题目描述
求单向链表中间的节点值,如果奇数个节点取中间,偶数个取偏右边的那个值。
输入描述
第一行 链表头节点地址 后续输入的节点数n
后续输入每行表示一个节点,格式 节点地址 节点值 下一个节点地址(-1表示空指针)
输入保证链表不会出现环,并且可能存在一些节点不属于链表。
输出描述
单向链表中间的节点值
用例
| 输入 | 00010 4 00000 3 -1 00010 5 12309 11451 6 00000 12309 7 11451 |
| 输出 | 6 |
| 说明 | 无 |
| 输入 | 10000 3 76892 7 12309 12309 5 -1 10000 1 76892 |
| 输出 | 7 |
| 说明 | 无 |
题目解析
用例1示意图如下
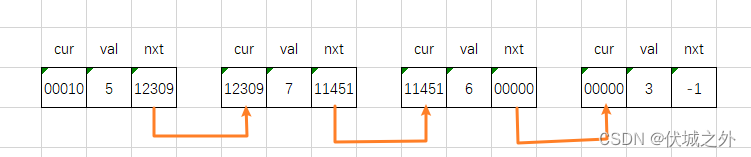
JS本题可以利用数组模拟链表
基于链表数据结构解题
JavaScript算法源码
/* JavaScript Node ACM模式 控制台输入获取 */const readline = require("readline");const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout,});const lines = [];let head;let n;rl.on("line", (line) => { lines.push(line); if (lines.length === 1) { [head, n] = lines[0].split(" "); } if (n && lines.length === n - 0 + 1) { lines.shift(); const nodes = {}; lines.forEach((line) => { const [addr, val, nextAddr] = line.split(" "); nodes[addr] = [val, nextAddr]; }); console.log(getResult(head, nodes)); lines.length = 0; }});function getResult(head, nodes) { const linkedlist = []; let node = nodes[head]; while (node) { const [val, next] = node; linkedlist.push(val); node = nodes[next]; } const len = linkedlist.length; const mid = len % 2 === 0 ? len / 2 : Math.floor(len / 2); return linkedlist[mid];}
Java算法源码
需要注意的是Java中LinkedList类的get(index)方法的时间复杂度不是O(1),而是O(n),这题建议使用ArrayList代替
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String head = sc.next(); int n = sc.nextInt(); HashMap<String, String[]> nodes = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { String addr = sc.next(); String val = sc.next(); String nextAddr = sc.next(); nodes.put(addr, new String[] {val, nextAddr}); } System.out.println(getResult(head, nodes)); } public static String getResult(String head, HashMap<String, String[]> nodes) { // LinkedList<String> link = new LinkedList<>(); ArrayList<String> link = new ArrayList<>(); String[] node = nodes.get(head); while (node != null) { String val = node[0]; String next = node[1]; link.add(val); node = nodes.get(next); } int len = link.size(); int mid = len / 2; return link.get(mid); }}
Python算法源码
# 输入获取head, n = input().split()nodes = {}for i in range(int(n)): addr, val, nextAddr = input().split() nodes[addr] = [val, nextAddr]# 算法入口def getResult(head, nodes): linkedlist = [] node = nodes.get(head) while node is not None: val, next = node linkedlist.append(val) node = nodes.get(next) length = len(linkedlist) mid = int(length / 2) return linkedlist[mid]# 算法调用print(getResult(head, nodes))
快慢指针解题
链表数据结构本质上来说没有索引概念,因为其在内存上不是一段连续的内存,因此索引对于链表结构而言没有意义。
但是从使用上来说,我又经常需要去获取链表结构的第几个元素,因此大部分语言都为链表结构提高了“假索引”,比如Java的LinkedList类,虽然提高了get(index)方法,但是其底层是通过遍历链表(通过next属性找到下一个节点)来找到对应“假索引”的元素的,即LinkedList每次都需要O(n)的时间复杂度才能找到index位置上的元素。
另外,链表还有一个常考问题,那就是链表长度未知的情况下,我们如何找到链表的中间节点?
此时,就要用到快慢指针。
所谓快慢指针,即通过两个指针遍历链表,慢指针每次步进1个节点,快指针每次步进2个节点,这样快指针必然先到达链表尾部,而当快指针到达链表尾部时,慢指针其实刚好就是在链表中间节点的位置(奇数个节点取中间,偶数个取偏右边的那个值)。
本题虽然给出了节点数,但是这些节点不一定属于同一个链表结构,因此本题的链表长度也是未知的,而本题要求的链表中间节点要求刚好和快慢指针找的中间节点吻合,因此本题最佳策略是使用快慢指针。
Java算法源码
import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Scanner;public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String head = sc.next(); int n = sc.nextInt(); HashMap<String, String[]> nodes = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { String addr = sc.next(); String val = sc.next(); String nextAddr = sc.next(); nodes.put(addr, new String[] {val, nextAddr}); } System.out.println(getResult(head, nodes)); } public static String getResult(String head, HashMap<String, String[]> nodes) { String[] slow = nodes.get(head); String[] fast = nodes.get(slow[1]); while (fast != null) { slow = nodes.get(slow[1]); fast = nodes.get(fast[1]); if (fast != null) { fast = nodes.get(fast[1]); } else { break; } } return slow[0]; }}JavaScript算法源码
/* JavaScript Node ACM模式 控制台输入获取 */const readline = require("readline");const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout,});const lines = [];let head;let n;rl.on("line", (line) => { lines.push(line); if (lines.length === 1) { [head, n] = lines[0].split(" "); } if (n && lines.length === n - 0 + 1) { lines.shift(); const nodes = {}; lines.forEach((line) => { const [addr, val, nextAddr] = line.split(" "); nodes[addr] = [val, nextAddr]; }); console.log(getResult(head, nodes)); lines.length = 0; }});function getResult(head, nodes) { let slow = nodes[head]; let fast = nodes[slow[1]]; while (fast) { slow = nodes[slow[1]]; fast = nodes[fast[1]]; if (fast) { fast = nodes[fast[1]]; } else { break; } } return slow[0];}Python算法源码
# 输入获取head, n = input().split()nodes = {}for i in range(int(n)): addr, val, nextAddr = input().split() nodes[addr] = [val, nextAddr]# 算法入口def getResult(head, nodes): slow = nodes.get(head) fast = nodes.get(slow[1]) while fast is not None: slow = nodes.get(slow[1]) fast = nodes.get(fast[1]) if fast is None: break else: fast = nodes.get(fast[1]) return slow[0]# 算法调用print(getResult(head, nodes))