springboot security
- 导入依赖
- 在资源目录里面放入静态资源页面
- 在Controller包里面放入控制和映射路径
- 用户认证
- 授权
- passwordEncoder源码
- encode
- matches
- roles
在 Spring Boot 中做权限管理,一般来说,主流的方案是 Spring Security ,但是,仅仅从技术角度来说,也可以使用 Shiro。
一般来说,Spring Security 和 Shiro 的比较如下:
Spring Security 是一个重量级的安全管理框架;Shiro 则是一个轻量级的安全管理框架
Spring Security 概念复杂,配置繁琐;Shiro 概念简单、配置简单
Spring Security 功能强大;Shiro 功能简单
…
虽然 Shiro 功能简单,但是也能满足大部分的业务场景。所以在传统的 SSM 项目中,一般来说,可以整合 Shiro。
在 Spring Boot 中,由于 Spring Boot 官方提供了大量的非常方便的开箱即用的 Starter ,当然也提供了 Spring Security 的 Starter ,使得在 Spring Boot 中使用 Spring Security 变得更加容易,甚至只需要添加一个依赖就可以保护所有的接口,所以,如果是 Spring Boot 项目,一般选择 Spring Security 。
这只是一个建议的组合,单纯从技术上来说,无论怎么组合,都是没有问题的。
关于shiro的学习后面再说
在学习springboot Security我们需要准备
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
</dependency>
在资源目录里面放入静态资源页面
在Controller包里面放入控制和映射路径
package com.gql.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @author gql
* @date 2021/11/23 - 19:14
*/
@Controller
public class RouterController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index"})
public String index() {return "index";}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "views/login";
}
@RequestMapping("/level1/{id}")
public String level1(@PathVariable("id") int id){return "views/level1/"+id;}
@RequestMapping("/level2/{id}")
public String level2(@PathVariable("id") int id){return "views/level2/"+id;}
@RequestMapping("/level3/{id}")
public String level3(@PathVariable("id") int id){return "views/level3/"+id;}}
用户认证
Public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页都可以访问但是功能页对应有权限的人
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
//这段代码通俗的讲就好像是指定一个人是vip用户,假如这个人是Vip1
//那么他就可以去访问资源目录下面的/level1/**所有的静态资源
//当然不能访问"/level2/**"或者"/level3/**"下的静态资源
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole(("vip2"))
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//没有权限默认会到登陆页面
http.formLogin();
//注销,开启了注销功能gql
http.logout();
}
授权
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//从内存读
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("zhangsan").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("gql").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("281913")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("ljk").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123")).roles("vip1");
}
}
在我们访问http://localhost:8080/时按道理应该访问index.html页面
但是spring boot集成security,启动项目不是出了自己的登录页面,而是下面莫名其妙的页面
个人感觉和Druid的监控页面类似

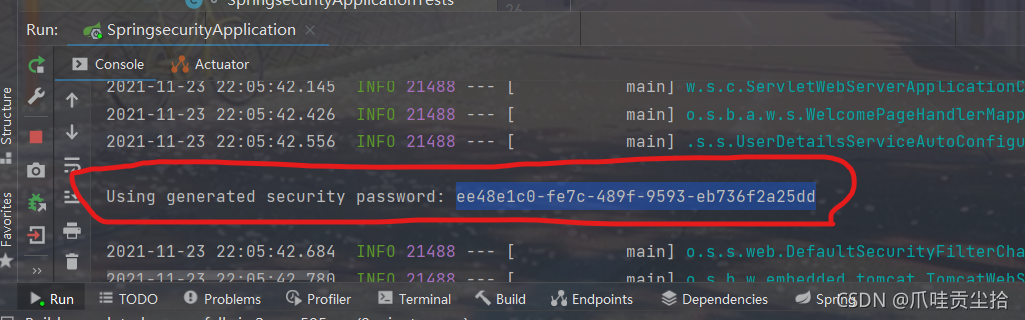
整了好久一直是这样,我使用自己定义的密码和用户名完全不可以,查阅相关的文件以后才发现其实这个是security默认给我们整的一个用户认证的功能,用户名是:user 密码是在启动的控制台打印出来的:
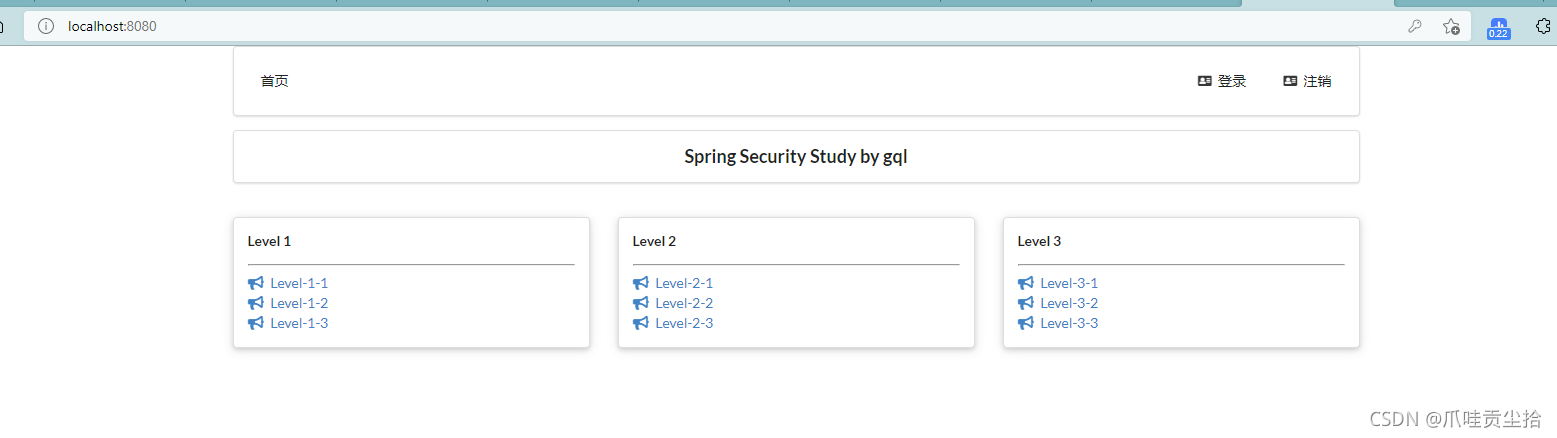
然后才能进去我们的页面
passwordEncoder源码
public interface PasswordEncoder {
/**
* Encode the raw password. Generally, a good encoding algorithm applies a SHA-1 or
* greater hash combined with an 8-byte or greater randomly generated salt.
*/
String encode(CharSequence rawPassword);
/**
* Verify the encoded password obtained from storage matches the submitted raw
* password after it too is encoded. Returns true if the passwords match, false if
* they do not. The stored password itself is never decoded.
*
* @param rawPassword the raw password to encode and match
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password from storage to compare with
* @return true if the raw password, after encoding, matches the encoded password from
* storage
*/
boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword);
/**
* Returns true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false. The default implementation always returns false.
* @param encodedPassword the encoded password to check
* @return true if the encoded password should be encoded again for better security,
* else false.
*/
default boolean upgradeEncoding(String encodedPassword) {
return false;
}
}
encode
该方法提供了明文密码的加密处理,加密后密文的格式主要取决于PasswordEncoder接口实现类实例
matches
匹配存储的密码以及登录时传递的密码(登录密码是经过加密处理后的字符串)是否匹配,如果匹配该方法则会返回true.
roles
这就相当于在游戏里面充值,你充值了,我就把你升级成VIP1,你就可以访问level1里面的东西,你继续充钱达到一定值,你就可以变成vip2的用户,你就可以在访问vip1和vip2都能访问的东西。以此类推