Python访问街区所有节点最短路径问题,并结合matplotlib可视化
- 1. 效果图
- 2. 源码
- 2.1 5个点全排列(递归+非递归算法)
- 2.2 python遍历全路径计算距离+matplot可视化
- 2.3 pyecharts可视化源码
- 参考
写这篇博客 基于博友的提问,这篇博客将介绍如何全排列街区的点,即规定起点不重复的走完所有街区,并找出最短路径。

 这个问题分拆分为三部分:
这个问题分拆分为三部分:
1. N个点除去起点,即N-1个点全排列;
2. 计算每一条路径,相邻节点的距离,并求和。
3. 为了更加直观,便于可视化,可以matplotlib、pyecharts绘制路线出来~
1. 效果图
规定起点A,所有路径 递归 & 非递归效果图:


最短路径,及其距离效果图:
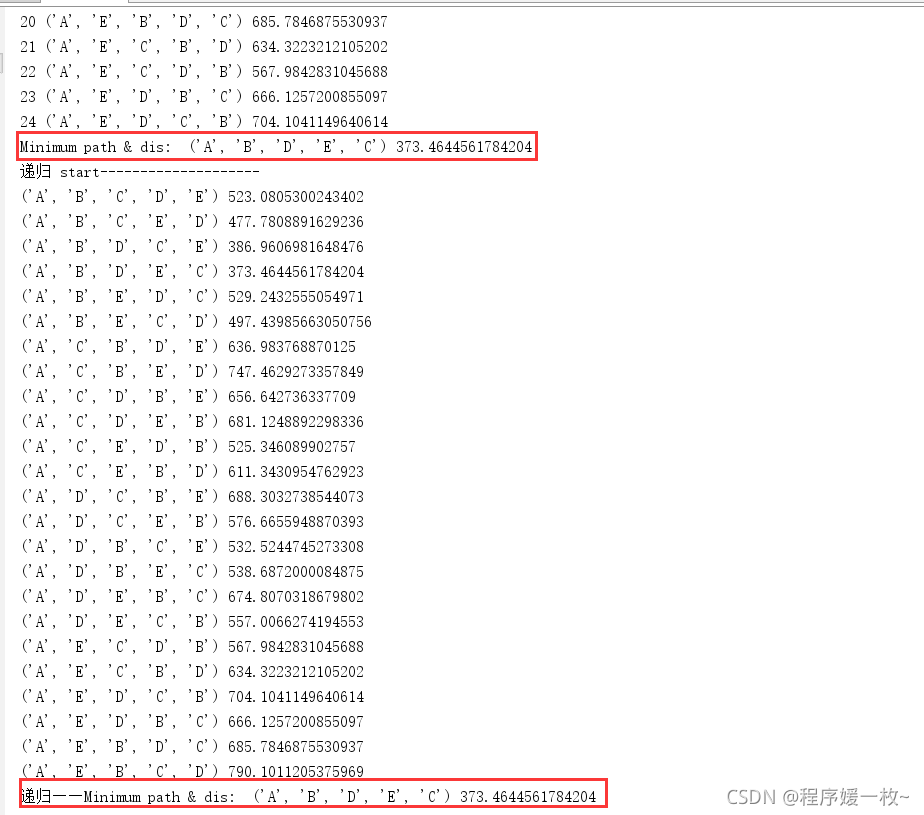
图中10个点的最短路径结果:
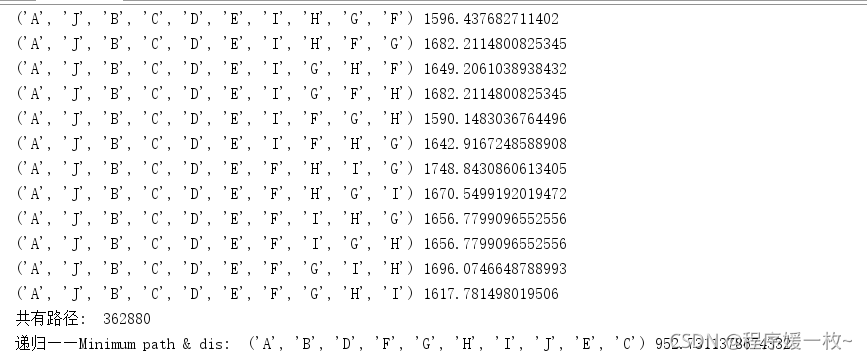
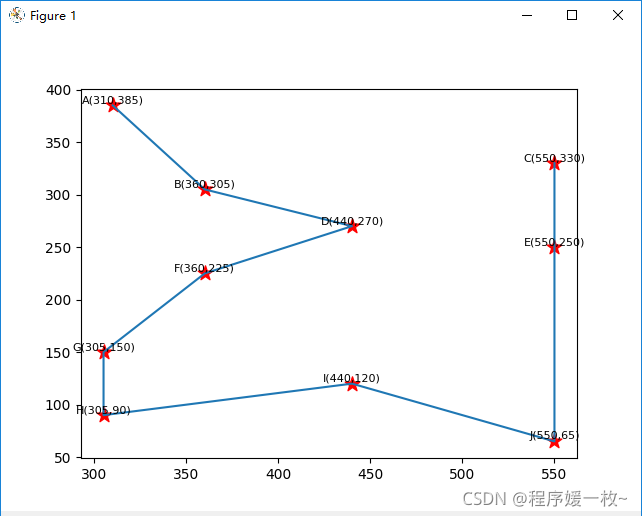
使用matplotlib 可视化街区点及最短路径如下图:
如上最短路径 A B D F G H I J E C 如下图,
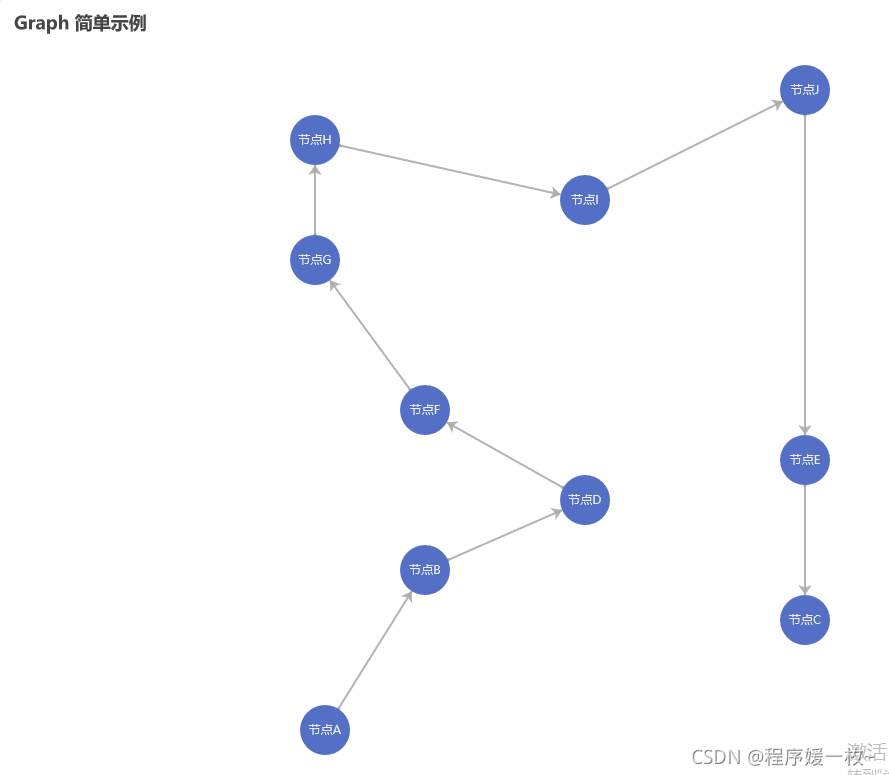
使用pyecharts绘制街区点及最短路径如下图:
2. 源码
2.1 5个点全排列(递归+非递归算法)
非递归的方法并不好,当点数有变化的时候需要对应修改代码
# 求最短路径问题(N个点全排列)
# 街区点
node = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
# 路径全排列走法
count = 0
# 非递归算法
# 非递归算法找到所有可能的路径,并计算总距离
for i in node:
for j in node:
for k in node:
for m in node:
for n in node:
if i != 'A': # 起点只能是A点
continue
# 同一个点不走第二次
if (i == j or i == k or i == m or i == n
or j == k or j == m or j == n
or k == m or k == n
or m == n):
continue
count = count + 1
print((count), (i, j, k, m, n))
print('递归 start--------------------')
# 递归方法解决
nodes = node.copy()
# 递归算法:
# 不重复的对n个点进行全排列
# positon,从数组下标哪个点开始全排列
def permutations(position):
if position == len(nodes) - 1:
print(nodes)
else:
for index in range(position, len(nodes)):
nodes[index], nodes[position] = nodes[position], nodes[index]
permutations(position + 1)
nodes[index], nodes[position] = nodes[position], nodes[index]
# permutations(0) # 全排列
permutations(1) # 从第2个点开始全排列
2.2 python遍历全路径计算距离+matplot可视化
# 求最短路径问题(python遍历全路径计算距离+matplot可视化)
import math
import numpy as np
# 街区点
node = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', "J"]
# 街区点对应坐标
node_coor = [(310, 385), (360, 305), (550, 330), (440, 270), (550, 250),
(360, 225), (305, 150), (305, 90), (440, 120), (550, 65)]
# 计算俩个坐标点的距离
def cal_dis(pt1, pt2):
x0, y0 = pt1
x1, y1 = pt2
# print('\t\tdis: ', pt1, pt2, math.sqrt((math.pow((x0 - x1), 2) + math.pow((y0 - y1), 2))))
return math.sqrt((math.pow((x0 - x1), 2) + math.pow((y0 - y1), 2)))
# 计算一条路径的总距离
def get_dis(nodes):
# 初始化总距离
total_dis = 0
# 遍历路径
for i in range(len(nodes) - 1):
# 根据相邻的俩个点计算距离
dis = cal_dis(node_coor[node.index(nodes[i])], node_coor[node.index(nodes[i + 1])])
total_dis = total_dis + dis
return total_dis
print('递归 start--------------------')
# 递归方法解决
dict_path_dis = {}
nodes = node.copy()
# 递归算法:
# 不重复的对n个点进行全排列
# positon,从数组下标哪个点开始全排列
def permutations(position):
if position == len(nodes) - 1:
dis = get_dis(np.array(tuple(nodes)))
dict_path_dis[tuple(nodes)] = dis
print(tuple(nodes), dis)
else:
for index in range(position, len(nodes)):
nodes[index], nodes[position] = nodes[position], nodes[index]
permutations(position + 1)
nodes[index], nodes[position] = nodes[position], nodes[index]
# 从下标1开始全排列,表示第一个值是固定的,此处是起点
permutations(1)
print('共有路径: ', len(dict_path_dis.keys()))
# 获取最小的value对应的key,即获取最短路径距离对应的路径
key_min = min(dict_path_dis.keys(), key=(lambda k: dict_path_dis[k]))
print('递归——Minimum path & dis: ', key_min, dict_path_dis[key_min])
print('绘图start——————————')
# 构建最短路径的街区点及坐标
min_node = np.array(key_min)
min_path_coor = []
for i in min_node:
min_path_coor.append(node_coor[node.index(i)])
print('min_node: ', min_node)
print('min_path_coor: ', min_path_coor)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots() # 创建一个图表
x1 = [x for (x, y) in min_path_coor]
y1 = [y for (x, y) in min_path_coor]
# ax.scatter(x1, y1, marker='*', c='red') # 绘制街区点
for node_name, (x, y) in zip(min_node, min_path_coor):
# 绘制坐标点及坐标点上方文字
plt.scatter(x, y, s=120, c='red', marker='*')
plt.text(x=x, y=y + 2, s=node_name + '(' + str(x) + ',' + str(y) + ')', ha='center', va='baseline',
fontdict={'color': 'black',
'size': 8}) # 中心点上方文字
ax.plot(x1, y1) # 绘制线
plt.show()
2.3 pyecharts可视化源码
可在该页面复制下方代码进行在线可视化:https://echarts.apache.org/examples/en/editor.html?c=graph-simple
option = {
title: {
text: 'Graph 简单示例'
},
tooltip: {},
animationDurationUpdate: 1500,
animationEasingUpdate: 'quinticInOut',
series: [
{
type: 'graph',
layout: 'none',
symbolSize: 50,
roam: true,
label: {
show: true
},
edgeSymbol: ['circle', 'arrow'],
edgeSymbolSize: [4, 10],
edgeLabel: {
fontSize: 20
},
data: [{
name: '节点A',
x: 310,
y: 385
}, {
name: '节点B',
x: 360,
y: 305
}, {
name: '节点C',
x: 550,
y: 330
}, {
name: '节点D',
x: 440,
y: 270
}, {
name: '节点E',
x: 550,
y: 250
}, {
name: '节点F',
x: 360,
y: 225
}, {
name: '节点G',
x: 305,
y: 150
}, {
name: '节点H',
x: 305,
y: 90
}, {
name: '节点I',
x: 440,
y: 120
}, {
name: '节点J',
x: 550,
y: 65
}],
links: [{
source: '节点A',
target: '节点B'
}, {
source: '节点B',
target: '节点D'
}, {
source: '节点D',
target: '节点F'
}, {
source: '节点F',
target: '节点G'
}, {
source: '节点G',
target: '节点H'
}, {
source: '节点H',
target: '节点I'
}, {
source: '节点I',
target: '节点J'
}, {
source: '节点J',
target: '节点E'
}, {
source: '节点E',
target: '节点C'
}],
lineStyle: {
opacity: 0.9,
width: 2,
curveness: 0
}
}
]
};
参考
- python实现四个数字的全排列