
0 引言
在前面的学习笔记中,我们经常使用echo命令和输出重定向来生成脚本文件或演示文件,其实Linux提供了一个可以从标准输入读取数据,并输出成文件的命令——tee。
1 tee命令 的帮助信息、功能、命令格式、选项和参数说明
1.1 tee命令 的帮助信息
我们可以输入命令 tee --help 来查看tee命令的帮助信息。
[purpleendurer @ bash ~] tee --helpUsage: tee [OPTION]... [FILE]...Copy standard input to each FILE, and also to standard output. -a, --append append to the given FILEs, do not overwrite -i, --ignore-interrupts ignore interrupt signals --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exitIf a FILE is -, copy again to standard output.GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>Report tee translation bugs to <http://translationproject.org/team/>For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'tee invocation'[purpleendurer @ bash ~] 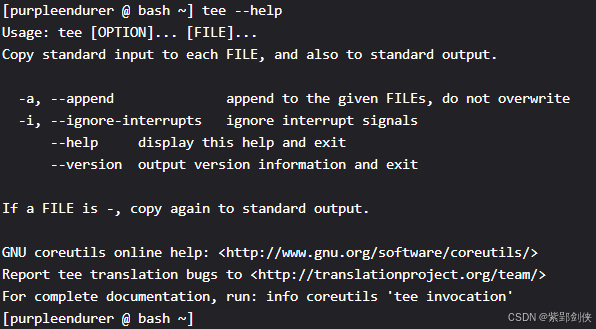
1.2 tee命令 的功能
tee 是一个简单的命令行实用程序,它接受输入并将输出写入文件和标准输出(即终端)。
tee命令和输出重定向都可以把输出内容保存到文件,但两者仍然存在差别:
输出重定向只能保存到1个文件,
tee允许我们把标准想要将输出重定向到多个文件。
Tee 命令是 GNU coreutils 的一部分,因此它预装在所有 Linux 发行版中。
1.3 tee命令 命令格式
tee [选项]... [文件]...
1.4 tee命令 选项说明
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -a, --append | 附加到给定的 FILE,不覆盖 |
| -i, --ignore-interrupts | 忽略中断信号 |
| --help | 显示此帮助并退出 |
| --version | 输出版本信息并退出 |
1.5 tee命令 参数说明
文件:将标准输入保存到的文件名
2 tee命令使用实例
2.1 将标准输入内容保存到多个文件
例如,将标准输入内容"I am purpleendurer"保存到文件 t1 和 t2的命令是:
tee t1 t2
[purpleendurer @ bash ~] tee t1 t2I am purpleendurerI am purpleendurer[purpleendurer @ bash ~] lsCode t1 t2[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat t1I am purpleendurer[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat t2I am purpleendurer[purpleendurer @ bash ~] 我们通过标准输入设备键盘输入 I am purpleendurer 回车并按Ctr+D保存
tee命令默认将标准输入的内容输出到标准输出设备,所以我们会看到两行 I am purpleendurer
随后我们使用ls命令查看当看目录,发现了新创建的文件t1和t2
接着我们使用cat命令查看文件t1和t2的内容,两个文件的内容都是我们刚才输入的 I am purpleendurer
2.2 将标准输入内容追加保存到多个文件,并且不将输入内容显示在标准输出设备上
我们仍然以文件t1和t2为例。
[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat t1 t2I am purplendurerI am purplendurer[purpleendurer @ bash ~] tee -a t1 t2 > /dev/nullLinux is good.[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat t1I am purplendurerLinux is good.[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat t2I am purplendurerLinux is good.[purpleendurer @ bash ~] 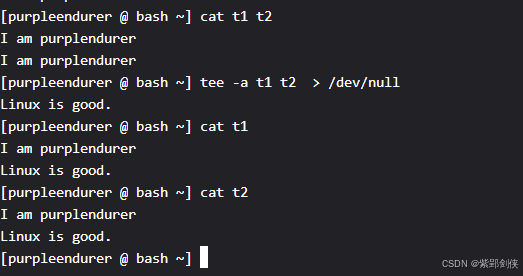
2.2.1 首先,我们使用cat命令查看文件t1和t2的内容,两个文件的内容都是:
I am purpleendurer
2.2.2 然后,我们使用命令带-a选项的tee命令
tee -a t1 t2 > /dev/null
将标准输入内容追加到文件t1 和 t2,并使用了
> /dev/null
将标准输出重定向到 /dev/null,这样tee命令就不会把输入的内容输出到标准输出设备上。
2.2.3 接着,我们输入:Linux is good 回车并按Ctrl+D保存。
2.2.4 最后,我们使用cat命令查看文件t1和t2的内容,两个文件的内容都是:
I am purpleendurer
Linux is good.
2.3 与echo命令和管道操作配合使用
[purpleendurer @ bash ~] echo Hello world | tee t3 t4Hello world[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat t3 t4Hello worldHello world[purpleendurer @ bash ~] 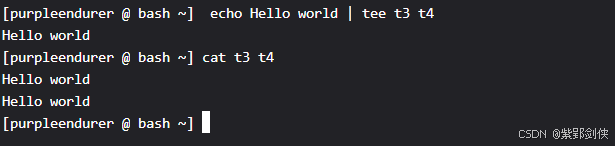
我们使用echo命令输出字符串Hello world,字符串Hello world经过管道输入到tee 命令,被tee 命令存入文件t3和t4。
使用cat命令查看文件t1和t2的内容,两个文件的内容都是字符串Hello world
所以命令
echo Hello world | tee t3 t4
相当于两条命令
echo Hello world > t3
echo Hello world > t4
通过管道操作,tee命令不会回显输入的字符串Hello world
2.4 将出错信息保存到文件
[purpleendurer @ bash ~] ifconfig | tee ibash: ifconfig: command not found[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat i[purpleendurer @ bash ~] ifconfig 2>&1 | tee ibash: ifconfig: command not found[purpleendurer @ bash ~] cat ibash: ifconfig: command not found[purpleendurer @ bash ~] 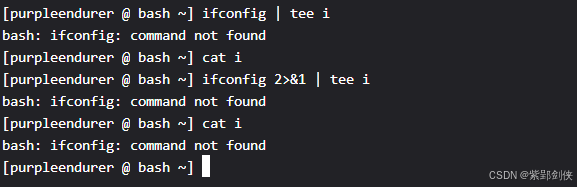
管道操作一般转发标准输出信息(1),不转发命令执行时反馈的出错信息(2)。
如果我们想将命令执行时反馈的出错信息也存储下来,可以使用l输出重定向
2>&1
将出错信息重定向到标准输出。其中1代表标准畀出,2代表出错信息。
在上面的例子里,命令
ifconfig
没有标准出错,只有出错信息:
bash: ifconfig: command not found
所以命令
ifconfig | tee i
中 没有信息通过管道输入给命令tee,也就没有信息存储到文件i
所以我们使用cat命令查看文件i是没有内容的。
当我们在ifconfig命令后面增加了 2>&1,命令变成
ifconfig 2>&1 | tee i
ifconfig命令的出错信息被重定向到标准输入,通过管道传输给tee命令并保存到文件1中。
这里我们使用cat命令查看文件i的内容,就是:
bash: ifconfig: command not found
