一、引言
蚁群算法(Ant Colony Optimization, ACO)是一种模拟蚂蚁觅食行为的启发式搜索算法。它由Marco Dorigo于1992年提出,适用于解决组合优化问题,如旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP)等。
受自然界中蚂蚁觅食行为的启发。蚂蚁在寻找食物的过程中,会在路径上释放信息素(pheromone),信息素的浓度影响其他蚂蚁选择路径的概率。通过这种方式,蚂蚁能够找到最优路径。
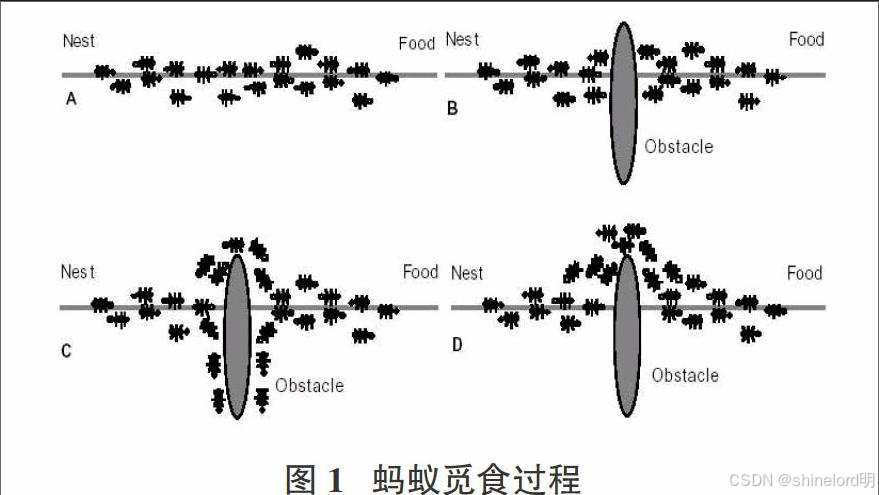
这种算法通过蚂蚁之间的信息素相互作用来寻找最优解,基于以下几个核心概念:
信息素:蚂蚁在行进过程中会在路径上留下信息素的浓度,其他蚂蚁依据信息素浓度选择路径,信息素的浓度会随时间衰减。
启发函数:用于指导蚂蚁的决策,通常根据问题目标来设计,例如在求解最短路径问题时,可以将启发函数设置为路径的倒数。
蚂蚁的决策:蚂蚁选择路径时会综合考虑信息素浓度和启发值。
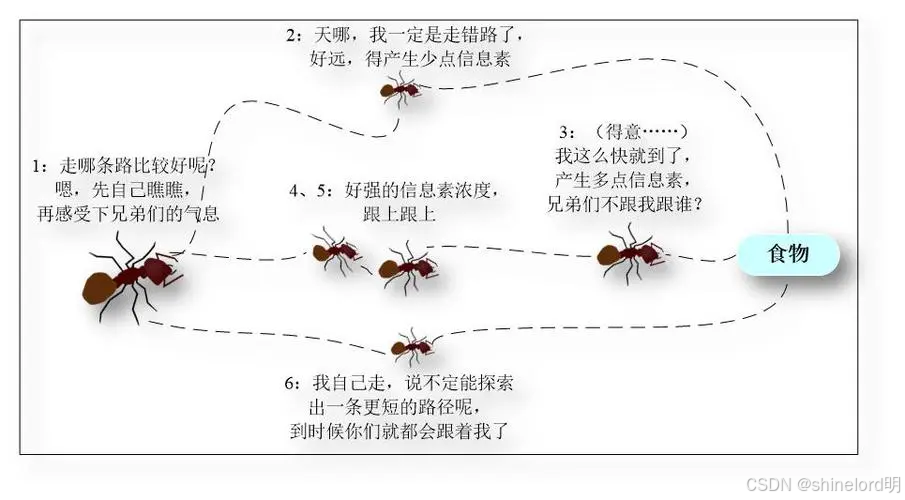
二、算法原理
蚁群算法的核心原理是利用蚂蚁在寻找食物过程中留下的信息素进行路径选择。蚂蚁在移动过程中会释放信息素,同时能够感知其他蚂蚁留下的信息素浓度,倾向于选择信息素浓度较高的路径。随着时间的推移,一条从食物源到蚁巢的最优路径会逐渐形成。
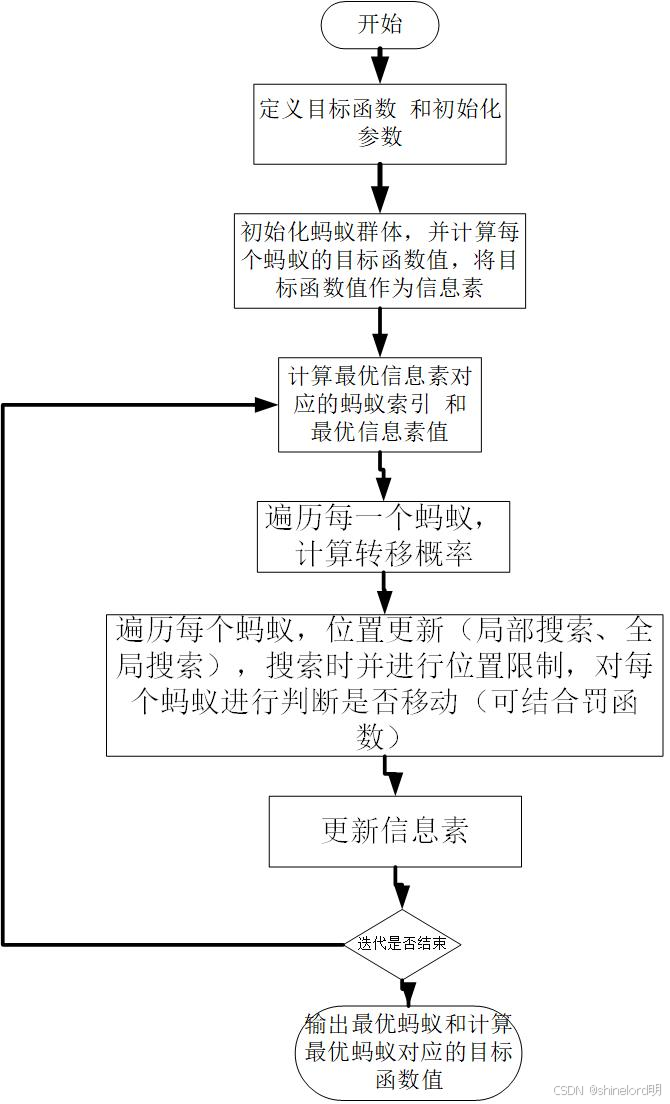
三、数据结构
蚁群算法中涉及的主要数据结构包括:
图:表示问题的状态空间,节点表示状态,边表示状态间的转移。信息素矩阵:记录每条边的信息素浓度。启发式信息矩阵:表示每条边的启发式信息,如距离的倒数。四、算法使用场景
蚁群算法适用于以下场景:
路径规划问题:如旅行商问题(TSP)寻找一条最短路径,经过所有城市且每个城市仅访问一次、车辆路径问题、优化配送路线,降低运输成本。
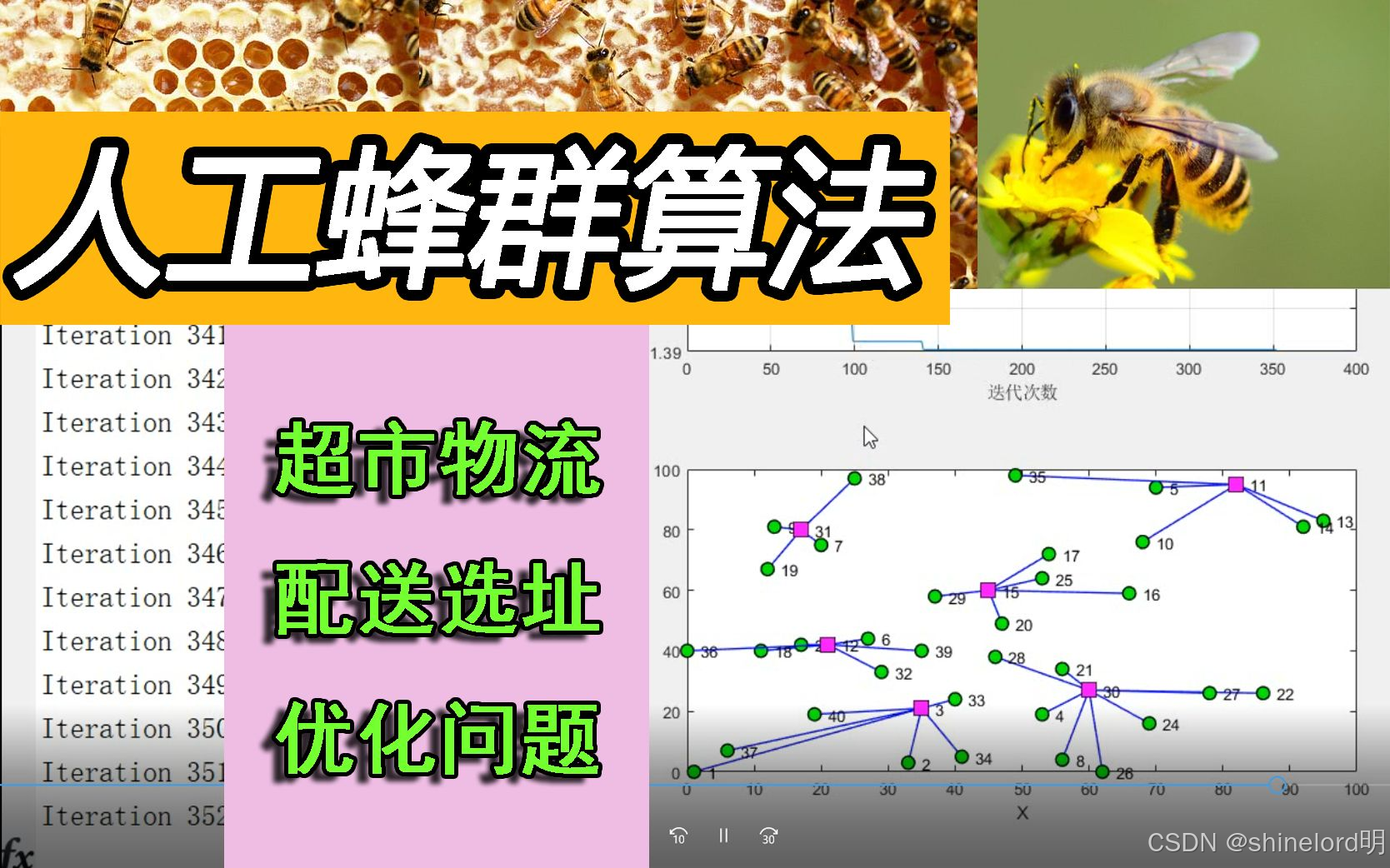
五、算法实现
初始化:设置蚂蚁数量、信息素浓度、启发函数等参数。
路径选择:每只蚂蚁根据信息素浓度和启发函数选择路径。
信息素更新:蒸发:信息素会随着时间的推移而蒸发,降低其浓度。增加:找到更优路径的蚂蚁会在路径上增加信息素。
迭代:重复路径选择和信息素更新,直到满足终止条件(如达到最大迭代次数或找到满意解)。
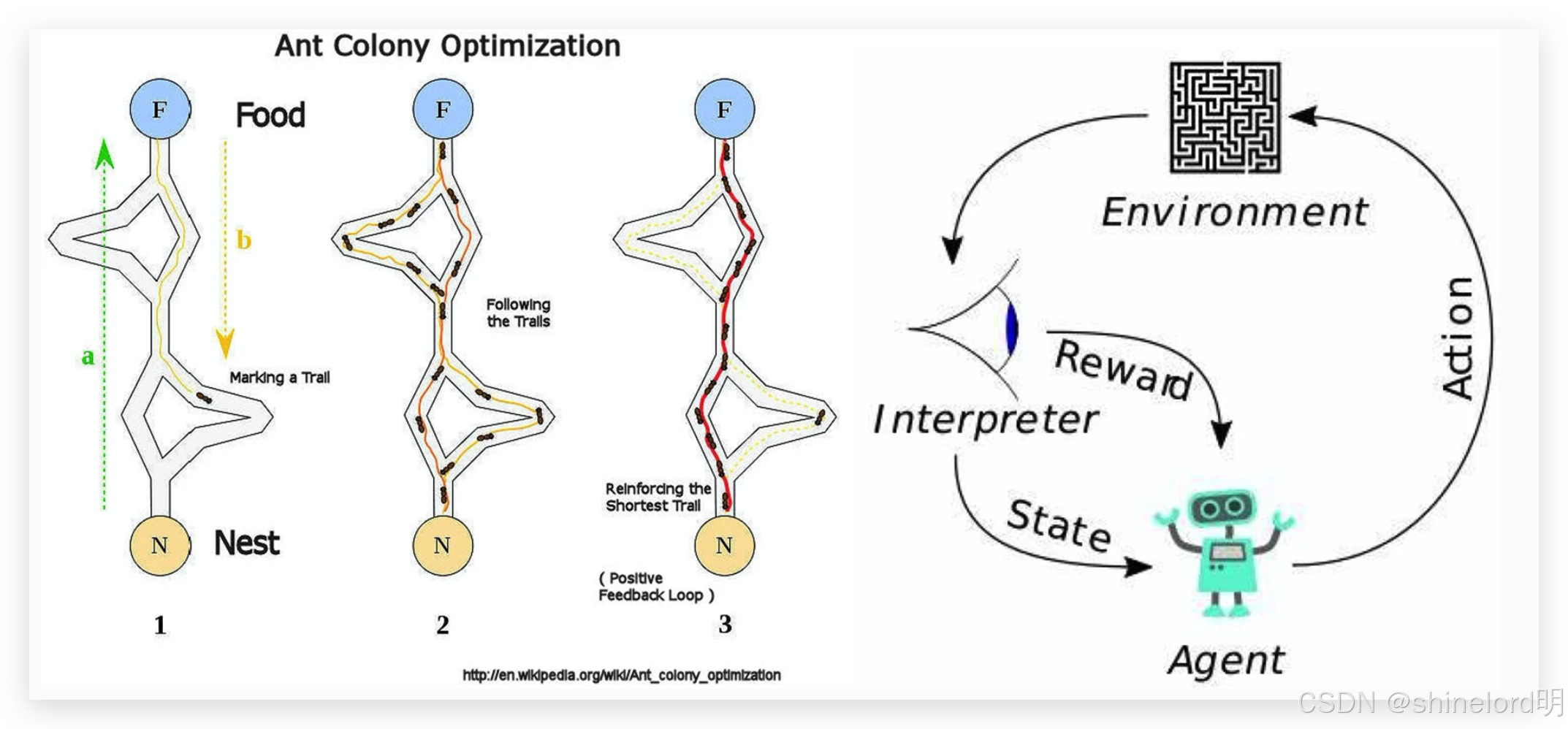
伪代码:
class AntColonyAlgorithm:def __init__(self, num_ants, num_iterations, alpha, beta, evaporation_rate):self.num_ants = num_antsself.num_iterations = num_iterationsself.alpha = alphaself.beta = betaself.evaporation_rate = evaporation_rateself.pheromone_matrix = np.ones((num_cities, num_cities))def update_pheromones(self):# 更新信息素self.pheromone_matrix *= (1 - self.evaporation_rate)def ant_solution(self, ant):# 蚂蚁找到一条可行路径的方法passdef solve(self):for _ in range(self.num_iterations):for ant in range(self.num_ants):self.ant_solution(ant)self.update_pheromones()六、同类算法对比
蚁群算法与其他启发式算法(如遗传算法、粒子群算法)对比如下:
| 特征/算法 | 蚁群算法 | 遗传算法 | 粒子群算法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 搜索机制 | 信息素更新、随机选择 | 选择、交叉、变异 | 粒子飞行路径、速度更新 |
| 收敛速度 | 中等 | 较快 | 较快 |
| 参数设置 | 多个参数 | 交叉率、变异率 | 粒子数、惯性权重 |
| 适用范围 | 优化组合、路径问题 | 全局优化 | 连续优化、全局优化 |
七、多语言代码实现
Java、Python、C++、Go等语言实现的蚁群算法代码框架。这里我们用Python实现一个简单的旅行商问题的算法示例。
Java
import java.util.*;public class AntColonyOptimization { private int numCities; private double[][] distances; private double[][] pheromones; private double alpha; // 信息素重要程度 private double beta; // 启发函数重要程度 private double evaporationRate; // 信息素蒸发率 private int numAnts; private int maxIterations; public AntColonyOptimization(int numCities, double[][] distances, int numAnts, int maxIterations, double alpha, double beta, double evaporationRate) { this.numCities = numCities; this.distances = distances; this.pheromones = new double[numCities][numCities]; this.numAnts = numAnts; this.maxIterations = maxIterations; this.alpha = alpha; this.beta = beta; this.evaporationRate = evaporationRate; initializePheromones(); } private void initializePheromones() { for (int i = 0; i < numCities; i++) { Arrays.fill(pheromones[i], 1.0); } } public void optimize() { for (int iteration = 0; iteration < maxIterations; iteration++) { double[] bestTour = new double[numCities]; double bestLength = Double.MAX_VALUE; for (int ant = 0; ant < numAnts; ant++) { double[] tour = constructTour(); double tourLength = calculateTourLength(tour); if (tourLength < bestLength) { bestLength = tourLength; bestTour = tour; } updatePheromones(tour, tourLength); } evaporatePheromones(); } } private double[] constructTour() { // 实现蚂蚁构造路径的逻辑 return new double[numCities]; // 示例返回 } private double calculateTourLength(double[] tour) { // 计算路径长度 return 0; // 示例返回 } private void updatePheromones(double[] tour, double tourLength) { // 更新信息素 } private void evaporatePheromones() { // 信息素蒸发 }}
Python
import numpy as npclass AntColonyOptimization: def __init__(self, num_cities, distances, num_ants, max_iterations, alpha, beta, evaporation_rate): self.num_cities = num_cities self.distances = distances self.pheromones = np.ones((num_cities, num_cities)) self.alpha = alpha self.beta = beta self.evaporation_rate = evaporation_rate self.num_ants = num_ants self.max_iterations = max_iterations def optimize(self): for _ in range(self.max_iterations): best_tour = None best_length = float('inf') for _ in range(self.num_ants): tour = self.construct_tour() tour_length = self.calculate_tour_length(tour) if tour_length < best_length: best_length = tour_length best_tour = tour self.update_pheromones(tour, tour_length) self.evaporate_pheromones() def construct_tour(self): # 实现蚂蚁构造路径的逻辑 return [] # 示例返回 def calculate_tour_length(self, tour): # 计算路径长度 return 0 # 示例返回 def update_pheromones(self, tour, tour_length): # 更新信息素 pass def evaporate_pheromones(self): # 信息素蒸发 self.pheromones *= (1 - self.evaporation_rate)C++
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <limits>class AntColonyOptimization {public: AntColonyOptimization(int numCities, const std::vector<std::vector<double>>& distances, int numAnts, int maxIterations, double alpha, double beta, double evaporationRate) : numCities(numCities), distances(distances), numAnts(numAnts), maxIterations(maxIterations), alpha(alpha), beta(beta), evaporationRate(evaporationRate) { pheromones.resize(numCities, std::vector<double>(numCities, 1.0)); } void optimize() { for (int iteration = 0; iteration < maxIterations; ++iteration) { std::vector<int> bestTour; double bestLength = std::numeric_limits<double>::max(); for (int ant = 0; ant < numAnts; ++ant) { auto tour = constructTour(); double tourLength = calculateTourLength(tour); if (tourLength < bestLength) { bestLength = tourLength; bestTour = tour; } updatePheromones(tour, tourLength); } evaporatePheromones(); } }private: int numCities; std::vector<std::vector<double>> distances; std::vector<std::vector<double>> pheromones; double alpha, beta, evaporationRate; int numAnts, maxIterations; std::vector<int> constructTour() { // 实现蚂蚁构造路径的逻辑 return {}; // 示例返回 } double calculateTourLength(const std::vector<int>& tour) { // 计算路径长度 return 0; // 示例返回 } void updatePheromones(const std::vector<int>& tour, double tourLength) { // 更新信息素 } void evaporatePheromones() { // 信息素蒸发 for (auto& row : pheromones) { for (auto& p : row) { p *= (1 - evaporationRate); } } }};Go
package mainimport ( "math")type AntColonyOptimization struct { numCities int distances [][]float64 pheromones [][]float64 alpha float64 beta float64 evaporationRate float64 numAnts int maxIterations int}func NewAntColonyOptimization(numCities int, distances [][]float64, numAnts, maxIterations int, alpha, beta, evaporationRate float64) *AntColonyOptimization { pheromones := make([][]float64, numCities) for i := range pheromones { pheromones[i] = make([]float64, numCities) for j := range pheromones[i] { pheromones[i][j] = 1.0 } } return &AntColonyOptimization{ numCities: numCities, distances: distances, pheromones: pheromones, alpha: alpha, beta: beta, evaporationRate: evaporationRate, numAnts: numAnts, maxIterations: maxIterations, }}func (aco *AntColonyOptimization) Optimize() { for iteration := 0; iteration < aco.maxIterations; iteration++ { var bestTour []int bestLength := math.MaxFloat64 for ant := 0; ant < aco.numAnts; ant++ { tour := aco.constructTour() tourLength := aco.calculateTourLength(tour) if tourLength < bestLength { bestLength = tourLength bestTour = tour } aco.updatePheromones(tour, tourLength) } aco.evaporatePheromones() }}func (aco *AntColonyOptimization) constructTour() []int { // 实现蚂蚁构造路径的逻辑 return []int{} // 示例返回}func (aco *AntColonyOptimization) calculateTourLength(tour []int) float64 { // 计算路径长度 return 0 // 示例返回}func (aco *AntColonyOptimization) updatePheromones(tour []int, tourLength float64) { // 更新信息素}func (aco *AntColonyOptimization) evaporatePheromones() { for i := range aco.pheromones { for j := range aco.pheromones[i] { aco.pheromones[i][j] *= (1 - aco.evaporationRate) } }}八、实际服务应用场景
考虑一个实际的配送服务场景,我们可以使用蚁群算法来优化货物配送路径。以下是该应用场景的框架代码(使用Python Flask作为后端服务):
from flask import Flask, request, jsonifyfrom ant_colony_optimization import AntColonyOptimizationapp = Flask(__name__)@app.route('/optimize-route', methods=['POST'])def optimize_route():data = request.jsonnum_cities = data['num_cities']num_ants = data['num_ants']aco = AntColonyOptimization(num_cities, num_ants)best_route, best_distance = aco.run()return jsonify({'best_route': best_route, 'best_distance': best_distance})if __name__ == '__main__':app.run(debug=True)蚁群算法是一种强大的优化工具,广泛应用于多个领域。通过模拟蚂蚁觅食的机制,蚁群算法能够有效地解决组合优化问题。开发者可以根据具体问题需要,灵活调整算法参数,并选择合适的编程语言实现。