一、背景介绍
一些报文在网络传输中,会存在丢包重传和延时的情况。渲染时需要进行适当缓存,等待丢失被重传的报文或者正在路上传输的报文。
jitter延时计算是确认需要缓存的时间
另外,在检测到帧有重传情况时,也可适当在渲染时间内增加RTT延时时间,等待丢失重传的报文
二、jitter实现原理
JitterDelay由两部分延迟造成:传输大帧引起的延迟和网络噪声引起的延迟。计算公式如下:
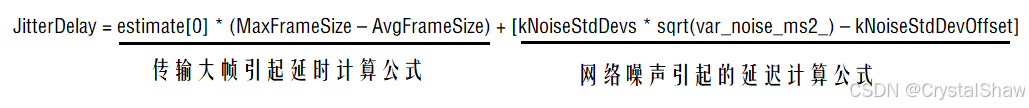
其中:
estimate[0]:信道传输速率的倒数
MaxFrameSize:表示自会话开始以来所收到的最大帧size
AvgFrameSize:表示平均帧大小,排除keyframe等超大帧
kNoiseStdDevs: 表示噪声系数2.33
var_noise_ms2_: 表示噪声方差
kNoiseStdDevOffset: 表示噪声扣除常数30
实现函数:
JitterEstimator::CalculateEstimate
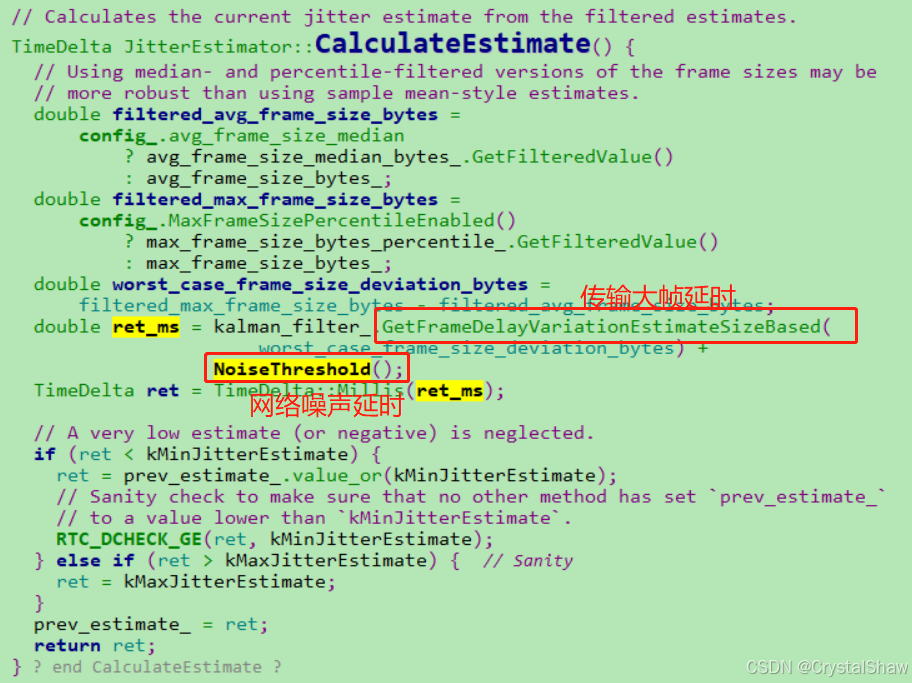
1、传输大帧引起的延迟
传输大帧引起的延迟
这个公式的原理是:[milliseconds] = [1 / bytes per millisecond] * [bytes]
实现函数:
double FrameDelayVariationKalmanFilter::GetFrameDelayVariationEstimateSizeBased( double frame_size_variation_bytes) const { // Unit: [1 / bytes per millisecond] * [bytes] = [milliseconds]. return estimate_[0] * frame_size_variation_bytes;}filtered_max_frame_size_bytes
= std::max<double>(kPsi * max_frame_size_bytes_, frame_size.bytes());
constexpr double kPsi = 0.9999;
filtered_avg_frame_size_bytes
是每一帧的加权平均值,但是需要排除key frame这种超大帧

estimate_[0]参数计算:
使用一个简化卡尔曼滤波算法,在处理帧延迟变化(frame_delay_variation_ms)的估计,考虑了帧大小变化(frame_size_variation_bytes)和最大帧大小(max_frame_size_bytes)作为输入参数。
void FrameDelayVariationKalmanFilter::PredictAndUpdate( double frame_delay_variation_ms, double frame_size_variation_bytes, double max_frame_size_bytes, double var_noise) { // Sanity checks. if (max_frame_size_bytes < 1) { return; } if (var_noise <= 0.0) { return; } // This member function follows the data flow in // https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kalman_filter#Details. // 1) Estimate prediction: `x = F*x`. // For this model, there is no need to explicitly predict the estimate, since // the state transition matrix is the identity. // 2) Estimate covariance prediction: `P = F*P*F' + Q`. // Again, since the state transition matrix is the identity, this update // is performed by simply adding the process noise covariance. estimate_cov_[0][0] += process_noise_cov_diag_[0]; estimate_cov_[1][1] += process_noise_cov_diag_[1]; // 3) Innovation: `y = z - H*x`. // This is the part of the measurement that cannot be explained by the current // estimate. double innovation = frame_delay_variation_ms - GetFrameDelayVariationEstimateTotal(frame_size_variation_bytes); // 4) Innovation variance: `s = H*P*H' + r`. double estim_cov_times_obs[2]; estim_cov_times_obs[0] = estimate_cov_[0][0] * frame_size_variation_bytes + estimate_cov_[0][1]; estim_cov_times_obs[1] = estimate_cov_[1][0] * frame_size_variation_bytes + estimate_cov_[1][1]; double observation_noise_stddev = (300.0 * exp(-fabs(frame_size_variation_bytes) / (1e0 * max_frame_size_bytes)) + 1) * sqrt(var_noise); if (observation_noise_stddev < 1.0) { observation_noise_stddev = 1.0; } // TODO(brandtr): Shouldn't we add observation_noise_stddev^2 here? Otherwise, // the dimensional analysis fails. double innovation_var = frame_size_variation_bytes * estim_cov_times_obs[0] + estim_cov_times_obs[1] + observation_noise_stddev; if ((innovation_var < 1e-9 && innovation_var >= 0) || (innovation_var > -1e-9 && innovation_var <= 0)) { RTC_DCHECK_NOTREACHED(); return; } // 5) Optimal Kalman gain: `K = P*H'/s`. // How much to trust the model vs. how much to trust the measurement. double kalman_gain[2]; kalman_gain[0] = estim_cov_times_obs[0] / innovation_var; kalman_gain[1] = estim_cov_times_obs[1] / innovation_var; // 6) Estimate update: `x = x + K*y`. // Optimally weight the new information in the innovation and add it to the // old estimate. estimate_[0] += kalman_gain[0] * innovation; estimate_[1] += kalman_gain[1] * innovation; // (This clamping is not part of the linear Kalman filter.) if (estimate_[0] < kMaxBandwidth) { estimate_[0] = kMaxBandwidth; } // 7) Estimate covariance update: `P = (I - K*H)*P` double t00 = estimate_cov_[0][0]; double t01 = estimate_cov_[0][1]; estimate_cov_[0][0] = (1 - kalman_gain[0] * frame_size_variation_bytes) * t00 - kalman_gain[0] * estimate_cov_[1][0]; estimate_cov_[0][1] = (1 - kalman_gain[0] * frame_size_variation_bytes) * t01 - kalman_gain[0] * estimate_cov_[1][1]; estimate_cov_[1][0] = estimate_cov_[1][0] * (1 - kalman_gain[1]) - kalman_gain[1] * frame_size_variation_bytes * t00; estimate_cov_[1][1] = estimate_cov_[1][1] * (1 - kalman_gain[1]) - kalman_gain[1] * frame_size_variation_bytes * t01; // Covariance matrix, must be positive semi-definite. RTC_DCHECK(estimate_cov_[0][0] + estimate_cov_[1][1] >= 0 && estimate_cov_[0][0] * estimate_cov_[1][1] - estimate_cov_[0][1] * estimate_cov_[1][0] >= 0 && estimate_cov_[0][0] >= 0);}2、网络噪声引起的延迟
网络噪声引起的延迟

constexpr double kNoiseStdDevs = 2.33; //噪声系数
constexpr double kNoiseStdDevOffset = 30.0;//噪声扣除常数
var_noise_ms2_ //噪声方差
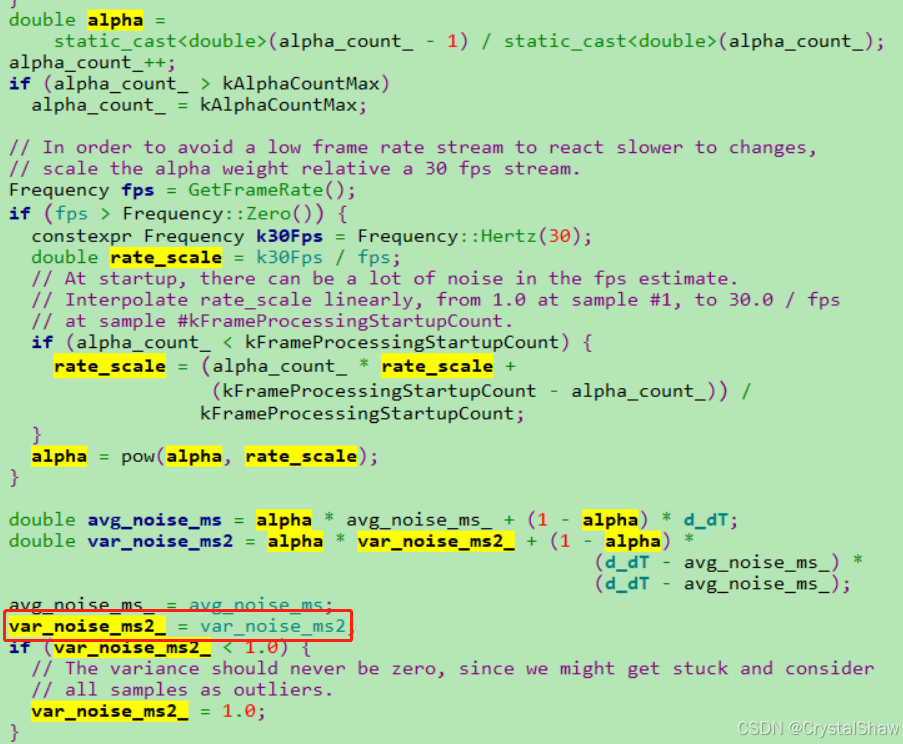
实现函数:

噪声方差var_noise_ms2计算
var_noise_ms2 = alpha * var_noise_ms2_ +
(1 - alpha) *(d_dT - avg_noise_ms_) *(d_dT - avg_noise_ms_);
实现函数:JitterEstimator::EstimateRandomJitter
其中:
d_dT = 实际FrameDelay - 评估FrameDelay
在JitterEstimator::UpdateEstimate函数实现

实际FrameDelay = (两帧之间实际接收gap - 两帧之间实际发送gap)
在InterFrameDelayVariationCalculator::Calculate函数实现
absl::optional<TimeDelta> InterFrameDelayVariationCalculator::Calculate( uint32_t rtp_timestamp, Timestamp now) { int64_t rtp_timestamp_unwrapped = unwrapper_.Unwrap(rtp_timestamp); if (!prev_wall_clock_) { prev_wall_clock_ = now; prev_rtp_timestamp_unwrapped_ = rtp_timestamp_unwrapped; // Inter-frame delay variation is undefined for a single frame. // TODO(brandtr): Should this return absl::nullopt instead? return TimeDelta::Zero(); } // Account for reordering in jitter variance estimate in the future? // Note that this also captures incomplete frames which are grabbed for // decoding after a later frame has been complete, i.e. real packet losses. uint32_t cropped_prev = static_cast<uint32_t>(prev_rtp_timestamp_unwrapped_); if (rtp_timestamp_unwrapped < prev_rtp_timestamp_unwrapped_ || !IsNewerTimestamp(rtp_timestamp, cropped_prev)) { return absl::nullopt; } // Compute the compensated timestamp difference. TimeDelta delta_wall = now - *prev_wall_clock_; int64_t d_rtp_ticks = rtp_timestamp_unwrapped - prev_rtp_timestamp_unwrapped_; TimeDelta delta_rtp = d_rtp_ticks / k90kHz; // The inter-frame delay variation is the second order difference between the // RTP and wall clocks of the two frames, or in other words, the first order // difference between `delta_rtp` and `delta_wall`. TimeDelta inter_frame_delay_variation = delta_wall - delta_rtp; prev_wall_clock_ = now; prev_rtp_timestamp_unwrapped_ = rtp_timestamp_unwrapped; return inter_frame_delay_variation;}评估FrameDelay = estimate[0] * (FrameSize – PreFrameSize) + estimate[1]
评估FrameDelay实现函数:
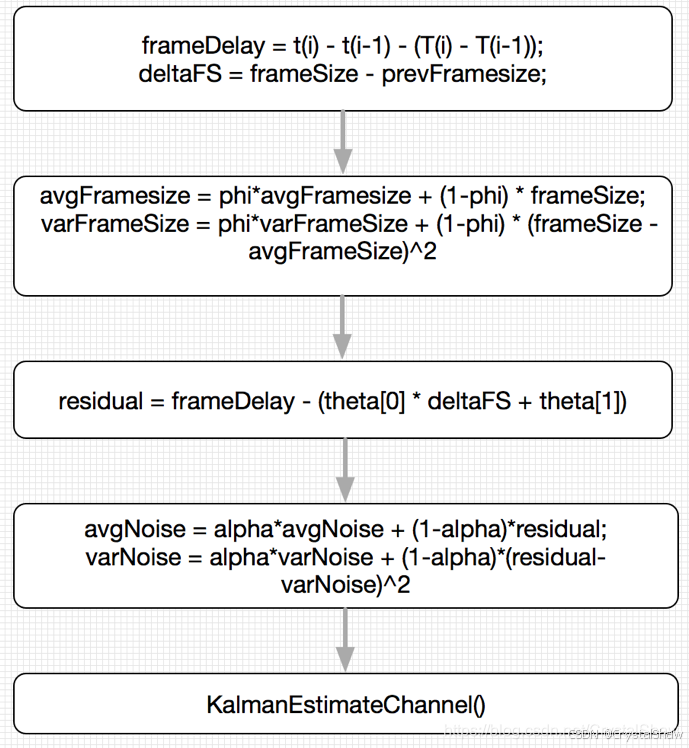
double FrameDelayVariationKalmanFilter::GetFrameDelayVariationEstimateTotal( double frame_size_variation_bytes) const { double frame_transmission_delay_ms = GetFrameDelayVariationEstimateSizeBased(frame_size_variation_bytes); double link_queuing_delay_ms = estimate_[1]; return frame_transmission_delay_ms + link_queuing_delay_ms;}3、jitter延时更新流程
三、RTT延时计算
VideoStreamBufferController::OnFrameReady函数,在判断帧有重传情况时,还会根据实际情况,在渲染帧时间里面增加RTT值。
![]()
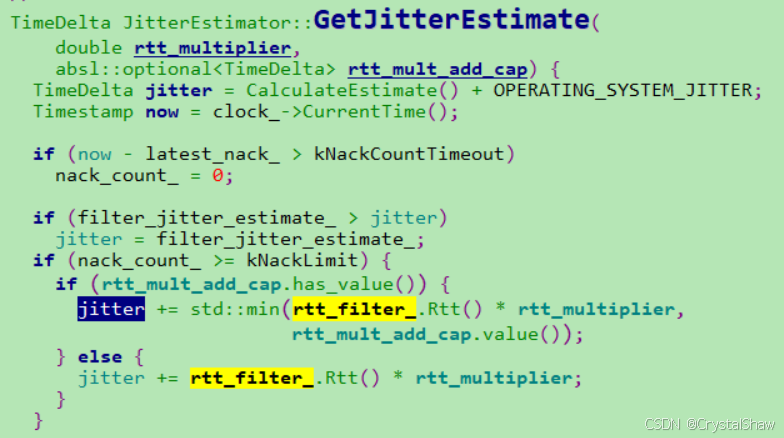
JitterEstimator::GetJitterEstimate根据实际配置,可以在渲染时间中适当增加一定比例的RTT延时值。
四、参考
WebRTC视频接收缓冲区基于KalmanFilter的延迟模型 - 简书在WebRTC的视频处理流水线中,接收端缓冲区JitterBuffer是关键的组成部分:它负责RTP数据包乱序重排和组帧,RTP丢包重传,请求重传关键帧,估算缓冲区延迟等功能... https://www.jianshu.com/p/bb34995c549a
https://www.jianshu.com/p/bb34995c549a
