文章目录
1.命令概述2.命令格式3.常用选项4.相关描述5.参考示例
1.命令概述
pwd(Print Working Directory)命令用于显示用户当前工作目录的完整路径。这是一个常用的命令,帮助用户确定他们目前所在的目录位置。
2.命令格式
基本的 pwd 命令格式非常简单:pwd [选项]
3.常用选项
-L(逻辑):打印出逻辑工作目录的名称,即包含符号链接的路径。-P(物理):显示不包含符号链接的物理路径,即实际路径。-help : 显示帮助并退出–version : 输出版本信息并退出 注意:在大多数情况下,如果不使用任何选项,pwd 默认表现类似于 -L 选项。
4.相关描述
pwd 是一个内置命令,意味着它内置于大多数现代 shell 中,如 bash 和 zsh。这使得 pwd 在几乎所有 Linux 系统和环境中都可用,并且执行速度很快。
pwd 的退出状态:
0:表示成功非零值:表示退出失败5.参考示例
基本用法:在终端输入 pwd,按回车。显示当前的工作目录。
xjc@ubuntu:~$ pwd/home/xjcxjc@ubuntu:~$ ^C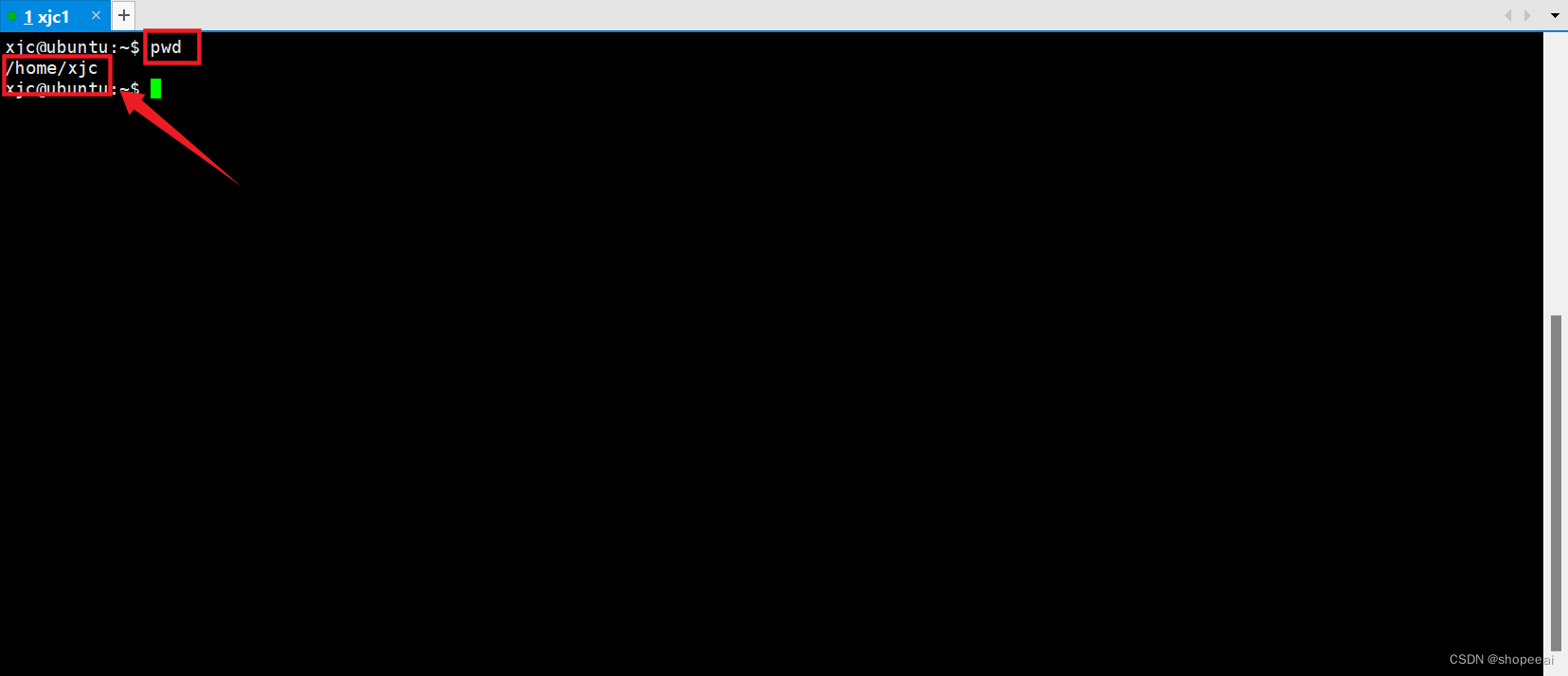
查看指定文件夹的路径
xjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$ cd /usr/localxjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$ pwd/usr/localxjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$
打印 pwd 的版本
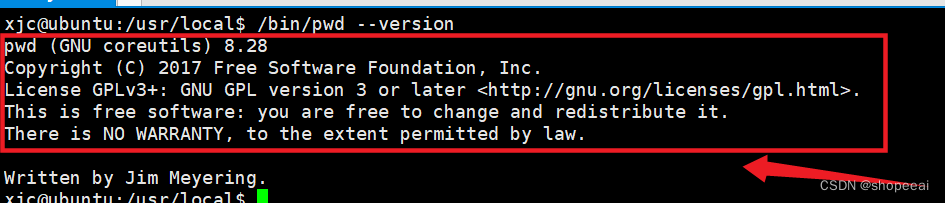
注意: ‘pwd’ 通常不带选项运行,且没有任何参数
重要: 注意刚才运行的是 “/bin/pwd” 而不是 “pwd”。
这有什么区别呢?直接使用“pwd”意味着使用 shell 内置的 pwd。shell 可能有不同版本的 pwd。当使用的是/bin/pwd 时,调用的是二进制版本的命令。虽然二进制的版本有更多的选项,但是它们两者都能打印当前的目录。
查看 pwd 命令的帮助信息
xjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$ /bin/pwd --helpUsage: /bin/pwd [OPTION]...Print the full filename of the current working directory. -L, --logical use PWD from environment, even if it contains symlinks -P, --physical avoid all symlinks --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exitIf no option is specified, -P is assumed.NOTE: your shell may have its own version of pwd, which usually supersedesthe version described here. Please refer to your shell's documentationfor details about the options it supports.GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>Full documentation at: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/pwd>or available locally via: info '(coreutils) pwd invocation'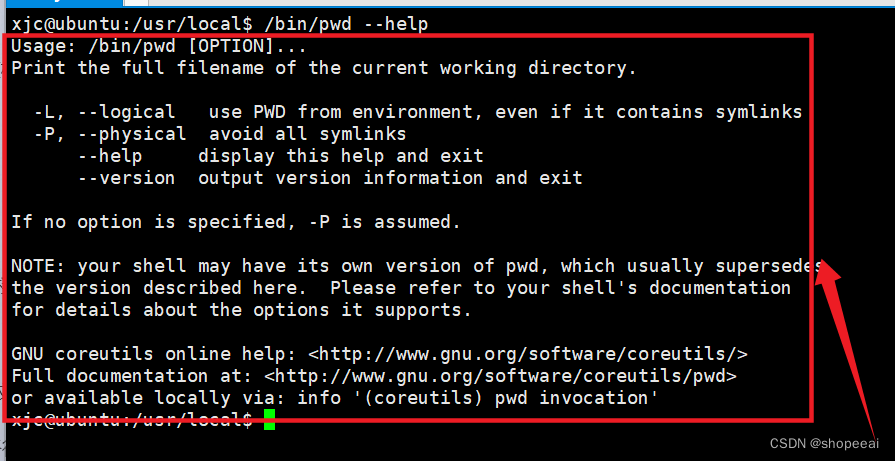
打印所有含有可执行 pwd 的路径
xjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$ type -a pwdpwd is a shell builtinpwd is /bin/pwdxjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$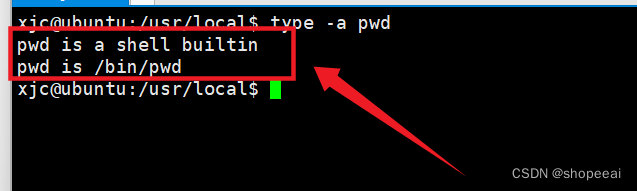
存储“pwd”命令的值到变量中(比如说:a ),并从中打印变量的值, 常用于观察 shell 脚本
xjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$ a=$(pwd)xjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$ echo $a/usr/localxjc@ubuntu:/usr/local$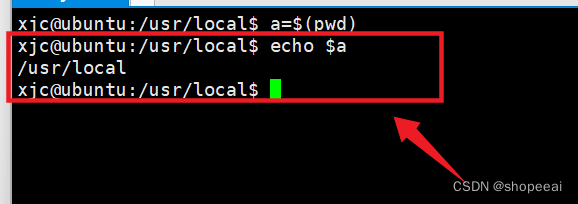
使用 -P 选项:如果你的当前工作目录是一个符号链接,使用 pwd -P 将显示该链接指向的实际目录。
首先,创建一个新目录,比如叫 real_dir,然后在另一个地方创建一个指向 real_dir 的符号链接 link_dir。
xjc@ubuntu:~$ mkdir /tmp/real_dirxjc@ubuntu:~$ ln -s /tmp/real_dir /tmp/link_dirxjc@ubuntu:~$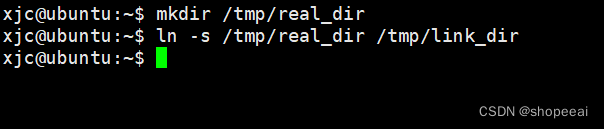
接下来,切换当前工作目录到这个符号链接 link_dir。
xjc@ubuntu:~$ cd /tmp/link_dir
使用 pwd 命令查看当前路径
xjc@ubuntu:/tmp/link_dir$ pwd/tmp/link_dirxjc@ubuntu:/tmp/link_dir$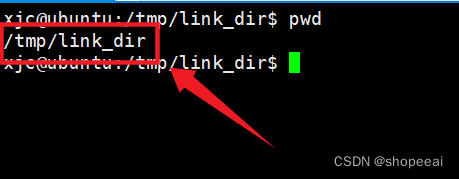
现在,使用 pwd -P 命令来获取实际路径,而不是符号链接的路径。
xjc@ubuntu:/tmp/link_dir$ pwd -P/tmp/real_dirxjc@ubuntu:/tmp/link_dir$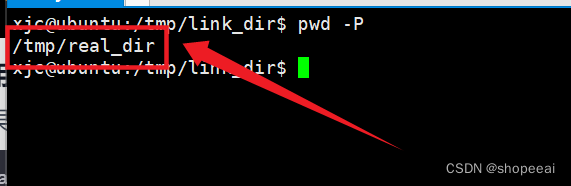
这里输出 的是 /tmp/real_dir,即使当前在符号链接目录 link_dir 中。
使用 -L 选项:如果你的当前工作目录是通过符号链接进入的,使用 pwd -L 将显示符号链接的路径。
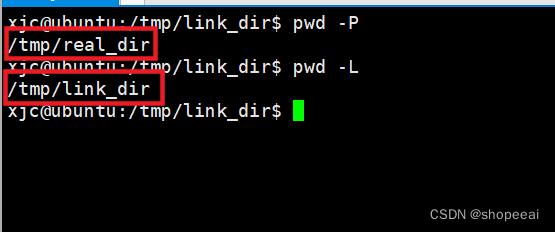
这里输出 的是 /tmp/link_dir,说明**pwd -L**** **显示的是符号链接的路径。