
个人主页

文章目录
⭐一、AVL树的概念?二、AVL树的性质?️三、AVL树的实现1. 树的基本结构2. 树的插入3. 树的旋转• 左单旋• 右单旋• 左右双旋• 右左双旋 ?四、AVL树的其它功能1. 树的查找2. 树的遍历3. 树的高度4. 树的大小 ?五、总结1. AVL树的优缺点2. 完整代码
⭐一、AVL树的概念
AVL树是一种高度平衡的平衡二叉树,相比于搜索二叉树,它的特点在于左右子树都为AVL树且树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
这里我们会引入一个新的概念叫做平衡因子。平衡因子也就是左右子树的高度差,我们可以通过平衡因子方便我们后续去观察和控制树是否平衡。
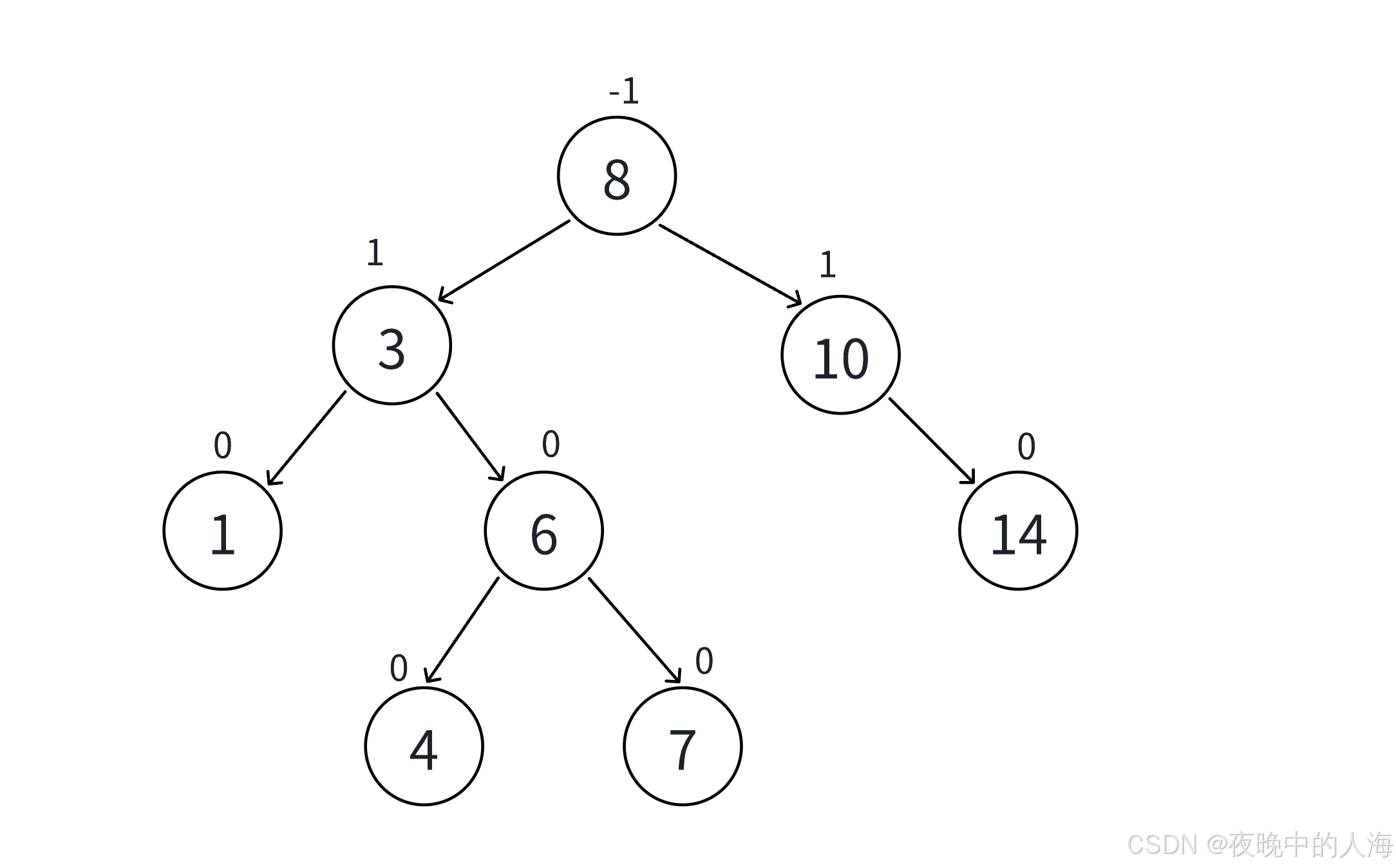
?二、AVL树的性质
AVL树主要有三大性质:
1.每棵树的左右子树都是AVL树。
2.左子树和右子树的高度之差的绝对值不超过1。
3.每个节点都会有一个平衡因子,且任何一个节点的平衡因子都为1、0、-1。
?️三、AVL树的实现
1. 树的基本结构
AVL树的结点包含了左右节点的指针以及父亲节点的指针,同时还有有key、value以及代表树平衡的平衡因子。
template<class K, class V>struct AVLTreeNode{pair<K, V> _kv;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;//平衡因子int _bf; AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _bf(0){}};2. 树的插入
树的插入按照搜索二叉树的规则进行插入。插入节点后更新平衡因子,如果没有违反规则(即没有导致节点的平衡因子变成2/-2),则插入结束;如果违反规则,则树会不平衡,需要进行旋转操作。
平衡因子的更新规则:
1.平衡因子 = 右子树高度 - 左子树高度。
2.只有子树高度的变化才会影响当前节点的平衡因子。
3.插入节点后会增加数的高度,若新增节点在parent的右子树,则parent的平衡因子++,相反在parent的左子树时,则平衡因子- -。
每更新完一个节点的平衡因子都需要进行以下判断:
1.如果parent的平衡因子等于1/-1时,说明parent原先的平衡因子为0,插入节点后左子树或右子树的高度增加了,说明还需要向上更新平衡因子。
2.如果parent的平衡因子等于0,说明parent原先的平衡因子为1/-1,插入节点后左右两棵子树从不平衡变平衡了,说明无需更新平衡因子。
3.如果parent的平衡因子等于2/-2时,说明parent原先的平衡因子等于1/-1,插入节点后插入到了较高的那一棵子树,说明此时以parent为根节点的子树已经不平衡了,需要进行旋转处理。
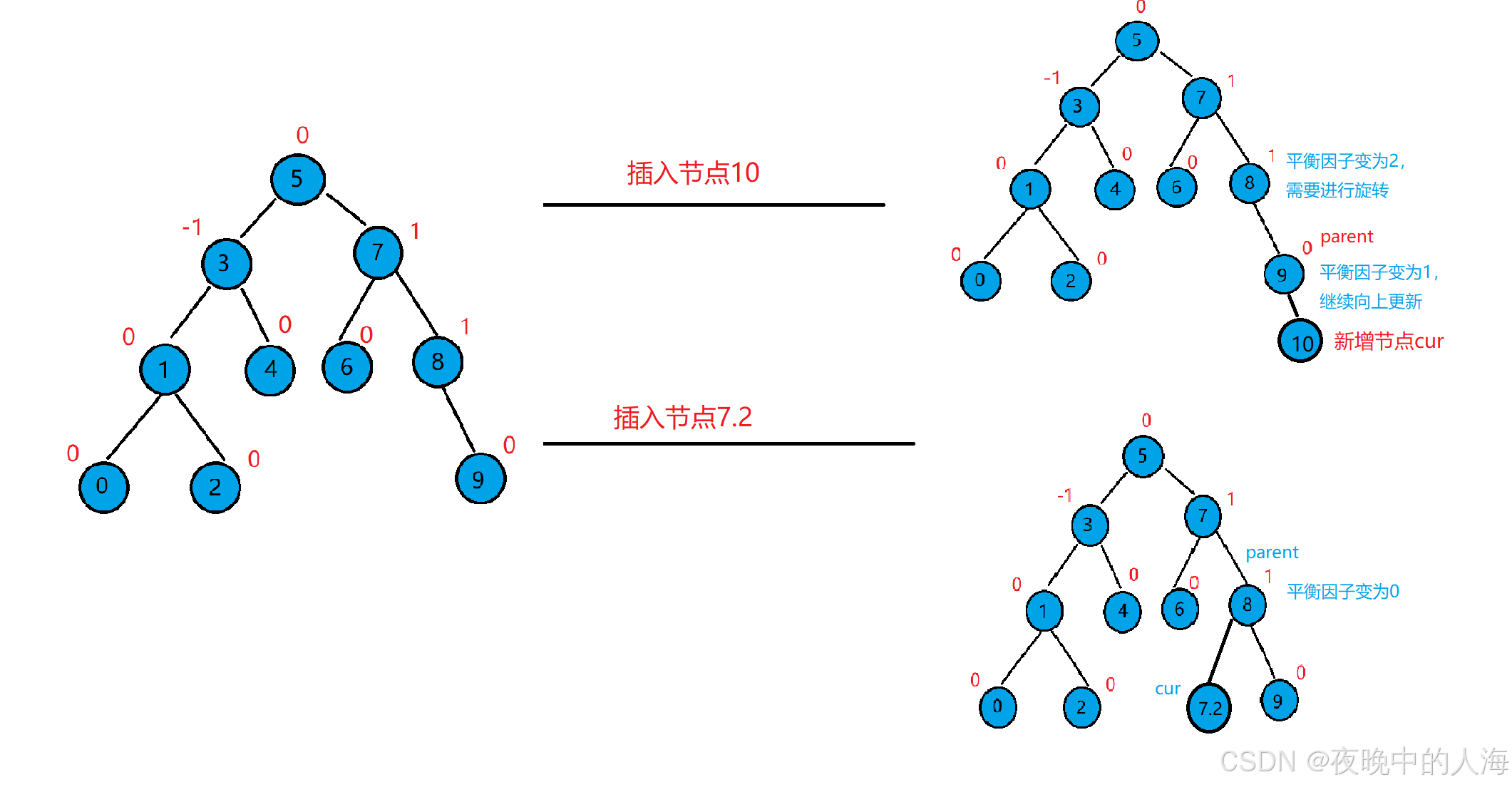
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){//如果树为空,则插入的节点就是根节点if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;//更新平衡因子while (parent){if (cur == parent->_left){parent->_bf--;}elseparent->_bf++;if (parent->_bf == 0){break;}else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1){//继续往上进行更新cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2){//不平衡,旋转处理if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateR(parent);}else if(parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateLR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else{assert(false);}}else{assert(false);}break;}return true;}3. 树的旋转
旋转的目的就是让树从失衡到平衡,降低树的高度。
旋转主要分为四种,分别为左单旋、右单旋、左右双旋和右左双旋。下面我们具体讲讲每一种旋转的内部逻辑。
• 左单旋
条件:新节点插入到子树较高的右侧。
我们用图来感受一下其旋转的过程:
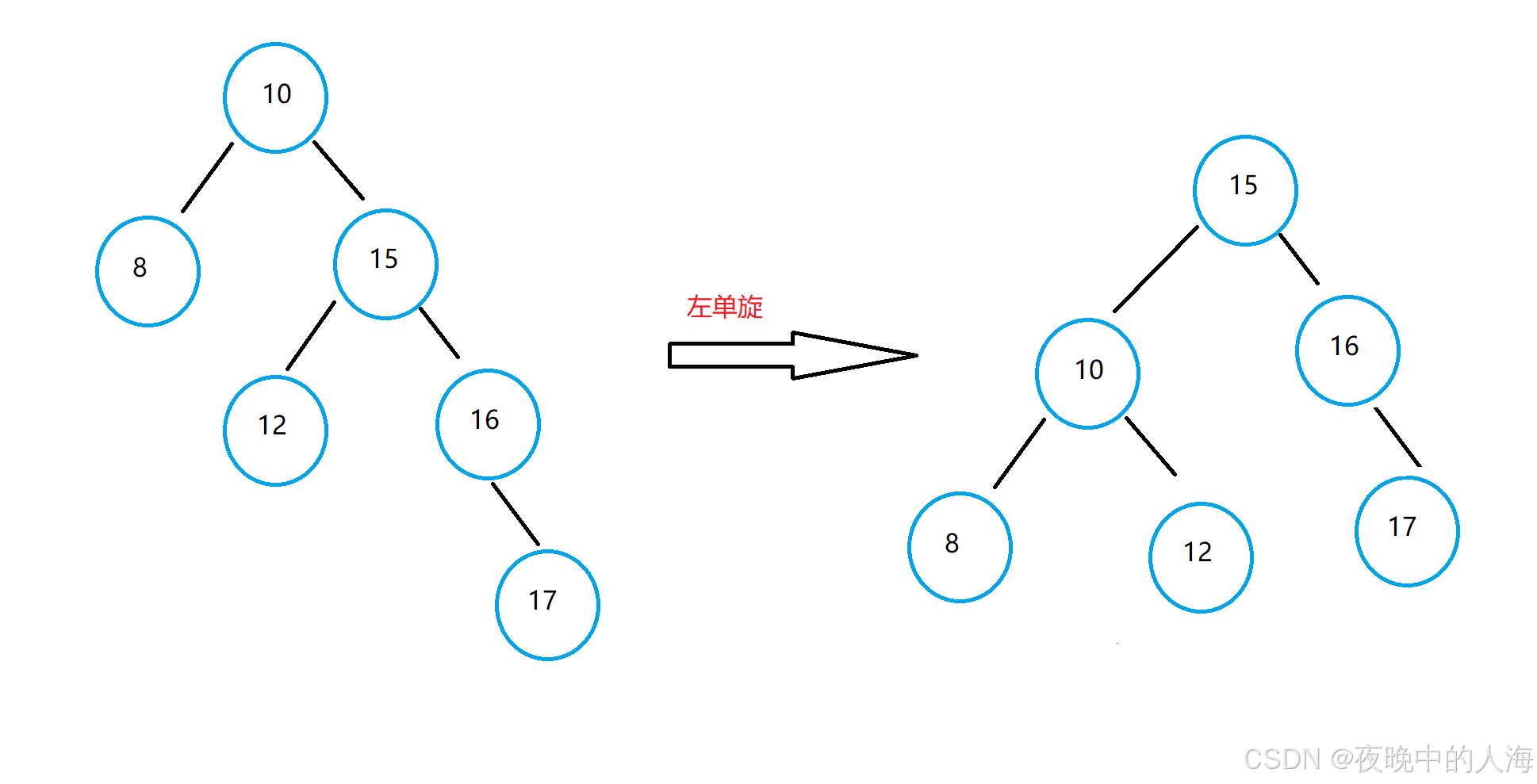
1.先将15的左子树的节点12变成10的右子树。
2.再将10变成15的左子树,15成为新树的根节点。
3.更新平衡因子
由于左单旋的情况很多,我们也可以用一张抽象图来表示:
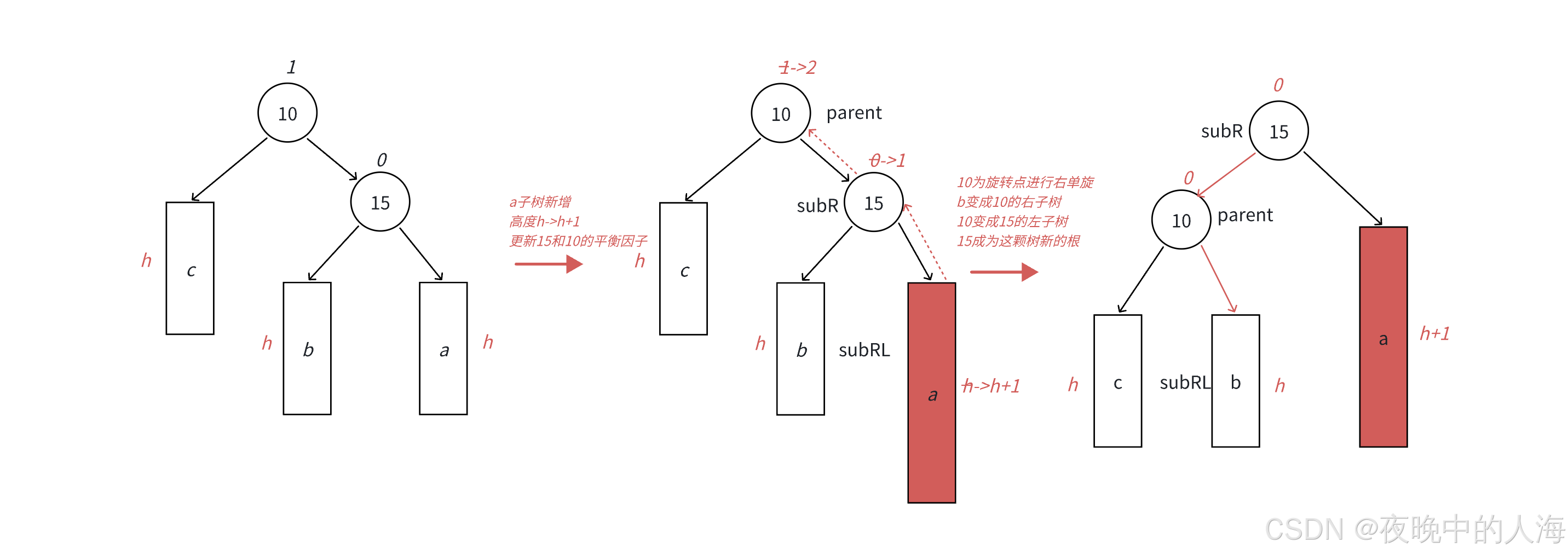
代码所示:
//左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subR;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;if (pparent == nullptr){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pparent == parent->_right){parent->_right = subR;}else{parent->_left = subR;}subR->_parent = pparent;}parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;}• 右单旋
条件:新节点插入到子树较高的左侧
用图来感受旋转的过程:
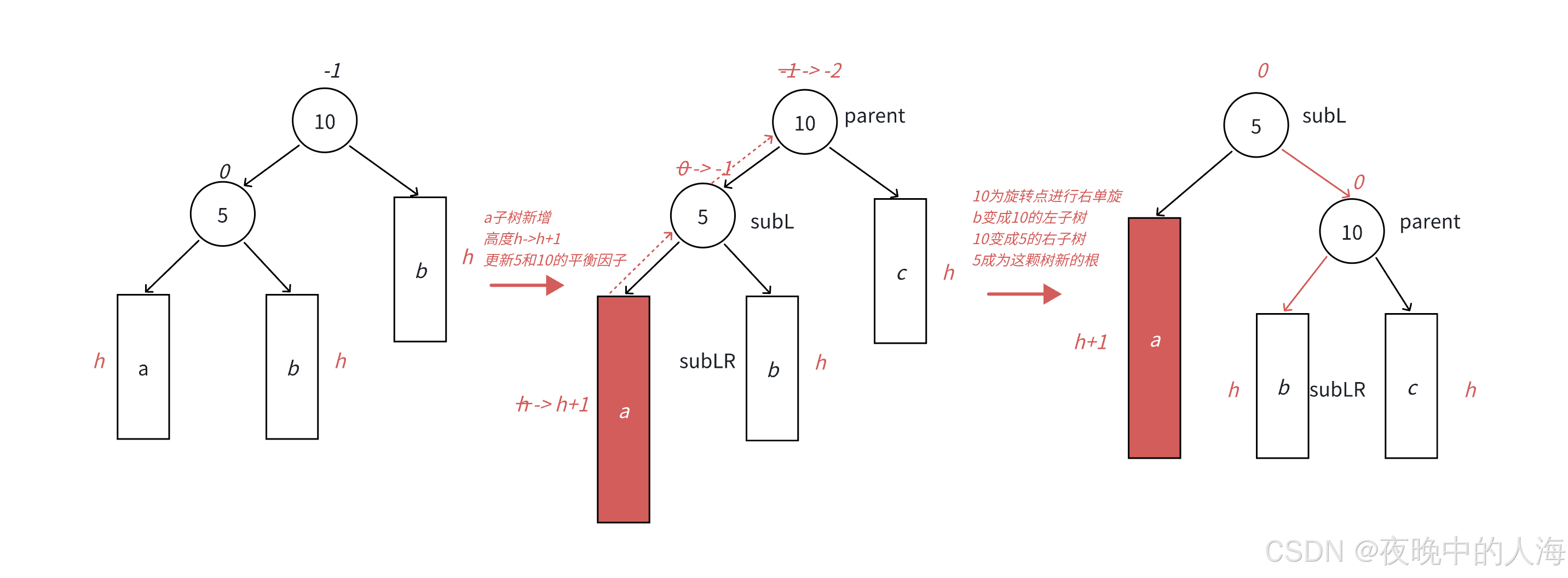
我们会发现和左单旋和相似
1.先将5的右子树的值b变成10的左子树。
2.再将10变成5的右子树,旋转完后5成为整棵树的根节点。
3.更新平衡因子。
代码所示:
//右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if(subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (pparent == nullptr){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pparent == parent->_left){parent->_left = subL;}else{parent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = pparent;}parent->_bf = subL->_bf = 0;}• 左右双旋
条件:新节点插入到较高左子树的右侧。
下面我们用图来演示一下其旋转过程:
1.插入新节点
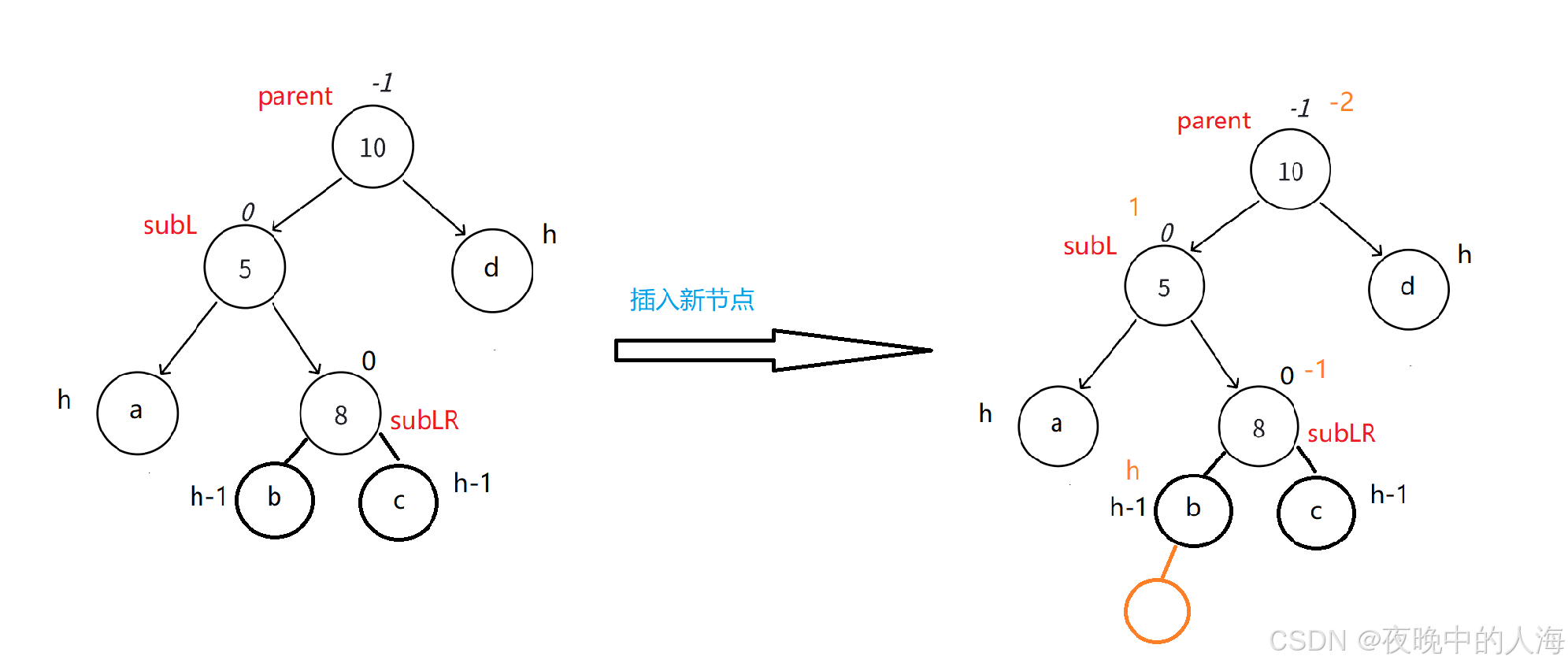
2.以节点5为旋转点进行左单旋
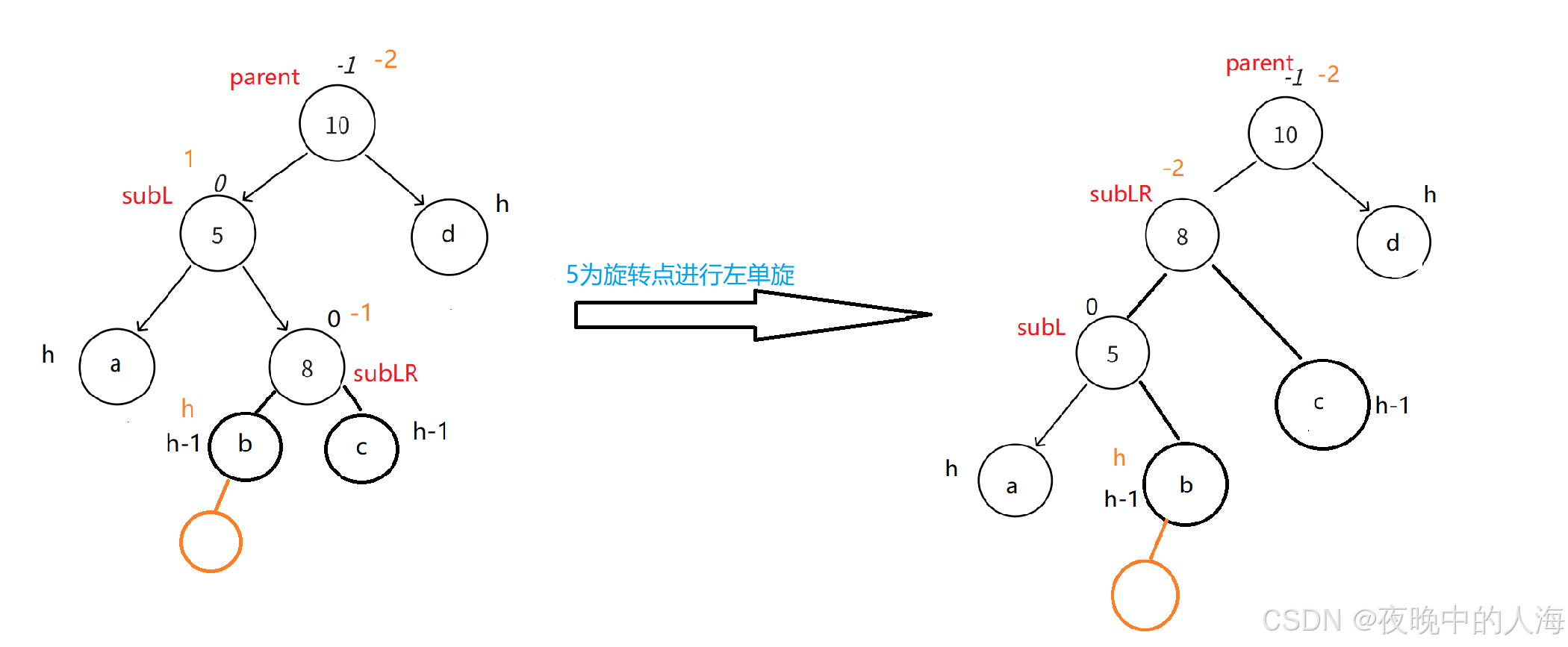
3.以节点为10进行右单旋
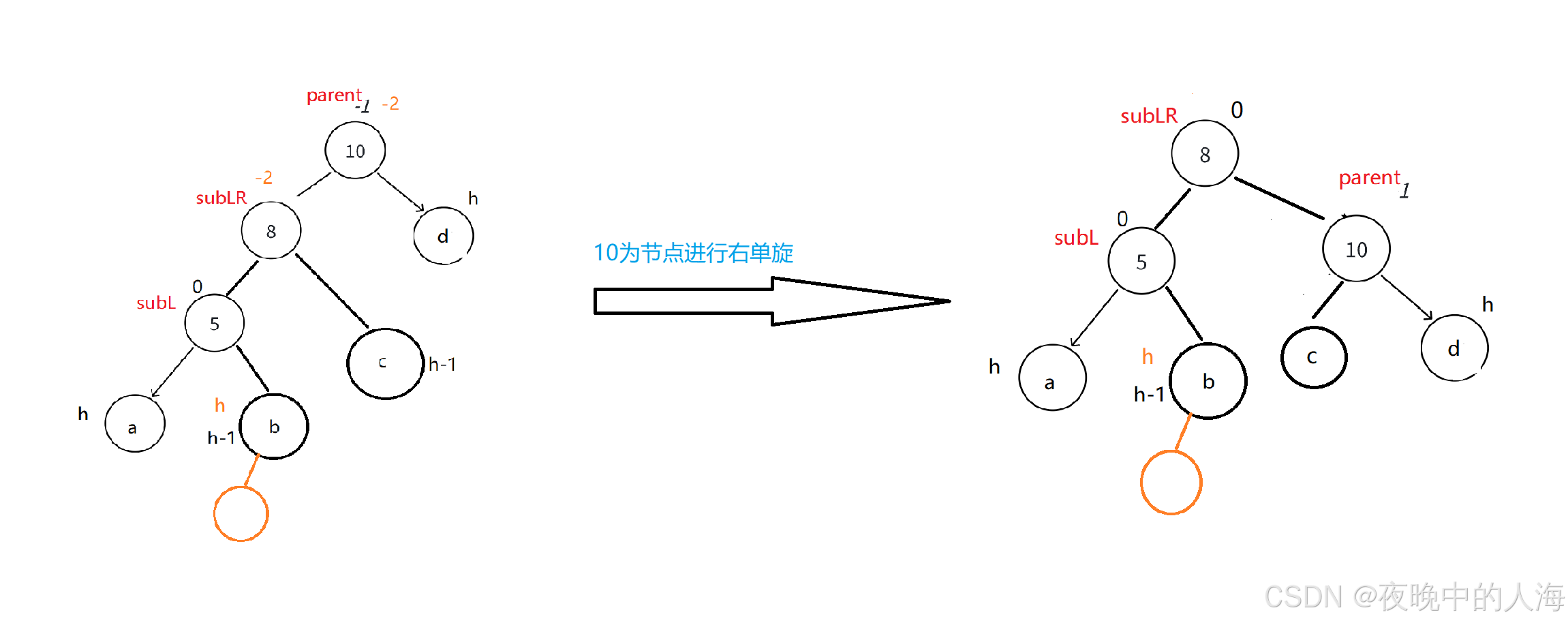
4.旋转完后更新平衡因子。
平衡因子又分为三种情况:
1.当subLR的平衡因子为-1时,左右双旋后parent、subL,subLR的平衡因子分别为1、0、0。
2.当subLR的平衡因子为1时,左右双旋后parent、subL,subLR的平衡因子分别为0、-1、0。
3.当subLR的平衡因子为0时,左右双旋后parent、subL,subLR的平衡因子分别为0、0、0。
代码所示:
//左右双旋void RotateLR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(parent->_left);RotateR(parent);if (bf == -1){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 1;}else if (bf == 1){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = -1;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}• 右左双旋
条件:插入到较高右子树的左侧
其旋转过程和左右双旋类似,这就不一一列举了。
旋转完过后也是需要更新平衡因子,平衡因子也是跟左右双旋一样有三种情况。
代码所示:
//右左双旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent);RotateL(parent);if (bf == 0){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){subR->_bf = 1;subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}?四、AVL树的其它功能
1. 树的查找
定义一个cur指针从树的根节点开始查找,按一下规则进行查找:
1.当key的值小于当前节点的值时,则在该节点的左边进行查找。
2.当key的值大于当前节点的值时,则在该节点的右边进行查找。
3.若key的值等于当前节点的值时,则说明查找成功,返回true。
4.若遍历完还没查找到该节点的值,则说明没有此节点,返回false。
代码所示:
Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}2. 树的遍历
我们遍历方式有前序、中序、后序、层序等方式,我们在这就采用中序遍历的方式来遍历树的每一节点。
代码所示:
void _Inorder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_Inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;_Inorder(root->_right);}3. 树的高度
int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;}4. 树的大小
返回左子树+右子树再加上根节点即可。
int _Size(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}return _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1;}?五、总结
1. AVL树的优缺点
优点:
**1.查找效率高:**由于AVL树总是保持平衡,其高度相对较低,因此查找操作的时间复杂度为O(log2N),效率较高。
2.结构稳定: AVL树的平衡性使得其结构相对稳定,不会出现极端不平衡的情况,从而保证了操作的稳定性和可靠性。
缺点:
1.插入和删除复杂: AVL树在插入和删除节点时,可能需要通过旋转操作来保持树的平衡,比较复杂。
2.可能导致性能下降: 在频繁插入和删除的场景下,AVL树需要不断地进行旋转操作来保持平衡,这就有可能导致性能降低。
2. 完整代码
#include<iostream>#include<assert.h>using namespace std;template<class K, class V>struct AVLTreeNode{// 需要parent指针,后续更新平衡因子可以看到pair<K, V> _kv;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;//平衡因子int _bf; // balance factorAVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_kv(kv), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _bf(0){}};template<class K,class V>class AVLTree{typedefAVLTreeNode<K, V> Node;public:bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;//更新平衡因子while (parent){if (cur == parent->_left){parent->_bf--;}elseparent->_bf++;if (parent->_bf == 0){break;}else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1){//继续往上进行更新cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2){//不平衡,旋转处理if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateR(parent);}else if(parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateLR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else{assert(false);}}else{assert(false);}break;}return true;}//右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if(subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (pparent == nullptr){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pparent == parent->_left){parent->_left = subL;}else{parent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = pparent;}parent->_bf = subL->_bf = 0;}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subR;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;if (pparent == nullptr){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pparent == parent->_right){parent->_right = subR;}else{parent->_left = subR;}subR->_parent = pparent;}parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;}//左右双旋void RotateLR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(parent->_left);RotateR(parent);if (bf == -1){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 1;}else if (bf == 1){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = -1;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}//右左双旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent);RotateL(parent);if (bf == 0){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){subR->_bf = 1;subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}void Inorder(){_Inorder(_root);cout << endl;}void Hight(){return _Hight(_root);}void Size(){return _Size(_root);}private:void _Inorder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_Inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;_Inorder(root->_right);}int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;}int _Size(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}return _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1;}Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}private:Node* _root = nullptr;};