hello,这次我来用C语言和栈和队列相关问题,希望大家多多支持
括号匹配题目:

OJ题目
首先我们不能用数量匹配来进行解答,因为你顺序不一定匹配
解析:
1、左括号入栈
2、右括号出栈顶左括号匹配
1.我们只需要找到右括号,判断左括号是否匹配
2、所以遇到左括号就采用进入栈的方式,遇到右括号,出栈顶左括号看是否匹配
typedef char STDataType;typedef struct Stack{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;}ST;void StackInit(ST* ps);void StackDestroy(ST* ps);void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);void StackPop(ST* ps);STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);int StackSize(ST* ps);bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);void StackInit(ST* ps){assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;//ps->top = -1ps->capacity = 0;}void StackDestroy(ST* ps){assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;}void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x){assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);if (tmp == NULL){printf("realloc fail\n");exit(-1);}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;}void StackPop(ST* ps){assert(ps);//assert(ps->top > 0);assert(!StackEmpty(ps));ps->top--;}STDataType StackTop(ST* ps){assert(ps);//assert(ps->top > 0);assert(!StackEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1];}int StackSize(ST* ps){assert(ps);return ps->top;}bool StackEmpty(ST* ps){assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;}bool isValid(char* s) { ST st; StackInit(&st); while(*s) { if (*s == '(' || *s == '{' || *s == '[') { StackPush(&st, *s); ++s; } else { if (StackEmpty(&st)) { StackDestroy(&st); return false; } STDataType top = StackTop(&st); StackPop(&st); if ((*s == '}' && top != '{') || (*s == ']' && top != '[') || (*s == ')' && top != '(')) { StackDestroy(&st); return false; } else { s++; } } } bool ret = StackEmpty(&st); StackDestroy(&st); return ret;}用队列实现栈
OJ题目 https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/description/
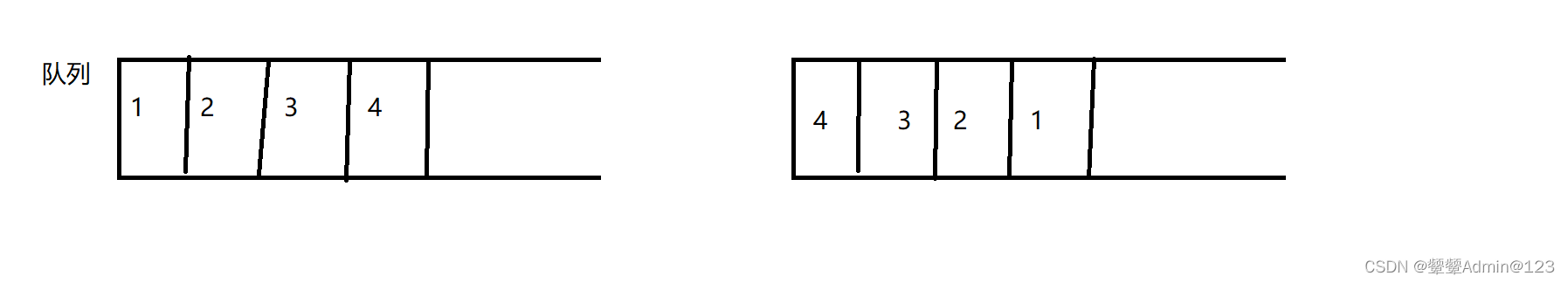
我们知道队列是先进先出,栈是先进后出(后入先出)
1、我们主要保证一个队列是空,然后把这个队列数据存入另外一个队列中,这个时候的队列所出的数据相当于就是栈出的数据。
2、所以插入数据是插到有数据的队列,如果两个都没有数据两个都行。
typedef struct { Queue q1; Queue q2; } MyStack;/** Initialize your data structure here. */MyStack* myStackCreate(int maxSize) { MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); QueueInit(&pst->q1); QueueInit(&pst->q2); return pst;}/** Push element x onto stack. */void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) { //给非空队列进行入队操作 if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) != 0) { QueuePush(&obj->q1, x); } else { QueuePush(&obj->q2, x); }}/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) { //把非空队列的除最后一个元素之外的剩余元素全部入队空队列 Queue* pEmpty = &obj->q1, *pNonEmpty = &obj->q2; if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) != 0) { pEmpty = &obj->q2; pNonEmpty = &obj->q1; } while(QueueSize(pNonEmpty) > 1) { QueuePush(pEmpty, QueueFront(pNonEmpty)); QueuePop(pNonEmpty); } int top = QueueFront(pNonEmpty); //队尾元素出队 QueuePop(pNonEmpty); return top;}/** Get the top element. */int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) { //获取非空队列的队尾元素 Queue* pEmpty = &obj->q1, *pNonEmpty = &obj->q2; if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) != 0) { pEmpty = &obj->q2; pNonEmpty = &obj->q1; } return QueueBack(pNonEmpty);}/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) { return !(QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) | QueueEmpty(&obj->q2));}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) { QueueDestory(&obj->q1); QueueDestory(&obj->q2); free(obj);}用栈实现队列

OJ题目 https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/
typedef struct { //入队栈 Stack pushST; //出队栈 Stack popST;} MyQueue;/** Initialize your data structure here. */MyQueue* myQueueCreate(int maxSize) { MyQueue* pqueue = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue)); StackInit(&pqueue->pushST, maxSize); StackInit(&pqueue->popST, maxSize); return pqueue;}/** Push element x to the back of queue. */void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) { //入队栈进行入栈操作 StackPush(&obj->pushST, x);}/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) { //如果出队栈为空,导入入队栈的元素 if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST) == 0) { while(StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) != 0) { StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST)); StackPop(&obj->pushST); } } int front = StackTop(&obj->popST); //出队栈进行出队操作 StackPop(&obj->popST); return front;}/** Get the front element. */int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) { //类似于出队操作 if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST) == 0) { while(StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) != 0) { StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST)); StackPop(&obj->pushST); } } return StackTop(&obj->popST);}/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) { return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) == 0 && StackEmpty(&obj->popST) == 0;}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) { StackDestroy(&obj->pushST); StackDestroy(&obj->popST); free(obj);}设计循坏队列
OJ题目 https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/

typedef struct { int* queue; int front; int rear; int k} MyCircularQueue;/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. *///创建一个可以存放k个元素的循环队列,实际申请的空间为k + 1MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) { MyCircularQueue* pcq = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue)); pcq->queue = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1)); pcq->front = 0; pcq->rear = 0; pcq->k = k; return pcq;}/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) { //判满 if((obj->rear+1)%(obj->k+1) == obj->front) { return false; } //队尾入队 obj->queue[obj->rear++] = value; //如果队尾越界,更新为最小值 if(obj->rear == obj->k+1) obj->rear = 0; return true;}/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) { //判空 if(obj->front == obj->rear) return false; //队头出队 ++obj->front; //如果队头越界,更新为最小值 if(obj->front == obj->k+1) obj->front = 0; return true;}/** Get the front item from the queue. */int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) { if(obj->front == obj->rear) return -1; else return obj->queue[obj->front];}/** Get the last item from the queue. */int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) { if(obj->front == obj->rear) return -1; //队尾元素再rear索引的前一个位置,如果rear为0, //则队尾元素在数组的最后一个位置 if(obj->rear == 0) return obj->queue[obj->k]; else return obj->queue[obj->rear-1];}/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) { return obj->front == obj->rear;}/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) { return (obj->rear+1)%(obj->k+1) == obj->front;}void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) { free(obj->queue); free(obj);}一些解析都在代码里啦
希望大家多多支持,更喜欢对你有帮助
