目录
1. auto和范围for
1.1 auto关键字
1.2 范围for
2. string的三种遍历方式
3. string类的常用接口说明
3.1 成员函数
3.2 Iterators:(迭代器)
3.2.1正向迭代器和反向迭代器
3.3 Capacity(容量)
3.4 Modifiers(修饰符)
3.5 Non-member function overloads(非成员函数重载)
3.6 operator []
string文档链接:cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string
https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string
在使用string类时,必须包含#include<string>头文件以及using namespace std;
1. auto和范围for
1.1 auto关键字
aotu的价值就是用来自动赋值,自动迭代,自动判断结束,底层就是迭代器
简化代码,替换了常类型
std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = dict.begin();//简化成auto it = dict.begin();1. auto类型的对象的类型是处于待定状态的,它是由初始化的内容所决定的
auto关键字是一个占位符,编译器执行该类型对象的定义时,先根据初始化的内容的类型A开等大的空间作为该对象的空间,A再替换auto(先占位置,后替换)
2. 用auto声明指针类型时,用auto和auto*没有任何区别,但用auto声明引用类型或者要修改内容时则必须加上引用&
、字符赋值,自动迭代,自动判断结束// 底层就是迭代器//for (auto ch : s2)这样写是拷贝 //修改内容要加上引用符号&for (auto& ch : s2){ //修改string里的值ch -= 2;cout << ch << " ";}cout << endl;cout << s2 << endl;3. 当在同一行声明多个变量时,这些变量必须是相同的类型,
//同为int类型,正确auto aa = 1, bb = 2;//类型不同,错误auto cc = 3, dd = 4.0;否则编译器将会报错,因为编译器实际只对第一个类型进行推导,然后会默认其他也是这个类型
4. auto不能作为函数的参数,也不能给缺省值
// 不能做参数void func2(auto a){}
但是可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用
// 可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用auto func3(){ return 3;}
5. auto不能直接用来声明数组
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int func1() { return 10; } // 不能做参数void func2(auto a) {}// 可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用 auto func3() { return 3; } int main() { int a = 10; auto b = a; auto c = 'a'; auto d = func1();// 编译报错:rror C3531: “e”: 类型包含“auto”的符号必须具有初始值设定项 auto e; cout << typeid(b).name() << endl; cout << typeid(c).name() << endl; cout << typeid(d).name() << endl; int x = 10; auto y = &x; auto* z = &x; auto& m = x; cout << typeid(x).name() << endl; cout << typeid(y).name() << endl; cout << typeid(z).name() << endl; auto aa = 1, bb = 2;// 编译报错:error C3538: 在声明符列表中,“auto”必须始终推导为同一类型 auto cc = 3, dd = 4.0;// 编译报错:error C3318: “auto []”: 数组不能具有其中包含“auto”的元素类型 auto array[] = { 4, 5, 6 }; return 0;}
#include<iostream>#include <string>#include <map>using namespace std;int main() { std::map<std::string, std::string> dict = { { "apple", "苹果" },{ "orange","橙子" }, {"pear","梨"} }; // auto的用武之地 //std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = dict.begin(); auto it = dict.begin(); while (it != dict.end()) { cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl; ++it; } return 0; }
1.2 范围for
1. for循环后的括号由冒号“ :”分为两部分:第一部分是范围内用于迭代的变量,第二部分则表示被迭代的范围,自动迭代,自动取数据,自动判断结束
2. 范围for的作用就是遍历数组和容器对象(主要用于容器)
// C++11的遍历for (auto& e : array) e *= 2;for (auto e : array)cout << e << " " << endl;加上&就可以修改其中的内容(e * = 2),如果不修改就可以不加
3. 范围for的底层就是迭代器,容器遍历实际就是替换为迭代器
#include<iostream>#include <string>#include <map>using namespace std;int main(){ int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; // C++11的遍历 for (auto& e : array) e *= 2; for (auto e : array) cout << e << " " << endl; string str("hello world"); for (auto ch : str) { cout << ch << " "; } cout << endl;return 0;}
2. string的三种遍历方式
#include<iostream>#include<string>#include<map>#include<list>using namespace std;//class string//{//private://char _buff[16];//char* _str;////size_t _size;//size_t _capacity;//};// string:: :展开string库// iterator:迭代器// it:使用迭代器定义的对象// begin():返回这块空间开始位置的迭代器// end:返回最后一个数据的下一个位置(\0)//string::iterator it = s2.begin();//while (it != s2.end())//{////cout << *it << " ";//++it;//}//cout << endl;void test_string1(){string s1;string s2("hello world");cout << s1 << s2 << endl;s2[0] = 'x';cout << s1 << s2 << endl;//访问+修改 第一种只支持数组,不支持树或者链表// 1、下标 + []for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){cout << s2[i] << " ";}cout << endl;// 2、迭代器 使用的偏少//string::iterator it = s2.begin();auto it = s2.begin();while (it != s2.end()){*it += 2;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;cout << s2 << endl;//只是简单的遍历用第三种// 3、字符赋值,自动迭代,自动判断结束// 底层就是迭代器//for (auto ch : s2)for (auto& ch : s2){ch -= 2;cout << ch << " ";}cout << endl;cout << s2 << endl;}
3. string类的常用接口说明
3.1 成员函数
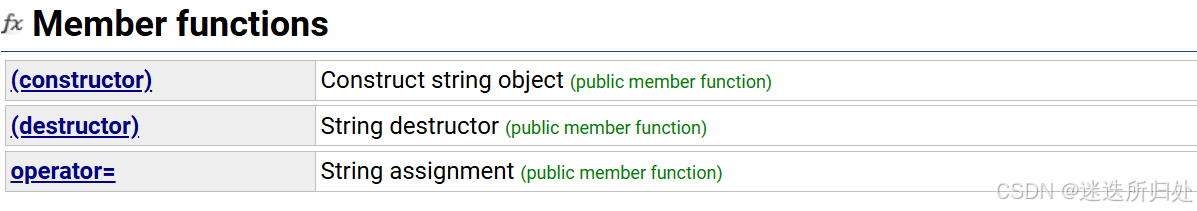
1. constructor(构造函数):
string(); | 创建一个空的string对象,也就是创建一个空的字符串 |
string (const char* s); | 以 C 当中 str 的方式 创建这个 string对象,最后以 " \0 " 结尾 |
string (size_t n, char c); | string类当中有 n 个 c 这个字符 |
string (const string& str); | 拷贝构造函数 |
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos); | 拷贝构造函数,从某一位置开始(pos),拷贝 len 个字符 |
string (const char* s, size_t n); | 构造一个string 类 ,在 s 常量字符串 的前n 个字符中拷贝 |

2.destructor(析构函数):string里的析构函数是自动析构的
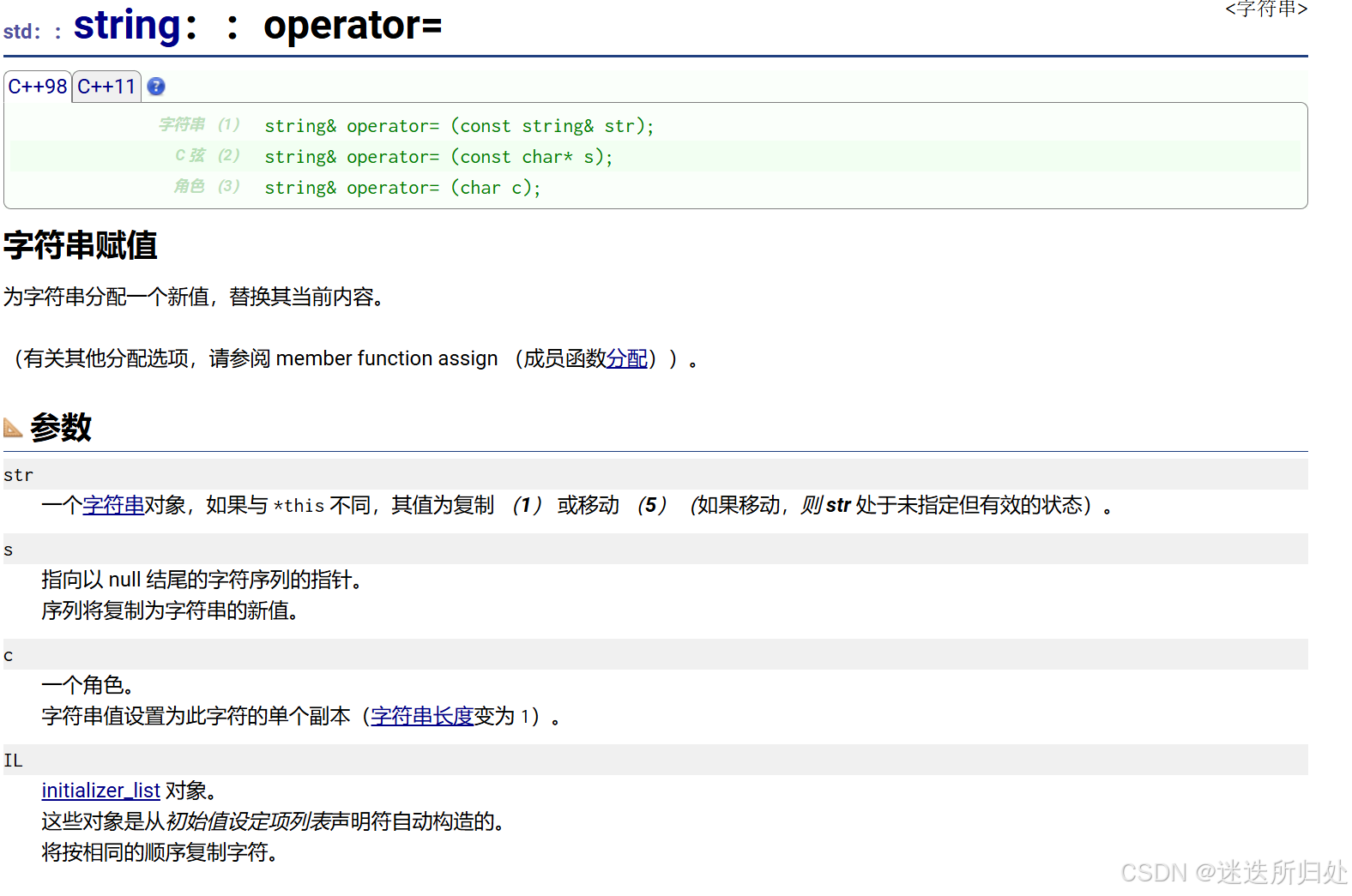
3. operator= (运算符=):
3.2 Iterators:(迭代器)
类似指针,但不全是指针
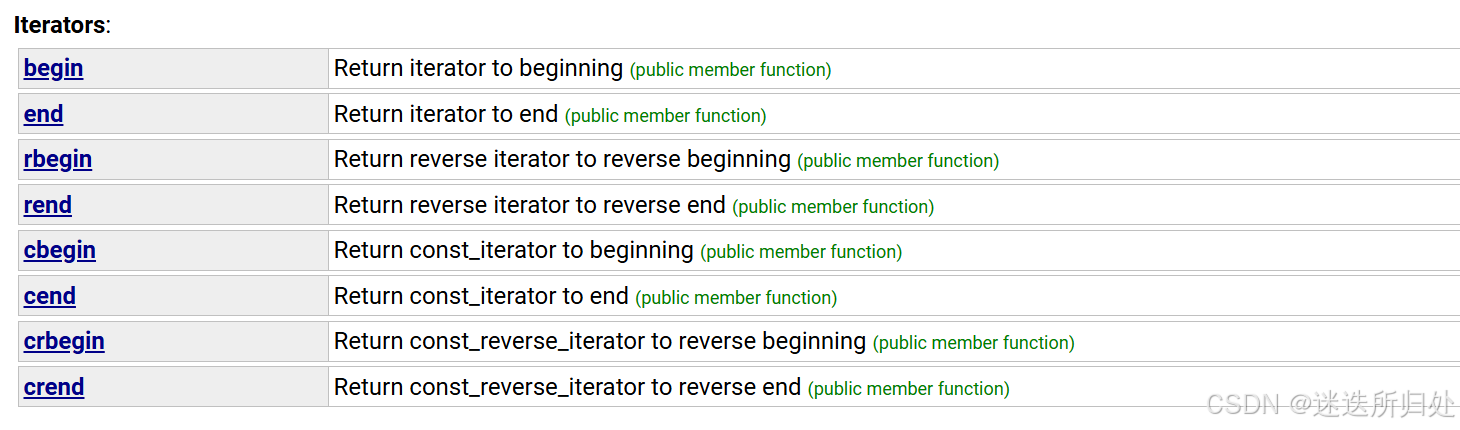
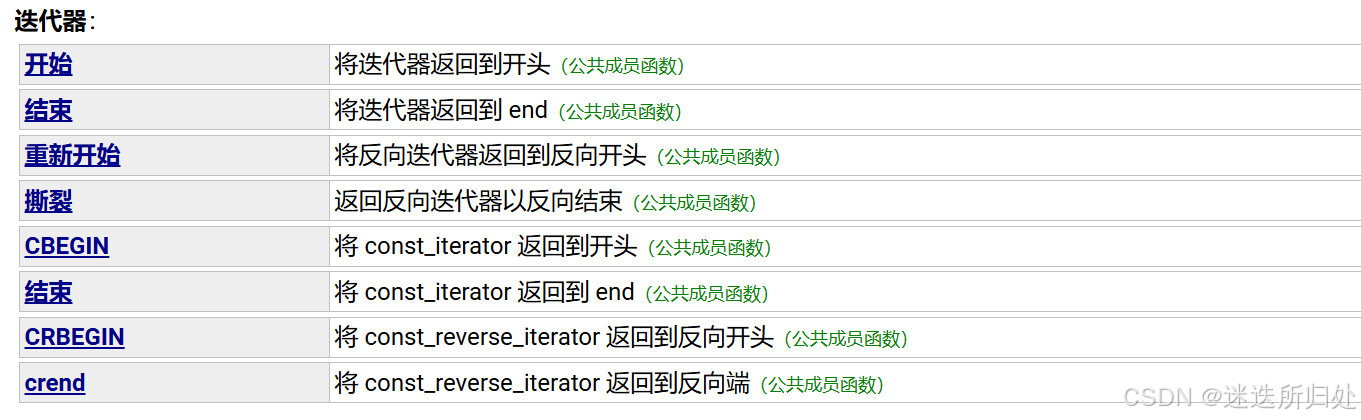
| begin:返回一个指向字符串的第一个字符的迭代器 |
| end:返回最后一个数据的下一个位置(\0) |
| rbegin:指向的是最后一个字符的位置 |
| rend:指向的是第一个字符的前一个位置 |
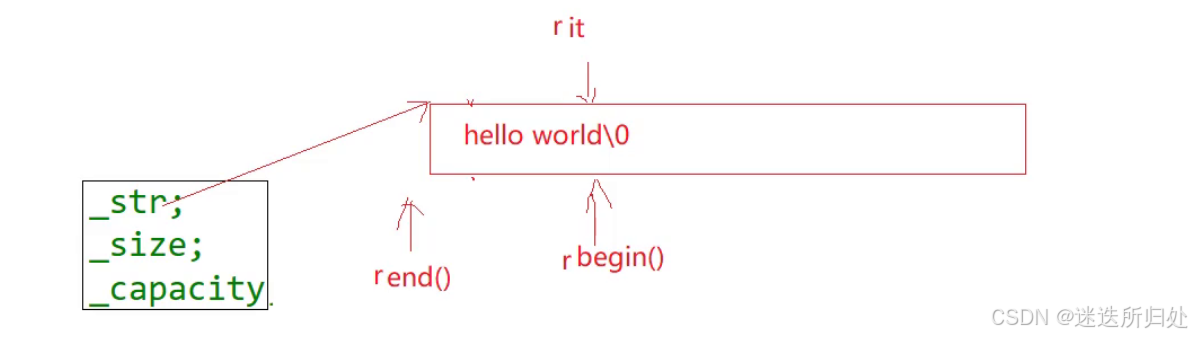
3.2.1正向迭代器和反向迭代器
const迭代器的特点是只能读不能写

正向:
1. Iterators 2. const_Iterators
| begin:返回一个指向字符串的第一个字符的迭代器 |
| end:返回最后一个数据的下一个位置(\0) |
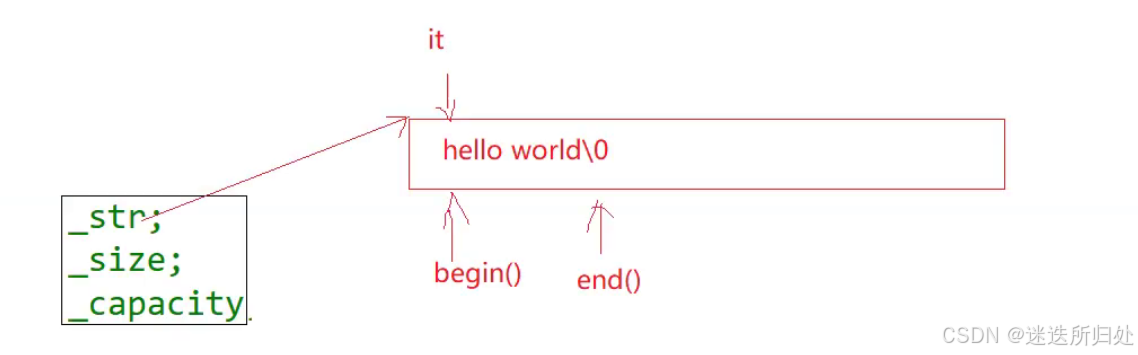 反向迭代器:倒着遍历使用
反向迭代器:倒着遍历使用
1. reverse_Iterators 2.const_reverse_Iterators
| rbegin:指向的是最后一个字符的位置 |
| rend:指向的是第一个字符的前一个位置 |
void test_string2(){string s2("hello world");string::iterator it = s2.begin();while (it != s2.end()){*it += 2;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;string::reverse_iterator rit = s2.rbegin();while (rit != s2.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;const string s3("hello world");//string::const_iterator cit = s3.begin();auto cit = s3.begin();while (cit != s3.end()){//*cit += 2;cout << *cit << " ";++cit;}cout << endl;//string::const_reverse_iterator rcit = s3.rbegin();auto rcit = s3.rbegin();while (rcit != s3.rend()){// *rcit += 2;cout << *rcit << " ";++rcit;}cout << endl;}
3.3 Capacity(容量)
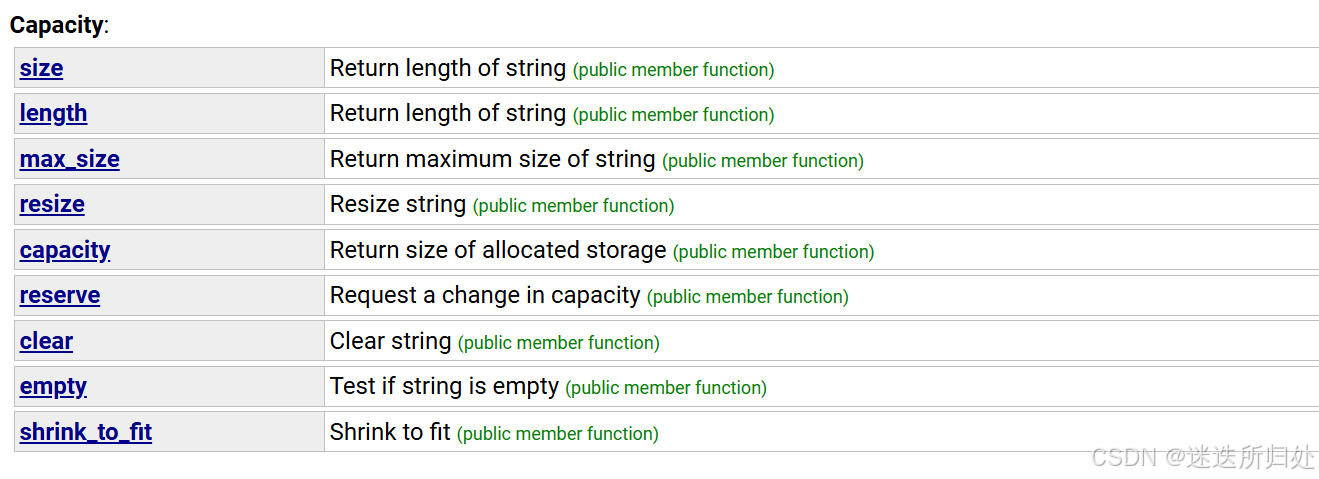
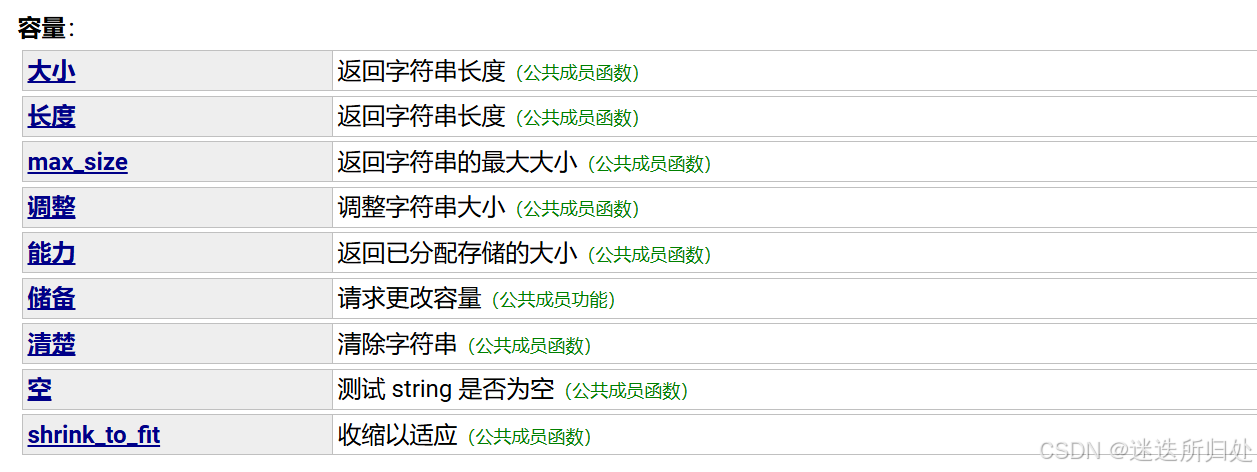
| size | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| empty | 判断字符串是否为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| reserve | 提前开辟好要开辟的空间,根据计划的大小更改调整字符串容量,长度最多大于 n 个字符 如果开辟100个空间,那么实际上开辟101个空间,多的一个给\0 为字符串预留空间** |
| resize | 将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充 ,string部分使用的不多 |
| clear | 清空所有的数据,但是不清除容量 |
| length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| capacity | 返回空间总大小 |
1. size与length底层实现原理完全相同,引入size的原因是因为length不具有通用性,size具有通用性,所以基本都是用size,但是length不能舍弃
2. clear只会将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小
3. resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不 同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变
4. reserve(size_t res_arg=0):为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参 数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小
// 测试string容量相关的接口// size/clear/resizevoid Teststring1(){// 注意:string类对象支持直接用cin和cout进行输入和输出string s("hello, bit!!!");cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.length() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;cout << s << endl;// 将s中的字符串清空,注意清空时只是将size清0,不改变底层空间的大小s.clear();cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;// 将s中有效字符个数增加到10个,多出位置用'a'进行填充// “aaaaaaaaaa”s.resize(10, 'a');cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;// 将s中有效字符个数增加到15个,多出位置用缺省值'\0'进行填充// "aaaaaaaaaa\0\0\0\0\0"// 注意此时s中有效字符个数已经增加到15个s.resize(15);cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;cout << s << endl;// 将s中有效字符个数缩小到5个s.resize(5);cout << s.size() << endl;cout << s.capacity() << endl;cout << s << endl;}
3.4 Modifiers(修饰符)
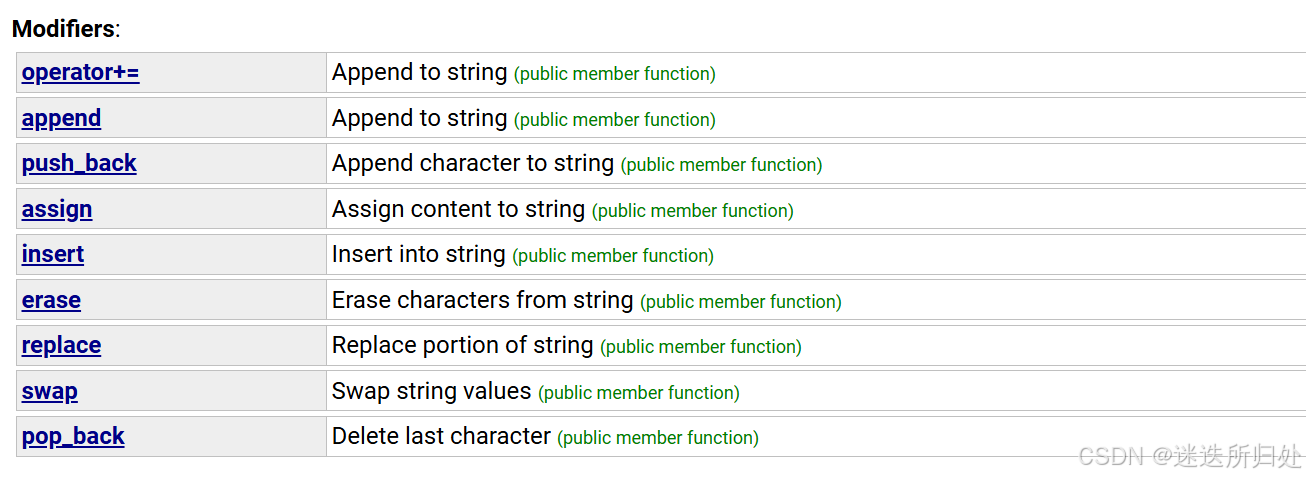
| operator+= | 在字符串后追加字符串str |
| append | 在字符串后追加一个字符串 |
| push_back | 在字符串后尾插字符 |
| c_str | 返回底层字符串的指针,兼容C语言 |
| find+npos | 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符,返回该字符在字符串中的 位置,正着找 |
| rfind | 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符,返回该字符在字符串中的 位置,倒着找 |
| substr | 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回 |
// 1. 插入(拼接)方式:push_back append operator+= // 2. 正向和反向查找:find() + rfind()// 3. 截取子串:substr()// 4. 删除:erasevoid Teststring5(){string str;str.push_back(' '); // 在str后插入空格str.append("hello"); // 在str后追加一个字符"hello"str += 'b'; // 在str后追加一个字符'b' str += "it"; // 在str后追加一个字符串"it"cout << str << endl;cout << str.c_str() << endl; // 以C语言的方式打印字符串// 获取file的后缀string file("string.cpp");size_t pos = file.rfind('.');string suffix(file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos)); //suffix:后缀cout << suffix << endl;// npos是string里面的一个静态成员变量// static const size_t npos = -1;// 取出url中的域名string url("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");cout << url << endl;size_t start = url.find("://");if (start == string::npos){cout << "invalid url" << endl;return;}start += 3;size_t finish = url.find('/', start);string address = url.substr(start, finish - start);cout << address << endl;// 删除url的协议前缀pos = url.find("://");url.erase(0, pos + 3);cout << url << endl;}3.5 Non-member function overloads(非成员函数重载)
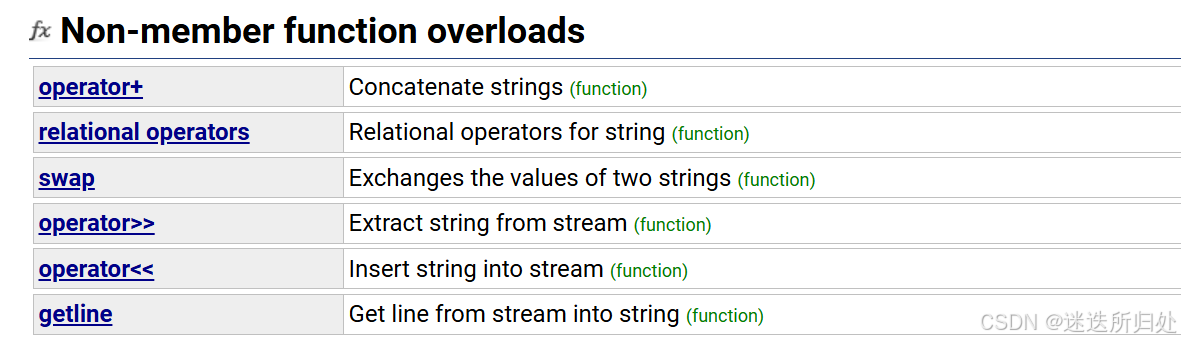
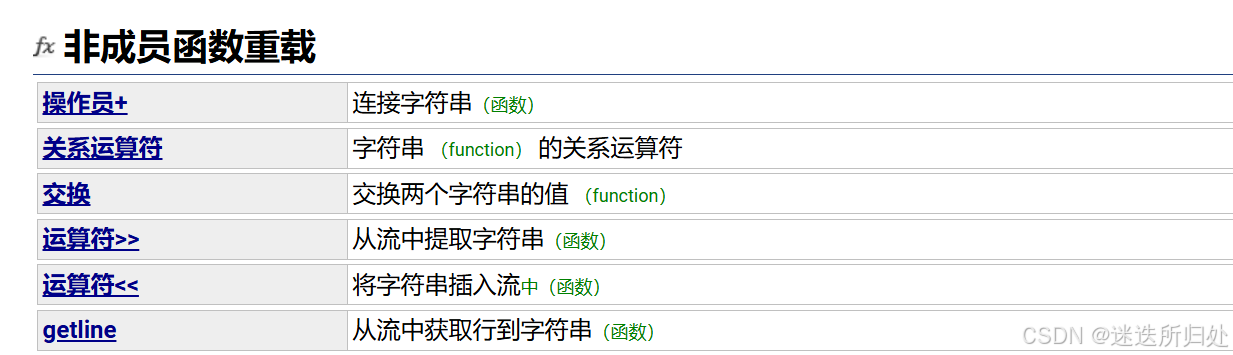
| operator+ | 可以string+字符串 或者 字符串+string |
| operator>> | 输入运算符重载 |
| operator<< | 输出运算符重载 |
| getline | 获取一行字符串 |
| relational operators | 大小比较 |
3.6 operator []
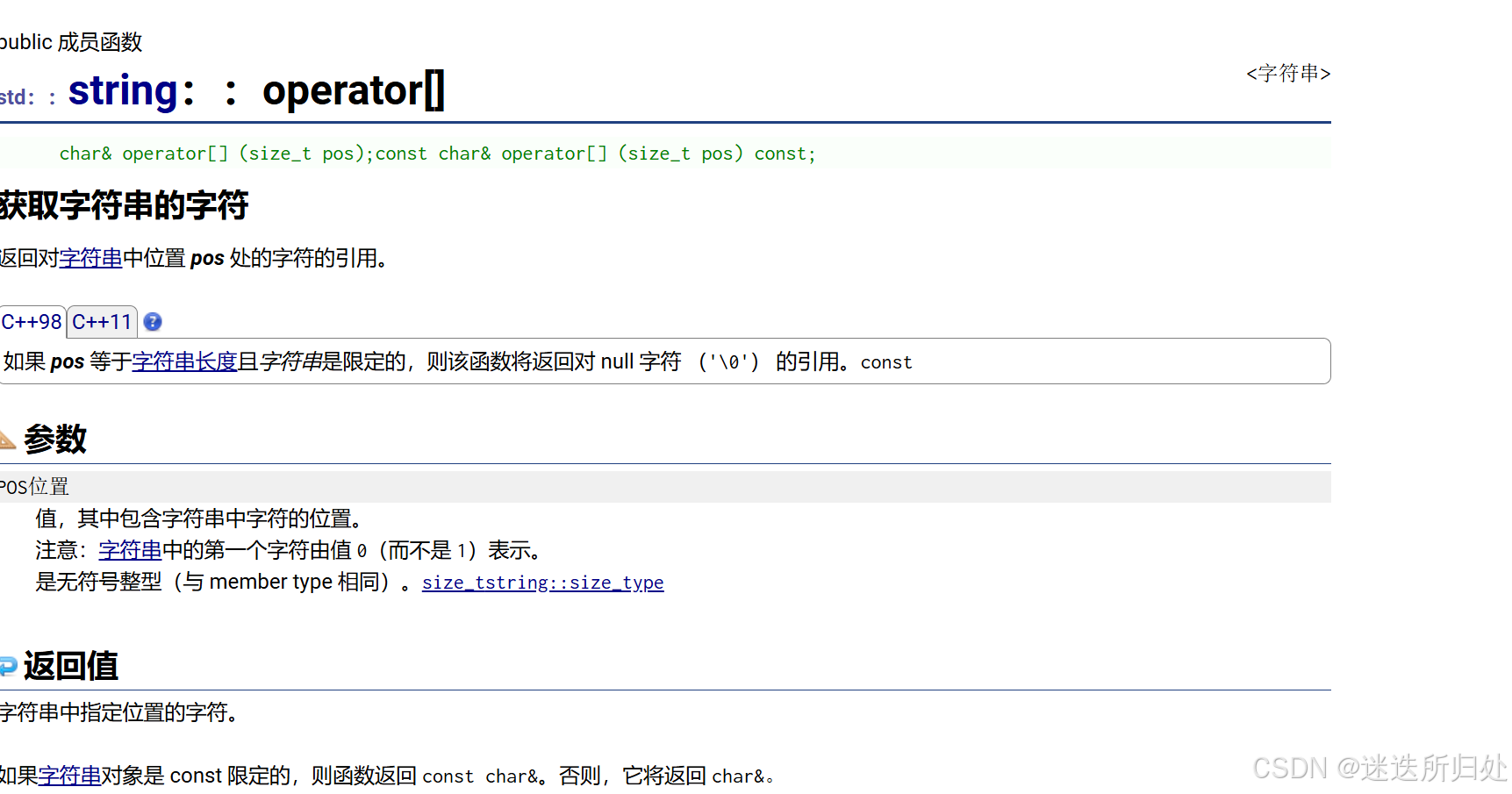
operator[] 在C当中 " [] " 这个操作符相当于是 解引用操作,只有在连续的空间当中才能使用这个 " [] " 这个操作符,比如在栈上开辟的数组和 堆上动态开辟的空间
那么在自定义类型string 类当中,我们也可以使用 " [] " 来访问这个字符串数组
使用 下标 + [] 的方式来访问string自定义类型
string s3("hello world");// 直接打s3 当中的内容cout << s3 << endl; // 下标 + []for (int i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++){cout << s3[i];}cout << endl; return 0;
| operator [] | 返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用 |
| begin+end | begin获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下一个位 置的迭代器 |
感谢观看~