纯小白Ubuntu20.04系统从零运行ORBSLAM3
前阵子安装ORBSLAM3,怕自己后面还需要,写一个过程当作自我备忘,如果能帮到其他人那就更好了
文章目录
**纯小白Ubuntu20.04系统从零运行ORBSLAM3**安装Ubuntu20.04配置环境新系统的一些准备安装git安装vi编辑器安装gcc、g++安装cv_bridge 安装opencv安装依赖项下载opencv4.2安装opencv查看版本号 安装各种库安装EIGEN库安装Pangolin库安装Boost库 安装ORBSLAM3下载ORBSLAM3修改文件 测试数据集下载EuRoC数据集运行EuRoC数据集下载RGBD-TUM数据集运行RGBD-TUM数据集
安装Ubuntu20.04
有很多教程这里就不展开了。
配置环境
新系统的一些准备
安装git
如果是新系统需要先安装git,在终端执行以下指令:
sudo apt-get install git安装vi编辑器
如果是新系统需要先安装vi编辑器,在终端执行以下指令:
sudo apt-get remove vim-commonsudo apt-get install vim安装gcc、g++
sudo apt-get install gccsudo apt-get install g++安装cv_bridge
在终端执行以下指令:
sudo apt-get install libopencv-devsudo apt-get install ros-noekit-cv-bridge安装opencv
安装依赖项
在终端执行以下指令:
sudo apt-get install build-essential libgtk2.0-dev libgtk-3-dev libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libjpeg-dev libswscale-dev libtiff5-devsudo apt install python3-dev python3-numpysudo apt install libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer1.0-devsudo apt install libpng-dev libopenexr-dev libtiff-dev libwebp-dev下载opencv4.2
在官网(https://opencv.org/releases/page/3/)将下载的opencv4.2解压至主目录,命名应该是opencv-4.2.0
安装opencv
在终端执行以下指令:
cd opencv-4.2.0mkdir buildcd buildcmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -D OPENCV_GENERATE_PKGCONFIG=YES ..makesudo make install查看版本号
在终端执行以下指令:
pkg-config --modversion opencv4终端应该会返回4.2.0,代表安装成功
安装各种库
安装EIGEN库
在终端执行以下指令:
sudo apt-get install libeigen3-dev安装Pangolin库
下载Pangolin0.6,解压到主目录,重命名为Pangolin
在终端执行以下指令安装依赖项:
sudo apt-get install libglew-dev libboost-dev libboost-thread-dev libboost-filesystem-devsudo apt-get install ffmpeg libavcodec-dev libavutil-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev libpng-dev在终端执行以下指令编译安装:
cd Pangolin mkdir build && cd buildcmake -DCPP11_NO_BOOST=1 ..make再在终端执行以下指令:
sudo make install再在终端执行以下指令进行验证:
cd ../examples/HelloPangolinmkdir build && cd buildcmake ..再在终端执行以下指令:
make./HelloPangolin如果成功会弹出窗口,一个立方体
安装Boost库
在官网http://www.boost.org/users/download/下载boost_1_77_0.tar.gz
解压后在终端执行以下指令进行安装:
tar -xvf boost_1_77_0.tar.gzcd ./boost_1_77_0./bootstrap.shsudo ./b2 install安装ORBSLAM3
下载ORBSLAM3
在终端执行以下指令:
git clone https://github.com/electech6/ORB_SLAM3_detailed_comments.git 下载完成后重命名为ORB-SLAM3
修改文件
首先在orbslam3文件夹下打开CMakeLists.txt
找到find_package(OpenCV 3.2),把版本号3.2改成自己的版本,也就是4.2。
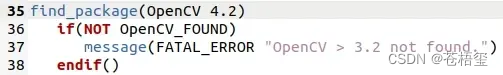
再找到find_package(Eigen3 3.1.0 REQUIRED),把版本号3.1.0删掉。
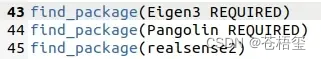
然后进入Thirdparty→DBoW2,打开CMakeLists.txt,找到find_package(OpenCV 3.2 QUIET),把版本号改成自己的版本,也就是4.2。
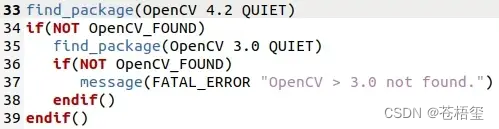
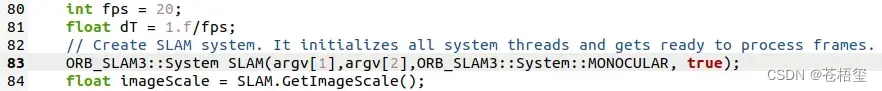
随后进入Examples→Monocular,打开mono_euroc.cc文件,把第83行的false改成true。(这一步是为了程序运行时能显示可视化窗口)
而后在ORB-SLAM3文件夹下右键打开终端执行以下指令刷新配置:
chmod +x build.sh ./build.sh测试数据集
下载EuRoC数据集
EuRoC数据集下载网址:
https://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets
在ORB-SLAM3文件夹下新建一个datasets文件夹,在datasets文件夹下新建一个MH01文件夹,打开kmavvisualinertialdatasets – ASL Datasets下载ASL Dataset Format列表下的Machine Hall 01数据集,将下载后的mav0文件拷贝到上文中新建的MH01文件夹中
(其他数据集参考https://blog.csdn.net/m0_60355964/article/details/125995064这篇文章)
运行EuRoC数据集
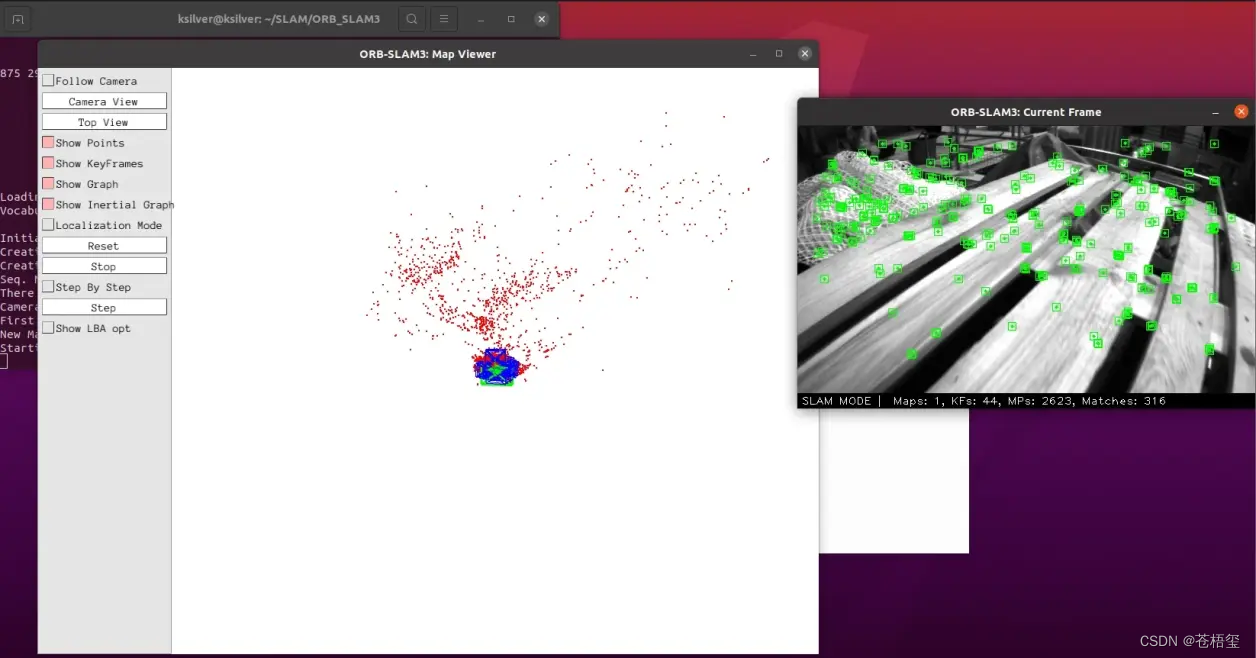
在ORB-SLAM3文件夹下右键打开终端执行以下指令:
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc ./Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt ./Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml ./datasets/MH01 ./Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/MH01.txt dataset-MH01_mono运行效果如下:
下载RGBD-TUM数据集
RGBD-TUM数据集下载网址: https://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/download
将下载的数据解压缩到ORBSLAM3文件夹中,以rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_walking_xyz为例。
下载配准文件associate.py
下载网址:https://cvg.cit.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/tools
或者自己在/ORB_SLAM3/Examples/RGB-D目录里面创建一个associate.py,将以下代码粘贴进去。
import argparseimport sysimport osimport numpy def read_file_list(filename): """ Reads a trajectory from a text file. File format: The file format is "stamp d1 d2 d3 ...", where stamp denotes the time stamp (to be matched) and "d1 d2 d3.." is arbitary data (e.g., a 3D position and 3D orientation) associated to this timestamp. Input: filename -- File name Output: dict -- dictionary of (stamp,data) tuples """ file = open(filename) data = file.read() lines = data.replace(","," ").replace("\t"," ").split("\n") #if remove_bounds: # lines = lines[100:-100] list = [[v.strip() for v in line.split(" ") if v.strip()!=""] for line in lines if len(line)>0 and line[0]!="#"] list = [(float(l[0]),l[1:]) for l in list if len(l)>1] return dict(list) def associate(first_list, second_list,offset,max_difference): """ Associate two dictionaries of (stamp,data). As the time stamps never match exactly, we aim to find the closest match for every input tuple. Input: first_list -- first dictionary of (stamp,data) tuples second_list -- second dictionary of (stamp,data) tuples offset -- time offset between both dictionaries (e.g., to model the delay between the sensors) max_difference -- search radius for candidate generation Output: matches -- list of matched tuples ((stamp1,data1),(stamp2,data2)) """ first_keys = list(first_list.keys()) second_keys = list(second_list.keys()) potential_matches = [(abs(a - (b + offset)), a, b) for a in first_keys for b in second_keys if abs(a - (b + offset)) < max_difference] potential_matches.sort() matches = [] for diff, a, b in potential_matches: if a in first_keys and b in second_keys: first_keys.remove(a) second_keys.remove(b) matches.append((a, b)) matches.sort() return matches if __name__ == '__main__': # parse command line parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=''' This script takes two data files with timestamps and associates them ''') parser.add_argument('first_file', help='first text file (format: timestamp data)') parser.add_argument('second_file', help='second text file (format: timestamp data)') parser.add_argument('--first_only', help='only output associated lines from first file', action='store_true') parser.add_argument('--offset', help='time offset added to the timestamps of the second file (default: 0.0)',default=0.0) parser.add_argument('--max_difference', help='maximally allowed time difference for matching entries (default: 0.02)',default=0.02) args = parser.parse_args() first_list = read_file_list(args.first_file) second_list = read_file_list(args.second_file) matches = associate(first_list, second_list,float(args.offset),float(args.max_difference)) if args.first_only: for a,b in matches: print("%f %s"%(a," ".join(first_list[a]))) else: for a,b in matches: print("%f %s %f %s"%(a," ".join(first_list[a]),b-float(args.offset)," ".join(second_list[b]))) 在ORBSLAM3文件夹中打开终端执行以下指令:
python3 ./Examples/RGB-D/associate.py ./rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_walking_xyz/rgb.txt ./rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_walking_xyz/depth.txt >./rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_walking_xyz/associations.txt就可以得到示例数据集的associations.txt
运行RGBD-TUM数据集
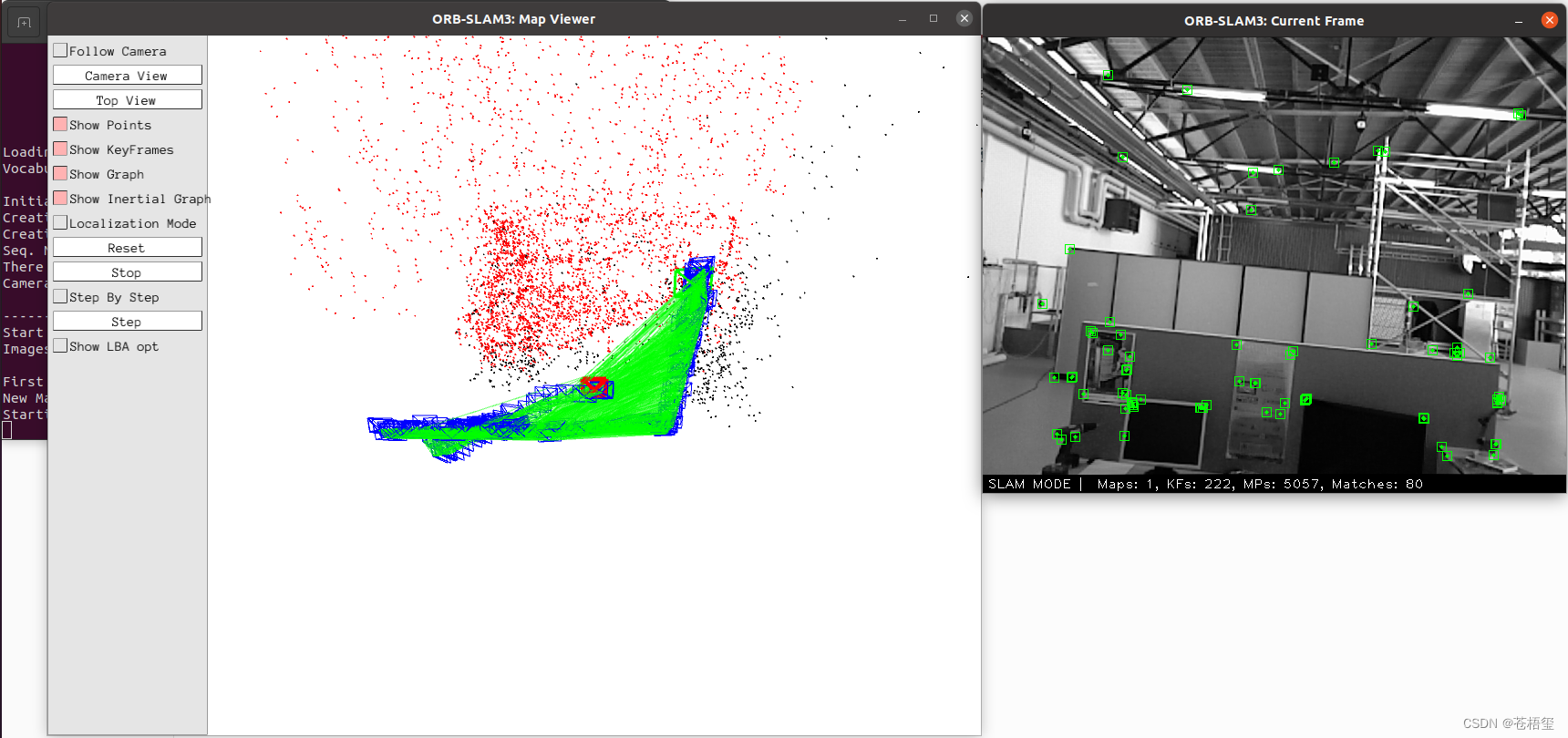
在ORBSLAM3文件夹中打开终端执行以下指令:
./Examples/RGB-D/rgbd_tum Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt ./Examples/RGB-D/TUM3.yaml ./rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_walking_xyz rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_walking_xyz/associations.txt其中TUM3.yaml为相机内参文件,注意数据集使用的是那个相机内参,rgbd_dataset_freiburg3_walking_xyz中“freiburg3”表示用的TUM3.yaml。
运行效果如下:
本篇文章主要参考以下文章:
1:https://blog.csdn.net/Prototype___/article/details/129286042
2:https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv24690326/
3:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43907136/article/details/130273186
4:https://blog.csdn.net/Welf688/article/details/124029171