目录
?前言?
? 概念
? 节点的定义
? 插入
? 旋转
1 . 新节点插入较高左子树的左侧---左左:右单旋
2. 新节点插入较高右子树的右侧---右右:左单旋
3. 新节点插入较高左子树的右侧---左右:先左单旋再右单旋
4. 新节点插入较高右子树的左侧---右左:先右单旋再左单旋
? 性能
? 完整代码
? 总结
?前言?
欢迎观看本期【C++杂货铺】,这期内容讲解AVL树,包括了什么是AVL树,如何实现AVL树,此外还会分析二叉搜索树的性能。
学习本期内容之前,需要你对什么是二叉搜索树有一定的了解,如果不会很了解,或忘记可以快速阅览下面这篇文章:
【C++杂货铺】二叉搜索树-CSDN博客

? 概念
在二叉搜索树中,规定比节点小的值都放在节点的左边,比几点大的值都放在节点的右边,可以大大缩短查找的效率。
但是如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率底下。
因此俄罗斯的两位数学家在1962年发明了一种解决上述问题的方法:当向二叉搜索树中插入新节点后,如果能保证每个节点的左右子树之差绝对值不超过1(需要对树中节点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度。
一颗AVL树必须具有以下性质:
1. 它的左右子树都是AVL树.
2. 左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1( -1 / 0 / 1).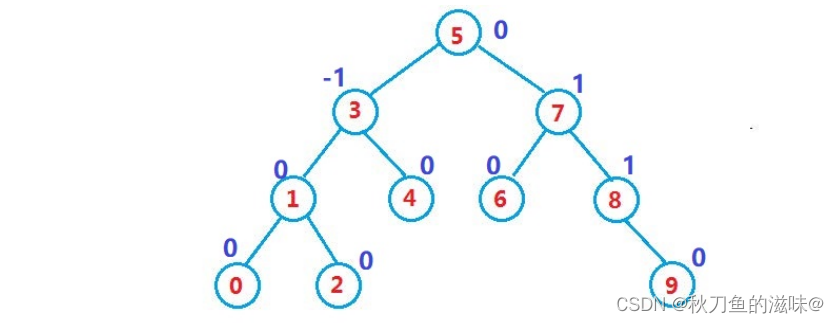
如果一颗二叉搜索树是高度平衡的,那么它就是AVL树。如果它有n个节点,其高度可以维持在O(log N) ,搜索时间复杂度O(log N)。
? 节点的定义
template<class T>struct AVLTreeNode{ AVLTreeNode(const T& data) : _pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr) , _data(data), _bf(0) {} AVLTreeNode<T>* _pLeft; // 该节点的左孩子 AVLTreeNode<T>* _pRight; // 该节点的右孩子 AVLTreeNode<T>* _pParent; // 该节点的双亲 T _data; int _bf; // 该节点的平衡因子};
? 插入
AVL树就是在二叉搜索树的基础上引入了平衡因子,因此AVL树也可以看成是二叉搜索树。
那么 AVL树的插入过程可以分为两步:
1. 按照二叉搜索树的方式插入新节点
2. 调整节点的平衡因子
bool Insert(const T& data){// 1. 先按照二叉搜索树的规则将节点插入到AVL树中// 2. 新节点插入后,AVL树的平衡性可能会遭到破坏,此时就需要更新平衡因子,并检测是否破坏了AVL树的平衡性 /* pCur插入后,pParent的平衡因子一定需要调整,在插入之前,pParent 的平衡因子分为三种情况:-1,0, 1, 分以下两种情况: 1. 如果pCur插入到pParent的左侧,只需给pParent的平衡因子-1即可 2. 如果pCur插入到pParent的右侧,只需给pParent的平衡因子+1即可 此时:pParent的平衡因子可能有三种情况:0,正负1, 正负2 1. 如果pParent的平衡因子为0,说明插入之前pParent的平衡因子为正负1,插入后被调整成0,此时满足 AVL树的性质,插入成功 2. 如果pParent的平衡因子为正负1,说明插入前pParent的平衡因子一定为0,插入后被更新成正负1,此 时以pParent为根的树的高度增加,需要继续向上更新 3. 如果pParent的平衡因子为正负2,则pParent的平衡因子违反平衡树的性质,需要对其进行旋转处理 */while (pParent){// 更新双亲的平衡因子if (pCur == pParent->_pLeft)pParent->_bf--;elsepParent->_bf++;// 更新后检测双亲的平衡因子if (0 == pParent->_bf){break;}else if (1 == pParent->_bf || -1 == pParent->_bf){pCur = pParent;pParent = pCur->_pParent;}else{ //根据不同情形,进行旋转 ...}}return true;}
? 旋转
1 . 新节点插入较高左子树的左侧---左左:右单旋
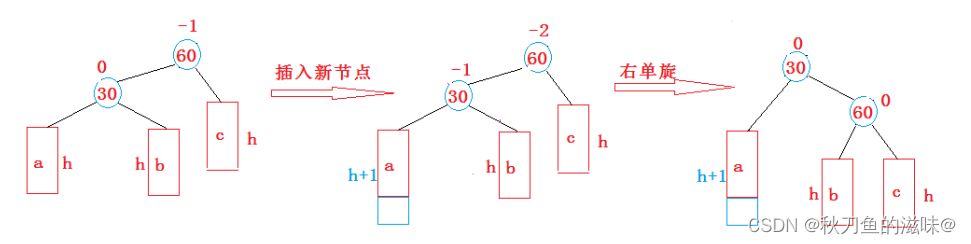
void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;subL->_right = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;_root->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == pparent->_right){pparent->_right = subL;}else{pparent->_left = subL;}subL->_parent = pparent;}subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;}2. 新节点插入较高右子树的右侧---右右:左单旋

void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;subR->_left = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){_root = subR;_root->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == pparent->_right){pparent->_right = subR;}else{pparent->_left = subR;}subR->_parent = pparent;}subR->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;}3. 新节点插入较高左子树的右侧---左右:先左单旋再右单旋
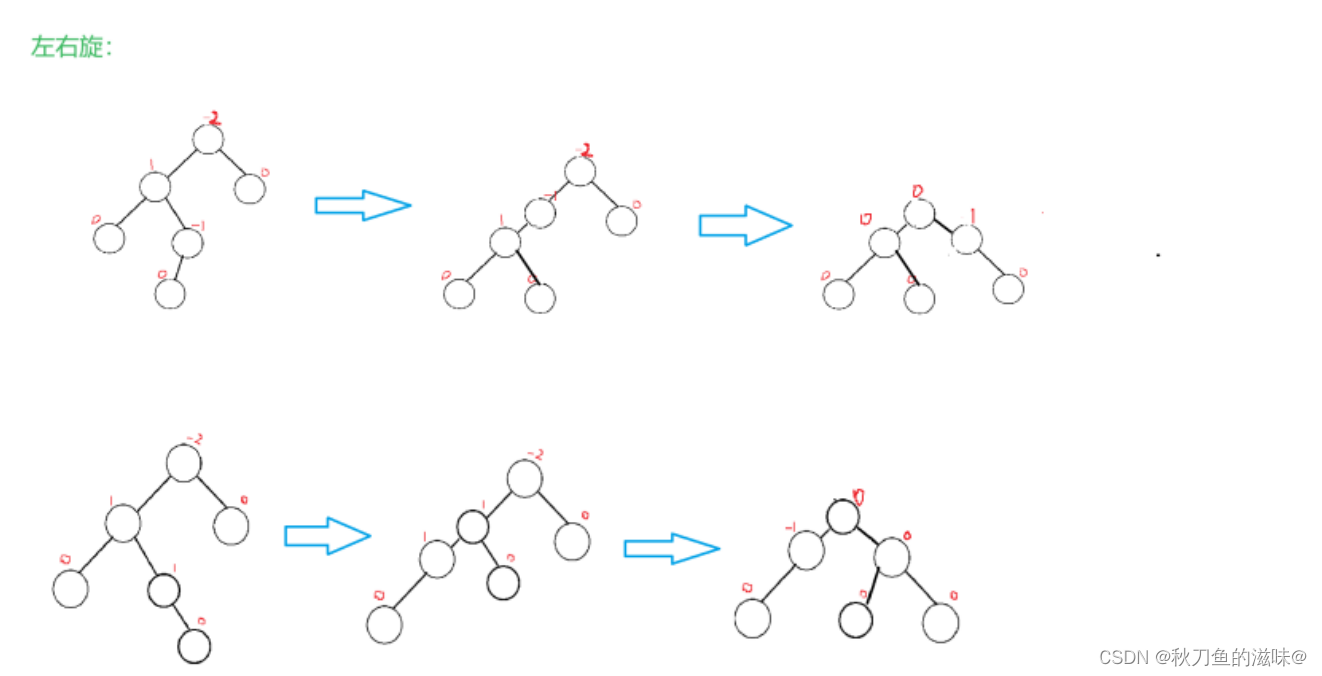
void RotateLR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(parent->_left);RotateR(parent);if (bf == 1){parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = -1;subLR->_bf = 0;}else if(bf == -1){parent->_bf = 1;subL->_bf = 0;subLR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}4. 新节点插入较高右子树的左侧---右左:先右单旋再左单旋
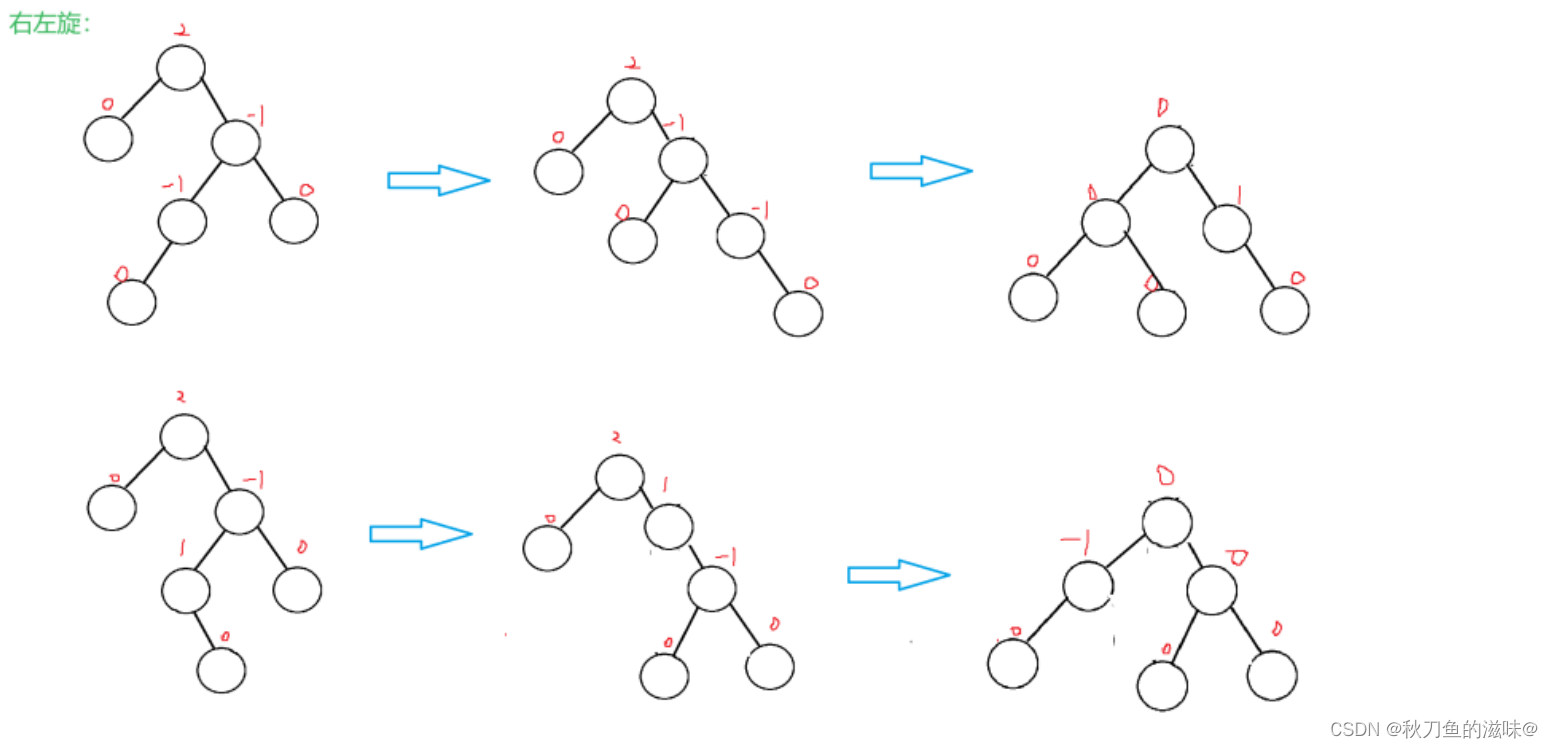
//右左单旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent->_right);RotateL(parent);if (bf == 1){subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;subR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 1;}else if(bf == 0){subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}Node* _root = nullptr;};AVL树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加入了平衡性的限制,因此要验证AVL树,可以分两步:
1. 验证其为二叉搜索树 如果中序遍历可得到一个有序的序列,就说明为二叉搜索树
2. 验证其为平衡树 每个节点子树高度差的绝对值不超过1(注意节点中如果没有平衡因子) 节点的平衡因子是否计算正确
? 性能
AVL树是一棵绝对平衡的二叉搜索树,其要求每个节点的左右子树高度差的绝对值都不超过1,这 样可以保证查询时高效的时间复杂度,即log2 N。但是如果要对AVL树做一些结构修改的操 作,性能非常低下,比如:插入时要维护其绝对平衡,旋转的次数比较多,更差的是在删除时, 有可能一直要让旋转持续到根的位置。因此:如果需要一种查询高效且有序的数据结构,而且数 据的个数为静态的(即不会改变),可以考虑AVL树,但一个结构经常修改,就不太适合。
? 完整代码
template<class T>struct AVLTreeNode{typedef AVLTreeNode<T> Node;AVLTreeNode(const T& val = T()):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _val(val), _bf(0){}Node* _left;Node* _right;Node* _parent;T _val;//平衡因子int _bf;};template<class T>class AVLTree{typedef AVLTreeNode<T> Node;public://插入bool Insert(const T& val){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(val);return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_val> val){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_val < val){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(val);if (parent->_val < val){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;//调整平衡因子while (parent){if (cur == parent->_right){parent->_bf++;}else{parent->_bf--;}if (parent->_bf == 0){break;}else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2){//ROTATE//1. 右单旋if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateR(parent);}//2. 左单旋else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}//3. 左右单旋else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateLR(parent);}//4. 右左单旋else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}break;}else{assert(false);}}return true;}//遍历void Inorder(){_Inorder(_root);}//判断是否是平衡二叉树bool IsBalance(){return _IsBalance(_root);}int Height(){return _Height(_root);}protected:int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;return max(_Height(root->_right), _Height(root->_left)) + 1;}bool _IsBalance(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return true;int leftsize = _Height(root->_left);int rightsize = _Height(root->_right);//检查右子树 - 左子树 < 2if (abs(rightsize - leftsize) >= 2){return false;}//检查平衡因子是否正确if (rightsize - leftsize != root->_bf)return false;return _IsBalance(root->_right)&& _IsBalance(root->_left);}void _Inorder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_Inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_val << endl;_Inorder(root->_right);}//左单旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;subR->_left = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parent == _root){_root = subR;_root->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == pparent->_right){pparent->_right = subR;}else{pparent->_left = subR;}subR->_parent = pparent;}subR->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;}//右单旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;subL->_right = parent;Node* pparent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;_root->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == pparent->_right){pparent->_right = subL;}else{pparent->_left = subL;}subL->_parent = pparent;}subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;}//左右单旋void RotateLR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(parent->_left);RotateR(parent);if (bf == 1){parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = -1;subLR->_bf = 0;}else if(bf == -1){parent->_bf = 1;subL->_bf = 0;subLR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){subLR->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}//右左单旋void RotateRL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent->_right);RotateL(parent);if (bf == 1){subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;subR->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == -1){subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 1;}else if(bf == 0){subRL->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}}Node* _root = nullptr;};? 总结
以上就是本期【C++杂货铺】的主要内容了,主要验证了什么是AVL树,即一颗绝对平衡的二叉搜索树,通过平衡因子进行旋转平衡。展示了AVL树的模拟实现代码,深入理解了AVL树。
最后,如果感觉本期内容对你有帮助,欢迎点赞,收藏,关注。Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ