前言
Hello,小伙伴们,经过了前面对C++基础知识的学习,我们今天就着重运用一下前面学习到的知识,来通过类和对象以及运算符重载的部分知识来实现,来完成我们的日期计算器。
日期计算器,顾名思义,就是可以通过日期和天数来进行年、月、日的转换、计算。
1.可以实现具体日期与天数的加减,并得到加减计算后的日期。
2.可以实现两个具体日期之间的加减,计算两日期之间相差的天数。

功能不是特别的复杂,我们现在就可以着手尝试了。
好,按例三连上车不迷路,开始我们今天的内容。
在看这篇文章的时候,强烈推荐大家先看看我之前的这两篇文章,来学习一下C++类和对象的基础:
http://t.csdnimg.cn/OY9mJ
http://t.csdnimg.cn/ZK1sA
1.日期类的定义
首先我们要定义一个日期类,运用我们刚学习的C++知识,我们这里直接看代码:
案例,我们还是先创建3个文件来实现我们的目的
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>class Date{public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);//~Date();private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};在这里,我们先来解决构造函数和析构函数的问题:
构造函数:
我们在Date.cpp文件中实现他的功能:
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}由于在日期类中,我们没有申请内存空间,也就是该类中不存在深度拷贝,因此我们就不需要自己单独实现析构函数。
2.日期类的打印(DatePrint)
完成构造函数后,我们就可以通过打印函数来显示我们定义的日期类的值:
首先我们要完成日期打印函数的声明:
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>class Date{public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);//~Date(); void DatePeint();//日期打印private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};接下来我们来实现日期类打印函数的功能:
void Date::DatePrint(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}接下来我们来展示一下这个函数的功能: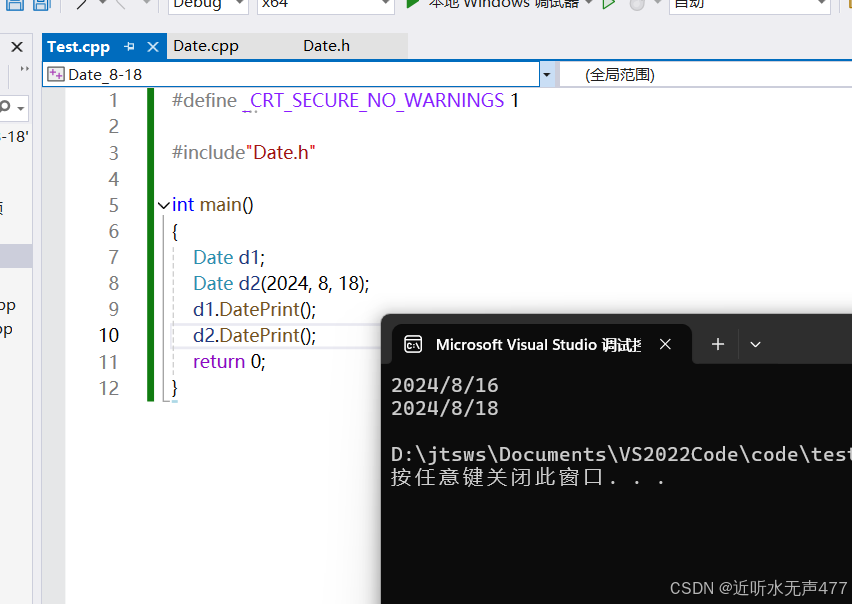
3.比较运算符的重载
前面我们学习了运算符重载方面的知识,我们接下来就设计及应用一下:
比较运算符的种类有很多,但是在运算符重载上实现的方法基本一样,这里借用我们前面学到的知识很容易就能实现:
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>class Date{public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);//~Date(); void DatePeint();//日期打印//比较大小运算符的重载bool operator==(Date& d);bool operator!=(Date& d);bool operator>(Date& d);bool operator<(Date& d);bool operator<=(Date& d);bool operator>=(Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};代码实现:
bool Date::operator==(Date& d){return _year == d._day && _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;}Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d1){_year = d1._year;_month = d1._month;_day = d1._day;return *this;}bool Date::operator!=(Date& d){return !(*this == d);}bool Date::operator>(Date& d){if (_year > d._year ){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month >d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day){return true;}return false;}bool Date::operator<(Date& d){return !(*this >= d);}bool Date::operator<=(Date& d){return *this < d || *this == d;}bool Date::operator>=(Date& d){return *this > d || *this == d;}运算符重载的实现逻辑十分的灵活,我们只需要实现几种基本的运算符重载,其他的我们就能够根据已知的运算关系,并运用或且非的逻辑关系来实现其余的运算符重载。
4.日期+= 和 +操作(日期加天数)的实现
首先我们还是先来定义这个运算符的重载:
要实现日期与天数的加操作,我们就好要得到每个月的天数:
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>class Date{public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);//~Date(); void DatePeint();//日期打印//比较大小运算符的重载bool operator==(Date& d);bool operator!=(Date& d);bool operator>(Date& d);bool operator<(Date& d);bool operator<=(Date& d);bool operator>=(Date& d);//获取每个月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month >= 1 && month <= 12);//因为这个数组会高频·的进行调用,所以使用静态数组就能极大地提高效率static int MonthDay[13] = { -1, 31,28, 31 ,30, 31,30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };//借用短路效应,适当的提高效率if ( month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return MonthDay[month];}Date& operator+=(int day);//日期与天数的加运算Date operator+(int day);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};实现的逻辑也十分的简单,我们先来看看代码:
Date& Date::operator+=(int day){if (day < 0){return (*this -= -day);}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date Date::operator+(int day){Date tmp = *this;tmp += day;return tmp;}接下来我们来看看效果
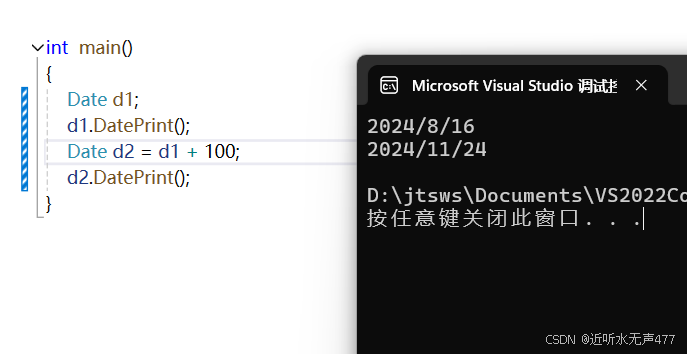
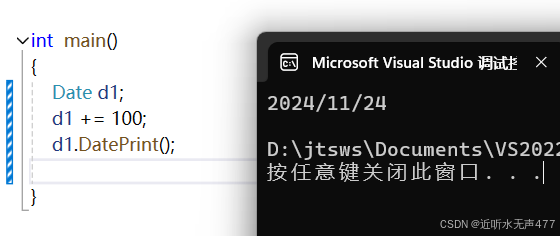
接下来,我们使用网上的日期运算器来验证一下答案是否正确:
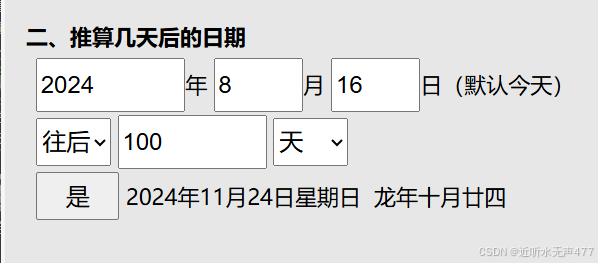
5.日期-=和 -操作(日期减天数)的实现
日期与天数的想减得到日期的算法和前面的相加算法也相似。
我们还是先来定义相减运算:
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>class Date{public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);//~Date(); void DatePeint();//日期打印//比较大小运算符的重载bool operator==(Date& d);bool operator!=(Date& d);bool operator>(Date& d);bool operator<(Date& d);bool operator<=(Date& d);bool operator>=(Date& d);//获取每个月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month >= 1 && month <= 12);//因为这个数组会高频·的进行调用,所以使用静态数组就能极大地提高效率static int MonthDay[13] = { -1, 31,28, 31 ,30, 31,30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };//借用短路效应,适当的提高效率if ( month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return MonthDay[month];}Date& operator+=(int day);//日期与天数的加运算Date operator+(int day);Date& operator+=(int day);//日期与天数的减运算Date operator+(int day);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};减运算符重载的实现与加运算符的实现逻辑基本相同,我们直接看代码:
Date& Date::operator-=(int day){if (day < 0){return (*this += -day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month--;while (_month <= 0){_year--;_month = 12;}}return *this;}Date Date::operator-(int day){Date tmp = *this;tmp -= day;return tmp;}接下来我们来测试一下运行效果:
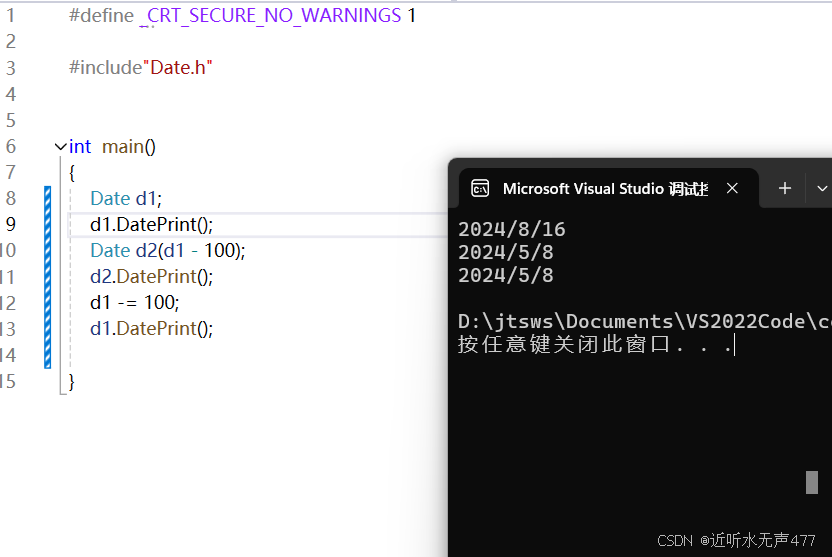
让我们用日期计算器来验算一下日期的计算结果是否正确:

6. 前置++(--)与后置++(--)
根据我们前面的基础知识,我们知道前置++(--)和后置++(--)的冲在式定义就是根据是否有参数来判断的,所以本质上他们的实现就与+=(-=)和-=(-) 相似。
首先来看定义:
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>class Date{public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);//~Date(); void DatePeint();//日期打印//比较大小运算符的重载bool operator==(Date& d);bool operator!=(Date& d);bool operator>(Date& d);bool operator<(Date& d);bool operator<=(Date& d);bool operator>=(Date& d);//获取每个月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month >= 1 && month <= 12);//因为这个数组会高频·的进行调用,所以使用静态数组就能极大地提高效率static int MonthDay[13] = { -1, 31,28, 31 ,30, 31,30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };//借用短路效应,适当的提高效率if ( month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return MonthDay[month];}Date& operator+=(int day);//日期与天数的加运算Date operator+(int day);Date& operator-=(int day);//日期与天数的减运算Date operator-(int day);//前置和后置的区别就是看式子中是不是有参数Date& operator++();Date& operator++(int );Date& operator--();Date& operator--(int);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};我们直接来代码:
Date& Date::operator++(){return (*this += 1);}Date& Date::operator++(int){Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;}Date& Date:: operator--(){return (*this -= 1);}Date& Date::operator--(int){Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;}简单的来看看效果,单独看这个的用处好像是不大,但是结合到接下来我们要实现的功能,这个重载式就会发挥很大的作用:
7.两日期之间相差的天数
首先我们还是先来定义这个重载式:
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>class Date{public:Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);//~Date(); void DatePeint();//日期打印//比较大小运算符的重载bool operator==(Date& d);bool operator!=(Date& d);bool operator>(Date& d);bool operator<(Date& d);bool operator<=(Date& d);bool operator>=(Date& d);//获取每个月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month >= 1 && month <= 12);//因为这个数组会高频·的进行调用,所以使用静态数组就能极大地提高效率static int MonthDay[13] = { -1, 31,28, 31 ,30, 31,30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };//借用短路效应,适当的提高效率if ( month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return MonthDay[month];}Date& operator+=(int day);//日期与天数的加运算Date operator+(int day);Date& operator-=(int day);//日期与天数的减运算Date operator-(int day);//前置和后置的区别就是看式子中是不是有参数Date& operator++();Date& operator++(int );Date& operator--();Date& operator--(int);//计算两个日期之间的天数差int operator-(const Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};大家在这个时候可以来想想,用什么方法能得到两个日期之间的天数差异:
想要实现这个方法其实十分的简单,我们先找到小的那个日期,再让这个日期++,记录他++的次数,直到他与那个较大的日期相等为止,记录得到的次数就是相差的天数。
接下来我们来实现一下代码:
int Date::operator-(const Date& d){Date small =d ;Date big = *this;int flag = 1;if (big < small){big = d;small = *this;flag *= -1;}int count = 0;while (small < big){small++;++count;}return (count - 1) * flag;}我们实现了代码,接下来我们来测试一下代码的效果:
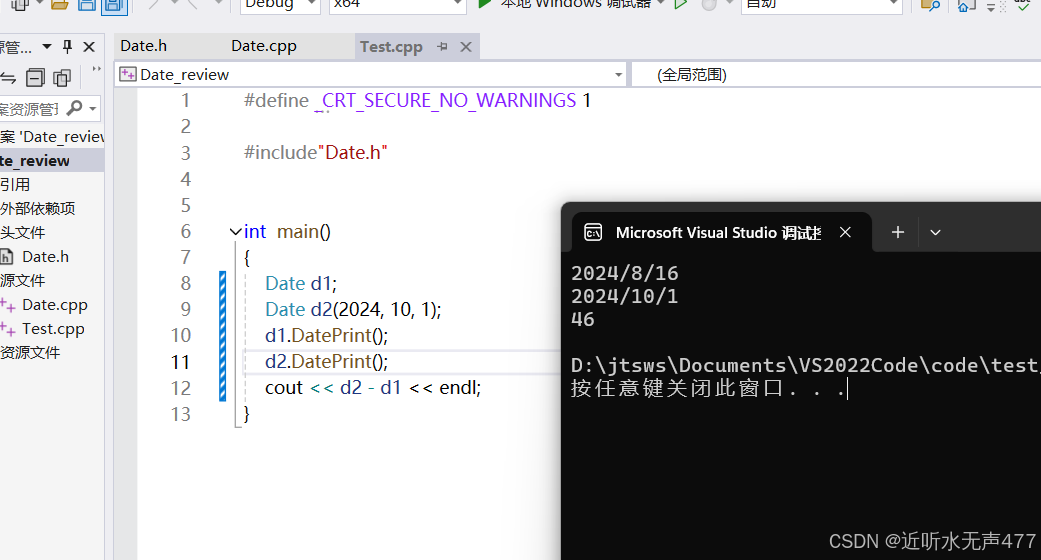
我们就简单测试一下从 8 月16号,到今年国庆节之间的天数差,然后我们就在网上的日期计算器上验算一下我们得结果:

8.代码展示
我们完成了日期计算器的, 接下来是代码展示:
Date.h
#pragma once#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>using namespace std;class Date{public:friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& out, Date& d);Date(int year = 2024, int month = 8, int day = 16);///~Date();//日期值的打印void DatePrint();//赋值运算符的重载Date& operator=(const Date& d1);//比较大小运算符的重载bool operator==(Date& d);bool operator!=(Date& d);bool operator>(Date& d);bool operator<(Date& d);bool operator<=(Date& d);bool operator>=(Date& d);//获取每个月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month >= 1 && month <= 12);//因为这个数组会高频·的进行调用,所以使用静态数组就能极大地提高效率static int MonthDay[13] = { -1, 31,28, 31 ,30, 31,30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };//借用短路效应,适当的提高效率if ( month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){return 29;}return MonthDay[month];}Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day);Date& operator-=(int day);Date operator-(int day);//前置++Date& operator++();Date& operator++(int );Date& operator--();Date& operator--(int);//计算两个日期之间的天数差int operator-(const Date& d);bool CheckDate(){if (_month >= 13 || _month <= 0){return false;}if (_day >= GetMonthDay(_year, _month)|| _day <= 0){return false;}return true;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;};//ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d); //& operator>>(istream& out, const Date& d);Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month, int day){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (!CheckDate()){cout << "输入非法日期!!" << "->";cout << *this;}}void Date::DatePrint(){cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;}bool Date::operator==(Date& d){return _year == d._day && _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;}Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d1){_year = d1._year;_month = d1._month;_day = d1._day;return *this;}bool Date::operator!=(Date& d){return !(*this == d);}bool Date::operator>(Date& d){if (_year > d._year ){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month >d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day){return true;}return false;}bool Date::operator<(Date& d){return !(*this >= d);}bool Date::operator<=(Date& d){return *this < d || *this == d;}bool Date::operator>=(Date& d){return *this > d || *this == d;}Date& Date::operator+=(int day){if (day < 0){return (*this -= -day);}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month >= 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;}Date Date::operator+(int day){Date tmp = *this;tmp += day;return tmp;}Date& Date::operator-=(int day){if (day < 0){return (*this += -day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month--;while (_month <= 0){_year--;_month = 12;}}return *this;}Date Date::operator-(int day){Date tmp = *this;tmp -= day;return tmp;}Date& Date::operator++(){return (*this += 1);}Date& Date::operator++(int){Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;}Date& Date:: operator--(){return (*this -= 1);}Date& Date::operator--(int){Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;}int Date::operator-(const Date& d){Date small =d ;Date big = *this;int flag = 1;if (big < small){big = d;small = *this;flag *= -1;}int count = 0;while (small < big){small++;++count;}return (count - 1) * flag;}ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d){out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;}istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d){cout << "请依次输入有效的年月日信息" << endl;while (1){in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;if (d.CheckDate()){break;}cout << "日期非法!!" << "->";cout << d;}return in;}Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"Date.h"int main(){Date d1;Date d2(2024, 10, 1);d1.DatePrint();d2.DatePrint();cout << d2 - d1 << endl;}好,今天的学习就到这里了,我们下期再见,拜拜!!!