目录
一. ? HashMap介绍1.1 特点1.2 底层实现 二. ? 结构以及对应方法分析2.1 结构组成2.1.1 成员变量2.1.2 存储元素的节点类型2.1.2.1 链表Node类2.1.2.2 树节点类2.1.2.3 继承关系 2.2 方法实现2.2.1 HashMap的数组初始化2.2.2 计算hash值2.2.3 添加元素put(K key,V value)方法2.2.4 数组扩容 三. ? 总结

一. ? HashMap介绍
1.1 特点
HashMap 是 Map 接口的接口实现类,它采用哈希算法实现,是 Map 接口最常用的实现类。 由于底层采用了哈希表存储数据,所以要求键不能重复,如果发生重复,新的值会替换旧的值。 HashMap 在查找、删除、修改方面都有非常高的效率。
1.2 底层实现
HashMap 底层实现采用了哈希表,既集合了数组(占用空间连续。 寻址容易,查询速度快)的优点,又集合了链表(增加和删除效率非常高)的优点。其实哈希表的本质就是”数组+链表“。
二. ? 结构以及对应方法分析
在HashMap中,当维互链表节点个数的过程中,链表节点数大于8时,则会转化成红黑树来存储,从而提高查询效率。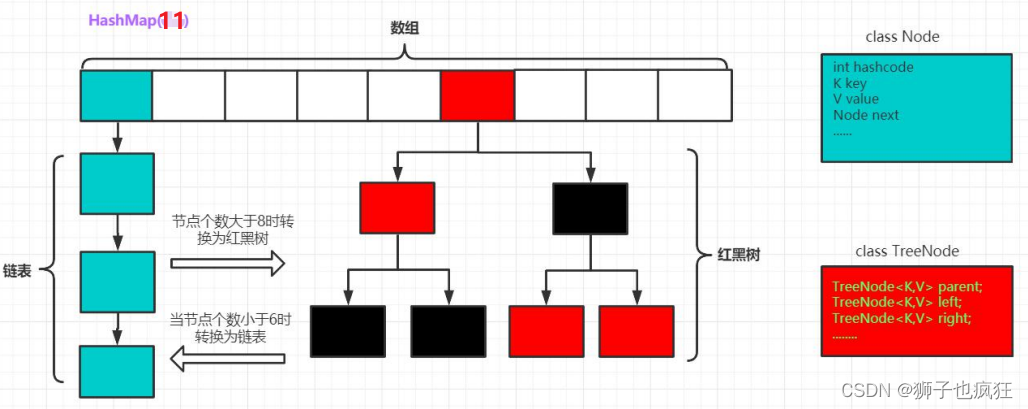
2.1 结构组成
2.1.1 成员变量
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4: 默认的初始容量为16,而且注解有说明这个默认初始化容量必须是2的倍数。
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30:最大初始化容量为2^30。
DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f:负载因子,用来决定数组什么时候开始扩容,即当数组长度达到75%时会进行扩容。
TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8:阈值,当前数组长度>64,会将节点个数大于8的链表做红黑树转换。
UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6:同理,当红黑树节点数小于6时,将这个红黑树转换成链表。
MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64:设置当数组长度超过多少时,才会对链表节点个数大于8的做红黑树转换。
transient Node<K,V>[] table:就是前面说的神秘的数组。(为啥是Node<K,V>l类型?)
/** * The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two. */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /** * The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified * by either of the constructors with arguments. * MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30. */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /** * The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a * bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a * bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater * than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in * tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon * shrinkage. */ static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; /** * The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a * resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at * most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal. */ static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; /** * The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified. * (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.) * Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts * between resizing and treeification thresholds. */ static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; /** * The table, initialized on first use, and resized as * necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two. * (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow * bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.) */ transient Node<K,V>[] table;2.1.2 存储元素的节点类型
既然说了哈希表是由数组+链表组成,而且到后面还会转为红黑树,那么他肯定会有对应的节点类。其源码类型如下:
2.1.2.1 链表Node类
/** * Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for * TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.) */ static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) return true; } return false; } }由源码可知,链表的Node节点类型实现了Map接口的内部接口类Entry<K,V>,这个接口定义的就是能操作HashMap的一个key——>value存储结构的一些行为(例如 获取键值对的key)。
成员遍历
hash:记录存储key的hash值,不可改变(final修饰)
key:记录key,不可改变(final修饰),所以hashmap的key是唯一的,不能重复。
value:记录value,可改变。
next:当前节点记录下一个节点的地址(由此可知,该链表是单向链表)
2.1.2.2 树节点类
/** * Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn * extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or * linked node. */static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red; TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, val, next); } /** * Returns root of tree containing this node. */ final TreeNode<K,V> root() { for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) { if ((p = r.parent) == null) return r; r = p; } }成员变量:
parent:记录父节点
left: 左子树
right:右子树
prev:前节点
red:记录红黑树的状态(true是红树,反之。)
2.1.2.3 继承关系
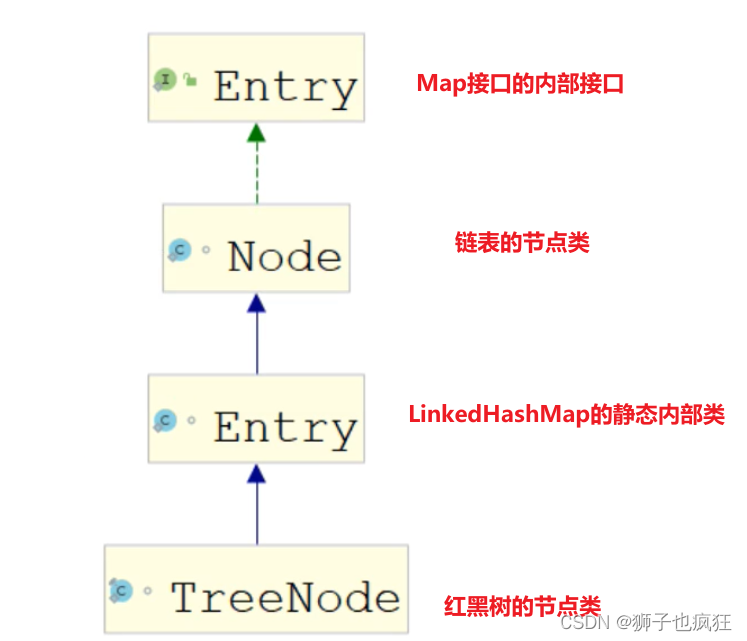
HashMap的数组既有链表,又有红黑树,为什么这个神秘的数组是Node类型?我觉得到这里就可以讲的通了:
链表节点类Node实现了Entry接口,而LinkedHashMap的内部类Entry又继承了Node类,而TreeNode又继承了Entry,所以红黑树的节点类是和链表的Node是有继承关系的,可以统一当成一个类型来看待,所以Node<K,V>类型的数组既可以存放链表,又可以存放红黑树。
2.2 方法实现
2.2.1 HashMap的数组初始化
在 JDK11 的 HashMap 中对于数组的初始化采用的是延迟初始化方式。通过 resize 方法
实现初始化处理。resize 方法既实现数组初始化,也实现数组扩容处理。
tips:啥叫延迟初始化?
向数组添加第一个元素的时候,才开始对数组做初始化处理。
/** * Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in * accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold. * Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the * elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move * with a power of two offset in the new table. * * @return the table */ final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold } else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold newCap = oldThr; else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; }首先,回到刚刚的HashMap的成员变量时,成员变量table只是作了一个声明,如图: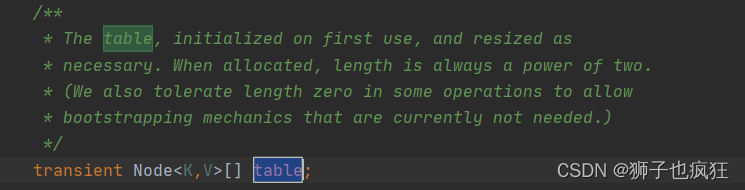
所以table为null,所以在执行int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length时,oldCap=0,而此时 threshold也为0,所以在执行第一个if的时候,两个变量都为0,所以直接执行else里面的语句。 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); 即将将初始化数组长度的成员变量(16)赋值给newCap,而下一句则是将下一次扩容的长度给newThr(此时为12),然后跳过if语句,给成员变量threshold重新赋值。再执行Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap],将newTab赋值给成员变量table,然后返回newTab,这样一次初始化完成。
2.2.2 计算hash值
在map的存储中,我们是根据key的hash值来存放元素的。所以需要对key的hash值进行一系列的运算:
1.获取key的hashCode。
2.根据hashCode计算出hash值。(但是由于要求要转换成table数组的长度-1的范围内,所以还需要一系列的运算。)
3.转化算法:hash = hashcode&(n-1)得到数组中的存放位置。
/** * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old * value is replaced. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) */public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);}static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);}这里是计算key的hash值的方法。先将key的hashcode值赋给h,然后与h的高16位进行异或运算(也就是h的低16位和高16位进行异或运算)。
下面来演示一下运算过程:
假定:key = 123456,使用计算器计算得到其二进制为: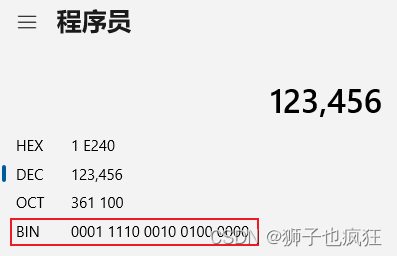
然后进行异或运算(相同为0,相异为1):
计算得到10进制为:
到这一步返回123457,下面回到putVal()方法:
/** * Implements Map.put and related methods * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to put * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. * @return previous value, or null if none */final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null;}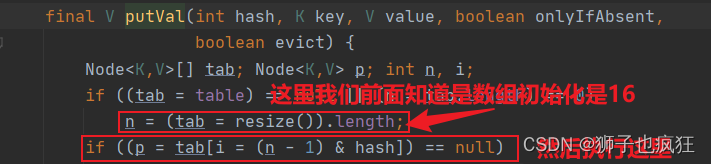
putVal方法拿到key的hashCode后,和15进行&运算(相同为1,相异为0):
最终得到存入数组位置为1。
2.2.3 添加元素put(K key,V value)方法
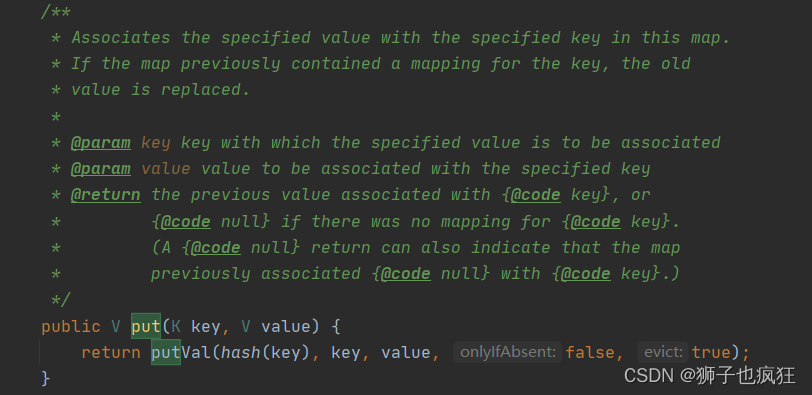
调用了putVal()方法(源码在上面)
putVal()主要是计算hash值从而获取元素在数组中的位置(前面已经分析过了)、如果该位置数组没有元素,则将新节点放入;我们都知道,hashMap对于key相同的值,是将其value值覆盖,key不变,以下则是实现方法: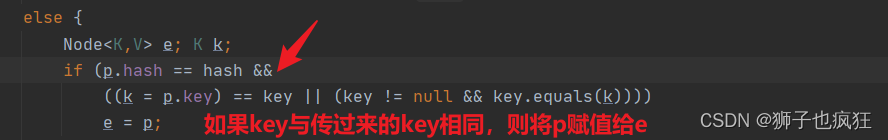
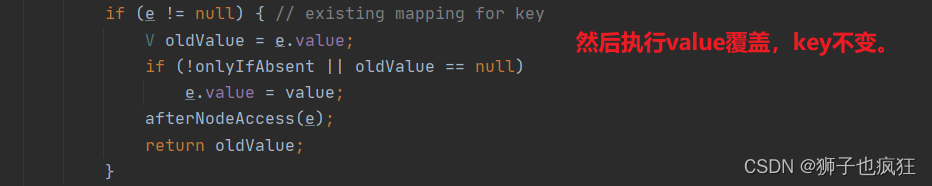 如果p节点与TreeNode节点是同类(红黑树),则将其挂到红黑树上:
如果p节点与TreeNode节点是同类(红黑树),则将其挂到红黑树上: 前面都不执行的话,最后就是挂载到数组所在位置的链表了末尾了:
前面都不执行的话,最后就是挂载到数组所在位置的链表了末尾了: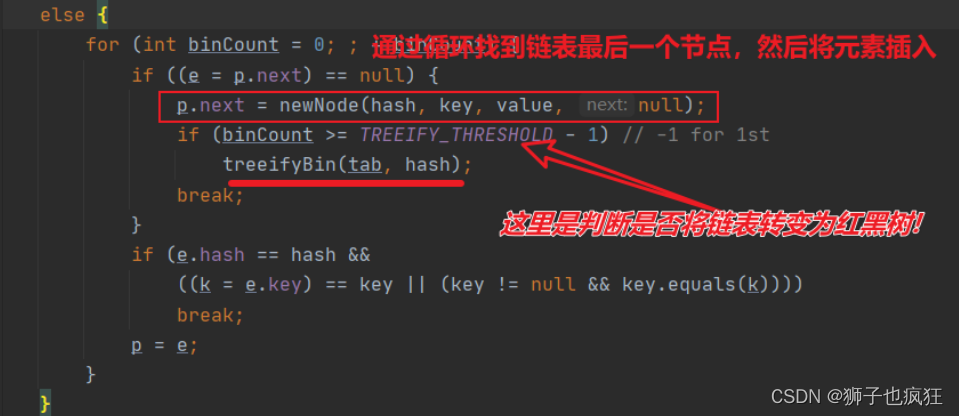
我们再来看看链表——>红黑树的方法( treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash))
/** * Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless * table is too small, in which case resizes instead. */ final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) { int n, index; Node<K,V> e; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null; do { TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); if (tl == null) hd = p; else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null); if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) hd.treeify(tab); } }在这里,我们看到:链表并不是马上做红黑树转换,而是先判断数组的长度是否大于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(这个前面有解释),小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY则会调用 resize()方法,对数组进行扩容处理。 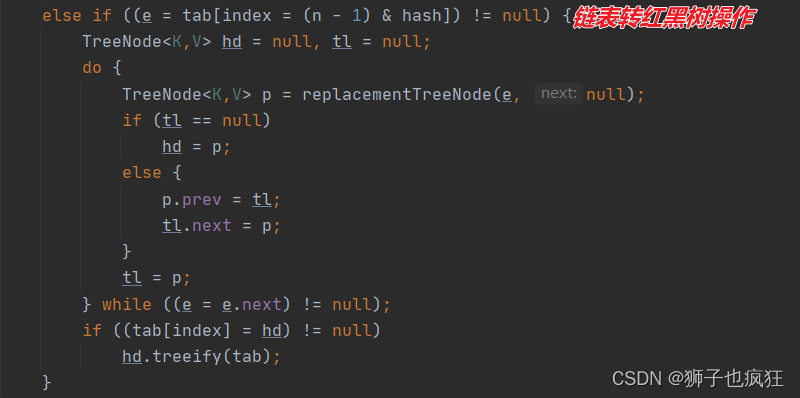
2.2.4 数组扩容
三. ? 总结
HashMap的底层是由哈希算法来实现的(即数组+链表的形式),数组长度大于64并且链表的节点个数大于8时,会将链表转变为红黑树,这样就大大减少了遍历的时间,提高效率,之所以一个数组能存储两种数据结构,就是因为数组的数据类型为链表的节点Node<K,V>,而红黑树节点TreeNode<K,V>跟Node有继承关系的。此外,HashMap是采用延时初始化的方式来初始化数组的,即用户添加第一个元素的时候才会调用resize() 初始化数组长度(16),以及预定数组下一次扩容长度(12)。还有就是hash值的计算以及添加元素等方法的原理,等待小伙伴们的探索哦!
学习源码知识,有助于帮助我们扎实内功,提升程序员的涵养,如果您不想直接在idea查看源码,也想了解他,可以关注博主,都给您整理好啦,好了,文章到这里就结束啦,咱们下期见,喜欢可以一键三连哦?