✨✨✨学习的道路很枯燥,希望我们能并肩走下来!
文章目录
目录
文章目录
前言
一 AVL树的概念
二 AVL树节点的定义
三 AVL树的插入
四 AVL树的旋转
五 AVL树的验证
六 AVL树的删除(了解)
七 AVL树的性能
八 AVL树全代码
总结
前言
本篇详细介绍了进一步介绍C++中的AVL树,让使用者对AVL树有更加深刻的认知,而不是仅仅停留在表面,更好的模拟,为了更好的使用. 文章可能出现错误,如有请在评论区指正,让我们一起交流,共同进步!
前面对map/multimap/set/multiset进行了简单的介绍,在其文档介绍中发现,这几个容器有个 共同点是:其底层都是按照二叉搜索树来实现的,但是二叉搜索树有其自身的缺陷,假如往树中 插入的元素有序或者接近有序,二叉搜索树就会退化成单支树,时间复杂度会退化成O(N),因此 map、set等关联式容器的底层结构是对二叉树进行了平衡处理,即采用平衡树(AVL树,红黑树)来实现。
一 AVL树的概念
二叉搜索树虽可以缩短查找的效率,但如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查 找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率低下。因此,两位俄罗斯的数学家G.M.Adelson-Velskii 和E.M.Landis在1962年 发明了一种解决上述问题的方法:当向二叉搜索树中插入新结点后,如果能保证每个结点的左右 子树高度之差的绝对值不超过1(需要对树中的结点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度。
一棵AVL树或者是空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉搜索树:
● 它的左右子树都是AVL树
● 左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1(-1/0/1)
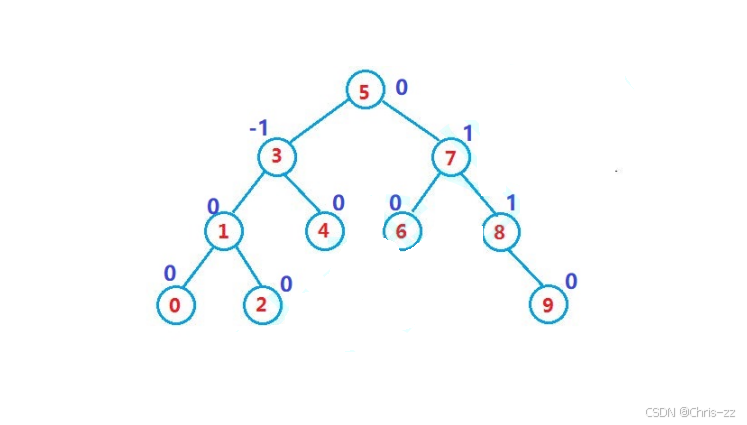 如果一棵二叉搜索树是高度平衡的,它就是AVL树。如果它有n个结点,其高度可保持在 O(log_2 n),搜索时间复杂度O(log_2 n)。
如果一棵二叉搜索树是高度平衡的,它就是AVL树。如果它有n个结点,其高度可保持在 O(log_2 n),搜索时间复杂度O(log_2 n)。
二 AVL树节点的定义
AVL树节点的定义:
template<class T>struct AVLTreeNode{AVLTreeNode(const T& data): _pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr), _data(data), _bf(0){}AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft; // 该节点的左孩子AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight; // 该节点的右孩子AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent; // 该节点的双亲T _data;int _bf; // 该节点的平衡因子};三 AVL树的插入
AVL树就是在二叉搜索树的基础上引入了平衡因子,因此AVL树也可以看成是二叉搜索树。那么 AVL树的插入过程可以分为两步:
1. 按照二叉搜索树的方式插入新节点
2. 调整节点的平衡因子
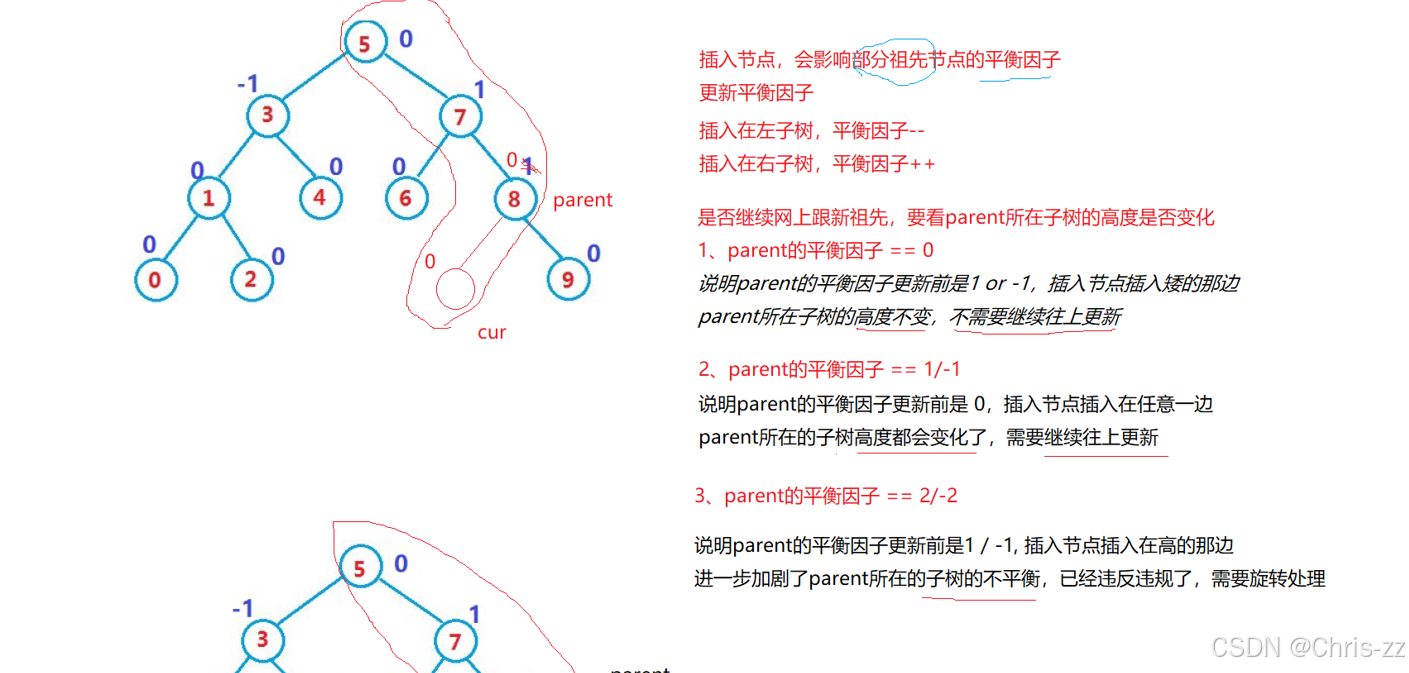
bool Insert(const T& data){if (_pRoot == nullptr){_pRoot = new Node(data);return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}else if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(data);if (parent->_data > data)parent->_pLeft = cur;elseparent->_pRight = cur;cur->_pParent = parent;while (parent){if (cur == parent->_pRight)parent->_bf++;elseparent->_bf--;if (parent->_bf == 0)return true;else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1){cur = parent;parent = cur->_pParent;}else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2){if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else{RotateLR(parent);}break;}else{assert(false);}}return true;}四 AVL树的旋转
如果在一棵原本是平衡的AVL树中插入一个新节点,可能造成不平衡,此时必须调整树的结构, 使之平衡化。根据节点插入位置的不同,AVL树的旋转分为四种:
1.新节点插入较高左子树的左侧---左左:右单旋
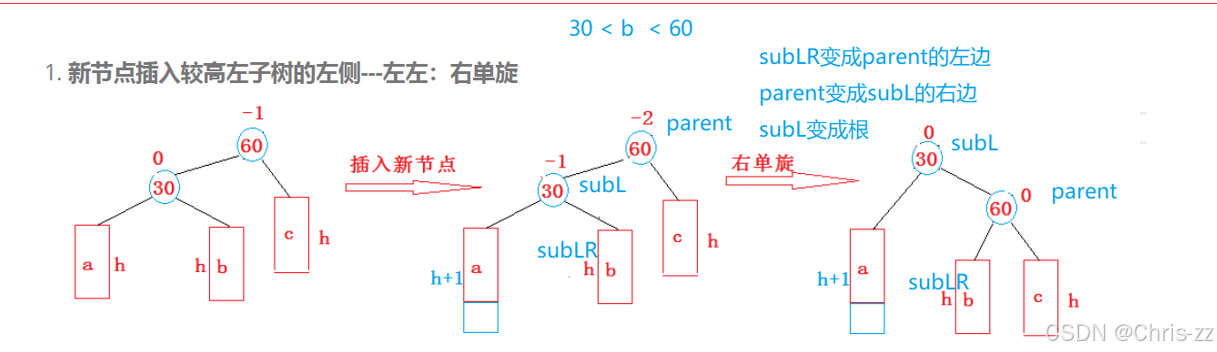
// 右单旋void RotateR(Node* pParent){Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;pParent->_pLeft = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_pParent = pParent;Node* parentParent = pParent->_pParent;subL->_pRight = pParent;pParent->_pParent = subL;if (parentParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subL;subL->_pParent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_pLeft){parentParent->_pLeft = subL;}else{parentParent->_pRight = subL;}}subL->_bf = pParent->_bf = 0;}2. 新节点插入较高右子树的右侧---右右:左单旋
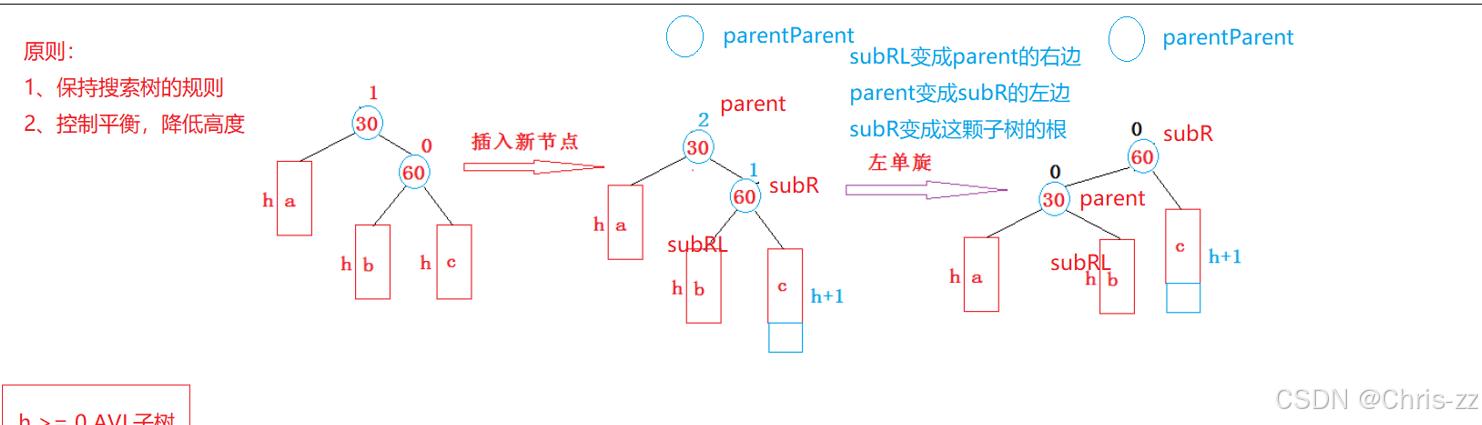
void RotateL(Node* pParent){Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;pParent->_pRight = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_pParent = pParent;Node* parentParent = pParent->_parent;subR->_pLeft = pParent;pParent->_pParent = subR;if (parentParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subL;subR->_pParent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_pLeft){parentParent->_pLeft = subR;}else{parentParent->_pRight = subR;}}subR->_bf = pParent->_bf = 0;}3. 新节点插入较高左子树的右侧---左右:先左单旋再右单旋
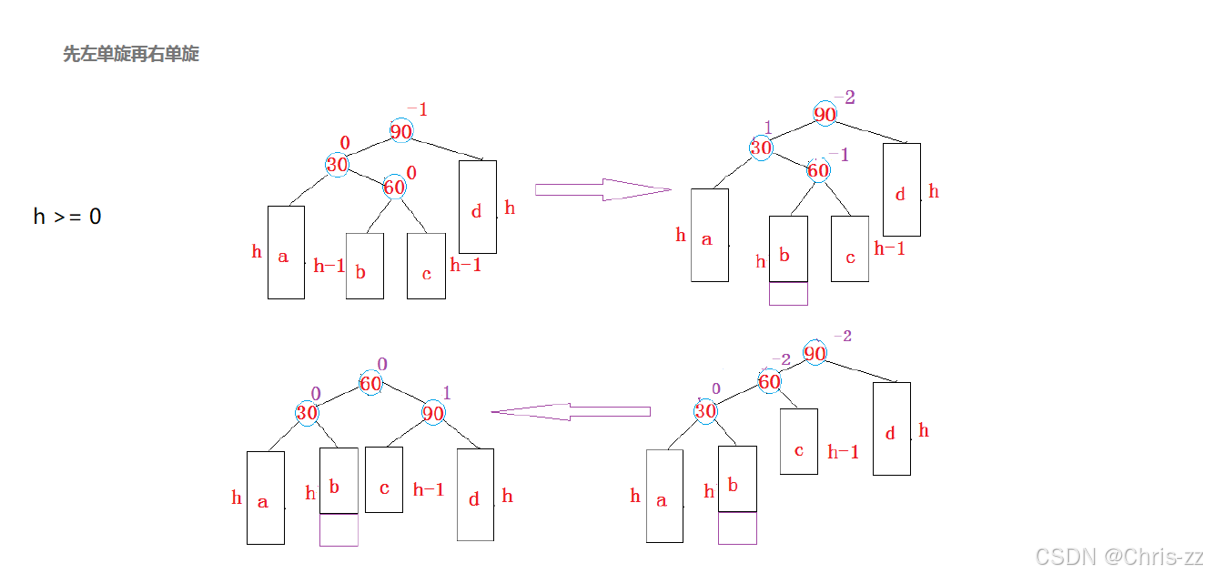 可以复用我们前面写的左右单旋的代码
可以复用我们前面写的左右单旋的代码
void RotateLR(Node* pParent){Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(pParent->_pLeft);RotateR(pParent);if (bf == 0){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){subL->_bf = -1;subLR->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){subL->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 1;}else{assert(false);}}4. 新节点插入较高右子树的左侧---右左:先右单旋再左单旋
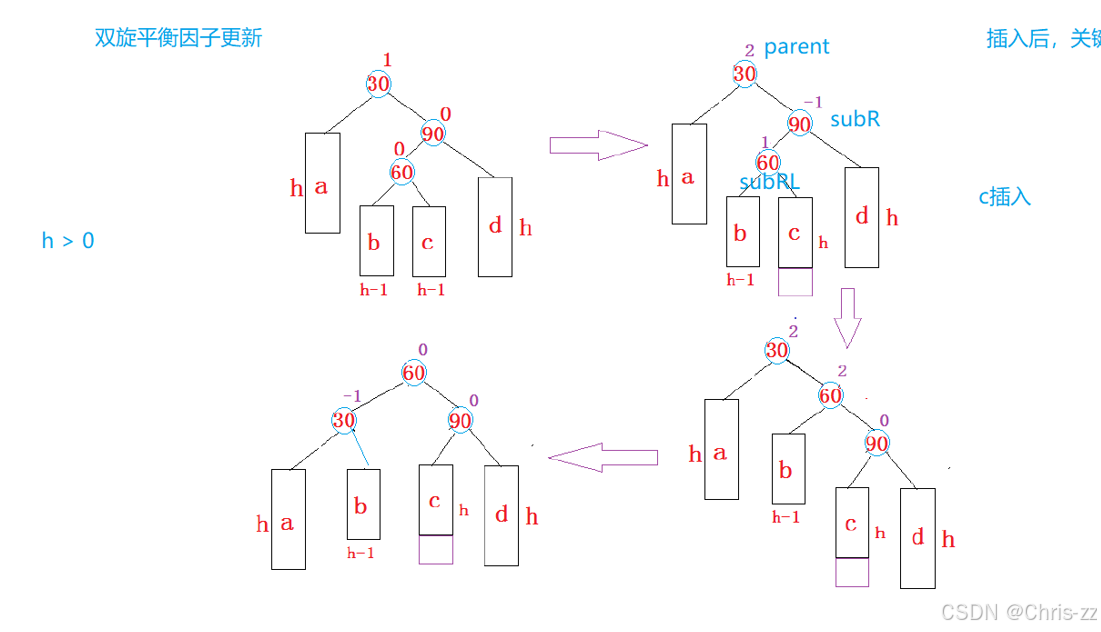
void RotateRL(Node* pParent){Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(pParent->_pRight);RotateL(pParent);if (bf == 0){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){subR->_bf = 1;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}总结:
假如以pParent为根的子树不平衡,即pParent的平衡因子为2或者-2,分以下情况考虑
1. pParent的平衡因子为2,说明pParent的右子树高,设pParent的右子树的根为pSubR
● 当pSubR的平衡因子为1时,执行左单旋
● 当pSubR的平衡因子为-1时,执行右左双旋
2. pParent的平衡因子为-2,说明pParent的左子树高,设pParent的左子树的根为pSubL
● 当pSubL的平衡因子为-1是,执行右单旋
● 当pSubL的平衡因子为1时,执行左右双旋
五 AVL树的验证
AVL树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加入了平衡性的限制,因此要验证AVL树,可以分两步:
1. 验证其为二叉搜索树
如果中序遍历可得到一个有序的序列,就说明为二叉搜索树
2. 验证其为平衡树
○ 每个节点子树高度差的绝对值不超过1(注意节点中如果没有平衡因子)
○ 节点的平衡因子是否计算正确
bool _IsAVLTree(Node* pRoot){ // 空树也是AVL树if (nullptr == pRoot)return true;int leftHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pLeft);int rightHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pRight);if (abs(rightHeight - leftHeight) > 1 ||rightHeight - leftHeight != pRoot->_bf)return false;return _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pLeft) && _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pRight);}size_t _Height(Node* pRoot){if (pRoot == nullptr)return 0;int LeftHeight = _Height(pRoot->left) + 1;int RightHeight = _Height(pRoot->right) + 1;return (LeftHeight > RightHeight) ? LeftHeight : RightHeight;}六 AVL树的删除(了解)
因为AVL树也是二叉搜索树,可按照二叉搜索树的方式将节点删除,然后再更新平衡因子,只不 错与删除不同的时,删除节点后的平衡因子更新,最差情况下一直要调整到根节点的位置。
参考《算法导论》或《数据结构-用面向对象方法与C++描述》殷人昆版。
七 AVL树的性能
AVL树是一棵绝对平衡的二叉搜索树,其要求每个节点的左右子树高度差的绝对值都不超过1,这 样可以保证查询时高效的时间复杂度,即$log_2 (N)$。但是如果要对AVL树做一些结构修改的操作,性能非常低下,比如:插入时要维护其绝对平衡,旋转的次数比较多,更差的是在删除时, 有可能一直要让旋转持续到根的位置。因此:如果需要一种查询高效且有序的数据结构,而且数 据的个数为静态的(即不会改变),可以考虑AVL树,但一个结构经常修改,就不太适合。
八 AVL树全代码
#pragma once#include<iostream>using namespace std;template<class T>struct AVLTreeNode{AVLTreeNode(const T& data = T()): _pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr), _data(data), _bf(0){}AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft;AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight;AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent;T _data;int _bf; // 节点的平衡因子};// AVL: 二叉搜索树 + 平衡因子的限制template<class T>class AVLTree{typedef AVLTreeNode<T> Node;public:AVLTree(): _pRoot(nullptr){}// 在AVL树中插入值为data的节点bool Insert(const T& data){if (_pRoot == nullptr){_pRoot = new Node(data);return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->left;}else if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->right;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(data);if (parent->_data > data)parent->_pLeft = cur;elseparent->_pRight = cur;cur->_pParent = parent;while (parent){if (cur == parent->_pRight)parent->_bf++;elseparent->_bf--;if (parent->_bf == 0)return true;else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1){cur = parent;parent = cur->_pParent;}else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2){if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else{RotateLR(parent);}break;}else{assert(false);}}return true;}// AVL树的验证bool IsAVLTree(){return _IsAVLTree(_pRoot);}private:// 根据AVL树的概念验证pRoot是否为有效的AVL树bool _IsAVLTree(Node* pRoot){if (nullptr == pRoot)return true;int leftHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pLeft);int rightHeight = _Height(pRoot->_pRight);if (abs(rightHeight - leftHeight) > 1 ||rightHeight - leftHeight != pRoot->_bf)return false;return _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pLeft) && _IsAVLTree(pRoot->_pRight);}size_t _Height(Node* pRoot){if (pRoot == nullptr)return 0;int LeftHeight = _Height(pRoot->left) + 1;int RightHeight = _Height(pRoot->right) + 1;return (LeftHeight > RightHeight) ? LeftHeight : RightHeight;}// 右单旋void RotateR(Node* pParent){Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;pParent->_pLeft = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_pParent = pParent;Node* parentParent = pParent->_pParent;subL->_pRight = pParent;pParent->_pParent = subL;if (parentParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subL;subL->_pParent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_pLeft){parentParent->_pLeft = subL;}else{parentParent->_pRight = subL;}}subL->_bf = pParent->_bf = 0;}// 左单旋void RotateL(Node* pParent){Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;pParent->_pRight = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_pParent = pParent;Node* parentParent = pParent->_parent;subR->_pLeft = pParent;pParent->_pParent = subR;if (parentParent == nullptr){_pRoot = subL;subR->_pParent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_pLeft){parentParent->_pLeft = subR;}else{parentParent->_pRight = subR;}}subR->_bf = pParent->_bf = 0;}// 右左双旋void RotateRL(Node* pParent){Node* subR = pParent->_pRight;Node* subRL = subR->_pLeft;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(pParent->_pRight);RotateL(pParent);if (bf == 0){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){subR->_bf = 1;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}// 左右双旋void RotateLR(Node* pParent){Node* subL = pParent->_pLeft;Node* subLR = subL->_pRight;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(pParent->_pLeft);RotateR(pParent);if (bf == 0){subR->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 1){subL->_bf = -1;subLR->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){subL->_bf = 0;subRL->_bf = 0;pParent->_bf = 1;}else{assert(false);}}private:Node* _pRoot;};
总结
✨✨✨各位读友,本篇分享到内容是否更好的让你理解AVL树,如果对你有帮助给个?赞鼓励一下吧!!
???世上没有绝望的处境,只有对处境绝望的人。
感谢每一位一起走到这的伙伴,我们可以一起交流进步!!!一起加油吧!!