询学生的所有信息,这些信息当中含有班级id(cid)--> <resultMap id="studentResultMapByStep" type="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid" /> <result property="sname" column="sname" /> <association property="clazz" select="com.chf.mapper.ClassMapper.selectByIdStep2" column="cid" /> </resultMap> <select id="selectByIdStep1" resultMap="studentResultMapByStep"> select sid,sname,cid from t_stu where sid = #{sid} </select></mapper><mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.ClassMapper"> <!--分步查询第二步:根据cid获取班级信息--> <select id="selectByIdStep2" resultType="Class"> select cid,cname from t_class where cid = #{cid} </select></mapper>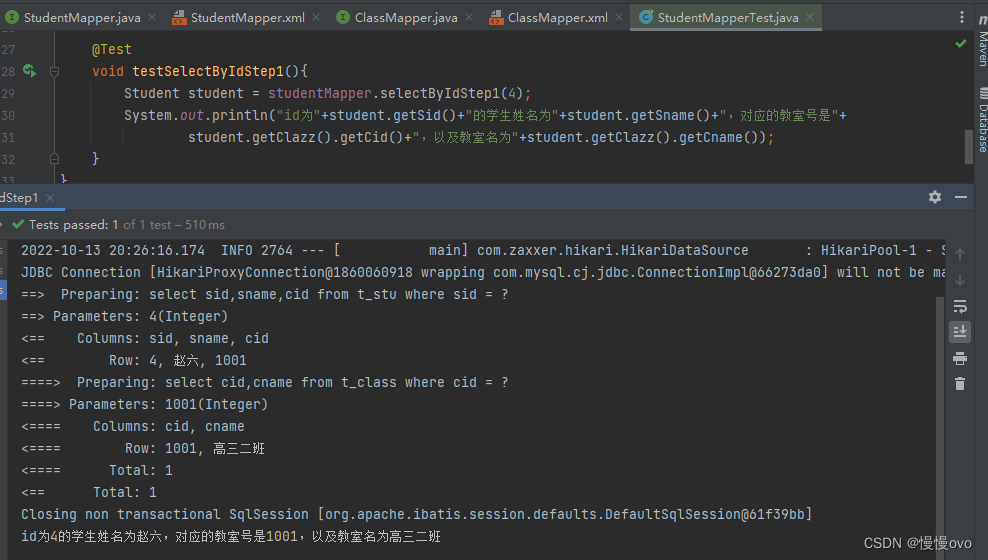
二、多对一延迟加载
实际开发中的模式:
把全局的延迟加载打开,如果某个映射文件不需要那么就在association标签里使用fetchType="eager"关闭
<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper"> <!--延迟加载的核心机制:用的时候再执行查询语句,不用的时候不查询,可以提高性能。默认情况下是没有开启延迟加载的,需要手动设置开启。开启延迟加载的方法:association标签中添加fetchType="lazy"但是这里只是开启默认的延迟加载,仅局限于此Mapper映射文件,需要在核心配置文件里设置如果开启了全局延迟加载,但又不想在某个映射文件中开启,那么就需要在association标签设置fetchType="eager"--> <resultMap id="studentResultMapByStep" type="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid" /> <result property="sname" column="sname" /> <association property="clazz" select="com.chf.mapper.ClassMapper.selectByIdStep2" column="cid" fetchType="lazy" /> </resultMap> <select id="selectByIdStep1" resultMap="studentResultMapByStep"> select sid,sname,cid from t_stu where sid = #{sid} </select></mapper>mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml type-aliases-package: com.chf.pojo configuration: log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #实际开发中,大部分都是需要使用延迟加载的 #延迟加载的全局开关,默认值false为不开启 lazy-loading-enabled: true三、一对多

一对多的实现,通常是在一的一方中有List集合属性。
在Class(教室)类中添加List<Student> studentList属性。
一对多的实现通常包括两种实现方式:
第一种方式:collection
第二种方式:分步查询
两个实体类如下:
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToStringpublic class Student { private Integer sid; private String sname; private Class clazz; }@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToStringpublic class Class { //教室类 private Integer cid; private String cname; private List<Student> studentList;}第一种方式:collection
<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.ClassMapper"> <resultMap id="classResultMap" type="Class"> <id property="cid" column="cid" /> <result property="cname" column="cname" /> <!--一对多,这里是collection,collection是集合的意思--> <!--ofType属性用来指定结合当中的元素类型即集合中的泛型--> <collection property="studentList" ofType="Student"> <id property="sid" column="sid" /> <result property="sname" column="sname" /> </collection> </resultMap> <select id="selectByCollection" resultMap="classResultMap"> select c.cid,c.cname,s.sid,s.sname from t_class c left join t_stu s on c.cid = s.cid where c.cid = #{cid} </select></mapper>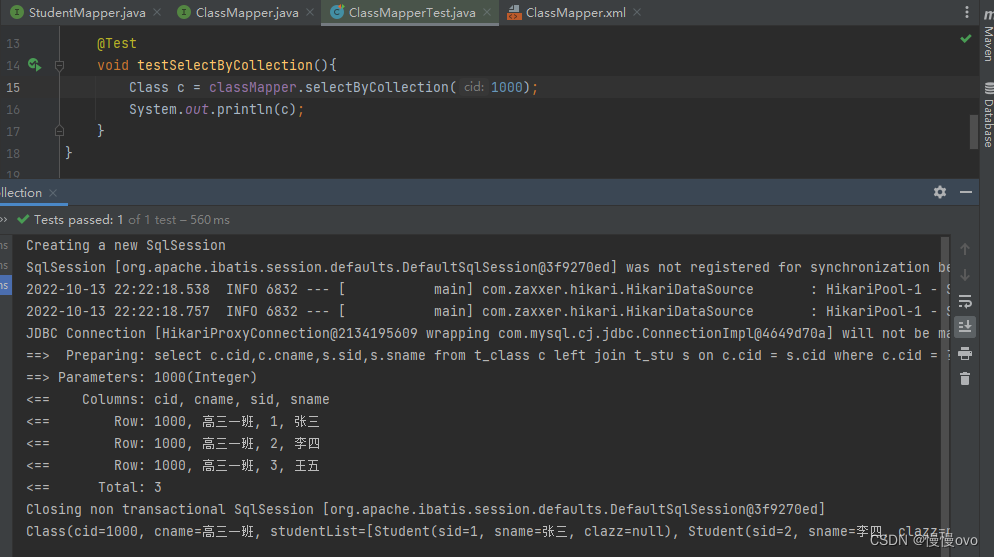
注意:控制台输出的clazz=null是没有问题的
第二种方式:分步查询
@Mapperpublic interface ClassMapper { /** * 分步查询第一步:根据班级编号获取班级信息 * @param cid * @return */ Class selectByStep1(Integer cid);}@Mapperpublic interface StudentMapper { /** * 根据班级编号查询学生信息 * @param cid * @return */ List<Student> selectByStep2(Integer cid);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.ClassMapper"> <!--分步查询第一句:根据班级的cid查询班级信息--> <resultMap id="classResultMapStep" type="Class"> <id property="cid" column="cid" /> <result property="cname" column="cname" /> <association property="studentList" column="cid" select="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper.selectByStep2" /> </resultMap> <select id="selectByStep1" resultMap="classResultMapStep"> select cid,cname from t_class where cid = #{cid} </select></mapper><mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.StudentMapper"><!--分步查询第二步:根据传过来的班级编号查询学生信息--> <select id="selectByStep2" resultType="Student"> select sid,sname from t_stu where cid = #{cid} </select></mapper>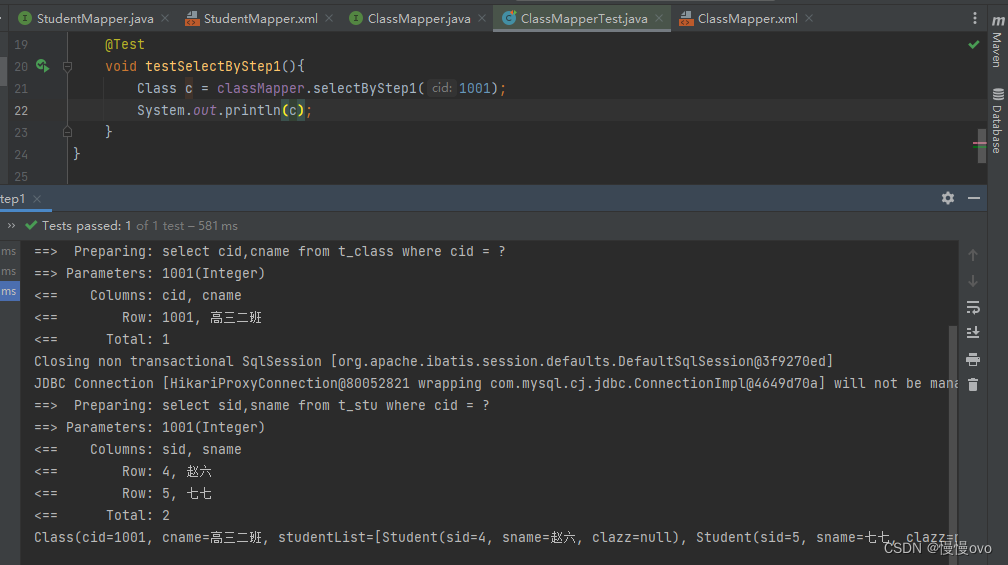
四、一对多延迟加载
与上面的多对一延迟加载相同,可以回去重新看一下。
6、MyBatis缓存机制
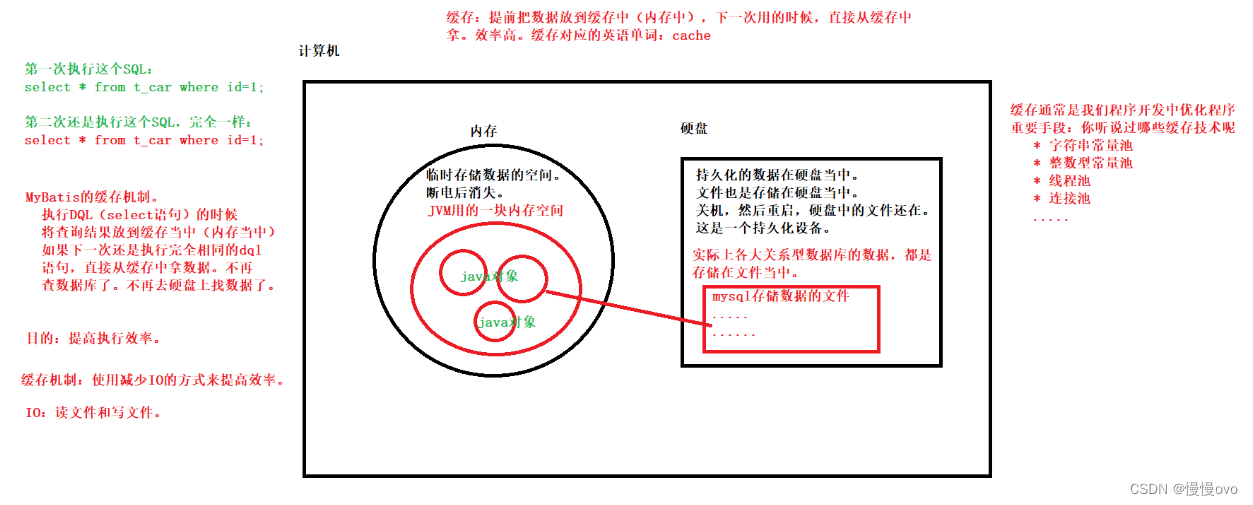
缓存:cache
缓存的作用:通过减少IO的方式来提高程序的执行效率。
MyBatis的缓存:将select语句的查询结果放到缓存(内存)当中,下一次还是这条select语句的话,直接从缓存中取,不需要查询数据库。一方面是减少了IO,另一方面不再执行繁琐的查找算法,效率大大提升。
MyBatis缓存包括:
一级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到SqlSession中。
二级缓存:将查询到的数据存储到SqlSessionFactory中。
其他集成第三方的缓存:比如EhCache【Java语言开发的】、Memcache【c语言开发的】等。
缓存只针对于DQL语句,也就是说缓存机制只对应select语句
一、一级缓存
一级缓存是默认开启的,不需要做任何配置(后半句指在纯MyBatis框架中)。
它的作用范围是在同一个SqlSession中,即在同一个SqlSession中共享。
原理:只要使用同一个SqlSession对象执行同一条SQL语句就会走缓存
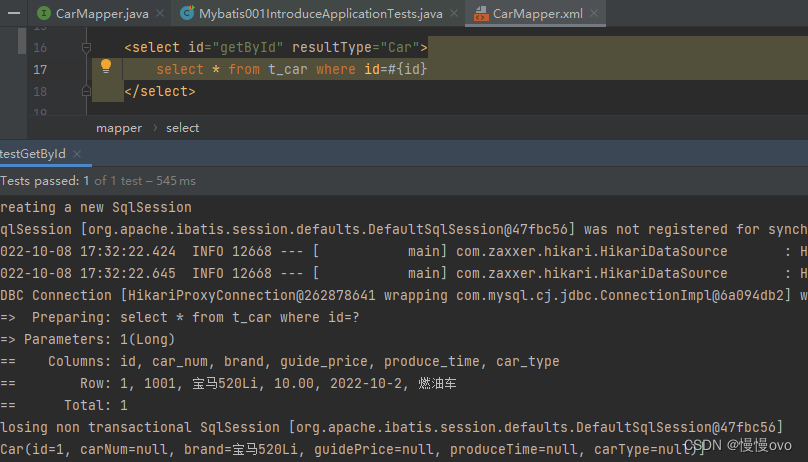
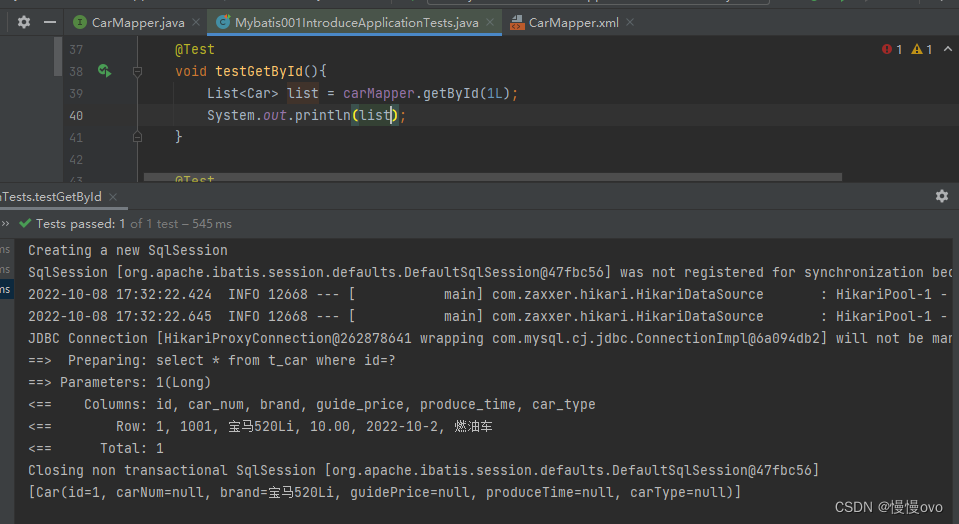
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToStringpublic class Car { private Long id; private String carNum; private String brand; private Double guidePrice; private String produceTime; private String carType;}@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 根据id获取Car信息 * @param id * @return */ Car selectById(Long id);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <sql id="selectAll"> id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type </sql> <select id="selectById" resultType="Car"> select <include refid="selectAll" /> from t_car where id = #{id} </select></mapper>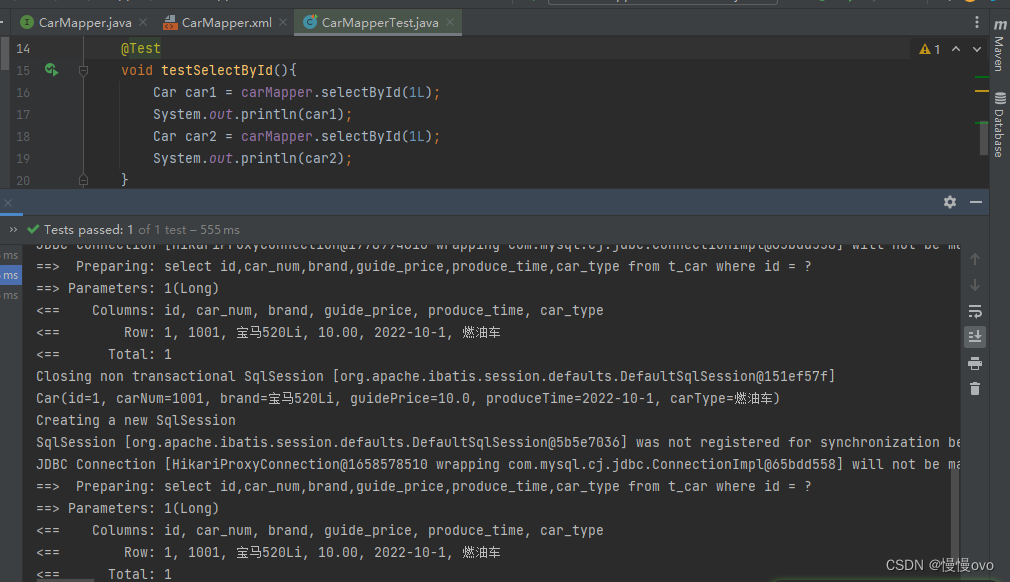
我们会发现在SpringBoot结合MyBatis中没有自动开启一级缓存机制,查询相同的id使用了两次查询。但是我们在方法名上添加@Transactional注解就会发现控制台发生了变化:只执行了一次查询语句。也就是说添加了@Transactional注解就能够使用一级缓存,换言之就是同一个SqlSession。
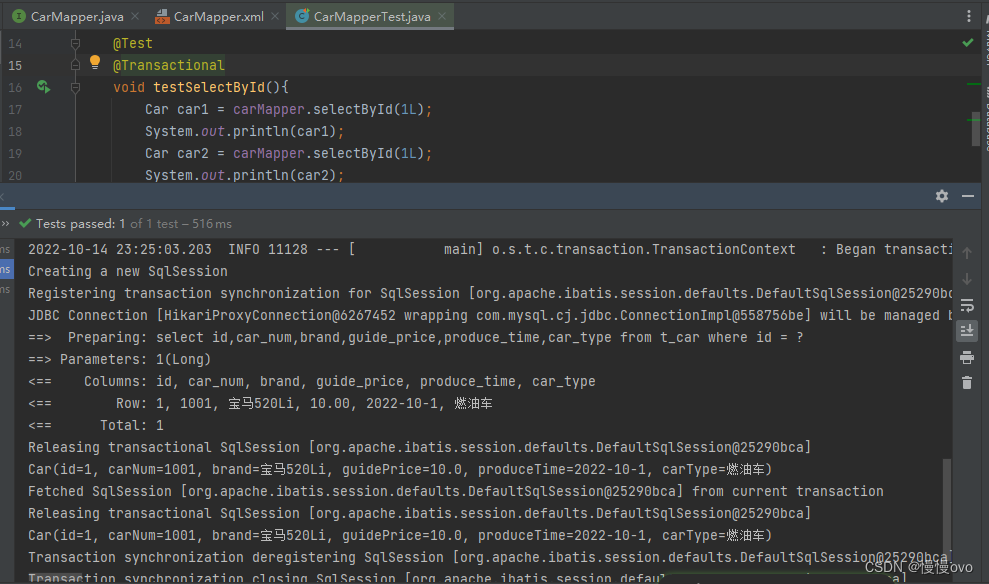
简单回顾一下在纯MyBatis框架中如何使一级缓存失效:
只要在第一次DQL和第二次DQL之间做了两件事中的任意一件就会使一级缓存清空。
1、执行了SqlSession的clearCache()方法,这是手动清空缓存
2、执行了INSERT或DELETE或UPDATE语句,不管是操作哪张表都会清空缓存
二、二级缓存
二级缓存的范围是SqlSessionFactory
使用二级缓存需要具备以下几个条件:
1、在核心配置文件添加cache-enabled: true(全局性地开启或关闭所以映射器配置文件已配置的任何缓存)
但这是默认开启的,所以可以不用添加
2、在需要的mapper映射文件中的<mapper></mapper>里添加<cache />
3、使用二级缓存的实体类对象必须是可序化的,也就是必须实现java.io.Serializable接口
4、纯MyBatis中需要将SqlSession对象关闭或提交之后,一级缓存才会被写入二级缓存中,此时二级缓存才可用
<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <cache /> <sql id="selectAll"> id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type </sql> <select id="selectById2" resultType="Car"> select <include refid="selectAll" /> from t_car where id = #{id} </select></mapper>@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor@ToStringpublic class Car implements Serializable { private Long id; private String carNum; private String brand; private Double guidePrice; private String produceTime; private String carType;}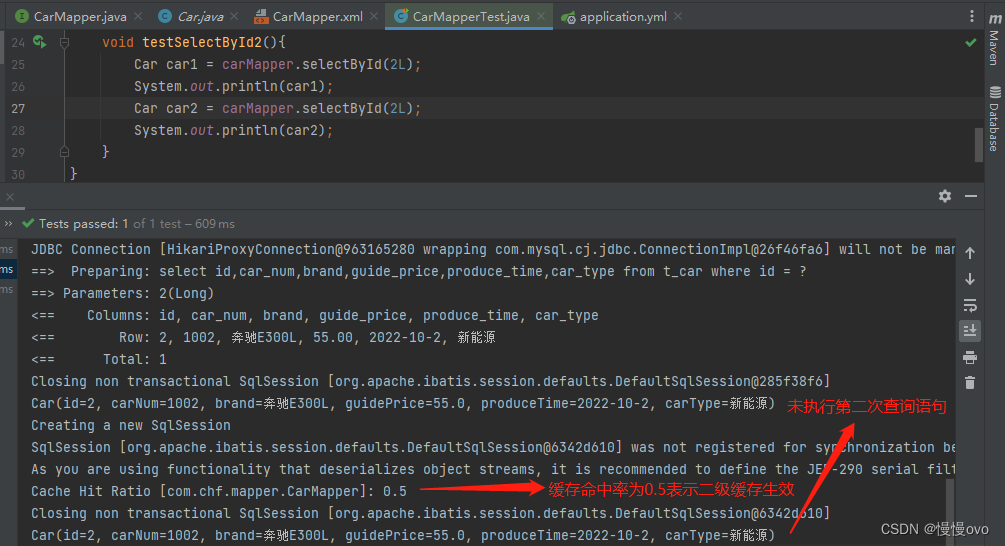
二级缓存的失效:只要两次查询之间出现了增删改操作,当然这样同样使一级缓存失效
7、MyBatis使用PageHelper
这是我在之前学习MyBatis中没有学习到的东西,由于学MyBatisPlus的时候接触到感觉陌生所以这里就重新学了。

一、limit分页
回顾MySQL的limit后面两个数字:
第一个数字:startIndex(起始下标,下标从0开始)
第二个数字:pageSize(每页显示的记录条数)
假设已知页码pageNum,还有每页显示的记录条数pageSize,第一个数字如何动态获取?
startIndex = (pageSize - 1) * pageSize
@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { /** * 分页查询 * @param startIndex 起始下标 * @param pageSize 每页显示的记录条数 * @return */ List<Car> selectByPage(@Param("startIndex") int startIndex, @Param("pageSize") int pageSize);}<mapper namespace="com.chf.mapper.CarMapper"> <sql id="selectAllColumn"> id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type </sql> <select id="selectByPage" resultType="Car"> select <include refid="selectAllColumn" /> from t_car limit #{startIndex},#{pageSize} </select></mapper>
二、PageHelper插件
使用PageHelper插件进行分页更加的快捷。
直接引入依赖即可,不需要配置核心配置文件
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId> <artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.2.12</version></dependency>这个极其重要,需要在核心启动类Application中的@SpringBootApplication注解后面添加
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = PageHelperAutoConfiguration.class)接下来就可以进行我们的测试了。
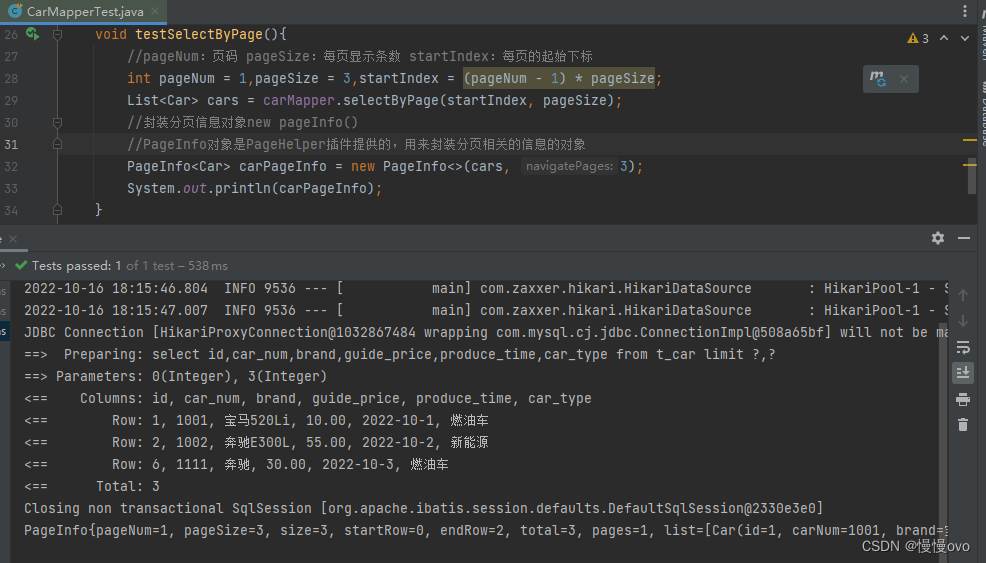
PageInfo
{
pageNum=1, pageSize=3, size=3, startRow=0, endRow=2, total=3, pages=1,
list=[Car(id=1, carNum=1001, brand=宝马520Li, guidePrice=10.0, produceTime=2022-10-1, carType=燃油车), Car(id=2, carNum=1002, brand=奔驰E300L, guidePrice=55.0, produceTime=2022-10-2, carType=新能源), Car(id=6, carNum=1111, brand=奔驰, guidePrice=30.0, produceTime=2022-10-3, carType=燃油车)], prePage=0, nextPage=0, isFirstPage=true, isLastPage=true, hasPreviousPage=false, hasNextPage=false, navigatePages=3, navigateFirstPage=1, navigateLastPage=1, navigatepageNums=[1]
}