一、栈的定义
定义:限定只在表的一端(表尾)进行插入和删除的线性表

特点:后进先出
二、顺序栈
基于数组实现
C++实现代码:
//头文件
#ifndef STACK_H_INCLUDED
#define STACK_H_INCLUDED
//栈的最大存储
const int MAX_SIZE=100;
//定义一个顺序栈类(使用模板)
//使用模板 优点 可以用来实现多种数据类型的存储
template <class DataType> class Stack{
private:
DataType *data; //数据域
int size; //栈的大小
int top; //栈顶下标
public:
Stack();
Stack(int s);
//~Stack();
void push(DataType t); //进栈
DataType pop(); //出栈 返回栈顶元素
DataType getTop(); //返回栈顶元素 不出栈
int length(); //求出栈的长度
void setNull(); //将栈置空
class Empty{}; //定义空类 用于抛异常
class Full{};
bool isFull(); //判断栈是否已满
bool isEmpty(); //判断栈是否为空
};
typedef Stack<char> CharStack;
typedef Stack<int> IntStack;
#endif // STACK_H_INCLUDED
//.cpp文件
#include "Stack.h"
//无参构造 栈的大小为最大存储
template <class DataType> Stack<DataType>::Stack(){
size=MAX_SIZE;
top=-1;
data=new DataType[MAX_SIZE];
}
//有参构造 栈的大小给定
template <class DataType> Stack<DataType>::Stack(int s){
size=s;
top=-1;
data=new DataType[size];
}
template <class DataType> bool Stack<DataType>::isFull(){
if(top+1==size){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
template <class DataType> bool Stack<DataType>::isEmpty(){
if(top==-1){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
//压栈 先判断栈是否已满 然后将top++
template <class DataType> void Stack<DataType>::push(DataType e){
if(isFull()){
throw Stack<DataType>::Full();
}else{
data[++top]=e;
}
}
//弹出 先判断栈是否为空 然后top--
template <class DataType> DataType Stack<DataType>::pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw Stack<DataType>::Empty();
}else{
return data[top--];
}
}
//得到栈顶元素 不弹出
template <class DataType> DataType Stack<DataType>::getTop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw Stack<DataType>::Empty();
}else{
return data[top];
}
}
//栈的长度
template <class DataType> int Stack<DataType>::length(){
return top+1;
}
//将栈清空
template <class DataType> void Stack<DataType>::setNull(){
top=-1;
}
template class Stack<char>;
template class Stack<int>;
//主函数
#include <iostream>
#include "Stack.h"
#include "Sta.cpp"
using namespace std;
//顺序栈
int main(){
CharStack charStack;
IntStack intStack(3);
try{
intStack.push(2);
intStack.push(60);
intStack.push(100);
cout<<"栈的长度:"<<intStack.length()<<endl;
}catch(IntStack::Full){
cout<<"STACK FULL!"<<endl;
}
try{
intStack.pop();
}catch(IntStack::Empty){
cout<<"STACK EMPTY!"<<endl;
}
cout<<"栈的长度:"<<intStack.length()<<endl;
return 0;
}
三、链栈
基于链表实现(不带头节点)
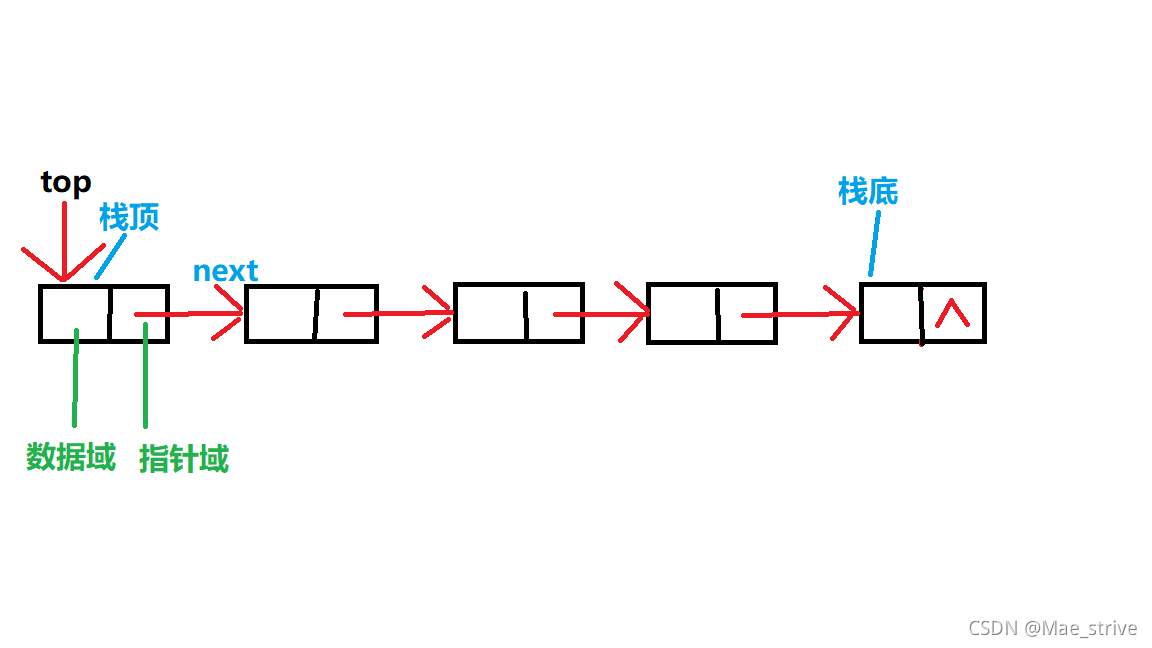
#ifndef LINKSTACK_H_INCLUDED
#define LINKSTACK_H_INCLUDED
template <typename DataType>
struct Node{
DataType data; //数据域
Node<DataType> *next; //指针域
};
template <typename DataType>
class LinkStack{
private:
Node<DataType> *top; //栈顶指针
public:
LinkStack();
~LinkStack();
void push(DataType x);
DataType pop();
DataType getTop();
bool isEmpty();
bool isFull();
};
typedef LinkStack<char> CharLinkStack;
typedef LinkStack<int> IntLinkStack;
#endif // LINKSTACK_H_INCLUDED
#include "LinkStack.h"
//构造函数 创建top指针
template <class DataType> LinkStack<DataType>::LinkStack(){
top=NULL;
}
//析构函数 释放资源
template <class DataType>LinkStack<DataType>::~LinkStack(){
Node<DataType> *p=NULL;
while(top!=NULL){
p=top->next;
delete top;
top=p;
}
}
//判断链栈是否为空
template <class DataType> bool LinkStack<DataType>::isEmpty(){
if(top==NULL){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
/*template <class DataType> bool LinkeStack<DataType>::isFull(){
}*/
//压入元素
template <class DataType> void LinkStack<DataType>::push(DataType x){
Node<DataType> *s=new Node<DataType>; //新定义一个Node结点指针
s->data=x;
s->next=top; //将结点的指针域指向栈顶top(即压入了一个新的元素)
top=s; //再让top指向结点
}
//弹出栈顶元素
template <class DataType> DataType LinkStack<DataType>::pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw "链栈为空,无法弹出元素";
}else{
DataType x=top->data;
Node<DataType> *p=new Node<DataType>;
p=top; //将栈顶指针先赋给p
top=top->next; //栈顶指针指向栈顶的下一个存储空间(即栈顶元素弹出)
delete p; //销毁p的空间
return x;
}
}
//返回栈顶元素
template <class DataType> DataType LinkStack<DataType>::getTop(){
return top->data;
}
template class LinkStack<char>;
template class LinkStack<int>;
#include <iostream>
#include "LinkStack.cpp"
using namespace std;
//链栈
int main()
{
IntLinkStack intLinkStack;
intLinkStack.push(20);
intLinkStack.push(15);
cout<<"栈顶元素:"<<intLinkStack.getTop()<<endl;
intLinkStack.pop();
cout<<"栈顶元素:"<<intLinkStack.getTop()<<endl;
return 0;
}
注意:
- C++分文件编写时需要在 .h中尾部加入代码,相当于为每个类型的模板定义了一个类型
typedef Stack<char> CharStack;
- .cpp文件中尾部加入代码,显示的声明要使用的模板类实例
template class Stack<char>;
- main 函数中实例化类对象
CharStack charStack;
- 利用模板实现,每个类的方法前都要加上
template <class DataType>