1.红黑树的概念
红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但在每个结点上增加一个存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是Red或 Black。 通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路 径会比其他路径长出俩倍,因而是接近平衡的。
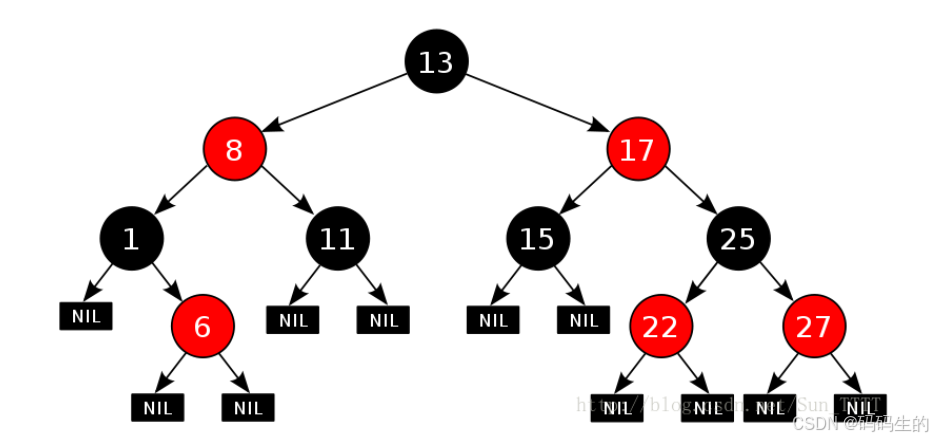
2.红黑树的性质!!!!!
1. 每个结点不是红色就是黑色
2. 根节点是黑色的
3. 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个孩子结点是黑色的
4. 对于每个结点,从该结点到其所有后代叶结点的简单路径上,均 包含相同数目的黑色结点
5. 每个叶子结点都是黑色的(此处的叶子结点指的是空结点)
3.红黑树节点的定义
enum color{RED,BLACK}; //列举color的各种可能情况template<class K, class V>struct RBTtreenode{RBTtreenode<K, V>* _left;RBTtreenode<K, V>* _right;RBTtreenode<K, V>* _parent;pair<K, V> kv;color col;RBTtreenode(const pair<K, V>& _kv):_left(nullptr) //左孩子, _right(nullptr) //右孩子, _parent(nullptr) //父亲, kv(_kv), col(RED){}};4.红黑树结构
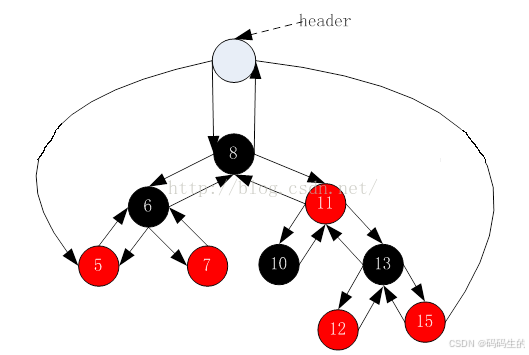
为了后续实现关联式容器简单,红黑树的实现中增加一个头结点,因为跟节点必须为黑色,为了 与根节点进行区分,将头结点给成黑色,并且让头结点的 pParent 域指向红黑树的根节点,pLeft 域指向红黑树中最小的节点,_pRight域指向红黑树中最大的节点,如下:
5.红黑树的插入!!!!
红黑树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加上其平衡限制条件,因此红黑树的插入可分为两步:
5.1按照二叉搜索的树规则插入新节点
if (root == nullptr){root = new node(_kv);root->col = BLACK;//规定根必须是黑的return true;}node* parent = nullptr; //比bst多了一个parentnode* cur = root; while (cur){parent = cur;if (cur->kv.first < _kv.first){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->kv.first > _kv.first){cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new node(_kv);cur->col = RED;//因为如果插入黑色的会使很多节点的一条路径上的黑色节点增多(相当于得罪了所有人),而插入红色则有可能只得罪父亲(如果父亲是红色的话)if (parent->kv.first < _kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;5.2 检测新节点插入后,红黑树的性质是否造到破坏
因为新节点的默认颜色是红色,因此:如果其双亲节点的颜色是黑色,没有违反红黑树任何 性质,则不需要调整;但当新插入节点的双亲节点颜色为红色时,就违反了性质三不能有连 在一起的红色节点,此时需要对红黑树分情况来讨论:
约定:cur为当前节点,p为父节点,g为祖父节点,u为叔叔节点
1. 情况一: cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红
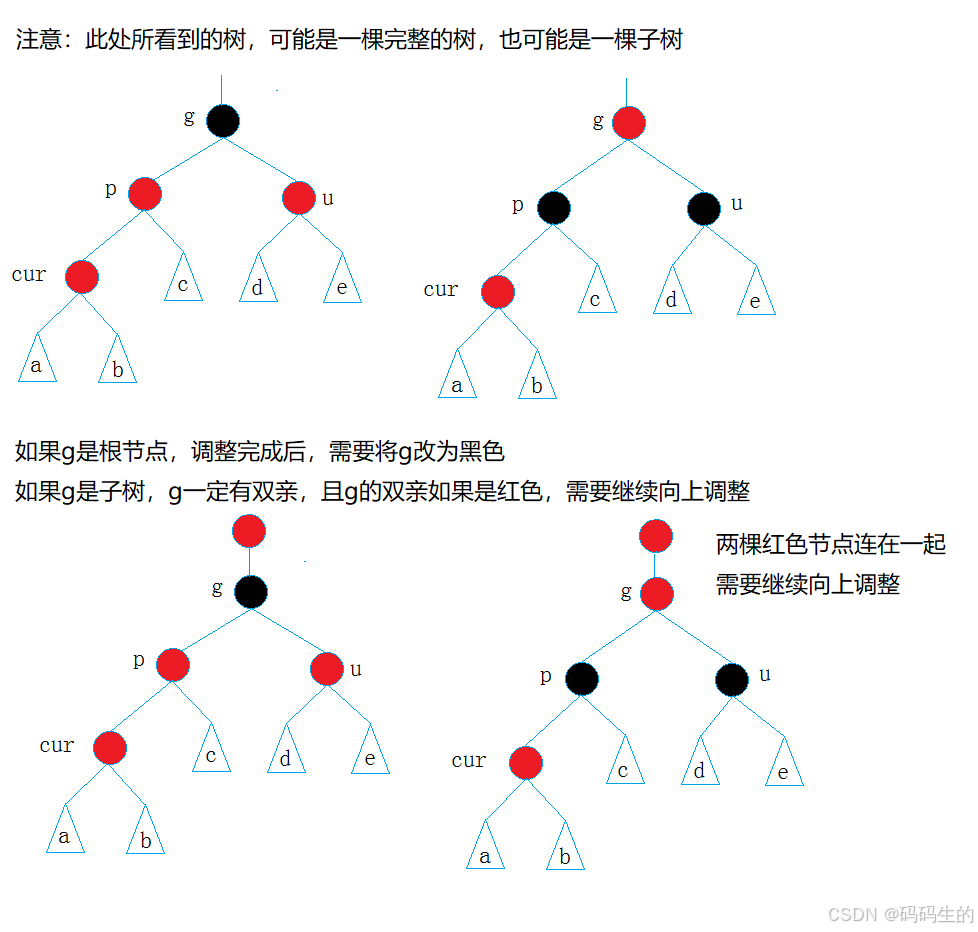
解决方式:将p,u改为黑,g改为红,然后把g当成cur,继续向上调整。
2.情况二(单旋+变色): cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑 (左左和右右)
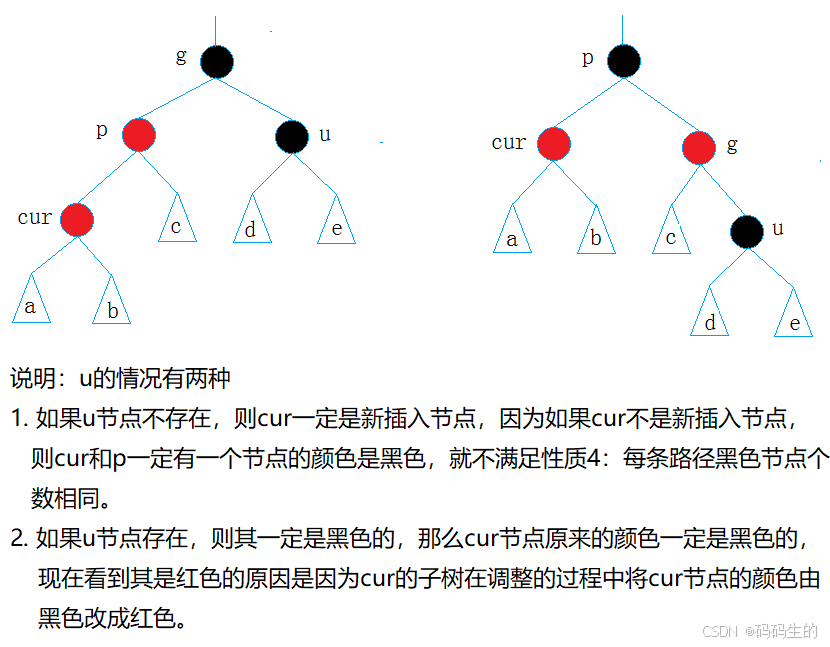
细分就是:(1)g->left==p,p->left==cur;左左
(2)g->right==p,p->right==cur;右右
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则进行右单旋转;
相反, p为g的右孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则进行左单旋转
p、g变色--p变黑,g变红
3.情况三(双旋+变色): cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑 (左右和右左)
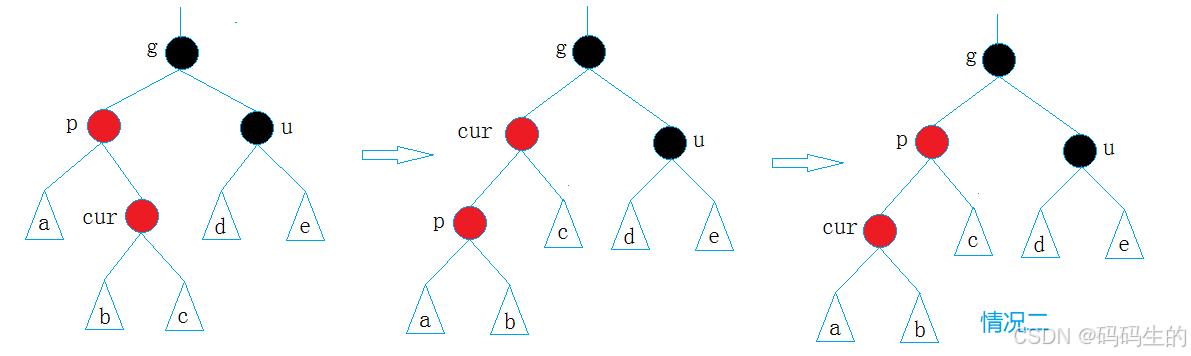
细分就是:(1)g->left==p,p->right==cur;左右
(2)g->right==p,p->left==cur;右左
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则针对p做左单旋转;
相反, p为g的右孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则针对p做右单旋转
则转换成了情况2!!!!!,然后再用情况2的旋转处理一下就行了
针对每种情况进行相应的处理即可。
while (parent&&parent->col == RED)//parent为黑不需要调整,如果cur变成root,parent就不存在退出循环{node* grandparent = parent->_parent;//祖父一定存在,因为只有根节点是没有祖父的,而根节点一定是黑色的if (parent==grandparent->_left){// g// p unode* uncle = grandparent->_right; //父亲在左则叔叔在右if (uncle && uncle->col == RED) //情况一.如果叔叔存在且为红色{//变色parent->col = uncle->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;//重置cur,parent,继续向上处理cur = grandparent;//变为祖父parent = cur->_parent;}else //叔叔不存在或为黑色,旋转加变色{// g// p// cif (cur == parent->_left) //情况二.单旋{rotateR(grandparent);parent->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}// g// p// celse //情况三.cur==parent->_right,双旋{rotateL(parent);//经历一次左旋后变成情况二!!!!!!!!!!!(cur和parent换位置)rotateR(grandparent);cur->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}break;//调整一次就结束了,所以经历过旋转后不需要重置cur,parent,grandparent}}else{// g// u p//node* uncle = grandparent->_left; //父亲在右则叔叔在左if (uncle && uncle->col == RED){parent->col = uncle->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;//cur = grandparent;parent = cur->_parent;}else{// g// u p// cif (cur == parent->_right){rotateL(grandparent);parent->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}else{// g// u p// crotateR(parent);rotateL(grandparent);cur->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}break;//调整一次就结束了,所以经历过旋转后不需要重置cur,parent,grandparent}}6.红黑树的验证
红黑树的检测分为两步:
1. 检测其是否满足二叉搜索树(中序遍历是否为有序序列)
2. 检测其是否满足红黑树的性质
1.中序输出
void inorder(){_inorder(root);}void _inorder(node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_inorder(root->_left);cout << root->kv.first << " ";_inorder(root->_right);}2.判断性质 (性质3和性质4)
bool check(node* it,int blacknum,int flag){if (it == nullptr){if (blacknum == flag)return true;elsereturn false;}else if (it->col == RED && it->_parent->col == RED)//十分巧妙,因为孩子的情况有很多,但父亲不是红就是黑,所以判断父亲更合适return false;else if (it->col == BLACK)blacknum++;return check(it->_left,blacknum,flag) && check(it->_right,blacknum,flag);}bool isbalance(){return _isbalance(root);}bool _isbalance(node* root){if (root == nullptr)return true;else if (root->col == RED)return false;int blacknum = 0;int flag = 0;node* k = root;while (k){if (k->col == BLACK)flag++;k = k->_left;//这里十分巧妙,因为如果为红黑树,从某一节点到空的所有路径上的黑节点数量是一致的,所以可以先随便选一条路径,算出这一条路径上的黑节点数作为基准值,在由递归去和其他路径比较}return check(root,blacknum,flag);}7.红黑树的删除
可参考:《算法导论》或者《STL源码剖析》
红黑树 - _Never_ - 博客园
8 红黑树与AVL树的比较
红黑树和AVL树都是高效的平衡二叉树,增删改查的时间复杂度都是O(log_2 N),红黑树不追 求绝对平衡,其只需保证最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍,相对而言,降低了插入和旋转的次数, 所以在经常进行增删的结构中性能比AVL树更优,而且红黑树实现比较简单,所以实际运用中红 黑树更多。
9 红黑树的应用
1. C++ STL库 -- map/set
2. Java 库
3. linux内核
4. 其他一些库
10.代码全览
rbt.h:
enum color{RED,BLACK}; //列举color的各种可能情况template<class K, class V>struct RBTtreenode{RBTtreenode<K, V>* _left;RBTtreenode<K, V>* _right;RBTtreenode<K, V>* _parent;pair<K, V> kv;color col;RBTtreenode(const pair<K, V>& _kv):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), kv(_kv), col(RED){}};template<class K, class V>class RBTtree{public:typedef RBTtreenode<K, V> node;bool insert(const pair<K, V>& _kv){if (root == nullptr){root = new node(_kv);root->col = BLACK;//规定根必须是黑的return true;}node* parent = nullptr; //比bst多了一个parentnode* cur = root; while (cur){parent = cur;if (cur->kv.first < _kv.first){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->kv.first > _kv.first){cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new node(_kv);cur->col = RED;//因为如果插入黑色的会使很多节点的一条路径上的黑色节点增多(相当于得罪了所有人),而插入红色则有可能只得罪父亲(如果父亲是红色的话)if (parent->kv.first < _kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;//开始调整while (parent&&parent->col == RED)//parent为黑不需要调整,如果cur变成root,parent就不存在退出循环{node* grandparent = parent->_parent;//祖父一定存在,因为只有根节点是没有祖父的,而根节点一定是黑色的if (parent==grandparent->_left){// g// p unode* uncle = grandparent->_right; //父亲在左则叔叔在右if (uncle && uncle->col == RED) //情况一.如果叔叔存在且为红色{//变色parent->col = uncle->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;//重置cur,parent,继续向上处理cur = grandparent;//变为祖父parent = cur->_parent;}else //叔叔不存在或为黑色,旋转加变色{// g// p// cif (cur == parent->_left) //情况二.单旋{rotateR(grandparent);parent->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}// g// p// celse //情况三.cur==parent->_right,双旋{rotateL(parent);//经历一次左旋后变成情况二!!!!!!!!!!!(cur和parent换位置)rotateR(grandparent);cur->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}break;//调整一次就结束了,所以经历过旋转后不需要重置cur,parent,grandparent}}else{// g// u p//node* uncle = grandparent->_left; //父亲在右则叔叔在左if (uncle && uncle->col == RED){parent->col = uncle->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;//cur = grandparent;parent = cur->_parent;}else{// g// u p// cif (cur == parent->_right){rotateL(grandparent);parent->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}else{// g// u p// crotateR(parent);rotateL(grandparent);cur->col = BLACK;grandparent->col = RED;}break;//调整一次就结束了,所以经历过旋转后不需要重置cur,parent,grandparent}}}//1.如果parent和uncle都为RED,则可以一起变黑// 2.parent为黑不处理// 3.uncle为黑或不存在,parent为红,旋转+变色root->col = BLACK;//最后以防万一让根变为黑return true;}void rotateL(node* parent)//左旋,(新节点插入到较高右子树的右侧)// 1.右右{node* subr = parent->_right;node* subrl = subr->_left;parent->_right = subrl;subr->_left = parent;node* ppnode = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subr;if (subrl) //subrl可能为空!!!!!!!{subrl->_parent = parent;}if (parent == root) //即如果parent->_parent==nullptr{root = subr;subr->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = subr;}else if (ppnode->_right == parent){ppnode->_right = subr;}subr->_parent = ppnode;}}void rotateR(node* parent)//右旋,(新节点插入到较高左子树的左侧)// 2.左左{node* subl = parent->_left;node* sublr = subl->_right;parent->_left = sublr;if (sublr) //sublr可能为空!!!!!!!sublr->_parent = parent;node* ppnode = parent->_parent;subl->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subl;if (root == parent){root = subl;subl->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = subl;}else if (ppnode->_right == parent){ppnode->_right = subl;}subl->_parent = ppnode;}}void inorder(){_inorder(root);}void _inorder(node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_inorder(root->_left);cout << root->kv.first << " ";_inorder(root->_right);}bool check(node* it,int blacknum,int flag){if (it == nullptr){if (blacknum == flag)return true;elsereturn false;}else if (it->col == RED && it->_parent->col == RED)//十分巧妙,因为孩子的情况有很多,但父亲不是红就是黑,所以判断父亲更合适return false;else if (it->col == BLACK)blacknum++;return check(it->_left,blacknum,flag) && check(it->_right,blacknum,flag);}bool isbalance(){return _isbalance(root);}bool _isbalance(node* root){if (root == nullptr)return true;else if (root->col == RED)return false;int blacknum = 0;int flag = 0;node* k = root;while (k){if (k->col == BLACK)flag++;k = k->_left;//这里十分巧妙,因为如果为红黑树,从某一节点到空的所有路径上的黑节点数量是一致的,所以可以先随便选一条路径,算出这一条路径上的黑节点数作为基准值,在由递归去和其他路径比较}return check(root,blacknum,flag);}private:node* root = nullptr;};test.cpp:
#include<iostream>using namespace std;#include"RBT.h"int main(){int arr[] = { 790,760,969,270,31,424,377,24,702 };//int arr[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };RBTtree<int, int> it;for (auto i : arr){it.insert(make_pair(i, i));}it.inorder();cout << endl << it.isbalance() << endl;return 0;}