目录
Blob类型字段
批量插入
数据库事务
Blob类型字段
概述:MySQL中,Blob是一个二进制大型对象,是一个可以存储大量数据的容器,它能容纳不同大小的数据。
说明:插入Blob类型的数据必须使用PreparedStatement,因为Blob类型的数据无法使用字符串拼接写。
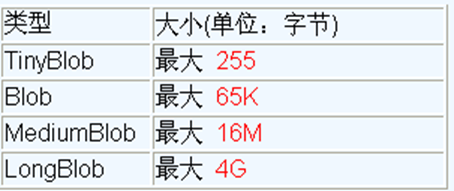
介绍:MySQL的四种Blob类型 (除了在存储的最大信息量上不同外,他们是等同的),实际使用中根据需要存入的数据大小定义不同的Blob类型。
注意:
- 如果存储的文件过大,数据库的性能会下降
- 如果在指定了相关的Blob类型以后,还报错:xxx too large,那么在mysql的安装目录下,找my.ini文件加上如下的配置参数:max_allowed_packet=16M,同时注意:修改了my.ini文件之后,需要重新启动mysql服务
代码实现:插入、查询Blob类型的数据
//向数据表customers中插入Blob类型的字段 @Test public void testInsert() throws Exception { //获取连接 Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into customers(name,email,birth,photo)values(?,?,?,?)"; PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //填充占位符 ps.setObject(1, "薛之谦"); ps.setObject(2, "xuezq@qq.com"); ps.setObject(3, "1983-7-17"); //操作Blob类型的变量 FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("x.jpg")); ps.setBlob(4, is); //执行 ps.execute(); JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps); } //查询数据表customers中Blob类型的字段 @Test public void testQuery() { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; InputStream is = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select id,name,email,birth,photo from customers where id=?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setInt(1, 22); //执行 rs = ps.executeQuery(); if (rs.next()) { int id = rs.getInt("id"); String name = rs.getString("name"); String email = rs.getString("email"); Date birth = rs.getDate("birth"); Customer cust = new Customer(id, name, email, birth); System.out.println(cust); //将Blob类型的字段下载下来,以文件的方式保存在本地 Blob photo = rs.getBlob("photo"); is = photo.getBinaryStream(); fos = new FileOutputStream("xzq.jpg"); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { fos.write(buffer, 0, len); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (is != null) is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if (fos != null) fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs); } }
批量插入
概述: 当需要成批插入或者更新记录时,可以采用Java的批量更新机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。
JDBC的批量处理语句包括三个方法:
- addBatch(String):添加需要批量处理的SQL语句或是参数
- executeBatch():执行批量处理语句
- clearBatch():清空缓存的数据
通常两种批量执行SQL语句的情况:
- 多条SQL语句的批量处理
- 一个SQL语句的批量传参
代码实现:向数据表中插入20000条数据
#数据库中提供一个goods表。创建如下: CREATE TABLE goods( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, NAME VARCHAR(20) );@Test public void testInsert4() { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //设置不允许自动提交数据 conn.setAutoCommit(false); String sql = "insert into goods(name)values(?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 1; i <= 20000; i++) { ps.setObject(1, "name_" + i); //1."攒"sql ps.addBatch(); if (i % 500 == 0) { //2.执行 ps.executeBatch(); //3.清空batch ps.clearBatch(); } } //提交数据 conn.commit(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("执行的时间:" + (end - start)); //执行的时间:703 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps); } }
数据库事务
说明:这里只介绍JDBC中的事务处理,基本的数据库事务介绍可以参考博主之前的文章。
概述:一组逻辑操作单元,使数据从一种状态变换到另一种状态。(一组逻辑操作单元,一个或多个DML操作)
特点:
- 数据一旦提交,就不可回滚
- 数据什么时候被提交?
- DDL操作一旦执行,会自动提交,set autocommit = false 对DDL操作失效
- DML默认情况下一旦执行,就会自动提交,通过set sutocommit = false,取消DML操作的自动提交
- 关闭数据库连接,数据就会自动的提交
- 当一个连接对象被创建时,默认情况下是自动提交事务
JDBC程序中让多个SQL语句作为一个事务执行:
- 调用Connection对象的setAutoCommit(false),以取消自动提交事务
- 在所有的SQL语句都成功执行后,调用commit(), 方法提交事务
- 在出现异常时,调用rollback()方法回滚事务
代码实现:用户AA向用户BB转账100
//**********考虑数据库事务情况下的转账操作**************** @Test public void testUpdateWithTx() { Connection conn = null; try { conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); System.out.println(conn.getAutoCommit()); //true //1.取消数据的自动提交 conn.setAutoCommit(false); String sql1 = "update user_table set balance = balance - 100 where user = ?"; update(conn,sql1,"AA"); //模拟网络异常 //System.out.println(10/0); String sql2 = "update user_table set balance = balance + 100 where user = ?"; update(conn,sql2,"BB"); System.out.println("转账成功!"); //2.提交数据 conn.commit(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); //3.回滚数据 try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } finally { //修改其为自动提交数据,主要针对于使用数据库连接池时 try { conn.setAutoCommit(true); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn,null); } } //通用的增删改操作 ----version 2.0(考虑上事务) public int update(Connection conn,String sql,Object ...args) { PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //1.预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement实例 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //2.填充占位符 for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { ps.setObject(i+1,args[i]); } //3.执行 return ps.executeUpdate(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4.资源关闭 JDBCUtils.closeResource(null, ps); } return 0; }