HEY, 各位这次是真的好久不见,本期推送来教大家如何使用MATLAB推公式并使用推出来的结果。
本文说白了就是讲符号表达式这个东西咋用,所使用最重要的函数就是syms,在开始前,首先要保证自己的MATLAB安装了Symbolic Math Toolbox工具箱!
1 公式显示
展示一下如何使用m-文件和实时编辑器使用syms函数并如何显示结果:
脚本(m-文件)
首先假如在m-文件编写如下代码(使用syms函数将x y 设置为符号变量,并生成了简单的公式,使用pretty函数更美观的展示公式),则运行结果如下:
syms x y% syms x% 等价于% x = sym('x')f = sin(x^3/y) + (y^3/x)pretty(f)% f =% % sin(x^3/y) + y^3/x% % / 3 \ 3% | x | y% sin| -- | + --% \ y / x实时脚本
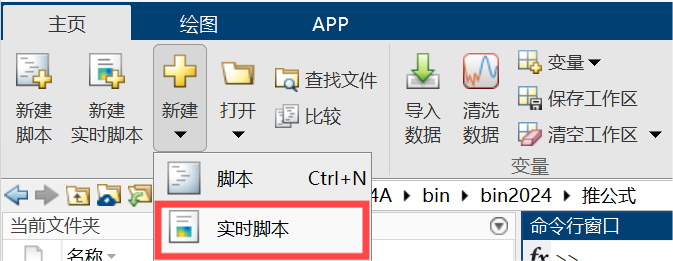
创建实时脚本:
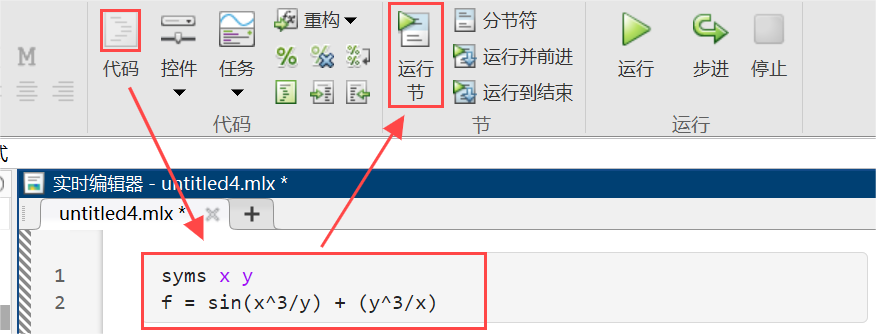
输入公式并运行:
结果显示:
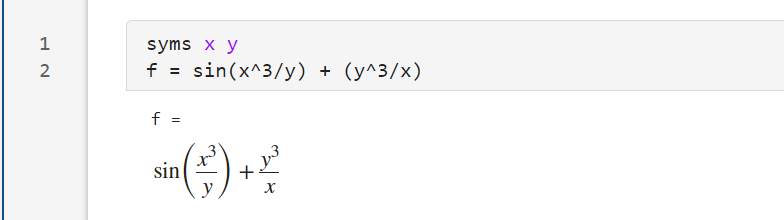
2 常用函数
展示一下常用的积分,极限,累加和等函数都是哪些?我们直接拿真正的数学题来算算得了:
不定积分与定积分(int)
吉林大学2021年数学分析题目(一(5))
求积分 ∫ d x 2 + tan 2 x \int \frac{d x}{2+\tan ^2 x} ∫2+tan2xdx
syms xf=1/(2 + tan(x)^2);int(f)ans = x − 2 atan ( 2 tan ( x ) 2 ) 2 x-\frac{\sqrt{2} \operatorname{atan}\left(\frac{\sqrt{2} \tan (x)}{2}\right)}{2} x−22 atan(22 tan(x))
吉林大学2021年数学分析题目(一(6))
求定积分 ∫ 0 3 arcsin x x + 1 \int_0^3 \arcsin \frac{x}{x+1} ∫03arcsinx+1x
syms xf=asin(x/(x + 1));% 变量是 x,积分上下限 0 - 3int(f, x, 0, 3)ans = π 2 − atan ( 7 3 ) + 3 asin ( 3 4 ) − 7 + 1 \frac{\pi}{2}-\operatorname{atan}\left(\frac{\sqrt{7}}{3}\right)+3 \operatorname{asin}\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)-\sqrt{7}+1 2π−atan(37 )+3asin(43)−7 +1
极限(limit)
吉林大学2021年数学分析题目(一(3))
求极限
lim x → 0 x 2 − ∫ 0 x 2 cos ( t 2 ) d t sin 10 x \lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{x^2-\int_0^{x^2} \cos \left(t^2\right) d t}{\sin ^{10} x} x→0limsin10xx2−∫0x2cos(t2)dt
这里对 cos ( t 2 ) \cos \left(t^2\right) cos(t2)积分涉及菲涅耳函数一般肯定算不出来,得洛,但MATLAB就直接硬刚就完事了嗷。
syms x tf = (x^2 - int(cos(t^2), t, 0, x^2))/(sin(x))^10limit(f, x, 0)f =
x 2 − 2 π C ( 2 x 2 π ) 2 sin ( x ) 10 \frac{x^2-\frac{\sqrt{2} \sqrt{\pi} \mathrm{C}\left(\frac{\sqrt{2} x^2}{\sqrt{\pi}}\right)}{2}}{\sin (x)^{10}} sin(x)10x2−22 π C(π 2 x2)
ans = 1 10 \frac{1}{10} 101
级数(symsum)
吉林大学2021年数学分析题目(一(9))
求级数 ∑ n = 1 ∞ 1 2 n ( 2 n − 1 ) \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \frac{1}{2^n(2 n-1)} ∑n=1∞2n(2n−1)1的和.
syms nsymsum(1/(2^n)/(2*n - 1), n, 1, inf)ans = 2 2 atanh ( 2 2 ) \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2} \operatorname{atanh}\left(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right) 22 atanh(22 )
导数(diff)
求 asin ( x ) 1 − x 2 \frac{\operatorname{asin}(x)}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} 1−x2 asin(x)的三阶导数:
syms xf = asin(x)/sqrt(1 - x^2);diff(f, x, 3)ans = 4 ( x 2 − 1 ) 2 − 15 x 2 ( x 2 − 1 ) 3 + 15 x 3 asin ( x ) ( 1 − x 2 ) 7 / 2 + 9 x asin ( x ) ( 1 − x 2 ) 5 / 2 \frac{4}{\left(x^2-1\right)^2}-\frac{15 x^2}{\left(x^2-1\right)^3}+\frac{15 x^3 \operatorname{asin}(x)}{\left(1-x^2\right)^{7 / 2}}+\frac{9 x \operatorname{asin}(x)}{\left(1-x^2\right)^{5 / 2}} (x2−1)24−(x2−1)315x2+(1−x2)7/215x3asin(x)+(1−x2)5/29xasin(x)
泰勒展开(taylor)
中国海洋大学2021年数学分析题目(1(2))
求二元函数 f ( x , y ) = ln ( 1 + x 2 + y 2 ) f(x, y)=\ln \left(1+x^2+y^2\right) f(x,y)=ln(1+x2+y2)在(0,0)到4阶项的泰勒展开式。
syms x yf=log(1 + x^2 + y^2);taylor(f, [x,y], [0,0], 'Order',5)ans = − x 4 2 − x 2 y 2 + x 2 − y 4 2 + y 2 -\frac{x^4}{2}-x^2 y^2+x^2-\frac{y^4}{2}+y^2 −2x4−x2y2+x2−2y4+y2
3 变量格式
我们可以用syms函数将字母变成符号变量,也能变成符号函数,符号矩阵,同时也可以设置变量的一些属性,比如非负性等属性。
符号变量性质
可以设置为 real | positive | integer | rational
比如我们运行如下代码,能看出预设变量是正数和不做预设的区别:
syms xf1 = sqrt(x^2)% f1 = sqrt(x^2)syms x positivef2 = sqrt(x^2)% f2 = x大家可能会好奇,嗯?只能设置为positive正数嘛,我想设置为负数咋办?更加复杂的设置可以通过assume函数来完成:
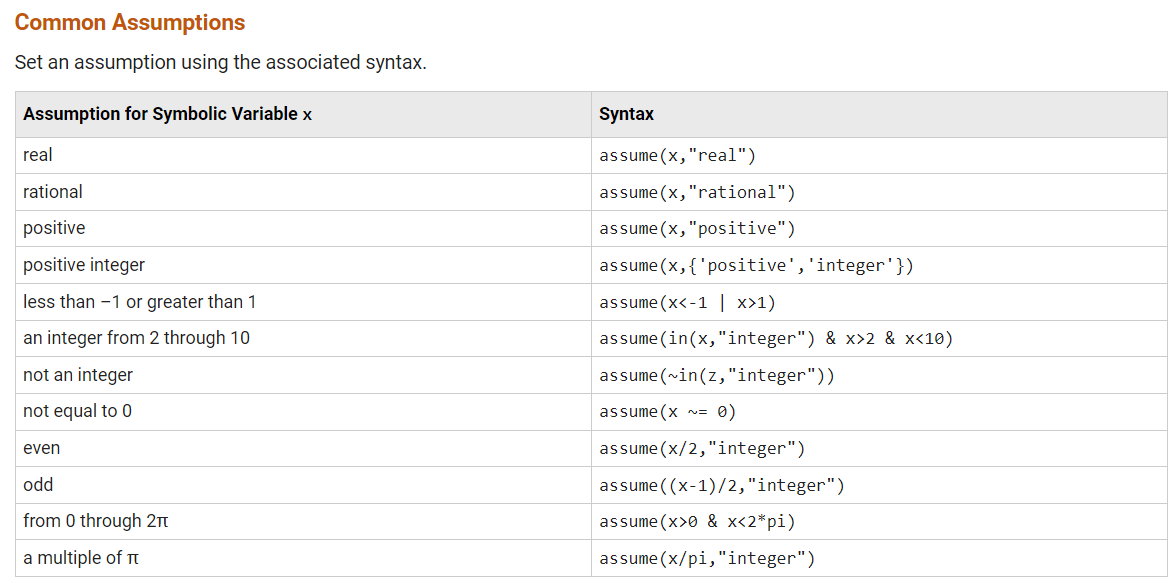
再随便举个例子:
syms xf = 1/abs(x^2 - 1);int(f, x)% ans = -atanh(x)/sign(x^2 - 1)assume(x^2 - 1 > 0)int(f, x)% ans = -atanh(x)符号矩阵
syms X [3,4]XX = $
\left(\begin{array}{llll}
X_{1,1} & X_{1,2} & X_{1,3} & X_{1,4} \
X_{2,1} & X_{2,2} & X_{2,3} & X_{2,4} \
X_{3,1} & X_{3,2} & X_{3,3} & X_{3,4}
\end{array}\right)
$
syms 'X_a%d%d' [2,2]X_aX_a = ( X a 11 X a 12 X a 21 X a 22 ) \left(\begin{array}{ll}X_{\mathrm{a} 11} & X_{\mathrm{a} 12} \\ X_{\mathrm{a} 21} & X_{\mathrm{a} 22}\end{array}\right) (Xa11Xa21Xa12Xa22)
符号函数
syms f(x,y)M = f(2,3) + f^2M(x, y) = f ( x , y ) 2 + f ( 2 , 3 ) f(x, y)^2+f(2,3) f(x,y)2+f(2,3)
符号函数矩阵
syms f(x,y) [2,2]ff(x, y) = ( f 1 , 1 ( x , y ) f 1 , 2 ( x , y ) f 2 , 1 ( x , y ) f 2 , 2 ( x , y ) ) \left(\begin{array}{ll}f_{1,1}(x, y) & f_{1,2}(x, y) \\ f_{2,1}(x, y) & f_{2,2}(x, y)\end{array}\right) (f1,1(x,y)f2,1(x,y)f1,2(x,y)f2,2(x,y))
将符号函数矩阵的元素替换的方法还是挺奇怪的:
f1_1(x,y) = 2*x;f2_2(x,y) = x^2 + 1;f = subs(f)f(x, y) = ( 2 x f 1 , 2 ( x , y ) f 2 , 1 ( x , y ) x 2 + 1 ) \left(\begin{array}{cc}2 x & f_{1,2}(x, y) \\ f_{2,1}(x, y) & x^2+1\end{array}\right) (2xf2,1(x,y)f1,2(x,y)x2+1)
再带入数值:
f(2,3)ans = ( 4 f 1 , 2 ( 2 , 3 ) f 2 , 1 ( 2 , 3 ) 5 ) \left(\begin{array}{cc}4 & f_{1,2}(2,3) \\ f_{2,1}(2,3) & 5\end{array}\right) (4f2,1(2,3)f1,2(2,3)5)
抽象矩阵
R2021A版本及以后,矩阵符号运算也被支持啦!!
x = symmatrix('x', [5,1]);A = symmatrix('A', [5,5]);% 等同于:% syms x [5,1] matrix% syms A [5,5] matrixf = x.'*A*x - x.'*xH = diff(f, x)inv(A)f = − x T x + x T A x -\boldsymbol{x}^{\mathrm{T}} \boldsymbol{x}+\boldsymbol{x}^{\mathrm{T}} \boldsymbol{A} \boldsymbol{x} −xTx+xTAx
H = x T A − 2 x T + x T A T \boldsymbol{x}^{\mathrm{T}} \boldsymbol{A}-2 \boldsymbol{x}^{\mathrm{T}}+\boldsymbol{x}^{\mathrm{T}} \boldsymbol{A}^{\mathrm{T}} xTA−2xT+xTAT
ans = A − 1 \boldsymbol{A}^{\mathrm{-1}} A−1
抽象复合函数
举个例子:
syms f1(x,y) f2(x,y) F(x,y)dFdx = diff(F(f1, f2), x)求解结果:
dFdx = D([1], F)(f1(x, y), f2(x, y))*diff(f1(x, y), x) + D([2], F)(f1(x, y), f2(x, y))*diff(f2(x, y), x)在实时编辑器中的显示:
dFdx = D 1 ( F ) ( f 1 ( x , y ) , f 2 ( x , y ) ) ∂ ∂ x f 1 ( x , y ) + D 2 ( F ) ( f 1 ( x , y ) , f 2 ( x , y ) ) ∂ ∂ x f 2 ( x , y ) \mathrm{D}_1(F)\left(f_1(x, y), f_2(x, y)\right) \frac{\partial}{\partial x} f_1(x, y)+\mathrm{D}_2(F)\left(f_1(x, y), f_2(x, y)\right) \frac{\partial}{\partial x} f_2(x, y) D1(F)(f1(x,y),f2(x,y))∂x∂f1(x,y)+D2(F)(f1(x,y),f2(x,y))∂x∂f2(x,y)
再举一个例子:
syms f(a,b) xdiff(f(x^2, x+1), x)ans = 2 x D 1 ( f ) ( x 2 , x + 1 ) + D 2 ( f ) ( x 2 , x + 1 ) 2 x \mathrm{D}_1(f)\left(x^2, x+1\right)+\mathrm{D}_2(f)\left(x^2, x+1\right) 2xD1(f)(x2,x+1)+D2(f)(x2,x+1)
4 公式化简
simplify
使用simplify函数可以对公式进行化简,例如:
syms xM = [(x^2 + 5*x + 6)/(x + 2), sin(x)*sin(2*x) + cos(x)*cos(2*x);(exp(-x*1i)*1i)/2 - (exp(x*1i)*1i)/2, sqrt(16)]S = simplify(M)M = ( x 2 + 5 x + 6 x + 2 cos ( 2 x ) cos ( x ) + sin ( 2 x ) sin ( x ) e − x i i 2 − e x i i 2 4 ) \left(\begin{array}{lc}\frac{x^2+5 x+6}{x+2} & \cos (2 x) \cos (x)+\sin (2 x) \sin (x) \\ \frac{\mathrm{e}^{-x \mathrm{i}} \mathrm{i}}{2}-\frac{\mathrm{e}^{x \mathrm{i}} \mathrm{i}}{2} & 4\end{array}\right) (x+2x2+5x+62e−xii−2exiicos(2x)cos(x)+sin(2x)sin(x)4)
S = ( x + 3 cos ( x ) sin ( x ) 4 ) \left(\begin{array}{cc}x+3 & \cos (x) \\ \sin (x) & 4\end{array}\right) (x+3sin(x)cos(x)4)
公式化简不到位
我们使用simplify时可能会遇到化简化的不完全的情况,例如:
∫ 0 + ∞ x 2 + 1 x 4 + 1 d x \int_0^{+\infty} \frac{x^2+1}{x^4+1} d x ∫0+∞x4+1x2+1dx
这个积分化简出来应该是个常数,但是simplify化简出来是个公式:
syms xf1 = (x^2 + 1)/(x^4 + 1);f2 = int(f1, x, 0, inf);f3 = simplify(f2) % f3 =% (2^(1/2)*(4*pi - log(- 1/2 - 1i/2)*1i + log(- 1/2 + 1i/2)*1i - log(1/2 - 1i/2)*1i + log(1/2 + 1i/2)*1i))/4明显化简的不够完全,可以多化简几步例如直接1000步:
f3 = simplify(f2, 'Steps',1000)% f3 = % (pi*2^(1/2))/2当然不同化简步数有着不同结果,例如:
不同化简步数
举个例子:
syms xexpr = ((exp(-x*1i)*1i) - (exp(x*1i)*1i))/(exp(-x*1i) + exp(x*1i));S = simplify(expr)S = − e 2 x i i − i e 2 x i + 1 \begin{aligned} & \mathrm{S}= -\frac{\mathrm{e}^{2 x i} \mathrm{i}-\mathrm{i}}{\mathrm{e}^{2 x \mathrm{i}}+1} \end{aligned} S=−e2xi+1e2xii−i
S10 = simplify(expr, 'Steps',10)S 10 = 2 i e 2 x i + 1 − i \begin{aligned} & S 10= \frac{2 i}{e^{2 x i}+1}-\mathrm{i} \end{aligned} S10=e2xi+12i−i
S30 = simplify(expr, 'Steps',30)S 30 = ( cos ( x ) − sin ( x ) i ) i cos ( x ) − i \begin{aligned} \mathrm{S} 30= \frac{(\cos (x)-\sin (x) \mathrm{i}) \mathrm{i}}{\cos (x)}-\mathrm{i} \end{aligned} S30=cos(x)(cos(x)−sin(x)i)i−i
S530 = simplify(expr, 'Steps',50)S 50 = tan ( x ) \mathrm{S} 50=\tan (x) S50=tan(x)
特殊化简
同时有些先平方再开方,或者外面套着ln函数的不好化简,可以设置IgnoreAnalyticConstraints属性为true.
syms xexpr = (log(x^2 + 2*x + 1) - log(x + 1))*sqrt(x^2);S = simplify(expr)S = − ( log ( x + 1 ) − log ( ( x + 1 ) 2 ) ) x 2 S=-\left(\log (x+1)-\log \left((x+1)^2\right)\right) \sqrt{x^2} S=−(log(x+1)−log((x+1)2))x2
S = simplify(expr, 'IgnoreAnalyticConstraints',true)S = x log ( x + 1 ) \mathrm{S}=x \log (x+1) S=xlog(x+1)
不同化简格式
使用All属性函数可以获取全部等效化简:
syms xexpr = cos(x)^2 - sin(x)^2;S = simplify(expr, 'All',true)S = ( cos ( 2 x ) cos ( x ) 2 − sin ( x ) 2 ) \begin{aligned} & \mathrm{S}= \\ & \left(\begin{array}{c} \cos (2 x) \\ \cos (x)^2-\sin (x)^2 \end{array}\right) \end{aligned} S=(cos(2x)cos(x)2−sin(x)2)
也可以和化简步数结合:
S = simplify(expr, 'Steps',10, 'All',true)S = ( cos ( 2 x ) 1 − 2 sin ( x ) 2 2 cos ( x ) 2 − 1 cos ( x ) 2 − sin ( x ) 2 cot ( 2 x ) sin ( 2 x ) e − 2 x i 2 + e 2 x i 2 ) \begin{aligned} & \mathrm{S}= \\ & \left(\begin{array}{c} \cos (2 x) \\ 1-2 \sin (x)^2 \\ 2 \cos (x)^2-1 \\ \cos (x)^2-\sin (x)^2 \\ \cot (2 x) \sin (2 x) \\ \frac{\mathrm{e}^{-2 x \mathrm{i}}}{2}+\frac{\mathrm{e}^{2 x \mathrm{i}}}{2} \end{array}\right) \end{aligned} S= cos(2x)1−2sin(x)22cos(x)2−1cos(x)2−sin(x)2cot(2x)sin(2x)2e−2xi+2e2xi
5 公式格式
就我化简出来既有 sin ( x ) \sin(x) sin(x) 也有 e x e^x ex ,但我偏偏不要,欸哪怕有复数我也要全 cos ( x ) \cos(x) cos(x) 的公式?怎么自由进行公式替换?
先从一个最简单的例子来看叭,假设我的公式是 sin ( x ) + cos ( x ) \sin(x)+\cos(x) sin(x)+cos(x) 我想自动让MATLAB将其替换为纯 sin ( x ) \sin(x) sin(x) 的公式咋办?此例子与问题来自@丁丁曜曜.
方法一 All 属性
可以使用 simplify 函数化简的时候选择 All 属性为true,就能展示所有的等价化简:
syms xexpr = sin(x)+cos(x);S = simplify(expr,'All',true)% S =% 2^(1/2)*sin(x + pi/4)% 2^(1/2)*cos(x - pi/4)% cos(x) + sin(x)例如题目中的式子就有三个等效化简,我们选择第一个只含 sin \sin sin 的化简即可:
S(1)% 2^(1/2)*sin(x + pi/4)方法二 sin 函数重写
借助rewrite函数,使用sin函数重写表达式并化简:
syms xexpr = sin(x) + cos(x);simplify(rewrite(expr, 'sin'))% 2^(1/2)*sin(x + pi/4)方法三 subs 替换
可以在化简前先把所有的 cos ( x ) \cos(x) cos(x) 使用 sin ( x + π / 2 ) \sin (x+\pi / 2) sin(x+π/2) 进行替换,再使用 simplify 函数化简,就可以得到只含有 sin ( x ) \sin(x) sin(x) 的公式:
syms xy = sin(x) + cos(x);% y = sin(x)+cos(x)y1 = subs(y, cos(x), sin(x+pi/2));y2 = simplify(y1)% y2 = 2^(1/2)*sin(x + pi/4)pretty(y2)% / pi \% sqrt(2) sin| x + -- |% \ 4 /方法四 combine 函数结合
不过只能生成cos的表达式:
syms xexpr = sin(x) + cos(x);sc = combine(expr, 'sincos')% 2^(1/2)*cos(x - pi/4)注:只能合并生成cos表达式是因为合并各项使用的公式导致的:
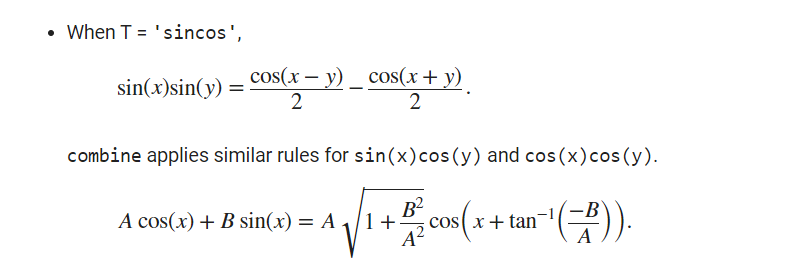
该函数用的不是特别多,详细描述可自行查看:
以下是更多与格式相关的函数讲解:
expand 详讲
与 combine 函数函数相对,expand 函数可以把公式展开:
syms x yexpand(cos(x + y))% ans = cos(x)*cos(y) - sin(x)*sin(y)rewrite 详讲
再详细讲讲rewrite这个函数叭,很有意思,能重写的格式很多,例如 sin ( x ) \sin(x) sin(x) 用 e x e^x ex 重写:
syms xsin2exp = rewrite(sin(x), "exp")sin 2 exp = e − x i i 2 − e x i i 2 \begin{aligned} & \sin 2 \exp = \frac{\mathrm{e}^{-x \mathrm{i}} \mathrm{i}}{2}-\frac{\mathrm{e}^{x \mathrm{i}} \mathrm{i}}{2}\end{aligned} sin2exp=2e−xii−2exii
arccos ( x ) \arccos(x) arccos(x) 用 ln \ln ln 重写:
syms xacos2log = rewrite(acos(x), "log") acot 2 log = log ( 1 − i x ) i 2 − log ( 1 + i x ) i 2 \begin{aligned} & \operatorname{acot} 2 \log = \frac{\log \left(1-\frac{\mathrm{i}}{x}\right) \mathrm{i}}{2}-\frac{\log \left(1+\frac{\mathrm{i}}{x}\right) \mathrm{i}}{2} \end{aligned} acot2log=2log(1−xi)i−2log(1+xi)i
全部重新格式:
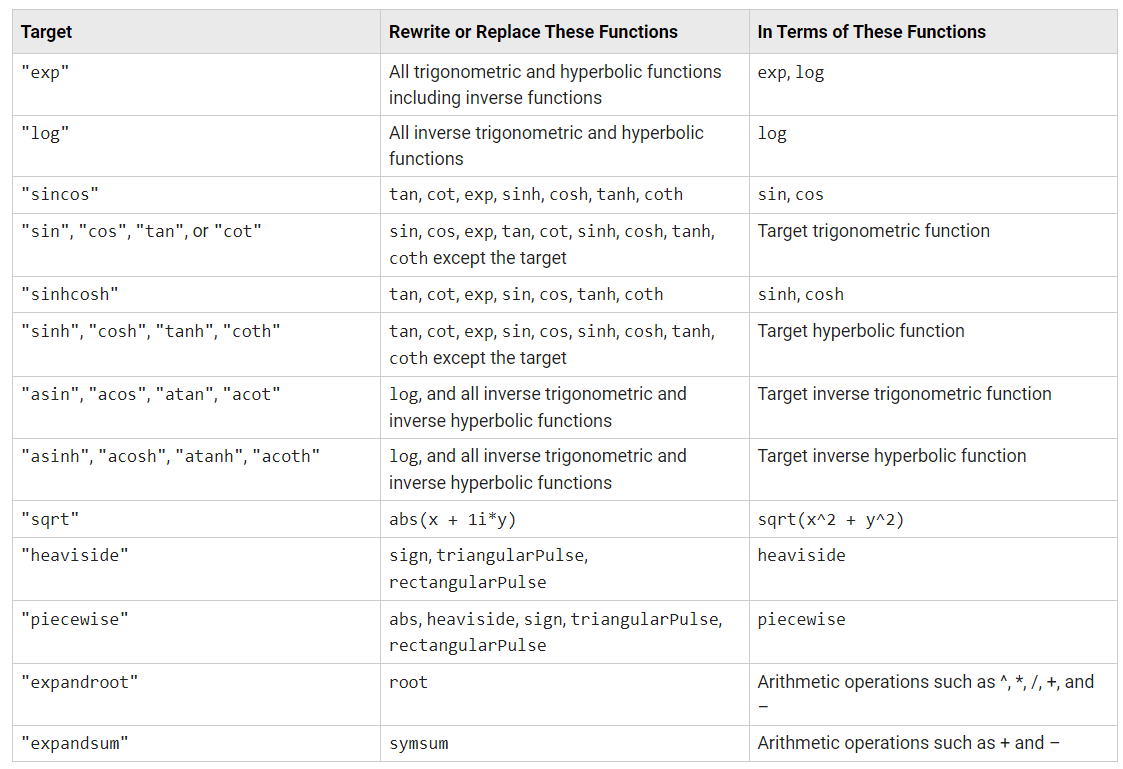
更多格式转换
其他特殊公式的特殊格式改写,请参见以下网址:
https://www.mathworks.com/help/symbolic/choose-function-to-rearrange-expression.html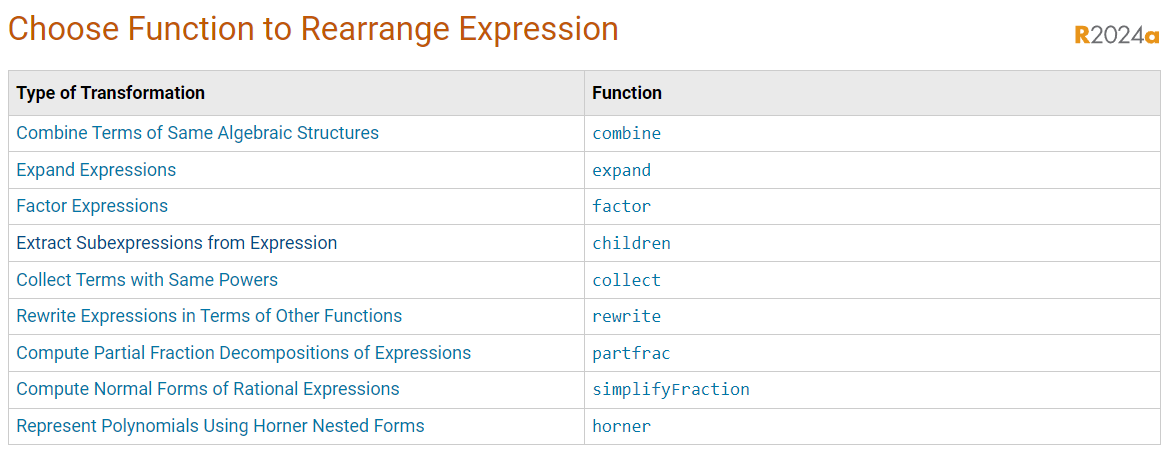
取消简写
一些复杂公式若有重复的部分则会自动简写,例如:
syms a b c d x f = a*x^3 + b*x^2 + c*x + d;outputAbbrev = sin(f) + cos(f) + tan(f) + log(f) + 1/foutputAbbrev =
$
\cos \left(\sigma_1\right)+\log \left(\sigma_1\right)+\sin \left(\sigma_1\right)+\tan \left(\sigma_1\right)+\frac{1}{\sigma_1}
$
where
$
\sigma_1=a x^3+b x^2+c x+d
$
可使用以下代码取消简写:
sympref('AbbreviateOutput', false);outputLong = sin(f) + cos(f) + tan(f) + log(f) + 1/foutputAbbrev =
cos ( a x 3 + b x 2 + c x + d ) + log ( a x 3 + b x 2 + c x + d ) + sin ( a x 3 + b x 2 + c x + d ) + tan ( a x 3 + b x 2 + c x + d ) + 1 a x 3 + b x 2 + c x + d \cos \left(a x^3+b x^2+c x+d\right)+\log \left(a x^3+b x^2+c x+d\right)+\sin \left(a x^3+b x^2+c x+d\right)+\tan \left(a x^3+b x^2+c x+d\right)+\frac{1}{a x^3+b x^2+c x+d} cos(ax3+bx2+cx+d)+log(ax3+bx2+cx+d)+sin(ax3+bx2+cx+d)+tan(ax3+bx2+cx+d)+ax3+bx2+cx+d1
5 公式使用与导出
公式用于数值计算
一个很简单的带入数值的方法:
syms x yf = (x^3 + y^2)^(log(x/y));M(x,y) = f;M(1,2)% ans = 1/5^log(2)M(1,x^3)% ans = (x^6 + 1)^log(1/x^3)M([1,1],[2,3])% ans = [1/5^log(2), 1/10^log(3)]fsurf(M)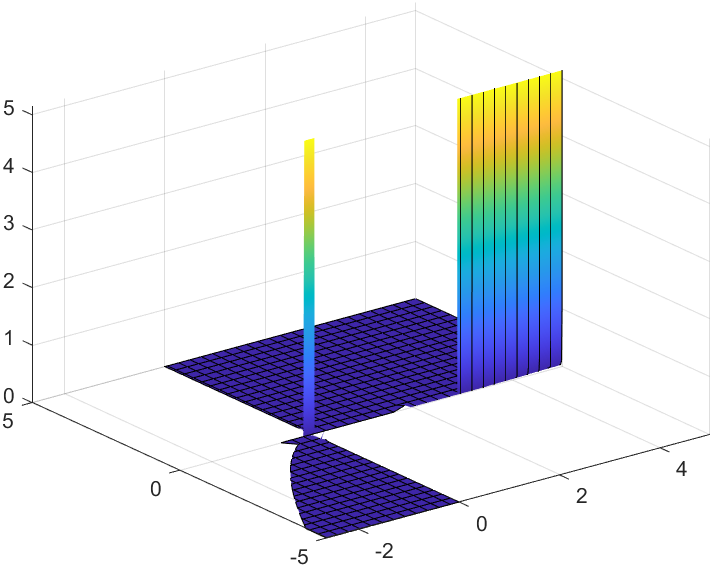
除此之外可以使用subs函数进行元素替换:
syms x yf = (x^3 + y^2)^(log(x/y));subs(f, [x,y], [1,2])% ans = 1/5^log(2)还可以转化为效率更高的匿名函数:
syms x yf = (x^3 + y^2)^(log(x/y));F = matlabFunction(f)% F =% 包含以下值的 function_handle:% @(x,y)(x.^3+y.^2).^log(x./y)F(1, 2)% ans = 0.3277F([1,2,3], [2,2,2])% ans = 0.3277 1.0000 4.0243变换成匿名函数依旧可以直接用fplot, fsurf等函数绘图:
syms x yf = (x^3 + y^2);F = matlabFunction(f)fsurf(F)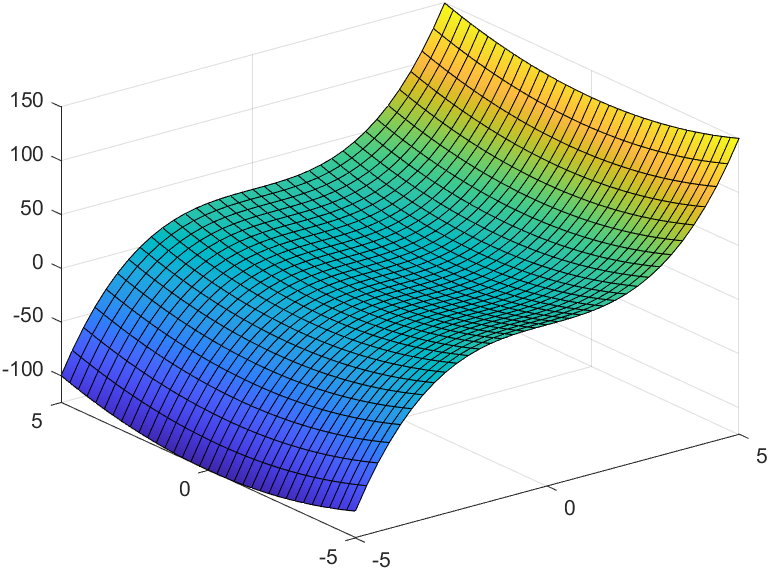
摘取矩阵的部分元素
假设我们求出公式来是个矩阵,但我们只想要他的某个元素而并不想要整个矩阵,那该咋办呢?直接使用formula函数即可获取矩阵每个位置的元素,再通过索引获取即可:
syms xH = [x^3, x^2 + 1; x, log(x)]^3;HM = formula(H);HM(1,1)% ans = x^3*(x*(x^2 + 1) + x^6) + (x^2 + 1)*(x*log(x) + x^4)公式存储
我们可以通过matlabFunction将结果存储为一个可调用的函数:
syms xsols = root(x^5 - x^4 - 1,x)matlabFunction(sols, "File","myfile.m");存储结果:
function sols = myfile%MYFILE% SOLS = MYFILE% This function was generated by the Symbolic Math Toolbox version 24.1.% 2024-07-10 22:53:59t0 = roots([1.0,-1.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,-1.0]);t2 = t0(1);t0 = roots([1.0,-1.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,-1.0]);t3 = t0(2);t0 = roots([1.0,-1.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,-1.0]);t4 = t0(3);t0 = roots([1.0,-1.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,-1.0]);t5 = t0(4);t0 = roots([1.0,-1.0,0.0,0.0,0.0,-1.0]);t6 = t0(5);sols = [t2;t3;t4;t5;t6];end当然也可以存储为mat文件:
syms xf = x^2 + 3;f = matlabFunction(f);% 存储为mat文件:save test.mat f% 导入mat文件并使用:T = load('test.mat');T.f(1)% ans = 4公式美化
为了导出的时候比较好看,可以对公式格式进行适当调整,注意,要是有不低于R2019b版本的MATLAB才有此功能:
syms KA = [-1, 0, 1; 1, 2, 0; 1, 1, 0];B = K^2*AB = ( − K 2 0 K 2 K 2 2 K 2 0 K 2 K 2 0 ) \left(\begin{array}{ccc}-K^2 & 0 & K^2 \\ K^2 & 2 K^2 & 0 \\ K^2 & K^2 & 0\end{array}\right) −K2K2K202K2K2K200
让其按照我们想要的格式进行输出:
displayFormula("B = K^2*A")( − K 2 0 K 2 K 2 2 K 2 0 K 2 K 2 0 ) = K 2 ( − 1 0 1 1 2 0 1 1 0 ) \left(\begin{array}{ccc}-K^2 & 0 & K^2 \\ K^2 & 2 K^2 & 0 \\ K^2 & K^2 & 0\end{array}\right)=K^2\left(\begin{array}{ccc}-1 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 & 0\end{array}\right) −K2K2K202K2K2K200 =K2 −111021100
公式标注
通过下划线和双下划线为变量添加角标:
syms F_a F_bFtot1 = F_a + F_bFtot1 = F a + F b F_a+F_b Fa+Fb
syms F__a F__bFtot2 = F__a + F__bFtot2 = F a + F b F^a+F^b Fa+Fb
再比如加入点:
syms x x_dot x_ddot c m keq1 = m*x_ddot - c*x_dot + k*x == 0eq1 = k x − c x ˙ + m x ¨ = 0 k x-c \dot{x}+m \ddot{x}=0 kx−cx˙+mx¨=0
更多标注:
suffix = ["ast"; "dag"; "deg"; "hat"; "tilde"; ... "vec"; "bar"; "ubar"; "dot"; "ddot"; "tdot"; ... "qdot"; "prime"; "dprime"; "tprime"; "qprime"];accentList = [suffix, sym("x_" + suffix)].'
公式导出
如果是在m文件编写的公式,可以使用latex函数将其转换为latex代码:
syms xS = [sym(1)/3 x; exp(x) x^2]latex(S)% ans = % '\left(\begin{array}{cc} \frac{1}{3} & x\\ {\mathrm{e}}^x & x^2 \end{array}\right)'当然也可以转换为mathml:
mathml(S)% ans =% '<math xmlns='http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML' display='block'>% <mrow>% <mo form='prefix'>(</mo>% <mtable>% <mtr>% <mtd>% <mfrac>% <mn>1</mn>% <mn>3</mn>% </mfrac>% </mtd>% <mtd>% <mi>x</mi>% </mtd>% </mtr>% <mtr>% <mtd>% <msup>% <mo>ⅇ</mo>% <mi>x</mi>% </msup>% </mtd>% <mtd>% <msup>% <mi>x</mi>% <mn>2</mn>% </msup>% </mtd>% </mtr>% </mtable>% <mo form='postfix'>)</mo>% </mrow>% </math>% '对于一部分版本的word,该代码是可以直接复制到word并转换为公式的,对于不能直接复制的情况,可以先复制到mathType再将其复制到word文档:
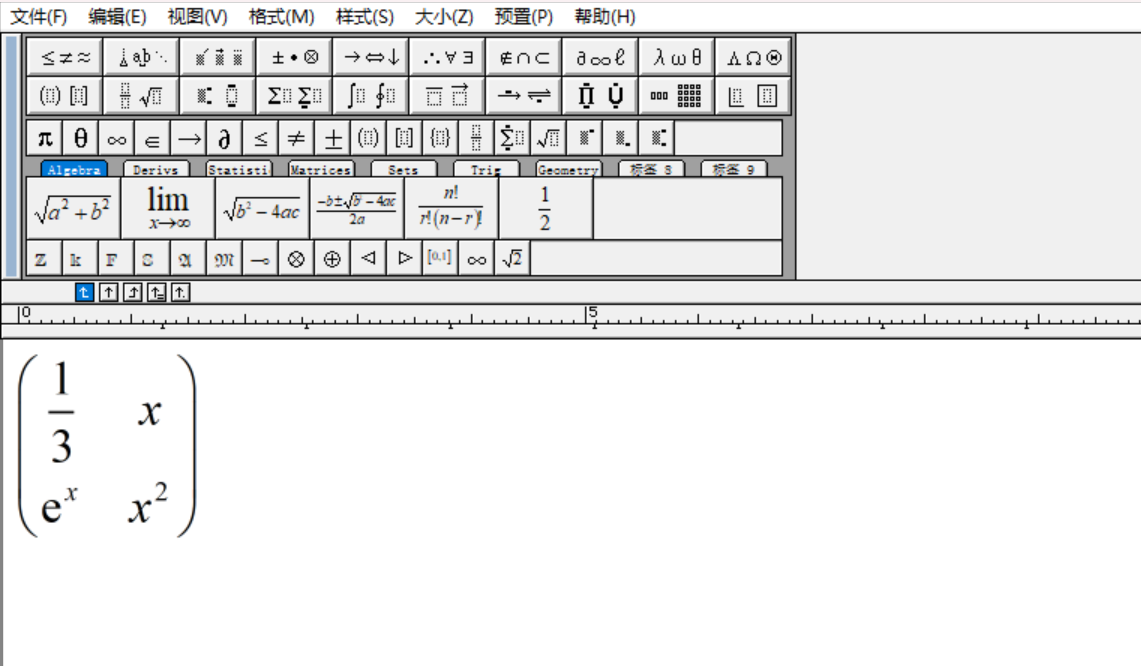
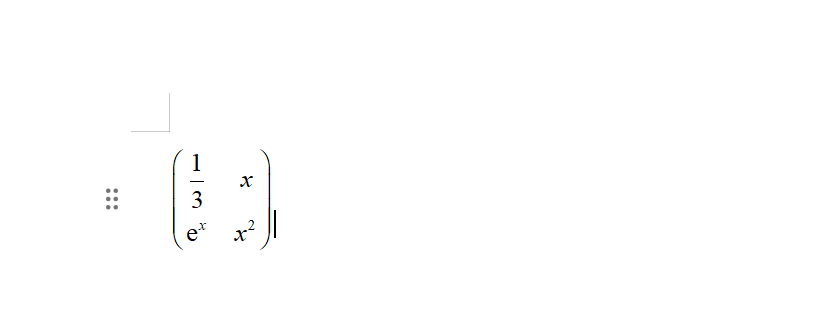
如果是在实时编辑器编写的代码,可以点击公式右上角三个点:
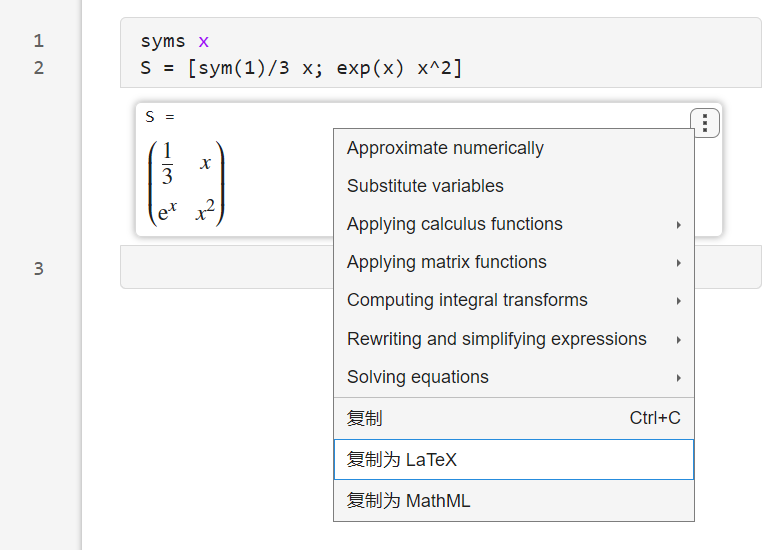
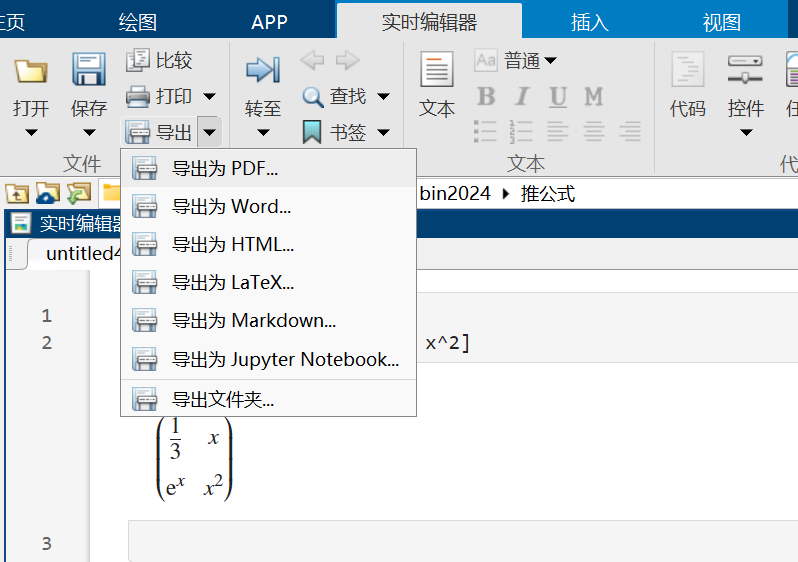
文件导出
如果在实时编辑器进行编写,可将图文导出为各种常用格式: