1.概念介绍
1.1开散列
开散列(Open Hashing),也叫链地址法,是一种解决哈希冲突的方法。每个哈希表槽位保存一个链表,所有散列到同一位置的元素都存储在该链表中。当插入元素发生冲突时,将新元素添加到相应槽位的链表末尾。
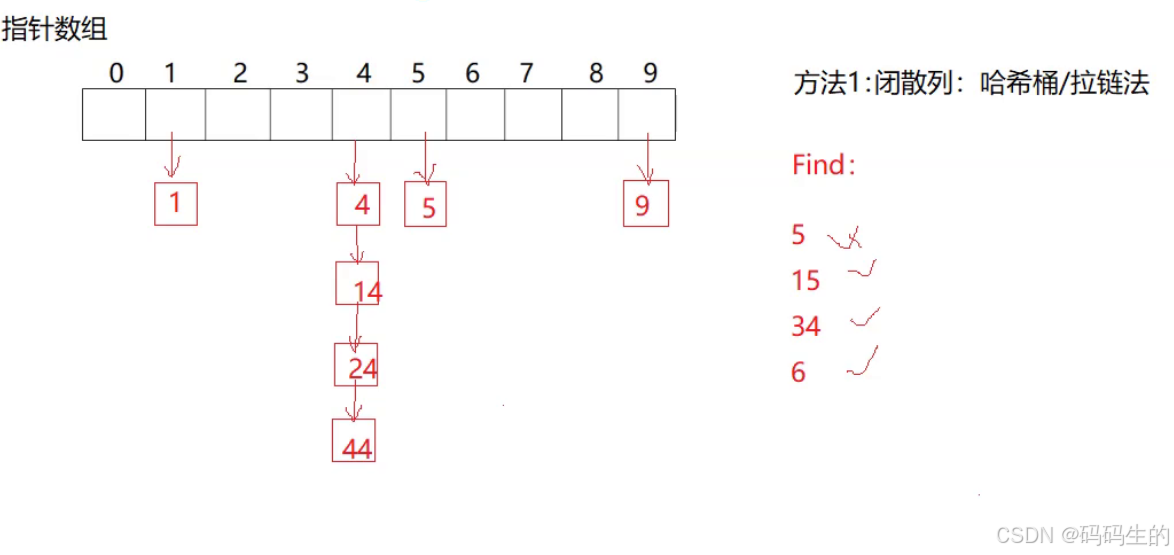
1.2闭散列
闭散列(Closed Hashing),也叫开放地址法,是一种解决哈希冲突的方法。当插入元素发生冲突时,通过寻找下一个空槽位来存储冲突元素,常见策略包括1.线性探测、2.二次探测等,不使用链表存储冲突元素。

2.模拟实现
2.1闭散列模拟实现
1.枚举——status
enum status //使用枚举保存数据的“状态”,如果为EMPTY,DELETE则可以插入{EMPTY,//记得EMPTY要写在最上面,这样,系统默认的构造函数才会将s初始化为EMPTYEXIST,DELETE};2.数组中的元素——hashdata
template<class K,class V>struct hashdata{pair<K, V> data; //数据status s; //状态};3.将key元素转化为可计算的形式——hashfunc
为了确定元素应当插入到哪个位置,需要把key取出来
template<class K>struct hashfunc //因为key不一定是整形,如果能强制转换成整形,那就要转换{size_t operator()(const K& key){return size_t(key); }};单独为string类写一份:
template<>struct hashfunc<string> //单独为k=string写一份,还记得嘛,这是模板的特化!!!!!!!这样,在初始化hashtable时就不用再传仿函数模板参数了{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t flag = 0;;for (auto e : key){flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同,防止第一步就发生冲突flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式}return flag;}};模板特化相关知识:移情别恋c++ ദ്ദി˶ー̀֊ー́ ) ——9.模板进阶-CSDN博客
4.容器——hashtable
私有成员:
private: vector<hashdata<K,V>> table; size_t num=0;//储存的关键字的个数2.2.hashtable的功能实现
1.初始化
hashtable(){table.resize(10);}2.插入!!!!!!
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (find(kv.first)){return false;}//负载因子,指关键字个数在总size中的占比,(越大代表发生hash冲突的概率越大)普遍超出0.7时就要扩容了,扩容需要重新开一份空间!!!!!!!!!因为映射关系被打乱了if (num * 10 / table.size() == 7)//这里很巧妙{size_t newsize = table.size() * 2;hashtable<K, V,hash> newtable;newtable.table.resize(newsize);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size();i++){if (table[i].s == EXIST){newtable.insert(table[i].data);}}table.swap(newtable.table);//记得交换一下}hash hf;//1.线性探测(解决hash冲突的方法)size_t position = hf(kv.first) % table.size();//应用映射公式 hash(key) = key % capacity (注意!!!!!这里要用table.size(),而不是table.capacity(),所以要除余while ((table[position]).s == EXIST)//如果当前的位置非空,则往后顺延一位!!!!!!{position++;position %= table.size();//positin走到底后回到0}table[position].data = kv;table[position].s= EXIST;++num; return true;}3.查找
hashdata<K, V>* find(const K& key)//查找是从确定的初始位置查找到nullptr!!!!!结束,因为没到nullptr前,都有可能是因为冲突导致数据后移{hash hf;size_t position =hf(key)% table.size();while (table[position].s != EMPTY){if (table[position].data.first == key&& table[position].s==EXIST){return &table[position];}position++;position %= table.size();}return NULL;}4.删除
bool erase(const K& key){hashdata<K, V>* ret = find(key);if (ret){ret->s = DELETE;--num;return true;}else{return false;}}2.3开散列模拟实现
开散列存储的本质是指针数组
1.数组中的元素——hashnode
template<class T> struct hashnode{T data; //数据hashnode* next;hashnode(T kv):data(kv),next(nullptr){}};2. 容器——hashtable
私有成员:
private:vector<node*> table;size_t num = 0;};2.4.hashtable内容实现
1.初始化
hashtable(){table.resize(10);}2.析构函数
~hashtable(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//最后置空}}3.查找
node* find(const K& key){hash hf;typeoft tt;size_t position = hf(key) % table.size();node* cur = table[position];while (cur){if (tt(cur->data)== key)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return nullptr;}4.插入
bool insert(const T& kv){hash hf;typeoft tt;if (find(tt(kv)))return true;if (num == table.size())//当负载因子等于1时要扩容{vector<node*> newtable;newtable.resize(table.size()* 2, nullptr);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;size_t newposition = hf(tt(cur->data)) % newtable.size();cur->next = newtable[newposition];newtable[newposition] = cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//数据原来的位置处一定要置空,否则会因为二次析构产生问题}table.swap(newtable);//直接交换两个哈希桶(底层指针的交换)}size_t position = hf(tt(kv)) % table.size();node* newnode = new node(kv);node* cur = table[position];//头插newnode->next = cur;table[position] = newnode;num++;}3. 迭代器的设置(以开散列为例)!!!!!!!!
1.hsiterator的设置与功能
//前置声明,因为哈希表用到了迭代器,迭代器也用到了哈希表,这叫做相互依赖,需要做前置声明template<class K, class T, class typeoft, class hash >class hashtable;template<class K, class T,class ref,class ptr, class typeoft,class hash=hashfunc<K>>struct hsiterator{typedef hashnode<T> node;const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &point;//这里使用引用是为了防止析构影响原来的tabletypedef hsiterator<K, T,ref,ptr, typeoft,hash> Self;node* _node;size_t place;hsiterator(node* node_, const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &_point,size_t _place):_node(node_),point(_point),place(_place){}Self operator++(){if (_node->next)//如果—_node->next不为空,那么桶里面还有数据,走next{_node = _node->next;}else //如果为空,那么需要走到下一个桶{typeoft tt;hash hf;//size_t head = hf(tt(_node->data)) % point.table.size();//找到初始位置,方便转移至下一个桶++place;while (place < point.table.size()){if (point.table[place]){_node = point.table[place];break;}else{place++;}}if (place == point.table.size()){_node = nullptr;}return *this;}}ref operator*(){return _node->data;}ptr operator->(){return &_node->data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}};2.hashtable中对hsiterator的封装
template<class K, class T, class ref, class ptr,class typeoft,class hash>friend struct hsiterator;//这里设置了友元,这样,hsiterator就可以直接取到hashtable的private成员table数组了typedef hsiterator<K, T,T&,T*, typeoft, hash> iterator;//普通迭代器typedef hsiterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, typeoft, hash> const_iterator;//const迭代器iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i])return iterator(table[i], *this, i);}return end();}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, *this, -1);//-1是随便给的}4.unorderedmap&&unorderedset封装
1.取出K元素(仿函数)
struct setkeyoft //仿函数{ const K& operator()(const K& key) { return key; }};2.迭代器封装
set的iterator全部使用const迭代器:
typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator iterator; typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator;/* iterator begin() { return table.begin(); } iterator end() { return table.end(); }*/ const_iterator begin()const { return table.begin(); } const_iterator end() const { return table.end(); }map的迭代器正常分类使用:
typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::iterator iterator;typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return table.begin();}iterator end(){return table.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return table.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return table.end();}5.代码全览
1.hash.h
#include<iostream>#include<vector>using namespace std;namespace close_address//闭散列{enum status //使用枚举保存数据的“状态”,如果为EMPTY,DELETE则可以插入{EMPTY,//记得EMPTY要写在最上面,这样,系统默认的构造函数才会将s初始化为EMPTYEXIST,DELETE};template<class K,class V>struct hashdata{pair<K, V> data; //数据status s; //状态};template<class K>struct hashfunc //因为key不一定是整形,如果能强制转换成整形,那就要转换{size_t operator()(const K& key){return size_t(key); }};template<>struct hashfunc<string> //单独为k=string写一份,还记得嘛,这是模板的特化!!!!!!!这样,在初始化hashtable时就不用再传仿函数模板参数了{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t flag = 0;;for (auto e : key){flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同,防止第一步就发生冲突flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式}return flag;}};//struct hashfuncstring //这是单独为string类写的转换仿函数//{//size_t operator()(const string& key)//{//size_t flag = 0;;//for (auto e : key)//{//flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同//flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式//}//return flag;//}//}; template<class K,class V,class hash=hashfunc<K>>//这里hash直接给了缺省值,如果K可以转化,就可以在初始化的时候可以不给hash的模板参数 class hashtable { public:hashtable(){table.resize(10);}hashdata<K, V>* find(const K& key)//查找是从确定的初始位置查找到nullptr!!!!!结束,因为没到nullptr前,都有可能是因为冲突导致数据后移{hash hf;size_t position =hf(key)% table.size();while (table[position].s != EMPTY){if (table[position].data.first == key&& table[position].s==EXIST){return &table[position];}position++;position %= table.size();}return NULL;}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (find(kv.first)){return false;}//负载因子,指关键字个数在总size中的占比,(越大代表发生hash冲突的概率越大)普遍超出0.7时就要扩容了,扩容需要重新开一份空间!!!!!!!!!因为映射关系被打乱了if (num * 10 / table.size() == 7)//这里很巧妙{size_t newsize = table.size() * 2;hashtable<K, V,hash> newtable;newtable.table.resize(newsize);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size();i++){if (table[i].s == EXIST){newtable.insert(table[i].data);}}table.swap(newtable.table);//记得交换一下}hash hf;//1.线性探测(解决hash冲突的方法)size_t position = hf(kv.first) % table.size();//应用映射公式 hash(key) = key % capacity (注意!!!!!这里要用table.size(),而不是table.capacity(),所以要除余while ((table[position]).s == EXIST)//如果当前的位置非空,则往后顺延一位!!!!!!{position++;position %= table.size();//positin走到底后回到0}table[position].data = kv;table[position].s= EXIST;++num; return true;}bool erase(const K& key){hashdata<K, V>* ret = find(key);if (ret){ret->s = DELETE;--num;return true;}else{return false;}}void print(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i].s == EXIST){//printf("[%d]->%d\n", i, table[i].data.first);cout << "[" << i << "]->" << table[i].data.first << endl;}else if (table[i].s == EMPTY){//printf("[%d]->空余\n", i);cout << "[" << i << "]->空余" << endl;}else{//printf("[%d]->删除\n", i);cout << "[" << i << "]->删除" << endl;}}} private: vector<hashdata<K,V>> table; size_t num=0;//储存的关键字的个数 }; void test1() { hashtable<int, int> it; int a[] = { 4,14,24,34,5,7,1 }; for (auto e : a) { it.insert(make_pair(e, e)); } it.insert(make_pair(3, 3)); it.insert(make_pair(3, 3)); it.insert(make_pair(-3, -3)); it.print(); cout << endl; it.erase(3); it.print(); } void test2() { hashtable<string, int> it; string arr[] = { "香蕉","苹果" ,"西瓜" ,"苹果" ,"香蕉" ,"香瓜" ,"苹果" ,"香蕉" }; for (auto e : arr) { auto f = it.find(e);//hashdata<K,V>* if (f) { f->data.second++; } else { it.insert(make_pair(e, 1)); } } it.print(); }}namespace open_address//开散列{template<class K>struct hashfunc //因为key不一定是整形,如果能强制转换成整形,那就要转换{size_t operator()(const K& key){return size_t(key);}};template<>struct hashfunc<string> //还记得嘛,这是模板的特化!!!!!!!这样,在初始化hashtable时就不用再传仿函数模板参数了{size_t operator()(const string& key){size_t flag = 0;;for (auto e : key){flag *= 31;//这一步可以保证abc,acb的flag不同,防止第一步就发生冲突flag += e;//本质是遍历整个string并使每个字母的ascii码相加,当然也可以使用其他的方式}return flag;}};template<class T>struct hashnode{T data; //数据hashnode* next;hashnode(T kv):data(kv),next(nullptr){}};//前置声明,因为哈希表用到了迭代器,迭代器也用到了哈希表,这叫做相互依赖,需要做前置声明template<class K, class T, class typeoft, class hash >class hashtable;template<class K, class T,class ref,class ptr, class typeoft,class hash=hashfunc<K>>struct hsiterator{typedef hashnode<T> node;const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &point;//这里使用引用是为了防止析构影响原来的tabletypedef hsiterator<K, T,ref,ptr, typeoft,hash> Self;node* _node;size_t place;hsiterator(node* node_, const hashtable< K, T, typeoft, hash> &_point,size_t _place):_node(node_),point(_point),place(_place){}Self operator++(){if (_node->next)//如果—_node->next不为空,那么桶里面还有数据,走next{_node = _node->next;}else //如果为空,那么需要走到下一个桶{typeoft tt;hash hf;//size_t head = hf(tt(_node->data)) % point.table.size();//找到初始位置,方便转移至下一个桶++place;while (place < point.table.size()){if (point.table[place]){_node = point.table[place];break;}else{place++;}}if (place == point.table.size()){_node = nullptr;}return *this;}}ref operator*(){return _node->data;}ptr operator->(){return &_node->data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}};template<class K, class T, class typeoft ,class hash = hashfunc<K>>class hashtable{public:typedef hashnode<T> node;template<class K, class T, class ref, class ptr,class typeoft,class hash>friend struct hsiterator;//这里设置了友元,这样,hsiterator就可以直接取到hashtable的private成员table数组了typedef hsiterator<K, T,T&,T*, typeoft, hash> iterator;//普通迭代器typedef hsiterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, typeoft, hash> const_iterator;//const迭代器iterator begin(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i])return iterator(table[i], *this, i);}return end();}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr, *this, -1);//-1是随便给的}const_iterator begin()const{for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){if (table[i])return const_iterator(table[i], *this, i);}return end();}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr, *this, -1);//-1是随便给的}hashtable(){table.resize(10);}~hashtable(){for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;delete cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//最后置空}}node* find(const K& key){hash hf;typeoft tt;size_t position = hf(key) % table.size();node* cur = table[position];while (cur){if (tt(cur->data)== key)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return nullptr;}bool insert(const T& kv){hash hf;typeoft tt;if (find(tt(kv)))return true;if (num == table.size())//当负载因子等于1时要扩容{vector<node*> newtable;newtable.resize(table.size()* 2, nullptr);//遍历旧表for (size_t i = 0; i < table.size(); i++){node* cur = table[i];while (cur){node* next = cur->next;size_t newposition = hf(tt(cur->data)) % newtable.size();cur->next = newtable[newposition];newtable[newposition] = cur;cur = next;}table[i] = nullptr;//数据原来的位置处一定要置空,否则会因为二次析构产生问题}table.swap(newtable);//直接交换两个哈希桶(底层指针的交换)}size_t position = hf(tt(kv)) % table.size();node* newnode = new node(kv);node* cur = table[position];//头插newnode->next = cur;table[position] = newnode;num++;}bool erase(const K& key){hash hf;typeoft tt;size_t position = hf(key) % table.size();node* cur = table[position];node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (tt(cur->data) == key){if (prev){prev->next = cur->next;delete cur;num--;}else{table[position] = nullptr;num--;}return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}return false;}private:vector<node*> table;size_t num = 0;};}2.myunorderedmap.h
#include"hash.h"using namespace open_address;namespace zone{template<class K, class V>class unorderedmap{public:struct setkeyoft{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& key){return key.first;}};typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::iterator iterator;typedef typename hashtable<K, pair<const K, V>, setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return table.begin();}iterator end(){return table.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return table.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return table.end();}bool insert(const pair<K,V>& key){return table.insert(key); }private:hashtable<K, pair<const K,V>, setkeyoft> table;};void testmap(){unorderedmap<string, string> it;it.insert(make_pair("sort","排序"));it.insert(make_pair("right","右"));it.insert(make_pair("left","左"));it.insert(make_pair("middle","中"));for (auto e : it){e.second += 'x';//map的value可改变,但key不能改变cout << e.first<<' '<<e.second<<endl;//记得加一个.first,因为重载的operator*,只会取得data,在map中就是pair<k,v>,所以要用.first取得key}}}3.myunorderedset.h
#include"hash.h"using namespace open_address;namespace zone{template<class K>class unorderedset{ public: struct setkeyoft //仿函数 { const K& operator()(const K& key) { return key; } }; typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator iterator; typedef typename hashtable<K,K,setkeyoft>::const_iterator const_iterator; /* iterator begin() { return table.begin(); } iterator end() { return table.end(); }*/ const_iterator begin()const { return table.begin(); } const_iterator end() const { return table.end(); } bool insert(const K& key) { return table.insert(key); } private: hashtable<K,K, setkeyoft> table;};void testset(){unorderedset<int> it;it.insert(2);it.insert(3);it.insert(14);it.insert(24);it.insert(34);unorderedset<int>::iterator arr = it.begin();while (arr != it.end()){//*arr += 5;//set的key不可修改cout << *arr << endl;++arr;}}}