
?个人主页:秋风起,再归来~
?系列专栏:C++从入门到起飞
?克心守己,律己则安
目录
1. 红⿊树的概念
2. 红⿊树的实现
2.1 构建整体框架
2.2 红黑树的插入
2.3 红黑树的验证
2.4 红黑树的其他简单接口
3、红黑树完整源码
4、完结散花
1. 红⿊树的概念
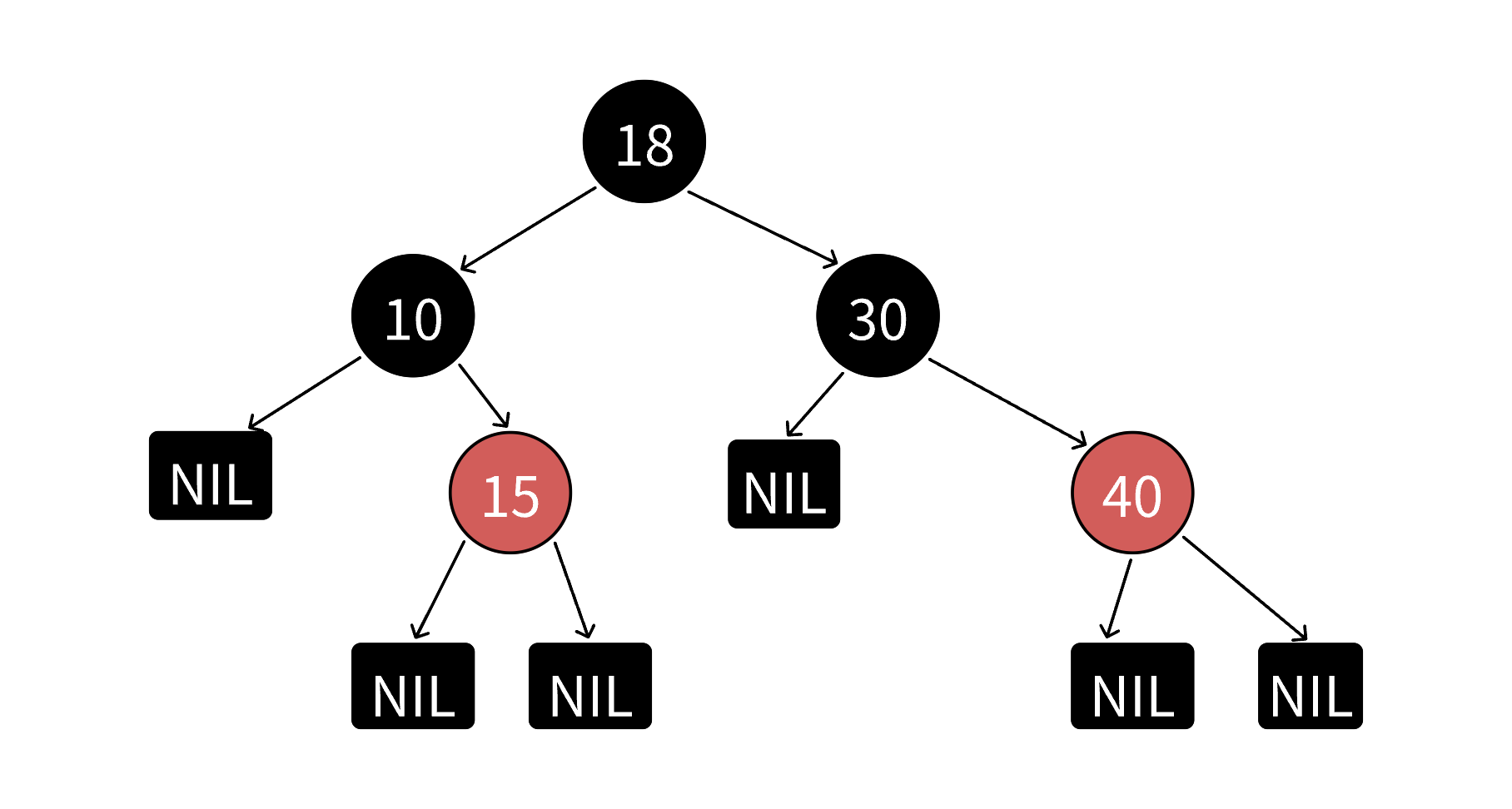
红⿊树是⼀棵⼆叉搜索树,他的每个结点增加⼀个存储位来表⽰结点的颜⾊,可以是红⾊或者⿊⾊。 通过对任何⼀条从根到叶⼦的路径上各个结点的颜⾊进⾏约束,红⿊树确保没有⼀条路径会⽐其他路 径⻓出2倍,因⽽是接近平衡的。
>红⿊树的规则:
1. 每个结点不是红⾊就是⿊⾊
2. 根结点是⿊⾊的
3. 如果⼀个结点是红⾊的,则它的两个孩⼦结点必须是⿊⾊的,也就是说任意⼀条路径不会有连续的 红⾊结点。
4. 对于任意⼀个结点,从该结点到其所有NULL结点的简单路径上,均包含相同数量的⿊⾊结点
说明:《算法导论》等书籍上补充了⼀条每个叶⼦结点(NIL)都是⿊⾊的规则。他这⾥所指的叶⼦结点 不是传统的意义上的叶⼦结点,⽽是我们说的空结点,有些书籍上也把NIL叫做外部结点。NIL是为了 ⽅便准确的标识出所有路径,《算法导论》在后续讲解实现的细节中也忽略了NIL结点,所以我们知道 ⼀下这个概念即可。
2. 红⿊树的实现
2.1 构建整体框架
枚举类型定义红黑色:
//枚举类型定义颜色enum Colour{RED,BLACK};红黑树每个节点的结构:
//节点结构(默认存储pair类型的key/val结构)template<class K, class V>struct RBTreeNode{RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _parent(nullptr), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr),_col(RED){}pair<K, V> _kv;RBTreeNode* _parent;RBTreeNode* _left;RBTreeNode* _right;Colour _col;//初始化为红色};红黑树整体结构
//红黑树template<class K,class V>class RBTree{typedef RBTreeNode Node;public: //各种接口的实现private:Node* _root=nullptr;};2.2 红黑树的插入
1、红黑树是特殊的二叉搜索数,所以我们进行插入时,还是先按照二叉搜索数的规则进行插入!
//如果树为空,在根插入并且颜色为黑色if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}//树不为空按搜索树规则先进行插入Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first)//小往左走{parent = cur;cur = parent->_left;}else if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)//大往右走{parent = cur;cur = parent->_right;}else{return false;//不支持相同元素的插入}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED;if (kv.first < parent->_kv.first)//K小插入在左边parent->_left = cur;else//K大插入在右边parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;2、插入成功后,我们就要维护红黑树的规则了。
>如果插入节点的父亲是黑色,那插入后依然符合红黑树的规则,我们不用处理。
>如果插入节点的父亲是红色,那么此时就有连续的红色节点,我们就要进行处理。
a、插入节点的叔叔存在且为红,我们只需要进行变色。

变色原理:因为parent的颜色为红,所以g的颜色一定为黑。插入前从g开始的路径的黑色节点的数量相同,要解决连续红色节点的问题,我们必然要把parent变黑色。但从g到cur路径的黑色节点多了一个,所以我们把g变红,在把u变黑就完美的解决了问题!
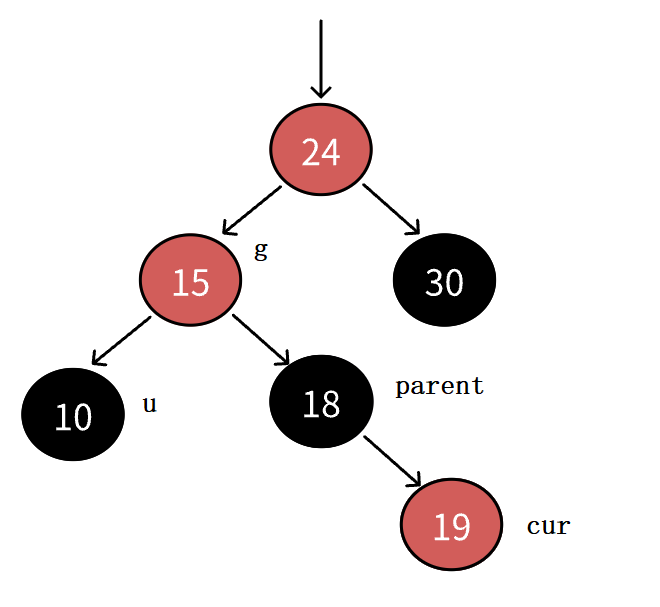
不过,g变红后,又可能会引起祖先节点的连续红色节点问题,所以我们还要继续向上维护红黑树的规则!
变色代码实现
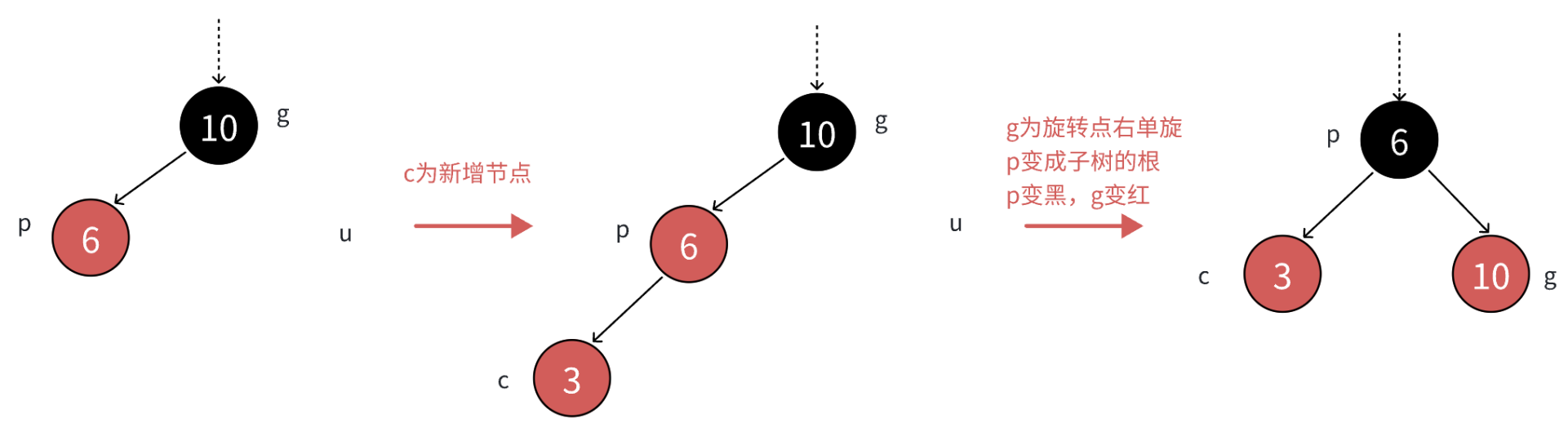
//插入后进行维护红黑树规则的逻辑//parent存在且为红while (parent&& parent->_col = RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;//p在g的右边if (parent == grandfather->_right){//g//upNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle&& uncle->_col = RED)//uncle存在且为红{//变色处理uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//更新cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else//uncle不存在或者存在且为黑{}}else//p在g的左边{//g//puNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle&& uncle->_col = RED)//uncle存在且为红{//变色处理uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//更新cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else//uncle不存在或者存在且为黑{}}}b、如果uncle不存在或者uncle存在且为黑,这时我们就要进行旋转加变色处理。
单旋+变色:
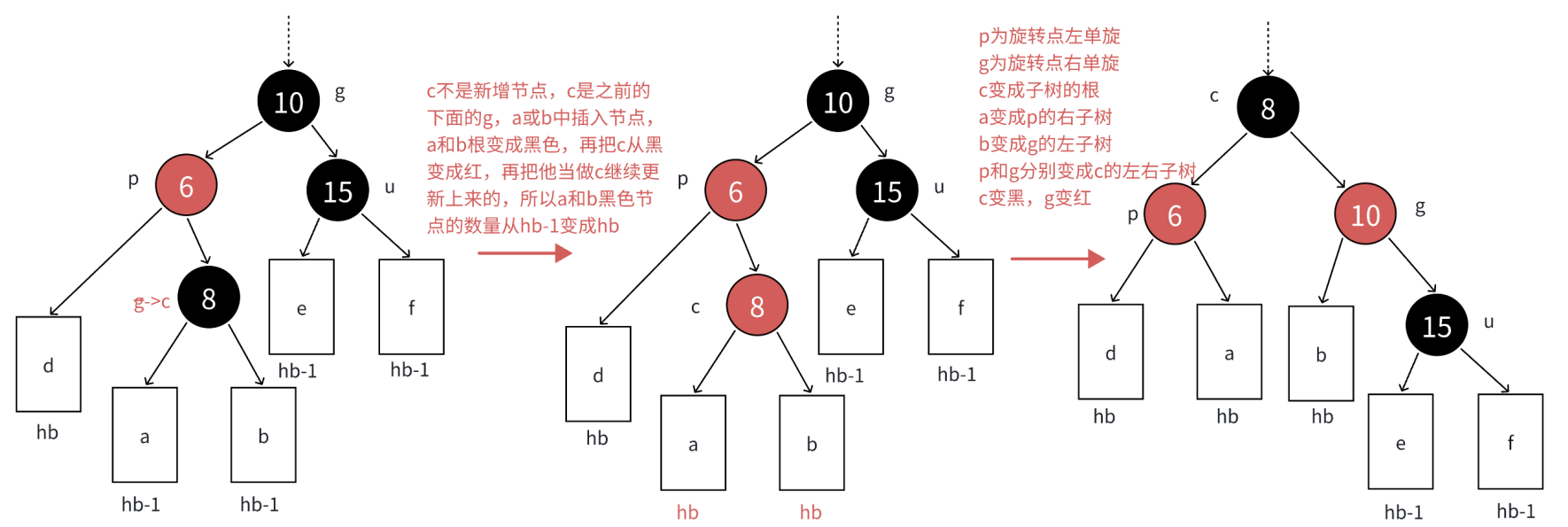
>如果uncle不存在,说明c一定是新增节点,如果c是变色后的节点,那么它在变色前一定是黑色,而从g开始的路径到c就多一个黑色节点!
>如果uncle存在且为黑,说明c一定是变色后的节点,如果c是新增的节点,那么从g开始的路径到u就多一个黑色节点!
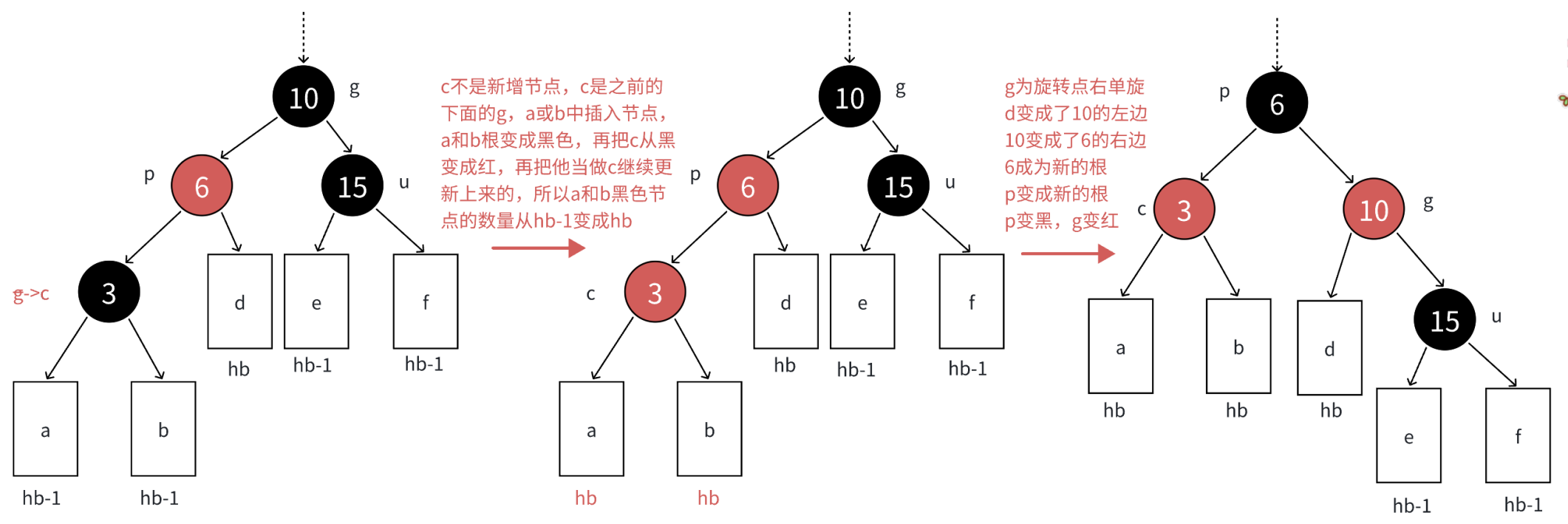
变色原理:我们根据c、p、g的位置来选择合理的旋转逻辑,然后再把p变黑,g变红即可解决问题!
双旋+变色:
c为红,p为红,g为⿊,u不存在或者u存在且为⿊,u不存在,则c⼀定是新增结点,u存在且为⿊,则 c⼀定不是新增,c之前是⿊⾊的,是在c的⼦树中插⼊,符合情况1,变⾊将c从⿊⾊变成红⾊,更新上 来的。
分析:p必须变⿊,才能解决,连续红⾊结点的问题,u不存在或者是⿊⾊的,这⾥单纯的变⾊⽆法解 决问题,需要旋转+变⾊。
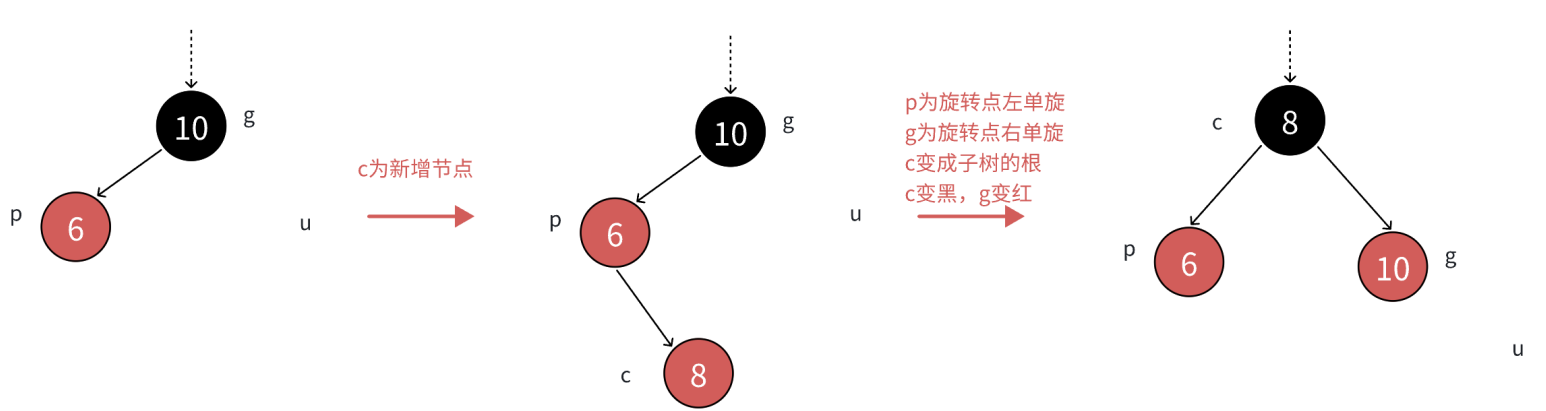
如果p是g的左,c是p的右,那么先以p为旋转点进⾏左单旋,再以g为旋转点进⾏右单旋,再把c变 ⿊,g变红即可。c变成课这颗树新的根,这样⼦树⿊⾊结点的数量不变,没有连续的红⾊结点了,且 不需要往上更新,因为c的⽗亲是⿊⾊还是红⾊或者空都不违反规则。
如果p是g的右,c是p的左,那么先以p为旋转点进⾏右单旋,再以g为旋转点进⾏左单旋,再把c变 ⿊,g变红即可。c变成课这颗树新的根,这样⼦树⿊⾊结点的数量不变,没有连续的红⾊结点了,且 不需要往上更新,因为c的⽗亲是⿊⾊还是红⾊或者空都不违反规则。
 插入完整代码:
插入完整代码:
bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){//如果树为空,在根插入并且颜色为黑色if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}//树不为空按搜索树规则先进行插入Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first)//小往左走{parent = cur;cur = parent->_left;}else if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)//大往右走{parent = cur;cur = parent->_right;}else{return false;//不支持相同元素的插入}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED;if (kv.first < parent->_kv.first)//K小插入在左边parent->_left = cur;else//K大插入在右边parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;//插入后进行维护红黑树规则的逻辑//parent存在且为红while (parent&& parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;//p在g的右边if (parent == grandfather->_right){//g//upNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED)//uncle存在且为红{//变色处理uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//更新cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else//uncle不存在或者存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_right){//g//up// c//以g为旋转点进行左单旋RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{//g//up// c//进行右左双旋RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}//旋转+变色后链接祖先节点的节点为黑,必然不会发生连续红色节点的情况直接break;break;}}else//p在g的左边{//g//puNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED)//uncle存在且为红{//变色处理uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//更新cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else//uncle不存在或者存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_left){//g//pu//c//以g为旋转点进行右单旋RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{//g//pu//c//进行左右双旋RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}//旋转+变色后链接祖先节点的节点为黑,必然不会发生连续红色节点的情况直接break;break;}}}//如果持续更新变色到根_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}2.3 红黑树的验证
>检查每条路径的黑色节点是否相等,是否有连续的红色节点
//检查每条路径的黑色节点是否相等,是否有连续的红色节点bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum){if (root == nullptr){// 前序遍历⾛到空时,意味着⼀条路径⾛完了 //cout << blackNum << endl;if (refNum != blackNum){cout << "存在黑色结点的数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}return true;}// 检查孩⼦不太⽅便,因为孩⼦有两个,且不⼀定存在,反过来检查⽗亲就⽅便多了 if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == BLACK){blackNum++;}return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);}>检查平衡
//检查平衡bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;if (_root->_col == RED)return false;// 参考值 int refNum = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK){++refNum;}cur = cur->_left;}return Check(_root, 0, refNum);}>插入一万个随机数看看是否平衡
void testInert(){const int N = 10000;RBTree<int, int> t;vector<int> v;srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr));for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){v.push_back(rand() + i);}for (auto e : v){t.insert({ e,e });}cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;}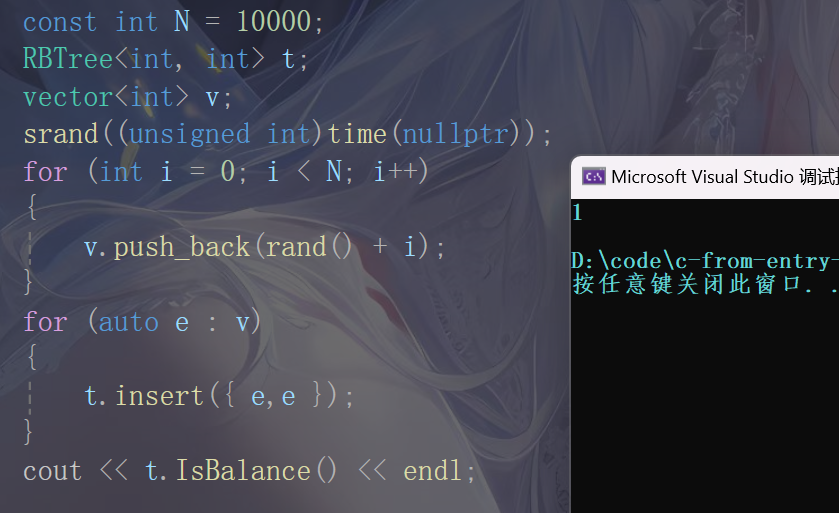
2.4 红黑树的其他简单接口
//默认构造RBTree() = default;//拷贝构造RBTree(const RBTree<K,V>& rbt){_root=_copy(rbt._root);}// 赋值重载RBTree<K, V>& operator=(RBTree<K, V> tmp){std::swap(_root, tmp._root);return *this;}//中序遍历void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);}//二叉树的析构~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);}private://递归拷贝Node* _copy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* newNode = new Node(root->_kv);newNode->_left = _copy(root->_left);newNode->_right = _copy(root->_right);return newNode;}//中序遍历void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_InOrder(root->_left);cout << "<" << root->_kv.first << "," << root->_kv.second << ">" << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}//二叉树的销毁void _Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_Destroy(root->_left);_Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}3、红黑树完整源码

#pragma once#include<iostream>using namespace std;//枚举类型定义颜色enum Colour{RED,BLACK};//节点结构(默认存储pair类型的key/val结构)template<class K, class V>struct RBTreeNode{RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _parent(nullptr), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr),_col(RED){}pair<K, V> _kv;RBTreeNode* _parent;RBTreeNode* _left;RBTreeNode* _right;Colour _col;//初始化为红色};//红黑树template<class K,class V>class RBTree{typedef RBTreeNode<K,V> Node;public://默认构造RBTree() = default;//拷贝构造RBTree(const RBTree<K,V>& rbt){_root=_copy(rbt._root);}// 赋值重载RBTree<K, V>& operator=(RBTree<K, V> tmp){std::swap(_root, tmp._root);return *this;}//中序遍历void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);}//二叉树的析构~RBTree(){_Destroy(_root);}//红黑树的查找Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}//红黑树的插入bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){//如果树为空,在根插入并且颜色为黑色if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}//树不为空按搜索树规则先进行插入Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first)//小往左走{parent = cur;cur = parent->_left;}else if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)//大往右走{parent = cur;cur = parent->_right;}else{return false;//不支持相同元素的插入}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED;if (kv.first < parent->_kv.first)//K小插入在左边parent->_left = cur;else//K大插入在右边parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;//插入后进行维护红黑树规则的逻辑//parent存在且为红while (parent&& parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;//p在g的右边if (parent == grandfather->_right){//g//upNode* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED)//uncle存在且为红{//变色处理uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//更新cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else//uncle不存在或者存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_right){//g//up// c//以g为旋转点进行左单旋RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{//g//up// c//进行右左双旋RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}//旋转+变色后链接祖先节点的节点为黑,必然不会发生连续红色节点的情况直接break;break;}}else//p在g的左边{//g//puNode* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED)//uncle存在且为红{//变色处理uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//更新cur继续向上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else//uncle不存在或者存在且为黑{if (cur == parent->_left){//g//pu//c//以g为旋转点进行右单旋RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{//g//pu//c//进行左右双旋RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}//旋转+变色后链接祖先节点的节点为黑,必然不会发生连续红色节点的情况直接break;break;}}}//如果持续更新变色到根_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}//检查平衡bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;if (_root->_col == RED)return false;// 参考值 int refNum = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK){++refNum;}cur = cur->_left;}return Check(_root, 0, refNum);}private://右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;Node* pParent = parent->_parent;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)//如果不为空subLR->_parent = parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (pParent == nullptr){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pParent->_left == parent){pParent->_left = subL;}else{pParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = pParent;}}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* pParent = parent->_parent;Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;if (pParent == nullptr){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pParent->_left == parent){pParent->_left = subR;}else{pParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = pParent;}}//检查每条路径的黑色节点是否相等,是否有连续的红色节点bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum){if (root == nullptr){// 前序遍历⾛到空时,意味着⼀条路径⾛完了 //cout << blackNum << endl;if (refNum != blackNum){cout << "存在黑色结点的数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}return true;}// 检查孩⼦不太⽅便,因为孩⼦有两个,且不⼀定存在,反过来检查⽗亲就⽅便多了 if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == BLACK){blackNum++;}return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);}//递归拷贝Node* _copy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* newNode = new Node(root->_kv);newNode->_left = _copy(root->_left);newNode->_right = _copy(root->_right);return newNode;}//中序遍历void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_InOrder(root->_left);cout << "<" << root->_kv.first << "," << root->_kv.second << ">" << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}//二叉树的销毁void _Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_Destroy(root->_left);_Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}private:Node* _root=nullptr;};
4、完结散花
好了,这期的分享到这里就结束了~
如果这篇博客对你有帮助的话,可以用你们的小手指点一个免费的赞并收藏起来哟~
如果期待博主下期内容的话,可以点点关注,避免找不到我了呢~
我们下期不见不散~~

